Rare earth minerals and resources in the world
Journal of Alloys and Compounds408–412(2006)
1339–1343
Rare earth minerals and resources in the world
Yasuo Kanazawa a,?,Masaharu Kamitani b
a Human Resource Department,National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology(AIST),
1-1-1Umezono,Tsukuba305-8568,Japan
b Institute for Geo-Resources and Environment,National Institute of Advanced Industrial
Science and Technology(AIST),1-1-1Higashi,Tsukuba305-8567,Japan
Available online17June2005
Abstract
About200rare earth(RE)minerals are distributed in a wide variety of mineral classes,such as halides,carbonates,oxides,phosphates, silicates,etc.Due to the large ionic radii and trivalent oxidation state,RE ions in the minerals have large coordination numbers(c.n.)6–10 by anions(O,F,OH).Light rare earth elements(LREEs)tend to occupy the larger sites of8–10c.n.and concentrate in carbonates and phosphates.On the other hand,heavy rare earth elements(HREEs)and Y occupy6–8c.n.sites and are abundant in oxides and a part of phosphates.Only a few mineral species,such as bastnaesite(Ce,La)(CO3)F,monazite(Ce,La)PO4,xenotime YPO4,and RE-bearing clay have been recovered for commercial production.Bayan Obo,China is the biggest RE deposit in the world.One of probable hypotheses for ore geneses is that the deposit might be formed by hydrothermal replacement of carbonate rocks of sedimentary origin.The hydrothermal ?uid may be derived from an alkaline–carbonatite intrusive series.Following Bayan Obo,more than550carbonatite/alkaline complex rocks constitute the majority of the world RE resources.The distribution is restricted to interior and marginal regions of continents,especially Precambrian cratons and shields,or related to large-scale rift structures.Main concentrated areas of the complexes are East African rift zones,northern Scandinavia-Kola peninsula,eastern Canada and southern Brazil.Representative sedimentary deposits of REE are placer-and conglomerate-types.The major potential countries are Australia,India,Brazil,and Malaysia.Weathered residual deposits have been formed under tropical and sub-tropical climates.Bauxite and laterite nickel deposit are the representative.Ion adsorption clay without radioactive elements is known in southern China.Weathering processes concentrate REE in a particular clay mineral-layer in the weathered crusts whose source were originally REE-rich rocks like granite and carbonatite.The production is increasing in recent years.However,the process of chemical extraction has brought environmental problems.
?2005Elsevier B.V.All rights reserved.
Keywords:Rare earth minerals;Rare earth resources;Bayan Obo ore deposit;Carbonatite;Ion adsorption clay
1.Introduction
It is said that rare earths are not rare in natural occurrence. It is true for light rare earth elements(LREEs).However, heavy rare earth elements(HREEs)are less common.Fur-thermore,RE resources are unevenly distributed in the world. The world mine production in2003is concentrated in sev-eral countries:China,India,CIS,Malaysia,and Sri Lanka [1].Especially,China occupies more than90%of the pro-duction.The other productive countries are USA,Australia, Canada,South Africa,Brazil,and others.Recent industrial demands for HREE would bring exhaustion of the resources ?Corresponding author.Tel.:+81298626279;fax:+81298626049.
E-mail address:y.kanazawa@aist.go.jp(Y.Kanazawa).in near future.Exploitation of RE resources also involves environmental problems.One of problems is due to radioac-tive elements associated with REE in the minerals.
Here,overview of RE minerals and the resources would be useful for the development from now on.In this paper,we ?rst present the mineralogical features of RE minerals.Sec-ondly,the ore deposit types and the world distribution of RE resources are presented with remarks for future developing.
2.Classi?cation of rare earth minerals and their crystal-chemical features
So far,a total of about200distinct species of RE miner-als have been described.And crystal structures of about the
0925-8388/$–see front matter?2005Elsevier B.V.All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2005.04.033
1340Y.Kanazawa,M.Kamitani/Journal of Alloys and Compounds408–412(2006)1339–1343
Table1
Classi?cation of rare earth minerals
Mineral class Mineral examples and chemical formulae
Halides Fluocerite-(F),CeF3
Carbonates
With?uoride Bastnaesite,(Ce,La)(CO3)F
Without?uoride Ancylite,(Ce,Sr,Ca)(CO3)(OH,H2O)
Borates Braistschite,(Ca,Na2)7CeB22O43·7H2O
Oxides and hydrates
AO2-type Cerianite,(Ce4+,Th4+)O2
ABO3-type Perovskite group,(Ca,Ce,Na,Sr)(Ti,Nb,Ta)O3
ABO4-type Fergusonite–Formanite,Y(Nb,Ta)O4–Y(Ta,Nb)O4
AB2(O,OH)6-type Euxenite group,(Y,Ca,Ce,U,Th)(Nb,Ta,Ti)2O6
A2B2O6(O,OH,F)-type Pyrochlore group,(Na,RE,K,U)2(Nb,Ta,Ti)2(O,OH,F) Others Hibonite,(Ca,Ce)(Al,Ti,Mg)12O19
Phosphates,arsenates and vanadates Apatite,(Ca,RE,Sr,Na,K)3Ca2(PO4)3(F,OH)
Monazite,(Ce,La)PO4
Xenotime,YPO4
Silicates(The following groups are based on the linkage manner of tetrahedral anionic group.)
Isolated group Cerite,(Ce,La,Ca)9(Fe3+,Mg)(SiO4)6[SiO3(OH)](OH)3
Garnet,(Ca,Fe,Mg,Mn,Y)3(Al,Cr,Fe,Mn,Ti,V,Zr)2(Si,Al)3O12
Sphene,CaTiSiO4
Diortho group Allanite,Ca(Ce,Y,Ca)Al(Al,Fe)(Fe,Al)(SiO4)3(OH)
Chain group Stillwellite,CeBSiO5
Ring group Eudialyte,(Na,Ca,Ce)6(Zr,Fe)2Si7(O,OH,Cl)22
Sheet group Gadolinite,(Y,Ce)2Fe2+Be2Si2O10
Framework group Kainosite,Ca2(Y,RE)2(Si4O12)CO3·H2O
Others Iimoriite,Y2(SiO4)(CO3)
half have been reported.Miyawaki and Nakai[2,3]stated that minerals,whose chemical formulae indicate signi?cant contents of rare earths,are de?ned as RE minerals,even if their contents appear unessential to the minerals.They have reviewed all the reported structures in“Crystal Structures of Rare Earth Minerals”,which is useful for database and a textbook on RE minerals.Here,we grouped RE minerals into conventional ways,such as halides,carbonates,oxides, phosphates,silicates,etc.in Table1with the chemical formu-lae.This classi?cation indicates that RE minerals distribute in a wide variety of mineral classes and structural types.In Table1,it is noticed that the important RE minerals,bast-naesite,monazite,and xenotime are expressed by simple chemical formulae.
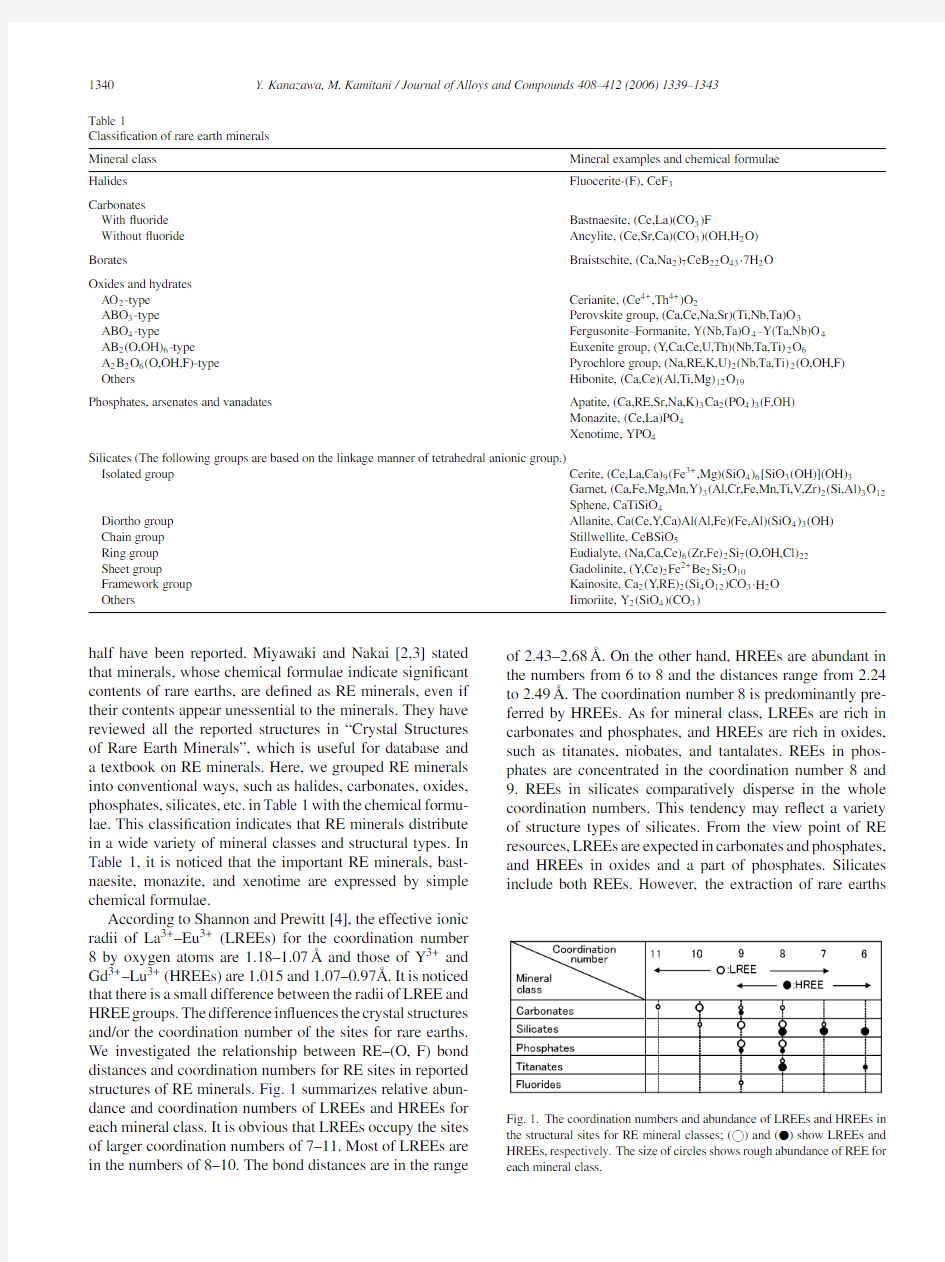
According to Shannon and Prewitt[4],the effective ionic radii of La3+–Eu3+(LREEs)for the coordination number 8by oxygen atoms are1.18–1.07?A and those of Y3+and Gd3+–Lu3+(HREEs)are1.015and1.07–0.97?A.It is noticed that there is a small difference between the radii of LREE and HREE groups.The difference in?uences the crystal structures and/or the coordination number of the sites for rare earths. We investigated the relationship between RE–(O,F)bond distances and coordination numbers for RE sites in reported structures of RE minerals.Fig.1summarizes relative abun-dance and coordination numbers of LREEs and HREEs for each mineral class.It is obvious that LREEs occupy the sites of larger coordination numbers of7–11.Most of LREEs are in the numbers of8–10.The bond distances are in the range of2.43–2.68?A.On the other hand,HREEs are abundant in the numbers from6to8and the distances range from2.24 to2.49?A.The coordination number8is predominantly pre-ferred by HREEs.As for mineral class,LREEs are rich in carbonates and phosphates,and HREEs are rich in oxides, such as titanates,niobates,and tantalates.REEs in phos-phates are concentrated in the coordination number8and 9.REEs in silicates comparatively disperse in the whole coordination numbers.This tendency may re?ect a variety of structure types of silicates.From the view point of RE resources,LREEs are expected in carbonates and phosphates, and HREEs in oxides and a part of phosphates.Silicates include both REEs.However,the extraction of rare
earths Fig.1.The coordination numbers and abundance of LREEs and HREEs in the structural sites for RE mineral classes;( )and(?)show LREEs and HREEs,respectively.The size of circles shows rough abundance of REE for each mineral class.
Y.Kanazawa,M.Kamitani/Journal of Alloys and Compounds408–412(2006)1339–13431341 Table2
Classi?cation of rare earth ore deposits
Deposit-type Mines
(1)Igneous
Hydrothermal Bayan Obo(China)
Carbonatites Mt.Pass(USA),Weshan,Maoniuping(China),Mount Weld(Austraria),Araxa,Catalao(Brazil) Alkaline rocks Khibiny,Lovozeiro(Russia),Posos de Caldas
Alkaline granites(Brazil),Strange Lake(Canada)
(2)Sedimentary
Placer Kerala(India),Western Australia,Queesland State(Australia),Richards Bay(south Africa) Conglomerate Elliot Lake(Canada)
(3)Secondary
Weathered residual of granite(ion-adsorption clay)Longnan,Xunwu(China)
from the minerals needs high energy(or high costs)because
of the strong chemical bonds in the structure.
The above ionic radii of rare earths are similar to those
of especially Na+(1.16?A),Ca2+(1.12?A),Th4+(1.06?A),
and U4+(1.00?A).Therefore,these elements are frequently
associated with rare earths in the crystals.The substitu-
tions between rare earths and the heterovalent ions are
commonly taken place in the mineral structures.Several
types of isomorphous substitutions of rare earth ions for
the heterovalent ions are observed mainly in oxides and
silicates.The commonest substitution in oxides,such as
titanates,niobates,and tantalates,is the coupled substitution
of Ca2++(Nb,Ta)5+?RE3++Ti4+.This substitution is frequently balanced by another substitution of O2??(OH, F)?.The usual substitution of2Ca2+?RE3++Na+is present in perovskite.Apatite in phosphates also takes
the same substitution.The substitution accompanied with
Th4+is expressed by Ca2++Th4+?2RE3+.A unique substitution,Ca2++(Al,Fe3+)?RE3++Fe2+,takes place in allanite of diortho group of silicates.In garnet structure, Ca2++Si4+?RE3++(Al,Fe3+)is a feasible substitution and results in synthetic Y AG and YIG.3.The ore deposit types of rare earths and the world distribution
The classi?cation of the deposit types is indicated in Table2based on Kamitani[5].The major deposits are clas-si?ed genetically into igneous,sedimentary,and secondary types.The world distribution corresponding to the classi?ca-tion is shown in Fig.2.
Bayan Obo,China is the biggest RE deposit in the world. The deposit was formed by hydrothermal replacement of the carbonate rocks of sedimentary origin,but the hydrothermal ?uids may be derived from an alkaline–carbonatite intrusive series[6–9].
Carbonatite/alkaline rocks constitute the majority of the world RE resources following Bayan Obo.More than 550carbonatite/alkaline complexes are distributed in the world[10].The distribution is restricted to interior and marginal regions of continents,especially Precambrian cratons and shields,or related to large-scale rift structures. Main concentrated areas of the complexes are the East African rift zones,northern Scandinavia-Kola peninsula, eastern Canada,and southern Brazil.The carbonatites
are Fig.2.Distribution of RE deposits in the world.
1342Y.Kanazawa,M.Kamitani/Journal of Alloys and Compounds408–412(2006)1339–1343
generally associated with ultrama?c and/or alkaline rocks, and in so many cases occur as isolated dykes,cylindrical intrusives and volcanic cones.The ages of complexes vary from Archean to Recent time,and each group of the complexes is closely related to their regional structural events.In East Africa,many carbonatites and alkaline rocks are arranged along the East African rifts and the related structurally weak zones.The Oldoinyo Lengai carbonatite, Tanzania that is famous for the eruption in1960,consists mainly of tuffs,agglomerates,and lava?ows of Na-rich carbonatites with ijolite,nepheline syenites,and phonolite ?ows[11].Carbonatites representing deeper substances are recognized in the northern Scandinavia-Kola peninsula,east-ern Canada,southern Brazil,etc.They are mostly associated with alkaline and ma?c to ultrama?c rock suites,such as ijolite,melteigite,jacupirangite,pyroxenite,and peridotite. Mountain Pass,USA has the high-grade and large-sized carbonatite-type deposits.The occurrence of the RE min-erals is considered primary igneous.The other deposits of hydrothermal and supergene origin in carbonatites also represent a large RE resource and occur at,for example, Araxa and Catalao I,Brazil and Mount Weld,Australia.A small amount of REE-bearing minerals are accompanied by granite,alkaline granite,and alkaline suite rocks.However, these are not economical for RE resources.In pegmatite-and skarn-stages,some RE minerals have formed but almost all of the deposits are also sub-economic.Carbon-atite/alkaline complexes contain a considerable amount of niobium,titanium,REE,copper,molybdenum,and phosp-horus.
Representative sedimentary deposits of REE are placer-and conglomerate-types.The detrital minerals originate from a wide variety of primary source rocks ranging from simple quartz veins to complexes of igneous and/or metamorphic ori-gin.Economic concentrations occur where source rocks have produced suf?cient quantities of valuable minerals and where geography and climate have provided suitable conditions for deposition.The placer deposits are widely distributed in the world.The major producing countries are Australia,India, Brazil,and Malaysia.Monazite and xenotime are the main RE minerals.They are associated with titanium minerals and zir-con.From a conglomerate-type deposit RE products enriched in Y-group have been recovered after uranium ore dressing in Elliot Lake,Blind river area,Canada.
Weathered residual deposits have been formed under trop-ical and sub-tropical climates.Weathering processes concen-trate REE in a particular mineral-layer in the weathered crusts whose source were originally REE-rich rocks like carbonatite and granite.Bauxite and laterite nickel deposits are the repre-sentatives.A new type of RE deposits is reported from Jiangxi province and its peripheral areas,South China[12–14],where granitoids containing comparatively much REE are perfectly weathered and almost the RE have been concentrated in clay layer in the weathered crusts.Chinese geologists are regarded as new type deposit“ion adsorption-type”(e.g.
[12]).4.Major RE deposits
4.1.Bayan Obo deposit,China
Bayan Obo Fe–REE–Nb deposit is located135km north-west of Baotou in Inner Mongol Autonomous Province.RE minerals closely associated with the iron ores have been recovered from the iron ore dressing plant.The reported total reserves are at least1.5billion metric t of iron(average grade 35%),at least48million t of RE oxides(REO)(average grade6%),and about1million t of niobium(average grade 0.13%)[6].Recent statistics shows89million t of REO in China[1].The principal RE minerals are bastnaesite and monazite and accompanied with a various kind of RE–Nb minerals,such as aeschynite,felgusonite,and columbite.
The rift system developed in the northern margin of the Sino-Korean massif during the Early-Middle Proteozoic era made a favourite tectonic setting for the depositions of Bayan Obo Group and the ore deposits.The host dolomites extend 18km from east to west and approximately2km in width. There are three main ore zones:the Main Ore Body,the East Ore Body,and the West Ore Body.The Main and the East ore bodies are being actively exploited at present.The Main ore bodies consist of tabular and/or lenticular bodies of REO-bearing magnetite and hematite iron ores.The average REO content in the Main Ore Body and the East Ore Body are6 and5%,respectively.There have been many discussions on the genesis of Bayan Obo deposit so far.One of considerable ore geneses is as follows.The original iron(hematite)ore bodies were formed syngenetically before REE–Nb mineral-ization.The hydrothermal?uid with an alkaline–carbonatite chemistry was derived from the upper mantle,and printed the REE–Nb mineralization over the original iron bodies[7]. In addition to Bayan Obo,many REE carbonatites are dis-tributed in China.Wushan and Maoniuping deposits produce LREE.
4.2.Mountain Pass carbonatite deposit,USA
Mountain Pass deposit is the second largest RE deposit following Bayan Obo.The carbonatite deposit is located near the border between the southern part of California and Nevada where Precambrian metamorphic rocks are widely distributed.Syenite,shonkinite,granite,and many carbon-atites intruded into the metamorphic basement.The Sulphide Queen carbonatite body is the main deposit with1000m long and250m wide,and mainly composed of dolomite and cal-cite accompanied with barite and a considerable amount of bastnaesite.The potassium-rich igneous rocks and intrusive carbonate rocks were formed approximately1400Ma[15]. The proved REO reserves are approximately28million t and the grade is5–10%REO.The recent mine production,how-ever,has been abruptly decreased into5000t/y due to several problems.
Y.Kanazawa,M.Kamitani/Journal of Alloys and Compounds408–412(2006)1339–13431343
4.3.Mount Weld carbonatite deposit,Australia
According to home pages of Lynas Co.Ltd.,Mount Weld carbonatite intrusive pipe is approximately3km in diame-ter located35km south of Laverton,W A,USA.The surface is strongly weathered.Nb–Ta,P,and REE are concentrated but considerable less radioactive elements of Th and U.The richest part of REE is the Central Lanthanide Deposit(CLD) where estimated reserve is7.7Mt at12%for917,000t REO. Bastnaesite is the main mineral of REE.
4.4.Placer deposits in Australia
Heavy minerals sand placer deposits containing RE min-erals are widely distributed along the Australian coast.They fall geographically and mineralogically into three distinct categories:the rutile–zircon–ilmenite deposits of the east coast,the ilmenite deposits of the south-west coast,and the ilmenite–zircon–rutile deposits of the Eneabba region of the west coast.The deposits of the east coast have been formed by wave,wind-brown,and their combination.The west coast,on the other hand,composed mainly of paleobeach placers and then the principal deposits are located at inland and10–100m above sea level.REE sands are monazite and xenotime. 4.5.Ion adsorption clay
The ion adsorption clay deposits of REE distribute over an extensive area of southern China,especially in Nanling area. The numerous small deposits occur as a result of lateritic weathering of granites that extensively intruded during Yan-shanian,Variscan-Indosinian,and Caledonian movements. In particular,granitic rocks of Yinshen age(195–130million years ago)are the most common host rocks for ion-adsorption deposits.Under warm and moist weather in subtropical zone, these granites have been suffered strong chemical and bio-logical weathering,in which REEs were adsorbed mainly on the surface of clay minerals as ion state,then forming ion adsorption type REE deposits.This type of deposits satis?es at least two major general requirements for their formation. First,there must be a suf?cient quantity of RE-bearing host rock.Second,the weathering or lateritic processes must be preserved for a long period without erosion.
The weathering crusts are divided into four layers based on mineral assemblages[16].(A)An upper layer of colluvium and soil:0–2m thick,(B)a strongly weathered layer enriched in REE:5–10m thick with kaolinite,quartz and mica,(C)a semi-weathered layer:3–5m thick with kaolinite and sericite, (D)a weakly weathered layer with the same mineral compo-sitions as the host rock.RE-ions were adsorbed by kaolinite and halloysite.The most abundant RE,which is enriched three–four times of the host occurs in the strongly weath-ered layer(B).Although ion-adsorption rare earth deposits are substantially low grade(0.05–0.2%),the mining and pro-cessing is easy.The deposits are mined by open-pit methods and no milling and/or ore dressing is required.The REOs can be produced by a very simple procedure.Some chemical acids are used for leaching of RE.The other advantage of the ion-adsorption type ores is the very low content of radioactive elements[17].
5.Concluding remarks
Recent demands for HREEs are increasing in high-tech industries.Extraction of HREEs from bastnaesite and mon-azite,even if xenotime causes the excessive production of LREEs and the harmful accumulation of radioactive ele-ments.One way to cope with the situation is to extract HREEs from ion-adsorption clay.This type of clay is produced only in the southern China.It is recommended to the other countries to investigate lateritic clay formed by weathering of granites. Otherwise R&D for mineral separation,smelting,and the recovery should be promoted including disposal of radioac-tive wastes.The protection of the environment is always a serious task for exploitation of natural resources. Acknowledgement
This work was partially supported by Institute for Geo-Resources and Environment,National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology.
References
[1]J.B.Hedrick,Mineral Commodity Summaries,January2004,U.S.
Geological Survey(2004)132–133.
[2]R.Miyawaki,I.Nakai,Rare Earths11(1987)133.
[3]R.Miyawaki,I.Nakai,in:E.Gshneidner Jr.(Ed.),Handbook on
the Physics and Chemistry of Rare Earths,vol.16,Elsevier Science Publishers B.V.,1993,pp.249–518.
[4]R.D.Shannon,C.T.Previtt,Acta Crystallogr.B25(1969)925–
945.
[5]M.Kamitani,Proceedings of International Conference on Rare Earth
Minerals and Minerals for Electronic Uses,1991,pp.181–191.
[6]L.J.Drew,Q.Meng,W.Sun,Lithos26(1990)42–65.
[7]R.Cao,S.Zhu,J.Wang,Chin.Sci.Chin.(Ser.B)38(1995)
1003–1014.
[8]G.Bai,Z.Yuan,Z.Zhang,L.Zheng,Demonstration of Geological
Features and Genesis of the Bayan Obo Ore Deposit,Geological Publishing House,1996,p.107.
[9]Y.Kanazawa,T.Nakajima,T.Takagi,Mining Geol.49(1999)
203–216.
[10]M.Kamitani,H.Hirano,Bull.Geol.Survey Jpn.41(1990)631–640.
[11]J.B.Dawson,in:O.F.Tuttle,J.Gittins(Eds.),Carbonatites,John
Wiley and Sons Ltd.,New York,1966,pp.155–168.
[12]Z.Yang,Sci.Geol.Sinica1(1987)70–80.
[13]Z.Den,J.Guillin Coll.Geol.(1988)39–48.
[14]C.Wu,D.Huang,Z.Guo,Acta Geol.Sinica4(1989)349–362.
[15]https://www.360docs.net/doc/3d3974957.html,nphere,J.Geol.72(1964)381–399.
[16]S.Peng,Proceedings of International Conference on Rare Earth Min-
erals and Minerals for Electronic Uses,1991,pp.33–42.
[17]A.L.Clark,S.Zheng,Proceedings of International Conference on
Rare Earth Minerals and Minerals for Electronic Uses,1991,pp.
577–601.
湖北三本院校录取分数线jaso
《高校报考资料》
目录
武汉大学东湖分校;华中师范大学汉口分校;华中科技大学武昌分校 武汉科技大学中南分校;湖北大学知行学院;武汉科技大学城市学院 三峡大学科技学院;江汉大学文理学院;湖北工业大学工程技术学院武汉工程大学邮电与信息工程学院;武汉科技学院外经贸学院 武汉工业学院工商学院;中南民族大学工商学院;长江大学工程技术学院长江大学文理学院;湖北工业大学商贸学院;湖北汽车工业学院科技学院郧阳医学院药护学院; 湖北民族学院科技学院 ;湖北经济学院法商学院 武汉体育学院体育科技学院 ;湖北师范学院文理学院 ;襄樊学院理工学院 孝感学院新技术学院;华中科技大学文华学院 ;中南财经政法大学武汉学院 ;中国地质大学江城学院 ;武汉理工大学华夏学院;华中师范大学武汉传媒学院 华中农业大学楚天学院 ;武汉大学珞珈学院 1.华中科技大学武昌分校招生与报考
文科湖北 录取分数线 年份最低最高平均投档录取人数录取批次 2010 -- 521.00 485.00 -- -- 本科三批 2009 445.00 500.00 473.00 -- 643 本科三批 2008 419.00 507.00 491.00 -- 559 本科三批 2007 447.00 506.00 482.00 -- 429 本科三批 2006 496.00 522.00 501.00 -- 390 本科二、三批2006 496.00 522.00 502.00 -- 390 本科三批 2006 461.00 478.00 470.00 -- 4 本科提前批 湖北文科2010年 专业设置及分数线 专业大类专业小类具体专业平均分最高分最低分批次经济学 经济学类国际经济与贸易487 521 -- 经济学类金融学491 509 -- 法学法学类法学484 498 -- 文学中国语言文学类汉语言文学483 496 -- 外国语言文学类英语484 497 -- 新闻传播学类新闻学483 506 -- 新闻传播学类广播电视新闻学483 500 -- 管理学工商管理类市场营销484 494 -- 工商管理类会计学488 509 -- 工商管理类财务管理485 498 -- 2009文科专业设置及分数线 专业大类专业小类具体专业平均分最高分最低分批次
地质勘探安全规程完整
地质勘探安全规程 1 范围 本标准规定了地质勘探工作野外作业、地质测绘、地球物理勘探、地球化学勘探、地质遥感、水文地质、环境地质、工程地质、海洋地质和钻探工程、坑探工程、地质实验测试等方面的安全要求以及职业健康要求。本标准适用于在中华人民共和国领域内的地质勘探(石油、天然气地质勘探除外)工作设计、生产和安全评价、管理。 本标准不适用于使用地质勘探技术手段和方法从事其延伸业的工作设计、生产和安全评价、管理。 2 规范性引用文件 下列文件中的条款通过本标准的引用而成为本标准的条款。引用文件最新版本,以及引用文件其随后所有的修改单(包括勘误的内容)或修订版均适用于本标准。 中华人民共和国放射性污染防治法(全国人大常委会2003) 中华人民共和国民用航空法(全国人大常委会1995) 危险化学品安全管理条例(国务院令第344号2002) GB6722-2003 爆破安全规程 GB18871-2002 电离辐射防护和辐射源安全基本标准 MH/T1010-2000 航空物探飞行技术规范 GB6067-1985 起重机械安全规程 GB5972-1986 起重机械用钢丝绳检验和报废实用规范 GB50194-1993 建设工程施工现场供用电安全技术规范 GB3787-1983 手持式电动工具的管理、使用、检查和维修安全技术规程 GB16424-1996 金属非金属地下矿山安全规程 3 术语和定义 下列术语和定义适用于本标准 3.1 地质勘探exploration 是指对一定地区内的岩石、地层、构造、矿产、地下水、地质灾害、地貌等地质情况进行勘察、调查研究的活动。包括地质测绘、地球物理勘探、地球化学勘探、地质遥感、水文地质、环境地质、工程地质、海洋地质和钻探工程、坑探工程、地质实验测试等。 3.2 艰险地区areas with hard ships and dangers 是指海拔3000m以上或者其他无人居住,自然条件恶劣、生存条件差的地质工作区。 3.3 野外作业open country work 是指在非城镇地区户外进行的地质勘探活动。 4 总则 4.1 地质勘探单位应贯彻“安全第一、预防为主”的安全生产方针,实行安全生产目标管理,逐步推广安全质 量标准化管理。 4.2 地质勘探单位应按照国家相关法律、法规、标准的要求,建立、健全以下安全生产规章制度:
浙江大学2017年地球科学学院推免生名单
浙江大学2017年地球科学学院推免生名单邢书强380地球科学学院070600大气科学 成亚380地球科学学院070704海洋地质 林晓青380地球科学学院070901矿物学、岩石学、矿床学 刘婷380地球科学学院070901矿物学、岩石学、矿床学 孔丽姝380地球科学学院070902地球化学 孙浩380地球科学学院070902地球化学 王安月380地球科学学院070902地球化学 刘乐380地球科学学院070904构造地质学 李含雪380地球科学学院070904构造地质学 王晓薇380地球科学学院0709Z4资源环境与区域规划 王依茹380地球科学学院0709Z4资源环境与区域规划 顾可欣380地球科学学院0709Z4资源环境与区域规划 宁蒙380地球科学学院0709Z4资源环境与区域规划 张佳380地球科学学院0709Z4资源环境与区域规划 施源380地球科学学院0709Z5资源勘查与地球物理 江金生380地球科学学院0709Z5资源勘查与地球物理 李延龙380地球科学学院0709Z6遥感与地理信息系统 金璐琦380地球科学学院0709Z6遥感与地理信息系统 傅颖颖380地球科学学院0709Z6遥感与地理信息系统 郑涵菲380地球科学学院0709Z6遥感与地理信息系统 第60页,共65 页 姓名拟录取学院代码拟录取学院拟录取专业代码拟录取专业名称备注 仇一帆380地球科学学院0709Z6遥感与地理信息系统 罗盖380地球科学学院0709Z6遥感与地理信息系统 曹晓裴380地球科学学院085217地质工程 钟翼380地球科学学院085217地质工程 钱伯至380地球科学学院085217地质工程
实习九 应用Core DRAW绘制地质图
实验九:应用CorelDRAW绘制地质图 1.实习目的 CorelDRAW 是面向对象的绘图程序,即矢量绘图软件,具有强大的图形和文字处理功能,可以处理多种形式的图形图像,具有极强的兼容性。地质研究中常应用该软件清绘、编辑及制作满足要求的成果图件。 本次实习要求掌握应用CorelDRAW绘制地质图的方法。 2. 技术基础 应用CorelDRAW绘制地质图一般是在底图的基础上进行清绘、编辑和修改。CorelDRAW 可识别图形的格式可分为两大类:一是矢量数据格式,导入系统后图形对象可直接编辑和处理,如Surfer软件以矢量方式输出的图形 [*.wmf] ;二是位图数据格式,此类图形是作为一个整体导入系统,图形对象不能单独编辑和处理,必须以创建新的曲线、多边形、文本的方式进行清绘,即图形矢量化。 本次实习采用第二种方式。 3.实习步骤 3.1 CorelDRAW启动 单击桌面上的[ CorelDRAW * ]快捷方式图标;或单击【开始】按钮,打开【程序】菜单的CorelDRAW 菜单项,选择级联菜单中的[ CorelDRAW * ] 命令即可启动应用程序。 除主程序以外,其它应用程序命令为: Graphics Utilities (图形实用程序) Productivity Tools (发布工具) Setup and Notes (安装和注释程序) Corel PHOTO-PAINT 10 (位图编辑和全彩色照片处理软件) Corel R.A.V. 1.0(网页矢量动画制作软件) CorelDRAW 10 CD (打开光驱中的安装和资料光盘) https://www.360docs.net/doc/3d3974957.html, (登录Corel 公司站点) 3.2 图形导入选择【文件】菜单中的【导入】命令,或单击窗口上方工具条中的 命令按钮,弹出【导入】对话框,在文件类型列表中选择与输入文件相匹配的文件类型,点击要输入的文件名称,点击【导入】按钮即可导入图形文件。 输入图形后界面如图所示。
物探测井安全操作规程
编号:SM-ZD-17613 物探测井安全操作规程Through the process agreement to achieve a unified action policy for different people, so as to coordinate action, reduce blindness, and make the work orderly. 编制:____________________ 审核:____________________ 批准:____________________ 本文档下载后可任意修改
物探测井安全操作规程 简介:该规程资料适用于公司或组织通过合理化地制定计划,达成上下级或不同的人员 之间形成统一的行动方针,明确执行目标,工作内容,执行方式,执行进度,从而使整 体计划目标统一,行动协调,过程有条不紊。文档可直接下载或修改,使用时请详细阅 读内容。 1.从事测井工作的人员,必须熟悉本工作岗位的安全防护规定,做到安全生产。 2.仪器设备在运输和搬运时要妥善包装,注意防潮、防震,汽车运输时不准与笨重的机械和管材等混装。 3.测井前,机场上一切妨碍测井和影响测井人员与设备安全的工作都必须停下来,待测井工作结束后方可继续进行。 4.夜间工作时,必须备有足够的照明。 5.布置井场时,必须将井口附近有可能掉入孔内的工具、物件移开。 6.仪器设备启用前,必须仔细检查外接电源的电压、频率等是否符合仪器设备的要求;各开关、旋钮是否在安全位置,接线是否正确,经反复核查确认无误后方可通电启用。 7.井下仪器在下井前应仔细检查其连接和密封情况,在与电缆连接处应留有弱点,其拉断强度不得大于电缆最大拉
信息工程专业介绍
信息工程专业介绍: 1.专业简介:信息技术是衡量一个国家现代化水平的重要标志,我国把信息技术列为21世纪发展战略计划的首位。信息工程是一门研究信息的产生、获取、传输、存储和显示技术的学科。信息工程专业培养在信息工程,重点是光电信息工程领域具有宽厚的理论基础、扎实的专业知识和熟练的实验技能的高级信息工程科技人才。毕业生将在光电信号的采集、传输、处理、存储和显示的科学研究、工程设计、技术开发和企业管理中展示才华。 2.主修课程:光电信息物理基础、光电子学、信号与系统、通信原理、图像处理、传感器原理技术、光电检测技术、自动控制理论、光纤通信、计算机通讯网络、工程光学、微机原理、计算机软件技术基础、计算机网络技术、计算机辅助设计、数字与模拟电子技术基础、电路基础以及有关数理基础和工程基础方面的课程。 3.毕业去向:本专业历年输送了大量优秀毕业生攻读硕士、博士学位。除此之外,主要为科研单位、高等院校、电信部门、信息产业部门、企事业单位及有关公司录用,从事光电信息工程与技术、通信工程与技术、光电信号检测、处理及控制技术等领域的研究、设计、开发应用和管理等工作。 电子信息工程专业 业务培养目标: 业务培养目标:本专业培养具备电子技术和信息系统的基础知识,能从事各类电子设备和信息系统的研究、设计、制造、应用和开发的高等工程技术人才。 业务培养要求:本专业是一个电子和信息工程方面的较宽口径专业。本专业学生主要学习信号的获取与处理、电厂设备信息系统等方面的专业知识,受到电子与信息工程实践的基本训练,具备设计、开发、应用和集成电子设备和信息系统的基本能力。 电子信息工程已经涵盖很广的范围。电话交换局里怎样处理各种电话信号,手机是怎样传递我们的声音甚至图象,我们周围的网络怎么样传递数据,甚至信息化时代军队的信息传递中如何保密等知识。我们通过一些基础知识的学习认识这些东西,并能够进行维护和更先进的技术和新产品的开发。 你首先要有扎实的数学知识,要学习许多电路知识,电子技术,信号与系统,计算机控制原理,信号与系统,通信原理等基本课程。自己还要动手设计、连接一些电路以及结合计算机的实验。譬如自己连接传感器的电路,用计算机自己设置小的通信系统,还会参观一些大的公司的电子和信息处理设备,对整体进行了解,理解手机信号、有线电视是如何传输的等,并能有机会在老师指导下参与大的工程的设计。 随着计算机和互联网日益深入到社会生活的多个层面,社会需求量相当大。现在是一个热门专业。 毕业后干什么——从事电子设备和信息系统的设计、应用开发以及技术管理等 随着社会信息化的深入,各行业大都需要本专业人才,而且薪金很高。可成为: 电子工程师——设计开发一些电子,通信器件,起薪一般2000元——6000元/月; 项目主管—策划一些大的系统,经验、知识要求很高,起薪一般4000元/月以上; 还可以继续进修成为教师,进行科研项目等 专业是个好专业:适用面比较宽,和计算机、通信、电子都有交叉;但是这行偏电,因此动手能力很重要;另外,最好能是本科,现在专科找工作太难了!当然大虾除外 本专业对数学和英语要求不低,学起来比较郁闷要拿高薪,英语是必需的; 吃技术这碗饭,动手能力和数学是基本功当然,也不要求你成为数学家,只要能看懂公式就可以了,比如微积分和概率统计公式,至少知道是在说些什么而线性代数要求就高一些,因为任何书在讲一个算法时,最后都会把算法化为矩阵计算(这样就能编程实现了,而现代的电子工程相当一部分工作都是编程) 对于动手能力,低年级最好能焊接装配一些小电路,加强对模拟、数字、高频电路(这三门可是电子线路的核心)的感性认识;工具吗就找最便宜的吧!电烙铁、万用表是必需的,如果有钱可以买个二手示波器电路图吗,无线电杂志上经常刊登,无线电爱好者的入门书对实际操作很有好处
摘要模板-南京大学地球科学与工程学院
摘要模板 碳循环与碳封存全国博士学术论坛论文摘要 参加的分论坛:二氧化碳地质与矿物封存技术 题目 作者一1, 作者二2, 作者三3 1.北京大学地球与空间科学学院, 造山带与地壳演化教育部重点实验室, 北京100871; 2.北京大学地球与空间科学学院, 造山带与地壳演化教育部重点实验室, 北京100871; 3.北京大学地球与空间科学学院, 造山带与地壳演化教育部重点实验室, 北京100871; 内容: 为了充分展示和交流我国碳循环与碳封存研究领域的最新研究成果, 进一步促进地球科学的发展与整体学术水平的提高, 决定于2011年12月25日~12月27日在南京召开“2011碳循环与碳封存全国博士生学术论坛”。我们热情地期待相关研究领域的同行们相聚南京。 图1 甘肃北山红岩地区叠加褶皱(其中白色实线:第一期褶皱(F1);虚线:第二期褶皱(F2);箭头向外:背斜;箭头向内:向斜) 表1 冈底斯含矿花岗斑岩与典型Adakitic岩( Defant et al., 1990; Drummond et al., 1990)对比
基金项目: 国国家自然科学基金项目(4073****,4090****,4087****);中国地调局调查项目(121201063****);国土资源部“深部探测计划”(20101****)联合资助 参考文献: 陈富文, 付建明. 2005. 南岭地区中生代主要成锡花岗岩地质地球化学特征与锡矿成矿规律[J]. 华南地质与矿产,(2): 12-21. 陈培荣, 张敏, 陈卫峰. 2007a. 大东山岩体[M] //周新民. 南岭地区晚中生代花岗岩成因与岩石圈动力学演化. 北京: 科学出版社: 382-394. 陈培荣, 张敏, 陈卫峰. 2007b. 九峰—诸广山岩体[M] //周新民. 南岭地区晚中生代花岗岩成因与岩石圈动力学演化. 北京: 科学出版社: 533-549. 高剑锋, 凌洪飞, 沈渭洲, 等. 2005. 粤西连阳复式岩体的地球化学特征及其成因研究[J]. 岩石学报, 21(6): 1645-1656. 通讯作者: 王**,男,教授,博士生导师,研究方向:成矿矿物学;E-mail: rcwang@https://www.360docs.net/doc/3d3974957.html, 作者简介: 王**,男,教授,博士生导师,研究方向:成矿矿物学;E-mail: rcwang@https://www.360docs.net/doc/3d3974957.html, 作者Email: rcwang@https://www.360docs.net/doc/3d3974957.html, 发稿日期:2012年4月16日
地球科学学院学生工作信息公示
地球科学学院学生工作信息公示 〔2017〕9号 2017年春季英才工程公示 经个人、集体申请,学工组审核,现将地球科学学院2017年春季学期英才工程评审结果公示如下。 学号姓名项目金额 20161002444 魏杰学习小组560 2016100410 吴洋综合素质提高类200 20161002695 冯柏林基础建设奖300 20161002695 冯柏林早操优秀奖200 20161001167 李世勇早操优秀奖200 20161003552 易昭阳早操优秀奖200 20161001063 张玉克早操优秀奖200 20161001210 尹海丹文明宿舍创建400 20161004018 王浩铭文明宿舍创建400 20161001051 杨丽莎综合素质提高类200 20161002205 黄媚韵综合素质提高类200 20161003241 谢逸豪综合素质提高类200 20161001165 姜东伶综合素质提高类200 20161000641 朱铭卿基础建设奖300 20161001521 余鑫鑫团旗领航项目300 20161001774 李志国学习小组480 20151001258 张超学习小组480 20161003977 王源涛学习小组480 20161001922 张彤文明宿舍创建400 20161000170 曹慧学习能力提升100 20161001128 刘鋆学习能力提升300 20161004036 华海锋综合素质提高类200 20161001774 李志国综合素质提高类200 20161000641 朱铭卿综合素质提高类200 20161003305 田真真综合素质提高类200 20161002921 尹峥综合素质提高类200 20161001521 余鑫鑫综合素质提高类200 20161003749 邹槿文明宿舍创建400 20161002126 王畅学习小组480 20161003347 周泽学习小组320 20161001063 张玉克基础建设奖300 20161001063 张玉克综合素质提高类200
地球物理勘探安全生产操作规程示范文本
地球物理勘探安全生产操作规程示范文本 In The Actual Work Production Management, In Order To Ensure The Smooth Progress Of The Process, And Consider The Relationship Between Each Link, The Specific Requirements Of Each Link To Achieve Risk Control And Planning 某某管理中心 XX年XX月
地球物理勘探安全生产操作规程示范文 本 使用指引:此操作规程资料应用在实际工作生产管理中为了保障过程顺利推进,同时考虑各个环节之间的关系,每个环节实现的具体要求而进行的风险控制与规划,并将危害降低到最小,文档经过下载可进行自定义修改,请根据实际需求进行调整与使用。 地球物理勘探包括电法勘探、磁法勘探等方法: 一、电法勘探: 1、发电机应有有效的漏电保护电路。仪器外壳、面板 旋钮、插孔等的绝缘电阻,应大于100MΩ/500V。工作电 流、电压不得超过仪器额定值,进行电压换档时应关闭高 压电源。 2、电路与设备外壳间绝缘电阻,应大于5 MΩ /500V。电路应配有可调平衡负载,严谨空载和超载运行电 路。 3、导线绝缘电阻每公里应大于2 MΩ/500V; 4、电法勘探、磁法勘探作业人员,应熟练掌握安全用
电和触电急救常识。 5、供电电极附近应设有明显的警示标志。 6、观测前,操作员和机电员应检查仪器和通讯工具性能,测量供电回路电阻,在确认人员离开供电电极后,方可进行试供电。 7、导线铺设,应避开高压输电线路;必须经过高压输电线路时,应有隔离保护措施。 8、在雷雨天气,禁止进行电法野外勘查作业。 二、磁法勘探 1、仪器操作应按仪器说明书或操作规程进行。禁止将仪器输出专用插口与其他仪器联接。 2、仪器工作不正常或出现错误指示时,应先排除电源不足、接触不良及电路短路等外部原因,再使用仪器自检程序检查仪器。仪器检修时应关机,焊接时应切断烙铁电源。
2019US News世界大学排名 地球科学专业
2019US News世界大学排名地球科学 专业 地球科学是关于地球的学科,从结构到地球形成的历史均有涉及,涵盖海洋学、石油地质学、地质学、地质化学、地球物理学、气候学等领域。这些就是USNews评出的地球科学领域世界顶尖的大学,共二百所,排名依据的是大学在这个领域的声誉和研究。 2019USNews世界大学学科排名:地球科学排名院校名称国家/地区1科罗拉多大学-博尔德美国2加州理工学院美国3苏黎世联邦理工学院瑞士4哥伦比亚大学美国5华盛顿大学美国6加州大学-伯克利美国7哈佛大学美国8麻省理工学院美国9普林斯顿大学美国10乌得勒支大学荷兰11加州大学-圣地亚哥美国12巴黎-萨克雷大学法国13牛津大学英国14马里兰大学-帕克美国15北京大学中国16中国地质大学中国17剑桥大学英国18加州大学-洛杉矶美国19布里斯托大学英国20利兹大学英国21加州大学-欧文美国22德克萨斯大学-奥斯汀美国23威斯康辛大学-麦迪逊美国24格勒诺布尔大学法国24斯德哥尔摩大学瑞典26斯坦福大学美国27澳大利亚国立大学澳大利亚27宾夕法尼亚州立大学-大学城美国29亚利桑那大学美国30东京大学日本31西南威尔士澳大利亚32耶鲁大学美国33图卢兹联邦大学法国34明尼苏达大学-双城美国35伦敦大学学
院英国35雷丁大学英国37伯尔尼大学瑞士38科罗拉多州立大学美国39南京大学中国39俄勒冈州立大学美国41杜伦大学英国42加州大学-圣塔芭芭拉美国42赫尔辛基大学芬兰44帝国理工学院英国45西澳大学澳大利亚46奥斯陆大学挪威47佐治亚理工学院美国48多伦多大学加拿大49密歇根大学-安娜堡美国50香港大学中国香港51爱丁堡大学英国52南安普顿大学英国53哥本哈根大学丹麦54卑尔根大学挪威55埃克塞特大学英国55夏威夷大学-马诺美国57加州大学-圣塔克鲁兹美国58不列颠哥伦比亚大学加拿大59清华大学中国60北京师范大学中国61索邦巴黎西岱联合大学法国62卡尔斯鲁厄理工学院德国63巴黎文理研究大学法国64康奈尔大学美国65苏黎世大学瑞士66芝加哥大学美国67科廷科技大学澳大利亚67不来梅大学德国69塔斯马尼亚大学澳大利亚70德克萨斯A M大学-学院站美国71阿姆斯特丹自由大学荷兰72阿尔伯塔大学加拿大73隆德大学瑞典74俄亥俄州立大学-哥伦布美国75加州大学-戴维斯美国75东安格利亚大学英国77波士顿大学美国77图卢兹第三大学法国79瓦格宁根大学及研究中心荷兰80迈阿密大学美国81墨尔本大学澳大利亚82里昂大学法国83麦吉尔大学加拿大84武汉大学中国85曼彻斯特大学英国86阿拉斯加大学-费尔班克斯美国87冰岛大学冰岛87波茨坦大学德国89莱斯特大学英国90罗格斯州立大学-新布伦瑞克美国91圣安德鲁斯大学英国92亚利桑那州立大学-坦佩美国93谢菲尔德大学英国94麦考瑞大学澳大利亚95南加州大学美国95乌普萨拉大学瑞典97阿德莱德大学澳大利亚98代尔夫特理
北京大学2019年地球与空间科学学院拟录取推荐免试博士研究
北京大学2019年地球与空间科学学院拟录取推荐免试博士研究生公示名单拟录取专业姓名复试成绩推荐学校本科专业备注 地图学与地理信息系统朱金顺86北京大学地理信息科学丁鼎78.5南京师范大学地理信息科学李犇74.7同济大学测绘工程 王雪辰74同济大学测绘工程 固体地球物理学许午川90北京大学地球物理学 苏培臻88北京大学地球物理学 高红涛85北京大学地球物理学 华思博84北京大学地球物理学 刘立超80北京大学地球物理学 于珍珍78山东科技大学勘查技术与工程 郑凯月76南京大学 地质学(地球物理学方向 ) 陆威帆75中国地质大学(武汉)地质与地球物理试验班 空间物理学崔博90北京大学空间科学与技术侯传鹏90北京大学空间科学与技术杨子浩88北京大学空间科学与技术李京寰88北京大学空间科学与技术 矿物学、岩石学、矿床学樊银龙91西北大学地质学(基地班)郜梦豪89东北大学资源勘查工程 兰春元88中国矿业大学(北京)资源勘查工程 苏懿88吉林大学地质学 薛莅治87北京大学地球化学 赵亚男86桂林理工大学地质学 地球化学姚瑶93.6中国地质大学(北京)宝石及材料工艺学刘帅奇93.3吉林大学勘查技术与工程赵旭炜91.3北京大学地球化学 古生物学与地层学 项楷84北京大学地质学 杨江南82北京大学地质学 构造地质学武于靖92北京大学地球化学 夏金凯91中国地质大学(北京)资源勘查工程 王召平90北京大学地质学 闫沛龙89吉林大学 理科试验班(李四光地球 物理班) 祝贺暄87中国石油大学(北京)资源勘查工程 地质学(材料及环境矿 物学) 张静宜90中国地质大学(武汉)宝石及材料工艺学 地质学(石油地质学)张书莞86.7北京大学地质学 白璐85西北大学地质学 李童83.2中国地质大学(北京)石油工程 凌坤82.7北京大学地质学 王璐81.3中国地质大学(北京)资源勘查工程柳晨73.7中国地质大学(北京)资源勘查工程 摄影测量与遥感 冀锐90.5北京大学地理信息科学 邓玉89.7武汉大学遥感科学与技术
扇三角洲沉积研究现状
Journal of Oil and Gas Technology 石油天然气学报, 2017, 39(3), 21-28 Published Online June 2017 in Hans. https://www.360docs.net/doc/3d3974957.html,/journal/jogt https://https://www.360docs.net/doc/3d3974957.html,/10.12677/jogt.2017.393024 文章引用: 孔令华, 冯强汉, 陈龙, 邵燕林, 胡忠贵. 扇三角洲沉积研究现状[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2017, 39(3): 21-28. The Current Situation of Fan Delta Sedimentary Research Linghua Kong 1, Qianghan Feng 2*, Long Chen 2, Yanlin Shao 1, Zhonggui Hu 1 1 School of Geoscience, Yangtze University, Wuhan Hubei 2 No. 3 Gas Production Plant, Changqing Oilfield Company, PetroChina, Wushen Banner Inner Mongolia Received: Dec. 10th , 2016; accepted: Feb. 11th , 2017; published: Jun. 15th , 2017 Abstract With the increasingly deepening of the study in fan delta, the study of terminology, the mechanism of hydrodynamic force, sedimentary facies, litho facie sand sequence stratigraphic characteristics and sedimentary pattern in fan delta were introduced based on literature investigations. The fan delta classification included tectonic setting, source supply system, gradient, channel mouth processes and texture-genetic classification. Traction current and gravity flow were alternated in hydrodynamics of fan delta, paroxysmal water flow was severe. Gradient and the diameter of transported particle size were positively correlated which showed the significance of gradient. According to petrological characteristics, a fine partition is performed on lithologic facies; the matching relation between sedimentary facies and lithofacies is strengthened; the idea of source to sink is combined with geomorphology, sedimentology, and basin analysis to provide a holistic analysis of the dynamic process of erosion, transportation of the deposition of fan delta; therefore the precision of reservoir prediction is improved. Keywords Fan Delta, Lithofacies, Sedimentary Facies, Idea of Source to Sink *通信作者。
航空地球物理勘探安全操作规程标准范本
操作规程编号:LX-FS-A73255 航空地球物理勘探安全操作规程标 准范本 In The Daily Work Environment, The Operation Standards Are Restricted, And Relevant Personnel Are Required To Abide By The Corresponding Procedures And Codes Of Conduct, So That The Overall Behavior Can Reach The Specified Standards 编写:_________________________ 审批:_________________________ 时间:________年_____月_____日 A4打印/ 新修订/ 完整/ 内容可编辑
航空地球物理勘探安全操作规程标 准范本 使用说明:本操作规程资料适用于日常工作环境中对既定操作标准、规范进行约束,并要求相关人员共同遵守对应的办事规程与行动准则,使整体行为或活动达到或超越规定的标准。资料内容可按真实状况进行条款调整,套用时请仔细阅读。 一、航空勘探活动,应执行国家空中交通安全管制法规,按规定程序申报批准取得航空勘探飞行权和观测权,并依法接受空中飞行监管。 二、飞机体内外航空物探仪器设备安装,应有具有航空器安装、维修专业技术资格单位承担。安装人员应该具有航空器安装、维修专业技术资格;且安装要考虑飞机整体平衡、配重。 三、飞行勘探工作开始前,勘探队应与飞行机组、飞行保障部门召开安全协调会,研究作业区域气象、地理条件,确定飞行高度;飞机起飞勘探作业
2020年(生物科技行业)生物工程介绍
(生物科技行业)生物工程 介绍
生物工程 目录[隐藏] 生物工程 主要课程 开办院校 现代生物工程技术 生物工程美国学校的排名 生物医学工程 生物工程专业 生物工程 主要课程 开办院校 现代生物工程技术 生物工程美国学校的排名 生物医学工程 生物工程专业 [编辑本段] 生物工程 (bioengineering;bion) 生物工程,是20世纪70年代初开始兴起的壹门新兴的综合性应用学科,90年代诞生了基于系统论的生物工程,即系统生物工程的概念。
所谓生物工程,壹般认为是以生物学(特别是其中的微生物学、遗传学、生物化学和细胞学)的理论和技术为基础,结合化工、机械、电子计算机等现代工程技术,充分运用分子生物学的最新成就,自觉地操纵遗传物质,定向地改造生物或其功能,短期内创造出具有超远缘性状的新物种,再通过合适的生物反应器对这类“工程菌”或“工程细胞株”进行大规模的培养,以生产大量有用代谢产物或发挥它们独特生理功能壹门新兴技术。1994年曾邦哲提出系统生物工程(中科院ZengBJ)的概念,基于系统生物学的生物工程技术(包括合成生物学开发细胞计算机、生物反应器和生物能源技术等)成为了21世纪的前沿技术。? 生物工程包括五大工程,即遗传工程(基因工程)、细胞工程、微生物工程(发酵工程)、酶工程(生化工程)和生物反应器工程。在这五大领域中,前俩者作用是将常规菌(或动植物细胞株)作为特定遗传物质受体,使它们获得外来基因,成为能表达超远缘性状的新物种——“工程菌”或“工程细胞株”。后三者的作用则是这壹有巨大潜在价值的新物种创造良好的生长和繁殖条件,进行大规模的培养,以充分发挥其内在潜力,为人们提供巨大的经济效益和社会效益。 生物工程的应用领域非常广泛,包括农业、工业、医学、药物学、能源、环保、冶金、化工原料等。它必将对人类社会的政治、经济、军事和生活等方面产生巨大的影响,为世界面临的资源、环境和人类健康等问题的解决提供美好的前景。 [编辑本段] 主要课程 无机化学和化学分析、有机化学、生物化学、化工原理、生化工程、微生物学、细胞生物学、遗传学、分子生物学、基因工程、细胞工程、微生物工程、生物工程下游技术、发酵工程设备等。
南京大学2016年研究生学业奖学金评审结果公示地球科学与工程学院
南京大学2016年研究生学业奖学金评审结果公示地球科学与工程学 院 029地球科学与工程学院DG1429002鲍谈二等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429003陈昕二等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429004崔键二等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429006康逊二等029地球科学与工程学院DZ1429007赖文直博029地球科学与工程学院DG1429008李石磊二等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429009李肃宁三等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429010刘欢三等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429011陆远志三等029地球科学与工程学院DZ1429012马安林直博029地球科学与工程学院DG1429013孟先强一等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429014庞润连一等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429015青龙二等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429016沈林伟一等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429017王静强一等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429018王小均二等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429019卫炜二等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429020吴海光二等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429022谢文逸二等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429023张文二等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429024赵凯二等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429025赵万伏三等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429026赵增霞二等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429027周巍二等
029地球科学与工程学院DG1429028周卫明二等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429029周雪瑶二等029地球科学与工程学院DZ1429031朱仁智直博029地球科学与工程学院DG1429032诸泽颖二等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429033曹少华二等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429034侯玉松二等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429035庞宇峰三等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429036乔文静二等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429037宋震二等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429038吴鸣一等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429040赵小二二等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429041曹鼎峰二等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429042董盛时二等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429043李长圣二等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429044史卜涛二等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429045王兴二等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429046吴静红一等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429048张培兴二等029地球科学与工程学院DG1429049周殷康三等 文章来源:文彦考研旗下南京大学考研网
北大考博辅导:北京大学地球与空间科学学院考博难度解析及经验分享
北大考博辅导:北京大学地球与空间科学学院考博难度解析及经验分 享 地球与空间科学学院2019 年招收博士研究生将试行以综合素质能力为基础的“申请-考核制”。申请人须按照我校博士生招生简章和我院的相关要求进行报名并提交申请材料。经我院研究生招生工作小组对申请人的材料审核评估后确认是否给予考核资格,对符合条件者通过考核确定是否录取。 一、院系简介 北京大学地球与空间科学学院于2001年10月26日正式成立。新组建的地球与空间科学学院由原北大地质学系、地球物理学系的固体地球物理学专业、空间物理学专业、北大遥感所以及城市与环境学系的GIS等专业组成。 新成立的北京大学地球与空间科学学院设有5个本科生专业(地质、地球化学、固体地球物理学、空间科学与技术、地理信息系统)、3个一级学科博士、硕士授权点,并设有地质学、地球物理学、地理学、测绘学四个博士后流动站。 学院共有中科院院士6名,教授51名/特聘研究员11名(其中长江特聘教授6名、长江讲座教授4名,国家杰出青年科学基金获得者9名,青年千人4名,百人计划7人,国家重点基础研究发展计划(973计划)首席科学家3名,北京市教学名师1名)、副教授37名/副研究员1名、讲师4名;设有国家理科基础科学人才培养基地1个(地质学),国家基金委创新群体3个,国家重点学科3个(构造地质学、固体地球物理学、地理信息系统),教育部重点实验室1个(造山带与地壳演化重点实验室),北京市重点实验室1个(空间信息集成与3S工程应用),北京市重点学科1个(空间物理学)。它是我国地球科学人才培养的重要基地,承担着为国家现代化建设输送地质学、地球物理学、空间科学、遥感、地理信息系统和测绘科学与技术等方面的高级专门人才的重任,是北京大学创建世界一流大学的一支重要力量。 二、招生信息 北京大学物理学院博士招生专业有10个: 070503 地图学与地理信息系统 研究方向:01. 地理信息系统方法02. 数字地球与智慧城市03. 空间信息智能处理与理解04. 空间分析方法和GIS建模05. 矿山空间信息应用工程06. 空间信息科学与信息工程
航空地球物理勘探安全操作规程示范文本
航空地球物理勘探安全操作规程示范文本 In The Actual Work Production Management, In Order To Ensure The Smooth Progress Of The Process, And Consider The Relationship Between Each Link, The Specific Requirements Of Each Link To Achieve Risk Control And Planning 某某管理中心 XX年XX月
航空地球物理勘探安全操作规程示范文 本 使用指引:此操作规程资料应用在实际工作生产管理中为了保障过程顺利推进,同时考虑各个环节之间的关系,每个环节实现的具体要求而进行的风险控制与规划,并将危害降低到最小,文档经过下载可进行自定义修改,请根据实际需求进行调整与使用。 一、航空勘探活动,应执行国家空中交通安全管制法 规,按规定程序申报批准取得航空勘探飞行权和观测权, 并依法接受空中飞行监管。 二、飞机体内外航空物探仪器设备安装,应有具有航 空器安装、维修专业技术资格单位承担。安装人员应该具 有航空器安装、维修专业技术资格;且安装要考虑飞机整 体平衡、配重。 三、飞行勘探工作开始前,勘探队应与飞行机组、飞 行保障部门召开安全协调会,研究作业区域气象、地理条 件,确定飞行高度;飞机起飞勘探作业前,飞机机组、勘 探队应分别对飞机、勘测仪器、设备进行全面检查。
四、勘探队长,应了解执行勘测飞行任务的飞机性能及其定检、发动机使用小时等情况。飞行勘测时,机上勘测技术人员应与飞机机组人员密切配合,随时检查记录飞行速度、离地高度,确保不突破飞行安全边界。 五、非封闭舱飞机飞行高度4000m以上勘测作业,应装备氧气瓶;海区飞行勘测作业,应配备救生衣。 六、航空勘探作业,应遵守航空磁测、航空遥感摄影技术规范规程。 七、航空勘探空勤技术人员,每天飞行时间不得超过8h,168h内最长飞行小时不得超过50h。 八、航空勘测活动,应执行《中华人民共和国航空法》及国务院民用航空主管部门有关规定。 请在此位置输入品牌名/标语/slogan Please Enter The Brand Name / Slogan / Slogan In This Position, Such As Foonsion
2011年本科三批各高校录取分数线(精)
院校名称 投档最低分 总分(含优惠语文数学外语 安徽财经大学商学院 539105116109安徽建筑工业学院城市建设学院 517 94109107安徽医科大学临床医学院 493109110111安阳师范学院人文管理学院413100 67 94北京城市学院 493100 93123北京第二外国语学院中瑞酒店管理学院505107 78128北京工商大学嘉华学院 532110108132北京工业大学耿丹学院535109113107北京化工大学北方学院 450100 93105北京交通大学海滨学院 437101 84115北京科技大学天津学院 548 96118 98北京理工大学珠海学院 537 97123107北京邮电大学世纪学院 543108120 98北京中医药大学东方学院 421115 86107渤海大学文理学院 452 94102103长春大学光华学院 461110 86108长春大学旅游学院 390 长春工业大学人文信息学院 437 98 83 94长春建筑学院 474 86110 90长春理工大学光电信息学院 474 85 96107长春师范学院 494 96114 93长江大学工程技术学院519102110 91长江大学文理学院 471 98 99113长沙理工大学城南学院 518 95116102长沙医学院 487103114110常州大学怀德学院 428 91 75 98成都东软学院 414 89 92106成都理工大学工程技术学院 532100123108成都理工大学广播影视学院 425 91 77 98成都信息工程学院银杏酒店管理学院 418103 85111说明:投档最低分中所列出的语、数、外单科成绩,是投档时若总分相同依次比对 院校名称 投档最低分 总分(含优惠语文数学外语 大连东软信息学院 425 94 83 76大连工业大学艺术与信息工程学院 472103 91 85大连科技学院 444100103100大连理工大学城市学院 536113115122大连医科大学中山学院 520100 98107电子科技大学成都学院 526104119112电子科技大学中山
