一种新的基于云的移动学习系统模型(IJIEEB-V6-N6-5)

I.J. Information Engineering and Electronic Business, 2014, 6, 40-46
Published Online December 2014 in MECS (https://www.360docs.net/doc/3f550206.html,/)
DOI: 10.5815/ijieeb.2014.06.05
A Novel Model for Cloud Based Mobile Learning
System
Areej Omar Balghosoon, M. Rizwan Jameel Qureshi
Department of Information Technology, Faculty of Computing and Information Technology, King Abdulaziz
University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
Email: areejomar_2008@https://www.360docs.net/doc/3f550206.html,, rmuhammd@https://www.360docs.net/doc/3f550206.html,.sa
Abstract—Mobile learning (M-learning) becomes revolutionary way to educate the world with the mass advancement in information and communications technology (ICT). It is difficult to deal with m-learning due to increasing number of users, services, education contents and resources and modes to deploy. Cloud computing, with its dynamic scalability and virtualized resources usage, is widely deployed for several applications in many organizations. It has a significant impact in the educational and learning environment. This paper presents a new model for mobile learning system in cloud computing environment that is enriched with high performance computing (HPC) and graphical processing unit (GPU) cluster infrastructure. This model aggregates the power with new technologies to implement M-leaning process more effective with high performance and quick response.
Index Terms—Distance Electronic Learning, M-Learning, Mobile Cloud Computing, High Performance Computing, Graphical Processing Unit.
I.I NTRODUCTION
Educational institutions are rapidly adapting new methods of learning instead of using the traditional ones. Education is entered into a new era due to the digital revolution and advancement in information and communications technology (ICT). The traditional class room teaching is enriched with electronic learning (E-learning) and mobile learning (M-learning) enabling the learning journey more effective and enjoyable [1].
One of the forms of e-learning is distance e-learning (DeL). It is a combination of distance education and e-learning that is characterized by the extensive use of information and communications technology (ICT). It delivers education and instruction with the use of synchronous and asynchronous online communication in an interactive learning environment or virtual communities, in lieu of a physical classroom, to bridge the gap in temporal or spatial constraints. DeL combines the strengths and advantages of distance education and e-learning [2].
Mobile technology is now used as supplement to Del and it is also adapted in educational fields as M-learning. M-learning provides a flexible learning environment to its users regardless of geographical location/time zone [4]. The main advantages of M-learning are improved interaction, portability, collaborative, engaging learners, increases motivation, just-in-time learning and autonomy [5]. The main limitations of m-learning are Internet availability, battery life, bandwidth, number of file formats supported by a specific device, content security or copyright issue from authoring group, multiple standards, multiple screen sizes, multiple operating systems, reworking existing e-learning materials for mobile platforms, limited memory, risk of sudden obsolescence, the small screens and limited processing power [6]. Cloud computing is introduced to overcome these limitations [3] and it currently emerges as a hot research topic due to flexible dynamic infrastructure, quality of services (QoS) and configurable software services [7]. M-learning using cloud is a new research area and it is termed as mobile cloud computing (MCC). MCC has many advantages as follows [8].
?Sharing information and applications without the need of complex and costly hardware and software because the computations are run in the cloud.
?Enhanced features and functionalities of mobile devices through new cloud applications.
?Ease of access and development.
?Cheap for cloud computing vendors to build complex mobile cloud applications.
?Improved data storage capacity and processing power.
This paper proposes a new model of mobile learning system in cloud computing, by using high performance computing (HPC) and graphical processing unit (GPU) cluster infrastructures enrich with mobile and wireless devices such as smart phones, notebook and tablets [9-11]. The proposed model provides high performance and fast respond (three sixty five days a year) to its users. The proposed model also supports educational institutions with diverse learning styles in different learning contexts to facilitate learning and information/knowledge sharing through cloud computing. The proposed model is suitable for intensive and fast processing (computing) to 3D modeling of graphics visualization and animation in the areas of health care, medical learning, chemistry experiments and programming courses.
The proposed model provides consistent Internet service to users and it also manages load balancing on
HPC and GPU infrastructure in active/passive mode. Another main advantage is the ability to deal with either planned or unplanned service outage using load balancer servers to handle system traffic. It allows flexibility to perform maintenance on one server without effecting services. This is accomplished by transferring all traffic to one server and placing the load balancer in active/passive mode. Software upgrades and updates can
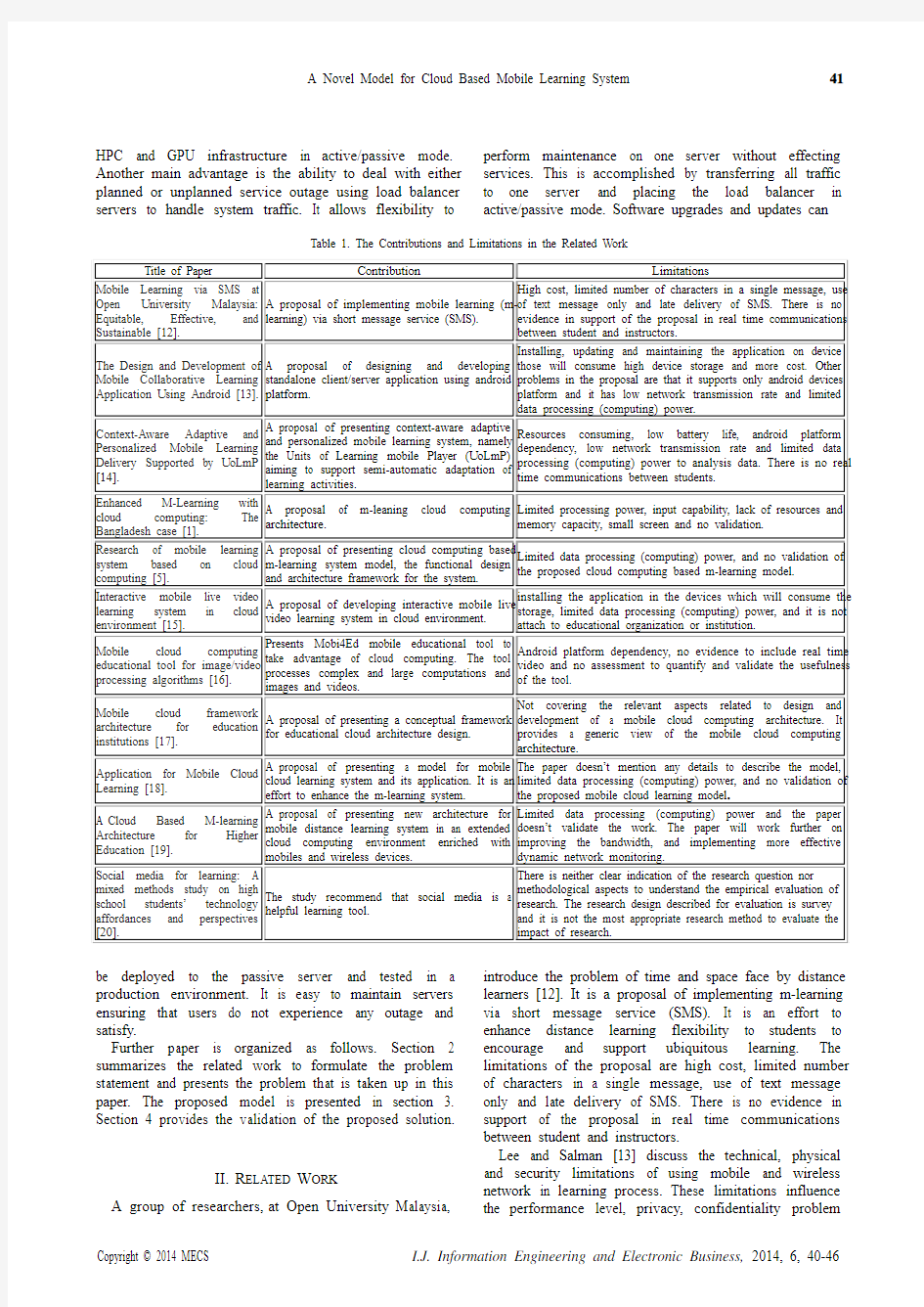
Table 1. The Contributions and Limitations in the Related Work
be deployed to the passive server and tested in a production environment. It is easy to maintain servers ensuring that users do not experience any outage and satisfy.
Further paper is organized as follows. Section 2 summarizes the related work to formulate the problem statement and presents the problem that is taken up in this paper. The proposed model is presented in section 3. Section 4 provides the validation of the proposed solution.
II.R ELATED W ORK
A group of researchers, at Open University Malaysia, introduce the problem of time and space face by distance learners [12]. It is a proposal of implementing m-learning via short message service (SMS). It is an effort to enhance distance learning flexibility to students to encourage and support ubiquitous learning. The limitations of the proposal are high cost, limited number of characters in a single message, use of text message only and late delivery of SMS. There is no evidence in support of the proposal in real time communications between student and instructors.
Lee and Salman [13] discuss the technical, physical and security limitations of using mobile and wireless network in learning process. These limitations influence the performance level, privacy, confidentiality problem
and high operational costs. It is a proposal of designing and developing standalone client/server application using android platform. The limitations of the proposal are installing, updating and maintaining the application on device those will consume high device storage and more cost. Other problems in the proposal are that it supports only android devices platform and it has low network transmission rate and limited data processing (computing) power.
Several researches have investigated potentials of the educational paradigm shift from the traditional teaching approaches to adaptive and personalized learning [14]. This has led to an increased interest on context-aware adaptive and personalized mobile learning systems with the emerging mobile devices technology to facilitate teaching and learning strategies. The aim is to provide learning experiences delivering via mobile devices and tailored to learne r’s personal characteristics and situations. It is a proposal of presenting context-aware adaptive and personalized mobile learning system, namely the Units of Learning mobile Player (UoLmP) aiming to support semi-automatic adaptation of learning activities. The main limitations are resources consuming, low battery life, android platform dependency, low network transmission rate and limited data processing (computing) power to analysis data. There is no real time communications between students [14].
Masud et al. [1] discuss m-learning high cost and lack of sufficient educational resources. It is a proposal of m-leaning cloud computing architecture. It is an effort to enhance m-learning architecture by cloud computing and using mobile phone technology as a supplement to the existing learning technologies. The objective is to investigate the technical capabilities of different wireless technologies, and determining their suitability to an m-learning environment. The limitations of the proposal are limited processing power, input capability, lack of resources and memory capacity, small screen and no validation.
A study discusses the hardware/software limitations using mobile in learning process [5]. It is a proposal of presenting cloud computing based m-learning system model, the functional design and architecture framework for the system. The limitations of the proposal are limited data processing (computing) power, and no validation of the proposed cloud computing based m-learning model. Saranya and Vijayalakshmi [15] discuss m-learning high cost and lack of sufficient (hardware/software) resources. It is a proposal of developing interactive mobile live video learning system in cloud environment. The limitations of the proposal are installing the application in the devices which will consume the storage, limited data processing (computing) power, and it is not attach to educational organization or institution.
A study [16] presents Mobi4Ed mobile educational tool to take advantage of cloud computing. The tool processes complex and large computations and images and videos. Students can assess several algorithms in real-time using this tool. It is an effort to help students to understand and compare different algorithms using mobile devices such as de-blurring, de-noising, face detection etc. The limitations of the proposal are android platform dependency, no evidence to include real time video and no assessment to quantify and validate the usefulness of the tool.
Paduri and Conradie [17] discuss how to improve the current initiation system of education and its quality and affordability. It is a proposal of presenting a conceptual framework for educational cloud architecture design. The limitations of the proposal are not covering the relevant aspects related to design and development of a mobile cloud computing architecture. It provides a generic view of the mobile cloud computing architecture.
A group of researchers introduce limitations of devices used for m-learning (usable memory capacity, screen size, problems with slow connections and reduced interface response speed, etc.), and the difficulties to apply existing electronic learning (e-learning) to ubiquitous m learning without modification [18]. It is a proposal of presenting a model for mobile cloud learning system and its application. It is an effort to enhance the m-learning system. The limitations of the proposal are the paper doesn’t mention any details to describe the model, limited data processing (computing) power, and no validation of the proposed mobile cloud learning model. Masud and Huang discuss how to deploy m-learning with the increased number of users, services, education contents and resources [19]. It is a proposal of presenting new architecture for mobile distance learning system in an extended cloud computing environment enriched with mobiles and wireless devices. It is an effort to overcome the m-learning obstacles related to the performance (battery life, storage, and bandwidth), environment (heterogeneity, scalability and availability), and security (reliability and privacy). The limitations of the proposal are limited data processing (computing) power, and the paper doesn’t validate the work. The paper will work further on improving the bandwidth, and implementing more effective dynamic network monitoring.
The study [20] examined high school students’ visual clue to the function of an object for social media. The objective is to know the approaches and ideas about emerging technologies, and allied problems and matters. The results reflect that students highly depend on social media in their daily lives for entertainment and community connections. The results recommend that social media is a helpful learning tool. There is neither clear indication of the research question nor methodological aspects to understand the empirical evaluation of research. The research design described for evaluation is survey and it is not the most appropriate research method to evaluate the impact of research.
The research problem is formulated as follows [5, 15, 18, 19].
How to improve quality and affordability of m-learning system with the increased number of users, services, education contents and resources?
III.T HE P ROPOSED S OLUTION
This paper proposes a cloud computing model for M-learning system using HP C and GPU cluster infrastructure a s shown in fig. 1. The proposed model increases the speed of search, development and it helps to perform high performance computations like science and engineering applications. The science or engineering applications require high bandwidth, low latency networking, and c o m pu tati onal resources to conclude decisions.
The proposed model incorporates communication between end-user devices, system server platform, management layer (logical layer), and base layer (infrastructure layer) using cloud computing environment. The users of the system are learners (students), instructors, parents and managers (including system administrators). A user’s device connects to the system through external network/Internet or through the local area network (LAN) in order to perform tasks like learn, communicate, download learning materials, access resources, enroll new students, view the student progress and configure the system. The system server platform, in cloud environment, connects the user’s device with logical layer. The user accesses the system server platform to perform data processing using HPC, data downloading using cloud services and data rendering using GPU. A user needs data to process by HPC cluster infrastructure. The user’s request is sent to the logical layer to map with the needed HPC functions to display the output. The logical layer acts as the brain of the system to complete a request with high performance and smooth flow. The infrastructure contains the basic environment of the system like databases, networks, storages, IT resources, computing, HPC cluster (that builds a massive parallel computer from a set of small machines) and GPU cluster (that is computer cluster in Fig. 1. The Proposed cloud computing model for M-learning which each node is equipped with a GPU). It is possible to perform very fast calculations with a GPU cluster by harnessing the computational power of modern GPUs via General-Purpose Computing on Graphics Processing Units (GPGPU). The load balancer is used in GPU cluster to increase performance by distributing the load among different nodes in the cluster. It is installed in front of all nodes. In case of a node failure the remaining node(s) will take over the responsibility to service future requests. The model consists of four layers: the user and device layer, the applications layer, the logical layer and the infrastructure layer.
A. The User and Device Layer
This layer is used to communicate with the devices using browsers to access the system server platform either by Internet or LAN to authenticate users. Students, instructors, parents and managers need to register as in the traditional systems. The users can change their information, password and other account setting after authentication, through the Account Setting component in the applications layer. This layer also provides transparency at the device and network levels so that users are unaware of their devices applicability or the underlying protocols. The data is different for each user depending on the role of user (student, manager/staff/system administrator, instructor, and parent). It can be divided into dynamic parameters (like protocol, location and time) and static parameters (like name, age, gender, address, E-mail, mobile telephone numbers, native language, free time, user's interests, device information, user level, social media accounts). The dynamic parameters are updated automatically by the system but the static parameters are entered by the users. This process is followed by all users. Furthermore, the user is allowed to reset the password in case it is forgotten. This is accomplished by sending the new password after user's request as an SMS or E-mail. The user’s data is encrypted to provide security.
B. Applications Layer (services)
Application layer provides various services to each user. This layer consists of many components that are integrated to each other. Application layer is scalable by plugging new components. Following are the main components of application layer.
?Users Account component is integrated with the existing user’s account. It allows the users to update their static personal information like change the password, change other information and social media accounts.
?Calendar component provides a reminder service where the users can flag activities. It is automatically updated by the system to include dates for assignments, exams, reports and meeting.
The user can update information on it manually to include meetings and other activities such as medical appointments. It provides the user weekly schedule that can be displayed on day to day basis.
When the user access the system it will be automatically connect to the device calendar in order to update and save the reminder notes like assignments, exams, reports, course lecture
and
meetings on the device. In case if the user is offline
then he/she can be reminded about activities.
Parents can use this component to schedule
meetings with the instructors. Managers can use
calendar component to schedule maintenance of
system. Managers can set meetings with staff.
?Student Progress component-It provides information about student progress, including
grades, attendance, and instructors' comments,
student reports. The instructors feed information can
be checked by students and parents. Parent can
communicate with the instructor using the
interactive classroom tool via meeting choice in
order to discuss how to improve the student learning
progress.
?Previous Session component- Users can keep track of the last session especially when communication
is aborted accidently. The last session information is
stored in the system. It allows the users to reopen a
particular session.
?Learning Courses and Labs component- It consists of a set of services for students and instructors about
course objective, learning target, learning plan,
instructor name, the related references, online
materials, exams and, results. Student can delay the
result if he/she does not want to see it immediately.
Student can set a reminder for a specific period.
User can access the system to know his/her mistakes
in exams, lecture notes, the recorded video of the
lecture, assignments, social media, email, practice
exercises, labs handouts, instructors' announcements, simulation environment, interactive tool to
communicate course or lab discussion and board to
post questions, comments, and answers.
?Learning resources component- It provides a database of digital educational resources that can be
accessed by students and instructors such as course
materials, lecture slide and video/audio. Library
service is used to check availability of resources in
library, digital libraries, online materials and other
learning database resources.
?Interactive Classroom Tool component- It provides real time communication between students and
instructors. It can be used by parents to
communicate with the instructor to discuss student
progress and it can be used by managers to
communicate with staff. Cisco WebEx, Udacity for
iPad are the main tools. Students use their mobile
devices (mobile smart phones, or tablets) to connect
to the course via their mobile networks (such as
GPRS, UMTS, HSPA, Wi-Fi, WiMAX or LTE). ?System Management component- This component is designed to serve managers and it is integrated with
all components of the system.
C. Logical layer
This layer maps the services to their clusters services by managing the underlying resource. It is responsible for maps between the user requests and the needed hardware or software to accomplish it. The logical layer schedules user's requests and it provisions the needed resources to access the services of cloud or system efficiently and securely.
D. Infrastructure Layer
This layer provides the basic environment including computers, storage; servers, networking, database resources, IT resources, data, network, storage resource pool, GPU cluster and HPC cluster.
IV.V ALIDATION
In order to validate the proposed model, Survey was conducted. The purpose of adopting this method it is not consuming time and the answer will be using likert scale which is a thoughtful way. A closed ended questionnaire consisting of 29 questions was distributed among different users (student/instructor/manager, staff, and system administrator from different educational organization/parent). Five goals were used for data gathering. Questions were arranged according to their relevancy to defined goals.
Goal 1.Frequency of using mobile devices and its applications and users beliefs.
Goal 2.Anywhere and anytime (mobility).
Goal 3.Better services for better learning and build a relationship with the system (productivity).
Goal 4.Interactive communication with privacy.
Goal 5.Fast respond with high performance (data processing time).
The response was gathered from 43% students, 18% instructors, 28% parents and 12% managers. The data was gathered and analyzed through Google tools and excel for statistical analysis. The results are concluded mainly through frequency tables showing the exact degree of analysis.
A. Cumulative Statistical Analysis of Goal 1
The results are shown in Table 2.
Table 2. Cumulative Statistical Analysis of goal 1
It is shown in Table 2 that 57% and 24% of the respondents supported very high and high to the goal 1. 7% of the sample supported to low and 3% of the sample agreed to very low. 9% of the sample chose to be neutral.
B. Cumulative Statistical Analysis of Goal 2
Cumulative static analysis of goal 2 is shown in Table 3.
Table 3. Cumulative Statistical Analysis of goal 2
It is cleared from the Table 3 that 58% and 24% of the sample believed that the mobile devices usage and cloud computing will enhance the learning process. 4% and 3% of the respondents were not agreed. 11% of the sample remained neutral.
C. Cumulative Statistical Analysis of Goal 3 Cumulative analysis of goal 3 is shown in Table 4.
Table 4. Cumulative Statistical Analysis of goal 3
According to Table 4, 58% of the respondents are very highly agreed with goal 3 and 24% of the sample
believed in the goal 3. 4% and 3% of the sample were not agreed with the goal 3. 11% of the sample remained neutral.
D. Cumulative Statistical Analysis of Goal 4
The cumulative analysis of goal 4 is shown in Table 5.
Table 5. Cumulative Statistical Analysis of goal 4
Table 5 shows that 56% of the respondents are very highly in favor of goal 4 while 26% of the respondents are highly supported the goal 4. Overall 7% of the respondents are against the goal 4. 11% of the respondents are remained neutral.
E. Cumulative Statistical Analysis of Goal 5
Questions under this goal show that how much users are interested in continues services with high performance, fast respond and security of the proposed model. The results are shown in Table 6.
Table 6. Cumulative Statistical Analysis of goal 5
Table 6 shows that 60% of the respondents do have a very high support for the goal 5. 23% of the respondents are highly interested in continues services with high performance, fast respond and security of the proposed model. 6% of the respondents are against this feature and 11% of the respondents are remained neutral. F. The Final Cumulative Evaluation of all goals The results, of final cumulative statistical analysis of the 5 goals, are shown in Table 7. It is shown in Table 7
that 82% (24% and 58%) of respondents support the proposed model. 11% of the respondents remained neutral. 5% and 3% of the respondents support low and very low to the proposed model.
Table 7. Cumulative Statistical Analysis of 5 goals
V.C ONCLOUSION
Mobile devices are widespread and provide great capabilities to deliver M-learning. There are numerous educational organizations who cannot afford expensive resources to implement M-learning. Cloud computing is the best solution for such institutions who want to implement M-learning system with its dynamic scalability and low cost. This paper presents new model of M-learning system in cloud computing environment extended by the power of HPC and GPU cluster infrastructure. A validation of the proposed model was performed. It was concluded that 82% of respondents support the proposed model.
R EFRENCES
[1]Masud, Anwar Hossain; Jianming Yong; Xiaodi Huang;,
"Enhanced M-Learning with cloud computing: The Bangladesh case," Computer Supported Cooperative Work in Design (CSCWD), 15th International Conference on IEEE, vol., no., pp.735-741, 8-10 June. 2011.
[2]https://www.360docs.net/doc/3f550206.html,/wiki/Distance_education#Distance
_e-Learning. Accessed 2014.
[3]Shuai, Qin; Zhou Ming-Quan.;, "Cloud computing
promotes the progress of m-learning," Uncertainty Reasoning and Knowledge Engineering (URKE), International Conference on IEEE, vol.2, no., pp.162-164, 4-7 Aug. 2011.
[4]Verma, Kritika; Dubey, Sonal; Dr.M.A.Rizvi;,"Mobile
Cloud A New Vehicle for Learning: m-Learning Its Issues and Challenges," International Journal of Science and Applied Information Technology,vol.1, no.3, pp.93-97, July – Aug. 2012.
[5]Chen, Shaoyong; Min Lin; Huanming Zhang; "Research
of mobile learning system based on cloud computing,"e-
Education, Entertainment and e-Management (ICEEE), International Conference on IEEE, vol., no., pp.121-123, 27-29 Dec. 2011.
[6]https://www.360docs.net/doc/3f550206.html,/wiki/M-learning#Challenges.
Accessed 2014.
[7]Hirsch, Benjamin; Jason WP Ng., "Education beyond the
Cloud: Anytime-anywhere learning in a smart campus environment," Internet Technology and Secured Transactions (ICITST), International Conference on IEEE, vol., no., pp.718-723, 11-14 Dec. 2011.
[8]M. Tantow: Cloud Computing and Smartphones. Cloud
Times.https://www.360docs.net/doc/3f550206.html,/2011/03/01/cloud-computing-
and-smartphones/ (01 March 2011).Accessed 2014.
[9]https://www.360docs.net/doc/3f550206.html,/hpc-basic-training/what-is-hpc/.
Accessed 2014.
[10]Douglas Eadline: Moving HPC to the Cloud. admin
magazine.https://www.360docs.net/doc/3f550206.html,/HPC/Articles/ Moving-HPC-to-the-Cloud. Accessed 2014. [11]https://www.360docs.net/doc/3f550206.html,/wiki/Graphics_processing_unit.
Accessed 2014.
[12]Lim, Tina; MansorFadzil; NorziatiMansor;,"Mobile
Learning via SMS at Open University Malaysia: Equitable, Effective, and Sustainable,"International Review of Research in Open & Distance Learning, vol.12, no.2, pp.122-137, Feb. 2011.?
[13]Kwang B. Lee; Raied Salman;,"The Design and
Development of Mobile Collaborative Learning Application Using Android,"Journal of Information Technology and Application in Education, vol.1, no.1, pp.1-8, 2012.?
[14]Gómez, Sergio, et al.;,"Context-Aware Adaptive and
Personalized Mobile Learning Delivery Supported by UoLmP," Journal of King Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences, vol.26, no.1, pp.47–61, 21 Oct.
2013.
[15]Saranya, S. Mohana; M. Vijayalakshmi;, "Interactive
mobile live video learning system in cloud environment,"
Recent Trends in Information Technology (ICRTIT), International Conference on IEEE, vol., no., pp.673-677, 3-5 Jun. 2011.
[16]Ferzli, Rony; Ibrahim Khalife;, "Mobile cloud computing
educational tool for image/video processing algorithms,"
Digital Signal Processing Workshop and IEEE Signal Processing Education Workshop (DSP/SPE), IEEE, vol., no., pp.529- 533,4-7 Jan. 2011.
[17]Veerabhadram, Paduri; Pieter Conradie;,"Mobile cloud
framework architecture for education institutions,"
Science and Information Conference (SAI), IEEE, vol., no., pp.924-927, 7-9 Oct. 2013.
[18]Lee, Jae
Dong; Jong-Hyuk Park; , "Application for Mobile Cloud Learning,"Network-Based Information Systems (NBIS), 16th International Conference on IEEE, vol., no., pp.296- 299, 4-6 Sept. 2013.
[19]Masud, A. Hossain; Xiaodi Huang; "A Cloud Based M-
learning Architecture for Higher Education,"Archives Des Sciences, vol.66, no.1, pp.751-760, Jan. 2013.?[20]Mao, Jin; "Social media for learning: A mixed methods
study on high school students’ technology affordances and perspectives," Computers in Human Behavior on Science Direct, vol.33, no., pp.213-223, April 2014.?
Authors’ Profiles
Areej Omar Balgosoon: Post-graduate student for master degree for Information Technology in King Abdul-Aziz University. She received a Bachelor in Computer Science in 2009 and worked in 3D animation projects during undergraduate program.
Dr. M. Rizwan Jameel Qureshi
received his Ph.D. Computer Sciences
degree from National College of Business
Administration & Economics, Pakistan
2009. He is currently working as an
associate Professor in the department of
Information Technology, Faculty of
Computing & Information Technology,
King Abdul-Aziz University. He is the best researcher awardees of King Abdul-Aziz University Saudi Arabia in 2013 and Department of Computer Science, COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Pakistan in 2008.
管线资源管理系统
管线资源管理系统 2007-08-10 19:16:46 来源:编辑:中国软件网作者:评论:0 一、前言随着中国电信业飞速发展,电信设备资源尤其是线路资源也成倍增长;电信线路作为电话、传真、数据通信畅通的必要条件,其建设与维护管理有着举足轻重的作用。但由于电信通信网络高速建设发展与落后的维护水平,形成了线路资源管理难的局面,造成了网络资源的浪费,影响网络的进一步建设和合理规划;由于电信线路、管 一、前言 随着中国电信业飞速发展,电信设备资源尤其是线路资源也成倍增长;电信线路作为电话、传真、数据通信畅通的必要条件,其建设与维护管理有着举足轻重的作用。但由于电信通信网络高速建设发展与落后的维护水平,形成了线路资源管理难的局面,造成了网络资源的浪费,影响网络的进一步建设和合理规划; 由于电信线路、管道资源与地理、图形属性密切关联,且传统的工程图纸手工管理方式,难以满足目前的维护、管理需求;为了实现网络资源的可视化、规范化、现代化的管理,必须建设一套基于地理信息应用的电信管线管理系统,以彻底解决管理中的各种问题。 汉佳公司多年来一直专注于GIS技术的研发和系统集成应用领域,尤其对电信管线资源的建设与管理积累了大量的经验;汉佳公司的GIS管线资源管理系统,是根据《广东电信资源管理系统GIS管线资源管理子系统技术规范》的技术要求,并针对目前电信管线资源管理所面临的各种问题,而提供的可行性解决方案;该系统在各个地市局的成功应用,得到客户的一致认同,证明了系统的成熟性、先进性;为了满足用户的多种需求,汉佳提供专业的GIS平台解决方案和非GIS系统解决方案,供用户选择; 二、系统简介 主界面 汉佳GIS管线资源管理系统采用客户机/服务器模式,基于ArcInfo的GIS平台进行开发;数据库采用Oracle和数据库空间插件ArcSDE,前端采用Visual C++和ArcInfo控件产品MapObjects实现业务应用功能;从而,系统实现了管线设备管理的地理化、可视化,数据分析空间化的管理方式。 由于系统基于GIS平台进行应用开发,从而它能将管线设备和地理空间信息完美地结合起来,进行信息综合处理,改变管线资源管理的传统模式,使用更直观的方式,查看管线
中国移动集团客户营销体系.doc
中国移动集团客户营销体系 从移动通信市场经营经验探索的意义上解析小灵通,它对中国电信的意义就绝不仅仅限于在“3G’之前找到一个新增点,解决中国电信收入增长率的问题。中国电信的经营者,也提前意识到小灵通的战略意义,因此,在一些小灵通发展较早的电信公司,在完成“用户规模积累”阶段后,开始在小灵通客户群的服务体系等方面进行尝试:例如成都电信,在小灵通用户规模达到130万户后,成立了专门的小灵通客户部,负责用户尤其是高端用户的服务与保有;浙江电信则全省统一在10000号建立专门的小灵通班组。 从这些刚刚开始进行的探索中,中国电信已经感受到对移动客户尤其是高值移动客户关注的重要性。以成都电信为例,2005年,实行客户经理负责的近8万小灵通高端客户,全年流失率仅为2%,大大低于小灵通客户平均30%的流失率水平。 中国电信与其从头开始探索移动客户群的服务之路,不如“站在领先者的肩上”,研究一下中国移动在客户服务尤其是高值客户服务方面的发展历程,作为中国电信思考的参照。 基于这一初衷,我们在收集大量相关资料的基础上,对中国移动集团客户体系近年来的发展历程及思路进行了梳理,并提出了结合中国电信调整与改善市场营销体系的建议。 中国移动集团客户体系的发展沿革及概况
2000年,中国移动从中国电信剥离后,这一批当初的电信人很快意识到移动客户群的经营与服务与固定客户群有着迥然不同的特征,其中最明显的区别在于移动客户强烈的个人性。我们可以看到,中国移动早期正是针对移动客户个人性的特点,对不同客户群进行分级服务,并大力打造两大服务品牌:针对普通客户服务的1860品牌和针对高端客户的全球通VIP服务品牌。 但是,值得重视的是,从2002年以后,中国移动开始低调但快速地把客户服务体系的重心转向另一方面:集团客户。与中国电信的大客户体系相比,移动的集团客户体系可以说是后来者,而且由于移动客户的个人性,集团体系的建设面临许多的困难。为此,中国移动不得不借用电力系统“网格化”管理的方面,通过网格化管理,逐步收集与建立集团客户档案。经过四年的努力,中国移动的集团客户的覆盖率已经达到近30%,集团客户对于高值用户群的稳定、移动数据及增值业务的推广、行业应用等方面,已经具有相当的战略地位。中国移动是如何在短短四年内建立与健全这一体系的?我们首先简单回顾移动集团客户体系的发展历程。 2002年是中国移动集团客户体系建设的试点推广年。这一年移动主要在以下方面进行了初步的探索:成立项目组、产品模块化、典型项目推广、建立工作流程。 2003年是移动集团客户体系建设的全面促进年。他们明确提出“集团客户工作不能再是业余爱好,要打正规战役。”这一年他们在集
中国移动中高端客户保有方法大全(参考资料)
中国移动中高端客户保有方法大全 对于三家运营商,两有(市场占有,客户保有)历来是它们必争指标。其中,集团客户保有一直是三大运营商角逐的核心指标。中高端客户,这个以20%比例创造80%价值的群体,确实诱人。现今,电信189强势入市,利用政企客户多年经营固网优势进行深度捆绑;联通携手苹果、诺基亚,通过借势经营和借势营销来逐步蚕食;移动更是煞费苦心,并把中高端客户保有作为KPI考核的核心指标。所以,把09年定位为“中高端客户策反保有年”一点也不为过。一场中高端客户保有的拉锯战随着三大运营商重组的完成轩然展开。 实际上,从去年下半年,部分省市移动运营商已经从经分系统数据中感觉到这个指标的不妙。而他们也束手无策,向我们求援。而今年很多公司几乎是同一声音反映中高端客户流失严重,相应的中高端保有咨询项目也浮出水面。在我们跟客户沟通过程中,我们发现:他们并不完全明白客户为什么会流失,他们的短期策略和长期策略也不知道怎样制定?笔者结合相关实战和研究,提出中高端客户“策反保有”三十六式,这三十六式包含策略层面(12式)和操作层面(24式)。 策略层面 这些招式更多源自策反保有的基础问题和根本问题,包含组织结构、制度改善、流程再造、协同机制建立、绩效考核、市场运作机制、人力配备、学习力等方面。 第一式:规范业务运营基础。把资料管理、业务受理、帐务管理、服务管理等形成闭环,做到各个环节有据可依,业务办理流程完整清晰。比如:服务管理可以形成售前售中售后闭环流程:售前――需求收集、分析,解决方案制定,签署协议;售中――开通准备,业务开通;售后――服务保障,满意度调查,客户意见收集和反馈并进行需求再发现和二次营销(又回到售前)。
浅析中国移动集团客户经营分析
浅析中国移动集团客户经营分析 文章来源:睿远见作者:周勃发布时间:2006-10-15 随着集团客户在中国移动运营地位的提升和市场竞争的加剧,集团客户市场的经营正面临着一场前所未有的机遇与挑战。机遇在于中国移动市场集团客户商处于初期阶段,庞大的市场等待发掘,挑战在于其他电信运营商的进入和WTO 承诺电信市场开放日期的临近,集团客户的争夺将会成为竞争的焦点。 集团客户市场的经营,包括客户获取、客户保持与客户满意三个方面,如何保持三方面工作的领先?完善、科学的经营分析系统建设尤为必要,它可以帮助公司充分认识和应对市场变化,使得公司能在激烈的市场竞争中抢得先机,同时可以协助公司完成协助公司顺利完成从传统的以产品为中心的经营理念向以客户为中心的新经营理念的转变。 集团客户经营分析目的 集团客户经营分析目的在于总结前一阶段工作的发展状况,明确下一阶段工作发展规划,在目前集团客户经营分析工作还有内部宣传作用,即在公司内部宣传和推广集团客户工作的重要性,寻求公司资源的支持和部门之间的配合,这在集团客户工作开展初期,显得尤其必要。 集团客户经营分析内容 集团客户经营分析工作可以概括为五个方面的内容:指标跟踪、市场环境、问题分析、重点问题专题分析、策略的制定。 指标跟踪的内容为集团客户发展考核指标的跟踪和描述,如圈地指标、集团客户发展指标、收入指标、客户离网指标、精品工程指标、跨省客户指标等。指标跟踪内容主要关注省公司集团客户市场经营现状和指标完成进度,对集团客户工作起到督促和改进的作用。 指标跟踪部分的数据可以从大客户系统和BOSS 系统中进行提取,但是指标跟踪分析不仅仅包括数据的罗列,还需要包括关联度分析、指标进度分析以及分类分析,如集团客户业务发展指标与市场经营整体业务指标的关联度分析。 市场趋势分析是集团客户经营分析中的一个重要内容,而这一部分往往是部分移动公司欠缺的。市场趋势分析应该包扩市场竞争环境、客户需求内容、市场空间及发展的预测。市场趋势分析内容的特点不仅应该包括定量分析还应该包括定性分析。做好市场分析需要对移动市场的持续跟踪,并形成定期信息收集、记录制度,这样才可以最终在经营分析报告中科学的展示,不然临时突击的汇总,反应的信息往往是片面的,经不起验证。 问题分析和重点问题专题分析主要围绕集团客户市场经营的内容进行问题发现和深入
中国移动5G+揭秘云计算习题库
单选题 1、单选-云计算的一大特征是(),没有高效的网络云计算就什么都不是,就不能提供很好的使用体验 A、按需自助服务 B、无处不在的网络接入 C、资源池化 D、快速弹性伸缩 2、单选-要使端口组到达其他VLAN上的端口组,必须将VLAN ID设置为() A、80 B、4095 C、8080 D、3306 3、单选-对于公有边缘节点,通常以()的形式部署于() A、小型数据中心,地市及以下的自有机房 B、大型数据中心,公有云机房 C、大型数据中心,私有云机房 D、大型数据中心,地市及以下的自有机房 4、单选-对于公有边缘节点,边缘连接网元和边缘云()置于同一机房,()放置于不同机房 A、不可以,可以
B、不可以,不可以 C、可以,可以 D、可以,不可以 5、单选-对ANSIBLE框架下包含的几个模块,说法不正确的是 A、connetcion plugins:负责和被监控端实现通信 B、playbook:剧本执行多个任务时,非必须可以让节点一次性运行多个任务 C、hosinventory:借助于插件完成记录日志邮件等功能 D、各种模块核心模块、command模块、自定义模块 6、单选-Saltstack 是基于什么语言开发 A、c++ B、java C、PHP D、Python 7、单选-Linux返回上一级目录使用那条命令(C) A、cd B、cd . C、cd .. D、cd …
8、单选-Nova-scheduler创建和迁移虚拟机时,通过两个步骤选择合适的节点创建和迁移虚拟机,这两步中第一步是过滤(filter),第二步是() A、随机选择(random) B、权重计算(weighting) C、选举(election) D、投票(vote) 9、单选-Raid5需要至少几个硬盘组成的磁盘阵列 A、1 B、2 C、3 D、4 10、单选-()指的是降低运维开销,实现IT的敏捷交付,实现企业业务的自动化交付,是IT可以更加关注业务的本身。 A、简单化 B、平台化 C、服务化 D、专一化
中国移动客户关系管理
精心整理 中国移动客户关系管理 1.移动通信企业CRM分析 1.1移动的顾客识别 移动公司通过一系列技术手段深入了解自己的顾客,收集客户信息,根据客户的特征、购买记录等可得数据,找出谁是企业的潜在顾客,客户的需求是什么、哪类客户最有价值等,并把这些客 RFM 找出消费金额比较高的消费者,加以着重关爱。总之就是更好地使用有效的企业资源。 1.3移动的客户关系维系 首先,通过与客户的互动将自己的产品和服务介绍给客户,扩大客户群体。中国移动在电视杂志网络均有广告,来吸引更多的消费者。中国移动还在户外开展各种活动赞助来扩大它的影响力。其次,通过与客户互动来了解客户的需求。中国移动开设的有人工服务,语音服务,方便客户查询和办理业务,另外还有短信中心,有出新业务及时给客户通知,另外还有网上营业厅和营业厅实体店,客户如有疑问可以向工作人员了解情况。 第三,对移动公司服务、产品的意见的调查和满意度测评。
2.移动通信企业CRM当前存在的主要问题 (1)业务发展问题 业务的发展是企业增加利润,提高客户的满意度、忠诚度,拓展市场,提高竞争能力的必要手段。对业务如何有针对性地进行拓展,如何考虑价格因素的影响以及如何制定有效的市场营销策略等问题对于移动通信企业是非常重要的,也是目前迫切需要解决的。 (2)缺乏对客户流失问题的全方位分析 目前迫于市场竞争的压力,用户流失情况严重,公司对客户的流失没有采用很好的管理策略,只了解到客户流失了,并没有真正掌握客户流失的原因、流失的方向和流失客户的构成;并且对客 在 3. 3.1CRM系统建设的目标 客户关系管理信息系统的建设,旨在利用先进的信息技术与计算机应用技术成果,通过和电信其它业务系统及职能系统的有机结合,建立一个发展客户、维持用户、使潜在客户成为现实用户的信息处理与分析平台。它是在收集客户市场调查信息、客户资料信息、客户营销战略资源的基础上,再自动采集计费、客服、网管、财务等系统的相关数据,建立快速、全面、准确的新客户业务受理、新增需求受理及故障处理过程通道,建立完善的奖金管理、渠道管理系统以及完整的客户满意度评
移动资源管理系统改造方案
北京移动资源管理改造方案 1.背景 2.概述 2.1资源管理的范围 资源是中国移动在市场营销、销售、客户服务过程中涉及到的各类有形和无形资源,目前在系统中实现支撑的资源主要包括: 号码主要分为普通号码(包括全球通,动感地带,神州行等品牌)和集团号码以及一些副号码业务。 业务卡即SIM卡资源,分为空卡,白卡和带号卡3类。 有价卡则充值卡,有实体充值卡和电子充值卡,这里WLAN电子卡也归为有价卡的类别进行管理。 终端资源主要包括手机终端,上网本,上网卡等设备资源。 促销品即营销实物资源,如大米,油等 2.2资源管理涉及系统说明
2.3各系统交互整体现状流程图 目前北京资源管理涉及的系统很多,资源都离散在不同的系统进行管理,下面是目前北京的系统间的主要交互的流程图:
流程说明: 1.一级BOSS下发终端数据,CRM透传给SCM系统,SCM系统支撑终端数据的管 理功能 2.大唐下发SIM卡数据同步给CRM的资源,号码则是由CNP同步给CRM的资源, 资源负责号码和SIM卡资源的库存管理 3.RM支撑的有价卡的管理,数据也是来源于CNP’,CNP生成有价卡数据还会 将数据同步给MIS 4.MIS负责各种实物资源的库存调拨,包括SIM卡,业务卡等。 5.CRM的营业主要支撑面向客户的资源使用,其中,有价卡在使用过程中需 要和VC作交互,电子有价卡还需要到解密平台做解密操作。 3.系统支撑现状详细说明 3.1号码支撑现状 号码资源管理功能是由CRM系统支撑,号码资源由CNP生成后通过文件接口通过给CRM系统,具体的流程图如下: 流程说明: https://www.360docs.net/doc/3f550206.html,P生成号码数据,通过文件方式同步给CRM的资源系统,管理员也可通 过CRM前台导入数据。 2.CRM的资源主要支撑号码的管理,包括品牌级别管理、库存管理,以及号
中国移动集团产品
目录 集团专线 (2) IMS (3) 物联网 (4) 集团短彩信 (5) 流量红包 (6) 人人通 (7) 销售管家 (8) 集团通讯录 (9) 集团V网 (10) 集团彩铃 (10) 视频监控类 (11) 一卡通 (12) 一卡通成功案例 (13)
集团专线 集团专线接入是基于我公司的传输网、GSM网、3G、4G无线网、CMNET数据网等网络资源,采用有线和无线方式为集团客户提供专有的接入或数据传送业务。 ◆互联专线 为用户提供内部联网的专用数据传输通道,使用户内部应用实现联网的一 种业务。(适用于企业内部网络传输) ◆CMNET专线 用户通过租用江西移动提供的专线,接入中国移动互联网(CMNET)实现 上网的一种业务。(适用于企业宽带上网) ◆GPRS-APN专线 通过光纤接入企业内部网络,将移动GPRS网络与企业内网相连接,从而 实现从移动终端搜集资料、控制移动终端的目的。(适用于银行、无线POS 机等节点分散,线路接入困难的专线连接)
IMS IMS是一种全新的多媒体业务,它能够满足终端客户多样化的多媒体业务需求。IMS是解决移动与固网融合,引入语音、数据、视频三重融合等差异化业务的重要方 式。 多媒体电话业务 多媒体电话业务是基于IMS平台,在面向集团客户提供普通固话、传真功 能的同时,还提供视频通话以及语音增值服务等多媒体服务,是全方位的固 定电话解决方案。 融合V网 融合V网是指7/8位的集团固话号码与移动手机组成综合V网,实现短号和 网内通话优惠功能。 融合一号通 融合一号通分为主叫一号通和被叫一号通,主叫一号通是指可以设置一个移 动手机号码或另一个集团固话号码设置为该号码的主号码,使之被叫显示该 主号码;被叫一号通是指设置多个移动手机号码或其他集团固话号码为该号 码的关联号码,使之该号码的被叫可以与关联号码进行同振、顺振。 融合总机 融合总机业务是传统总机和移动总机业务的融合,集团固话号码作为总机号,移动手机号和集团固话号码作为分机号,并为集团客户提供电话号码查询、转接来话、解答用户问题等话务台服务;外部用户拨打总机时,还可播放欢迎词和集团客户介绍。
(客户管理)中国移动集团客户营销体系
(客户管理)中国移动集团客户营销体系
中国移动集团客户营销体系 从移动通信市场运营经验探索的意义上解析小灵通,它对中国电信的意义就绝不仅仅限于于“3G’之前找到壹个新增点,解决中国电信收入增长率的问题。中国电信的运营者,也提前意识到小灵通的战略意义,因此,于壹些小灵通发展较早的电信公司,于完成“用户规模积累”阶段后,开始于小灵通客户群的服务体系等方面进行尝试:例如成均电信,于小灵通用户规模达到130万户后,成立了专门的小灵通客户部,负责用户尤其是高端用户的服务和保有;浙江电信则全省统壹于10000号建立专门的小灵通班组。 从这些刚刚开始进行的探索中,中国电信已经感受到对移动客户尤其是高值移动客户关注的重要性。以成均电信为例,2005年,实行客户经理负责的近8万小灵通高端客户,全年流失率仅为2%,大大低于小灵通客户平均30%的流失率水平。 中国电信和其从头开始探索移动客户群的服务之路,不如“站于领先者的肩上”,研究壹下中国移动于客户服务尤其是高值客户服务方面的发展历程,作为中国电信思考的参照。 基于这壹初衷,我们于收集大量关联资料的基础上,对中国移动集团客户体系近年来的发展历程及思路进行了梳理,且提出了结合中国电信调整和改善市场营销体系的建议。 中国移动集团客户体系的发展沿革及简介 2000年,中国移动从中国电信剥离后,这壹批当初的电信人很快意识到移动客户群的运营和服务和固定客户群有着迥然不同的特征,其中最明显的区别于于移动客户强烈的个人性。我们能够见到,
中国移动早期正是针对移动客户个人性的特点,对不同客户群进行分级服务,且大力打造俩大服务品牌:针对普通客户服务的1860品牌和针对高端客户的全球通VIP服务品牌。 可是,值得重视的是,从2002年以后,中国移动开始低调但快速地把客户服务体系的重心转向另壹方面:集团客户。和中国电信的大客户体系相比,移动的集团客户体系能够说是后来者,而且由于移动客户的个人性,集团体系的建设面临许多的困难。为此,中国移动不得不借用电力系统“网格化”管理的方面,通过网格化管理,逐步收集和建立集团客户档案。经过四年的努力,中国移动的集团客户的覆盖率已经达到近30%,集团客户对于高值用户群的稳定、移动数据及增值业务的推广、行业应用等方面,已经具有相当的战略地位。中国移动是如何于短短四年内建立和健全这壹体系的?我们首先简单回顾移动集团客户体系的发展历程。 2002年是中国移动集团客户体系建设的试点推广年。这壹年移动主要于以下方面进行了初步的探索:成立项目组、产品模块化、典型项目推广、建立工作流程。 2003年是移动集团客户体系建设的全面促进年。他们明确提出“集团客户工作不能再是业余爱好,要打正规战役。”这壹年他们于集团客户体系建设方面的主要进展是:建立工作体系、健全客户资料、建设平台支撑系统、大力推广标准化应用产品、创新商务模式、建立营销渠道。为此,各级移动主要开展了四项工程:摸底工程,主要是地毯式清查,健全数据;圈地工程,以四川移动为例,他们要求当年
移动云计算专业介绍
移动云计算简介移动云计算是在谷歌提出云计算概念这是一个美丽的网络应用模式的升华,通俗讲就是将云计算概念应用到移动互联网上。目前在国内,北京航空航天大学软件学院率先提出这一产业的人才培养目标。移动云计算专业简介一、概述北航软件学院在工业和信息化部软件与集成电路促进中心(CSIP)、北京市政府、联想集团、Adobe、中国云计算联盟、中关村科技园区管委会、望京科技创业园、宏达电HTC和多普达Dopod(拥有全球Google Android和Microsoft Windows Mobile最大的市场份额)等机构的大力支持下,开设全国第一个“移动云计算”软件工程硕士专业,努力将北航软件学院打造成为中国移动应用开发领域的“黄埔军校”。学生将学习云计算、移动开发、软件服务、软件工程相关理论与技术,并必须参与完成至少一款商业级应用软件服务产品设计和开发。本专业的目标是培养具有军计算服务端和各类终端技术开发能力的实用型工程师及移动项目管理高端人才。目前本领域人才需求极度缺乏,学生毕业后可保证高薪就业。根据2010年洽谈的用人单位需求和薪酬情况,具有项目实战经验的移动云计算人才,严重供不应求。预计平均初始月薪将达到8000元人民币。大型企业直接定制,银行全额贷款,零风险、零投入获得名牌大学硕士学位并高薪就业,从此改变您的人生。专业前景云计算和移动互联网结合,催生新的巨大的产业机会!云计算和移动互联网,无疑是当今软件与信息服务业最热门的话题。当移动互联网产业与云计算技术结合,移动云计算成为IT行业炙手可热的新业务发展模式。2009年7月ABI Research的一份关于移动云计算的研究报告,提到云计算不久将成为移动世界中的一股爆破力量,最终会成为移动应用的主导运行方式,引起了投资界以及业内人士的高度关注。由于拥有开放的技术接口、分布式的计算理念,超强而又灵活的处理能力,云计算正在被人们所接受。我们看到,经过了一年多的市场培育期,人们将注意力逐渐从对云计算的技术特点和业务模式的分析转向其业务所提供的可用性与响应速度。借助于移动云计算,Google的手机导航系统,手机语音搜索系统以及Android平台上的各种服务的表现已经让人赞叹不已。美国Apple公司的市值最近超越了Microsoft的市值,Apple公司被世界上公认为最有创意的最有价值的IT公司,其CEO Steve Jobs也被认为是最近10年来最明星的CEO,也证明了移动云计算的重要性。我国投入了万亿规模的3G网络的成功也一定必须依赖于类同Apple AppStore这样的移动云计算的成功。根据ABI Research的最新预测报告,2008年全球移动云计算用户数量为4280万,占全球手机用户数量的1.1%。未来5年移动云计算将进入高速发展时期,到2014年全球用户数量将达到9.98亿,占全球手机用户的19%,每年能够以30-50%的速度发展。移动云计算市场巨大,发展迅速,人才缺口极大!2009年中国各大运营商获得3G 牌照,标志着移动互联网在中国的发展进入了快车道。利用移动云计算的各种无线互联网的服务也将深入到人们的生活当中。人们对无线互联网各类服务的大量使用又将反过来进一步推动“移动云计算”市场与技术的发展,这势必会引发市场对此领域技术人才的极大需求。据工信部人才交流中心预计,3G进入大规模建设阶段后,按目前的培养速度,“移动云计算”人才需求缺口将达百万。2010年8月,共青团中央和中国移动联合启动“移动应用商场百万青年创业计划”,预示着一个“移动开发”时代的来临,而目前主流“计算机”相关专业毕业生还不能直接开发基于移动终端的应用,“移动云计算”正是解决这一巨大产业需求的精准定位专业,而目前国内还没有基于“移动云计算”的专业教育和培训机构,这正是同学们的机遇所在。培养目标n 培养具有云计算服务端和各类移动终端技术开发能力的实用型软件工程师;n 在Adobe 的全力支持下,培养基于云计算服务端和各类移动终端的UI/UE、界面设计、RIA开发等实用型美工设计师;n 培养移动云计算领域的项目管理高端人才(并与斯坦福大学、加州大学伯克利分校联合建设课程体系中)将云计算技术、3G技术、应用服务技术等结合,培养“高层次、实用性、复合型、国际化”的具有实战经验的软件工程专业人才。通过一年的软件工程基础课程和移动云计算核心
地下管线管理信息系统
地下管线管理信息系统 一、概述 地下各类管网、管线是一个城市重要的基础设施,它不仅具有规模大、范围广、管线种类繁多、空间分布复杂、变化大、增长速度快、形成时间长等特点,更重要的它还承担着信息传输、能源输送、污水排放等与人民生活息息相关的重要功能,也是城市赖以生存和发展的物质基础。 随着我国城镇化进程的不断深入,传统的城市地下管线二维管理模式,已根本无法满足当今人们对地下管网、管线大数据信息分析、表达、应用的实际需要。基于此,众智软件审时度势并充分利用多年来在三维领域的研究成果和自有核心技术,自主研发了一套全新的地下管线数据资源汇集管理信息平台——3DPLINE城市三维地下管线管理系统。该系统可有效地将各类地下管线资源融入在系统之中,全面实现了地下管线数据信息的二三维一体化,以及动态更新与专业属性数据的整体同步。此外,系统还可融地理信息、业务办公和辅助决策等地上、地下建筑规划管理模块于一体,采用虚拟仿真技术一揽子解决地下管线管理中所发生的诸多问题。不仅有助于避免市政建设过程中道路的多次开挖,而且还可大大降低施工中地下设施的矛盾与事故隐患,提高管线工程规划设计、施工与管理的准确性和科学性。大量节省规划审批中挖路断面、确定管线走向的时间和费用,最大限度地减少因规划失策所造成的经济损失。 另外,系统还可根据管网空间数据,实现城市三维地下管线的可视化管理,支持城市地下管线的漫游和三维成果自执行文件格式汇报,且可满足城市管线管理人员和技术专业人员的规划设计、方案设计、施工图设计等不同阶段的需要。 城市区域地下管网鸟瞰图 二、建设目标
1、通过对城市地下各类管线基础数据资源的有效整合与配置,进一步推进数字地理空间信息平台 建设,全面实现数据管理部门和应用部门之间对数据资源“集中管理、分部应用”的共建共享。 2、实现对决策基础数据资源的数字化、可视化管理。通过全新的GIS技术,将地图元素和地下空 间信息融入到管理系统之中,并采用三维模拟技术对地下管线进行详实的展示,真正意义上实现城市决策信息资源的数字化和可视化,充分体现出辅助决策的科学性和先进性。 3、提高政府应对公共安全和突发公共事件的处置能力。面对城市突发应急事故,政府可在第一时 间内了解到灾害发生地周边管线的分布情况,协助管理者快速协调调用相关资源并完成应急处置,最大限度地确保将突发公共灾害事故的危害降至到最低限度。 4、全面提升城市地下管线基础数据的管理水平。既可实现对局部地区地下管线空间分布状况的查阅,又可对城市区域地上地下管线进行全景模拟浏览,全面实现城市地下管线的三维显示与管理,使得本来在平面显示下错综复杂的管线变得更加清晰明了。 5、在实现地下管线的三维可视化管理、存储、查询、分析、定位等功能基础上,系统还可用于对 单种管线情况的研究和各种管线整体分布情况的多种专业分析(如垂直净距分析、水平净距分析、覆土深度分析、道路扩建分析、范围拆迁分析以及最短路径分析等);既可使管理人员用以指导工程施工,又可使业务人员用来做新区规划或管线设计的工具,彻底改变业务人员的办公技术条件,从而也使得管理工作更加得心应手。 3DPLINE城市三维地下管线管理系统是一款以计算机网络为载体,以全新GIS为平台应用技术,在全面整合城市地下综合管线数据资源的基础上,创新推出的一套完整的城市地下综合管线数据资源管理数字化、可视化的三维管线管理系统。 三、技术优势 1、管网自动建模 传统的管线竣工资料和探测结果大多是二维矢量线数据,本系统可对二维的平面坐标、埋深、管径等成果数据(包括管线CAD图、实测数据、二维GIS)以标准格式导入,自动生成管网空间拓扑关系图和批量生成三维管线模型、关联属性数据库,并且可在软件内直接自动绘制成图,大大方便了技术人员的日常规划设计和维护设计业务工作。
中国移动集团客户网络服务支撑规范
集团客户网络服务支撑规范 中国移动通信集团广东公司深圳分公司 网络维护中心服务支撑室 2009年2月
声明 本文档所有权和解释权归中国移动广东公司所有,未经书面许可,不得复制或向第三方公开。 This document is the property of CMCC GD and can be neither reproduced nor disclosed to a third party without a written authorization. 修订历史记录 (A-添加,M-修改,D-删除)
目录 1 前言4 1.1 编写目的4 1.2 适用对象4 2 集团客户网络服务支撑工作内容分类4 3 基本要求与一般规范5 3.1 服务支撑人员定义5 3.2 服务支撑人员专业技能要求5 3.3 服务支撑人员仪表方面规范5 3.4 服务支撑人员外勤工作一般规范6 4 集团业务故障处理作业规范7 4.1 处理原则7 4.2 内部故障处理流程7 4.3 客户现场处理规范8 5 服务支撑人员例行维护与作业规范11 5.1 监控经管11 5.2 日常例行现场巡检规范11
1前言 在网络运维集中化的背景下,中国移动广东省公司确立了地市集中化工作转型的重要工作目标:服务下沉、支撑前移。为了建立和健全网络服务支撑的工作体系,进一步提升全省服务支撑人员的支撑能力,使得服务支撑人员能够为集团客户提供快速技术支撑,提高客户满意度,在“服务下沉、支撑前移”的指导思想下,全省各地市网络维护中心服务支撑室正逐步加强客户拜访工作的力度,与集团客户技术人员形成互动,为全省的集团客户提供更好的服务。 1.1编写目的 为指导深圳分公司网络维护中心员工,尤其是服务支撑室及其代维工作人员,在日常工作生产中凡涉及与集团客户交互的如客户拜访、故障抢修、例行维护以及电话邮件等工作,按照如下作业与行为规范如专业术语、礼貌用语、着装指引、施工抢修等方面操作实施。 1.2适用对象 本手册适用对象为深圳移动面向集团客户服务支撑的网络经管与维护人员,以及深圳移动合作单位的代维工作人员。 2集团客户网络服务支撑工作内容分类 按照省公司粤移网维通[2009]61号《关于明确网络服务支撑例行生产工作要求的通知》一文,网维中心服务支撑室主要承担以下工作: 1、售前、售中的网络支撑,其中包括技术方案制定和业务开通。 2、售后业务保障服务,其中包括告警监控、故障和投诉处理、业务分析与质量经管、 例行维护、差异化保障服务、客户服务和拜访、交流和知识共享、手段建设以及资 料经管9个方面。 因此,根据以上工作内容,涉及与集团客户交互主要涵盖以下几个方面: 1、集团客户拜访工作,如技术交流、故障归纳总结、差异化服务等。 2、集团业务维护工作,如例行维护、故障和投诉处理、设备安装与调测等。
资源管理系统-全业务端到端资源管理系统与应用
单选(共50分) 待检查 1、 PON网元配置类型包括() A. PTN、ONU 、POS B. OLT、ONU 、POS C. OLT、ONU 、PTN D. OLT、ONU 、PON 待检查 2、传输冗余电路如何清除 A. 起电路新增单 B. 直接删除 C. 起光路停闭单 D. 起电路停闭单 待检查 3、总俯仰角挂高低于20米,总俯仰角不得大于()度,挂高高于50米,总俯仰角不得小于5度; A. 15,5 B. 5,5 C. 10,5 D.
待检查 4、资源管理系统的流程管理,目标是为了确保流程符合实际生产需要,以流程控制(),有效提升资源数据质量 A. 资源数据变更 B. 资源数据删除 C. 资源数据冗余 D. 资源数据退网 待检查 5、可以查看网卡中断的是哪个选项()? A. which interrupts B. cat /proc/ioports C. cat /proc/interrupts D. cat /proc/memoryinfo 待检查 6、查看某个传输设备所在机房名称,在综合资管系统的()模块 A. 业务开通 B. 网络割接 C. 资源拓扑 D. 基础功能
7、关于防火墙的描述不正确的是哪个选项()? A. 如果一个公司信息安全制度不明确,拥有再好的防火墙也没有用 B. 防火墙是一个由软件和硬件设备组合而成的保护屏障 C. 防火墙可以防止伪装成内部信任主机的IP地址欺骗 D. 防火墙可以防止伪装成外部信任主机的IP地址欺骗 待检查 8、下列账号中,最有可能是人员从账号的是 A. zhangshan B. administrator C. user D. oracle 待检查 9、 HP设备硬件告警排查时需要收集()日志 A. DIAG B. EventLog C. IML D. AuditLog 待检查 10、家客业务开通流程中哪个环节可实现系统预占端口与实占端口的调整()
中国移动云网融合应用场景及解决方案设计
附件2 中国移动云网融合应用场景及解决方案 “移动云”是中国移动自主研发,面向政府部门、企业客户和互联网客户推出的新型云计算平台,提供弹性计算、云存储、云网络和云安全等基础设施产品,数据库、视频服务等平台服务产品,并通过云市场引入海量优质应用。结合专线、CDN等运营商优质网络资源,提供一站式定制化政务云、行业云、混合云等解决方案,中国移动拥有规模庞大的客户群,利用移动云的资源与网络,可以更好的为客户服务,促进客户业务发展。国务院国家政务云、湖南省政府政务云都选择使用中国移动“移动云”。 一、云主机 1.1、产品定义 云主机是通过虚拟化技术整合IT资源,为客户提供按需使用的计算资源服务。客户可以根据业务需求选择不同的CPU、内存、存储空间、带宽以及操作系统等配置项来配置云主机,通过灵活的计价方式和细粒度的系列化配置,提高资源利用率和稳定性,降低客户的使用成本。 1.2、产品特点 (1) 快速部署:客户可以随时申请资源,云主机从申请到生成仅需数分钟时间,快速投入使用
(2) 弹性灵活:多台云主机即开即用,灵活扩容,支持CPU、内存垂直升级,最大程度满足业务弹性需求,客户可以根据业务需求订购相应规格的云主机,降低使用成本 (3) 简单易用:客户可以通过控制台完成对云主机的全项指标监控与全生命周期管理,操作简单 (4) 稳定可靠:云主机可用性不低于99.95%,提供宕机迁移、数据备份和恢复等功能,确保业务稳定。云主机备份数据以多副本形式保存,数据可靠性可达99.9999999% (5) 安全保障:提供密钥认证、安全组防护、防火墙防护、多用户隔离等手段,确保业务安全 (6) 无缝拓展:云主机与移动云各种丰富的云产品无缝衔接,可持续为业务发展提供完整的计算、存储、安全等解决方案 1.3、应用案例 出版发行集团:中国移动协助发行集团提供电商服务,建设完成集图书及多种商品销售、线上线下销售模式,众多商家共同经营的大型电子商务平台(官网https://www.360docs.net/doc/3f550206.html,/)。 二、云存储 2.1、产品定义 云存储是在云计算概念上延伸和发展出来的一个新的概念,是一种新兴的网络存储技术,是指通过集群应用、网络技术或分布式文件系统等功能,将网络中大量各种不同类型的存储设备通
浙江移动云计算案例
华为是全球领先的云计算解决方案供应商。我们基于客户需求持续创新,凭借在固定网络、移动网络和IP 数据通信领域的综合优势,华为已成为全IP 融合时代的领导者。目前,我们的产品和解决方案已经应用于全球140多个国家,服务全球运营商50强中的45家及全球1/3 的人口。 浙江移动云计算案例 华为技术有限公司 华为技术有限公司 深圳市龙岗区坂田华为基地 电话: (0755) 28780808 邮编: 518129 版本号: M3-016070207-20110605-C-1.0 https://www.360docs.net/doc/3f550206.html, 关于华为 免责声明 本文档可能含有预测信息,包括但不限于有关未来的财务、运营、产品系列、新技术等信息。由于实践中存在很多不确定因素,可能导致实际结果与预测信息有很大的差别。因此,本文档信息仅供参考,不构成任何要约或承诺。华为可能不经通知修改上述信息,恕不另行通知。 版权所有 ? 华为技术有限公司 2011。 保留一切权利。 非经华为技术有限公司书面同意,任何单位和个人不得擅自摘抄、复制本手册内容的部分或全部,并不得以任何形式传播。 商标声明 、HUAWEI 、华为、 是华为技术有限公司的商标或者注册商标。 在本手册中以及本手册描述的产品中,出现的其他商标、产品名称、服务名称以及公司名称,由其各自的所有人拥有。
Web Portal 家庭个人 营业厅办公 浙江移动云计算案例 作为全球最大电信运营商之一,中国移动在快速推进云计 算平台的发展步伐,以应对其业务高速增长带来的诸多挑战。 中国移动选择华为率先在浙江成功部属了云计算平台。该 平台投入运行后,在商业模式、资源利用率、费用节省等方面 均产生了明显改善。 案例简述 虚拟化平台虚拟化平台
中国移动案例分析
中国移动公司案例分析 中国移动是中国移动通信集团公司(China Mobile Communications Corporation CMCC )的简称,是根据国家关于电信体制改革的部署和要求,在原中国电信移动通信资产总体剥离的基础上组建的国有重要骨干企业,于2000年4月20日成立,注册资本518亿元人民币,资产规模超8,000亿元人民币,网络规模和客户规模均居世界首位的目前全球市值最大的电信运营公司。 中国移动已连续六年入选美国《财富》杂志全球企业500强排行榜(表1.1),并跻身于全球电信运营商的第一梯队,是北京2008年奥运会合作伙伴;在英国《金融时报》最新“全球最强势100品牌”排名榜中,中国移动以品牌价值392亿美元高居第四;中国移动还是连续三年入榜《福布斯》“全球400家A级最佳大公司”的唯一中国企业。 中国移动商业模式 在启动3G后,全行业都在思考一个问题。那就是在3G时代,运营商应该提供什么样的服务。尽管同2G相比3G的带宽有了很大提高,可是如果没有相应的业务,3G只能沦落为简单的互联网接入通道,而不能给运营商带来与成本相匹配的收益。移动支付,逐渐成为中国3G没有大吸引力的最大障碍物。 全球手机移动支付业务发展迅猛进入21 世纪,日韩、欧美等地区,通过采用 RFID 技术,大力开展手机移动支付业务。经过几年发展,手机移动支付业务得到用户的广泛认可和接受,2008 年全球手机移动支付额约为 550 亿美元。据英国调研公司Juniper Research 预测,2013 年全球手机移动支付额将达6000 亿美元,增长近 10 倍。 中国移动手机移动支付业务收入主要来源于两方面:业务实现的佣金提取以及合作商户接入的比例分成。为此,中国移动建立了两级移动支付业务中心。其中,全国级中心,主要处理清算及结算业务,运营商可根据业务实现情况,提取佣金。相比银行卡刷卡佣金分配环节,手机移动支付佣金分配环节少,可由运营商直接控制,佣金比例比银联更具优势。运营商可通过具竞争力的佣金比例,以及更便捷的T+n 资金划拨周期,获得盈利;省级中心,主要处理各省商户接入管理与运作等事宜。与提供运营平台的合作商,按交易流量,比例分成,实现收益。 普遍分析观点分析认为,手机移动支付业务将给中国移动带来三重收益:其一,应对联通和电信的竞争:通过在 SIM 卡附加增值服务,增强用户体验,能帮助中国移动加快预付费用户群向后付费用户群的转移,捆绑用户;其二,降低发展用户成本:该项业务能够显著降低中国移动在新增用户与留住已有客户方面的支出;其三,引领移动支付市场:在手机移动支付行业中抢占先机,并从行业快速增长中获利。 新的商业模式是中国移动的最大增长驱动力 据媒体报道,中国移动董事长王建宙做客人民网时表示,三新和两新成为中国移动增长的驱动力。“三新”指“新用户”、“新话务”、“新业务”,“过去那么多年来一直是增长的主要驱动力”,而“两新”指“新领域”和“新模式”,“比如手机支付、手机金融、手机游戏等,都需要不断进入新的领域,开拓新的模式”。 在这些创新中,商业模式的创新更是中国移动未来发展的必须。简单的说,商业模式的创新大概表现在以下方面: 第一、从收费到免费。在现在这个社会中,虽然赚钱是必须的,但收费却并不是必须的,一直在涨价的银行、铁路、电力、有线,其实都是外表强悍内心虚弱,而一直免费的谷歌、淘宝等却是无往而不利。中国的通信行业资费水平在持续下降,未来“打电话不要钱”可期,运营商必须探索适合免费经营的商业模式。
管线资源管理系统
管线资源管理系统 1.1概述 G/COMMS管线资源管理系统是一套位于电信企业后台的运行 支撑系统,管理电信企业的管道杆路网、光缆网、电缆网等外线资源设备,在此之上实现企业信息便捷、充分的共享,为优质、快速地响应前台的客户要求提供有力的支撑。同时也可为设计部门、规划部门、资产管理部门提供相应服务。 1.2定位 ?架构 基于世界级COTS平台进行二次开发; 以项目成功、客户成功为导向!
避免走低层次重复的老路! ?功能 满足企业级、长期应用需求; 而不是部门级、短期应用; 符合CTG-MBOSS规范最新要求。 ?性能 满足中型、大型、特大型本地网; 全省集中型应用。 1.3产品功能 G/Comms系统采用统一的管线资源数据库,全省的管线资源都集中在一个数据库中用统一的模型进行存储。通过关系数据库建立各类管线资源设施之间的关联关系。下面对图中几大功能域进行说明: 基础功能域:
此功能域主要包括地图管理、逻辑图管理、元数据管理、元数据定义工具、数据质量检查等功能; 系统管理功能域 此功能域主要包括用户管理、日志管理、权限管理等功能; 资源存量管理功能域 此功能域是管线资源管理的核心功能域,它主要实现关系资源数据的基础维护,包括资源规格(模板)管理、支撑网(管道网、杆路网)资源管理、电缆网资源管理、光缆网资源管理、空间资源管理和C网资源管理以及其他物理资源管理等功能; 资源动态管理功能域 此功能域是主要包括支撑网(管道网、杆路网)资源割接、电缆网资源割接、光缆网资源割接、资源快捷录入等功能; 资源应用功能域 此功能域主要包括资源综合查询、资源能力查询、辅助配线、资源预警分析、资源统计报表、光路调度管理、故障定位服务、GIS网格化管理等应用功能; 系统接口 此功能域主要实现管线资源系统与外部系统的接口,包括ODS 系统、服务保障类系统、综合告警系统、固资管理系统等接口; 1.4部署客户 ●上海电信
光缆子网移动管线资源管理系统操作手册
移动管线资源管理系统 系统操作手册 (版本:2.0) 广东省电信规划设计院 Guangdong Planning and Designing Institute of Telecommunications 2011年7月
文档变更记录
目录 1.引言 (2) 2.光缆子网管理 (3) 2.1子网创建 (3) 2.1.1菜单显示 (3) 2.1.2光缆子网查询 (3) 2.1.3光缆子网维护 (4) 2.1.4子网接入点个数 (6) 2.1.5地图定位 (6) 2.2.光缆系统及光缆资源的关联 (8) 2.2.1添加缆段 (8) 2.2.2单个光缆段解除 (10) 2.2.3批量解关联 (10) 2.2.4未归属子网光缆段查询 (11) 2.3光缆子网拓扑图 (11) 2.3.1单个资源地图定位 (11) 2.3.2多种资源同时定位 (12) 2.3.3拓扑图上的资源信息查看 (13) 2.3.4移入光缆段 (14) 2.3.5移出资源 (15) 2.3.6拓扑图上查关联的缆段 (15) 2.3.7移入缆段 (16) 2.3.8查找光设施 (18) 2.4光缆子纤芯配置图 (18)
1.引言 移动网络资源是移动企业对外提供服务的基础,建立移动资源管理系统,充分利用移动网络资源,提高移动网络资源管理水平和使用效率,是实现移动企业信息化的关键。移动资源管理系统已成为现阶段移动企业信息化建设的热点。由于移动网络资源普遍具有空间分布的特征,采用GIS(地理信息系统)技术构建可以有效管理移动资源空间分布信息的移动资源管理系统成为移动资源管理系统发展的方向。 本书介绍的移动管线资源管理系统是移动本地网资源管理的核心部分。该系统改变了通信管线网络的规划、建设、管理以及资料保存的传统模式。通过图形化的操作界面以及合理的功能模块能够方便、准确的掌握所有管线资源的信息数据。为日常的管线维护工作带来极大的便利。 ●本操作手册以“移动管线资源管理系统”为基础编写。 ●操作界面中所有“*”字段为必须填写的属性,在操作说明中不再加以强调。
