Pacific Krill Prevents Triglyceride Accumulation in Adipocytes by Suppressing PPARc and CEBPa

Water-Soluble Extract of Pacific Krill Prevents Triglyceride Accumulation in Adipocytes by Suppressing PPAR c and C/EBP a Expression
Hidetoshi Yamada1*,Tomohiro Ueda2,Akira Yano1
1Iwate Biotechnology Research Center,Kitakami,Iwate,Japan,2Iwate Fisheries Technology Center,Kamaishi,Iwate,Japan
Abstract
Background:Pacific Krill(Euphausia pacifica)are small,red crustaceans,similar to shrimp,that flourish in the North Pacific and are eaten in Japan.
Methods and Findings:We investigated the effect of a water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill on adipocytes and discovered that this extract suppressed triglyceride accumulation in adipocytes.Furthermore,the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill suppressed the expression of two master regulators of adipocyte differentiation,peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma(PPAR c)and CCAAT enhancer binding protein alpha(C/EBP a).C/EBP b promotes PPAR c and C/EBP a expression,but the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill did not inhibit the expression of C/EBP b or C/EBP b-mediated transcriptional activation.The Pacific Krill extract was more effective than a PPAR c antagonist in suppressing PPAR c and C/EBP a expression.
Conclusions:These results indicated that the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill was not simply a PPAR c antagonist,but that it prevented triglyceride accumulation in adipocytes by suppression of PPAR c and C/EBP a via a pathway that is independent of C/EBP b.
Citation:Yamada H,Ueda T,Yano A(2011)Water-Soluble Extract of Pacific Krill Prevents Triglyceride Accumulation in Adipocytes by Suppressing PPAR c and C/ EBP a Expression.PLoS ONE6(7):e21952.doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0021952
Editor:Joseph Najbauer,City of Hope National Medical Center and Beckman Research Institute,United States of America
Received January8,2011;Accepted June15,2011;Published July7,2011
Copyright:?2011Yamada et al.This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License,which permits unrestricted use,distribution,and reproduction in any medium,provided the original author and source are credited.
Funding:This work was supported by a fund from the Basic Biotechnology Project of Iwate Prefecture,Japan,and Grants-in-Aid from the Sanriku Foundation.
The funders had no role in study design,data collection and analysis,decision to publish,or preparation of the manuscript.
Competing Interests:The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
*E-mail:hyamada@ibrc.or.jp
Introduction
Obesity increases the likelihood of various diseases,including type 2diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.Foods that suppress absorption of glucose and lipids[1,2]and increase the metabolism of fat[3–6]are regarded as anti-obesity foods.Several anti-obesity foods were studied to identify the bioactive compounds and the physiological function of the compounds that are responsible for their anti-obesity effects.Foods that prevent fat accumulation also seem to be effective in preventing obesity,but only a few studies have investigated the foods that specifically prevent fat accumulation. Body fat is mainly stored in adipose tissue.Adipose tissue is generally regarded as mesodermal in origin,and mature adipocytes develop from mesenchymal stem cells(MSCs)via a preadipocyte stage[7].Increases in adipose tissue mass seem to depend on adipocyte hypertrophy because mature adipocytes have low proliferative potential.Recently,however,it was shown that, in adults,the number of adipocytes could increase by adipogenesis, the differentiation of preadipocytes to mature adipocytes[8]. Adipogenesis and adipocyte hypertrophy may occur reiteratively as an individual becomes obese;therefore,inhibition of adipogen-esis may be an effective approach to the prevention of fat accumulation.
Adipogenesis is regulated by PPAR c and C/EBP a expression with the retinoid X receptor(RXR).The PPAR c-RXR complex promotes the expression of target genes and adipocyte differen-tiation.C/EBP a is a transcription factor that is required for adipocyte maturation[9].
Pacific Krill are small,red crustaceans,similar to shrimp,that flourish in the North Pacific,and they have been part of Japanese diet for seventy years.They have a high content of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids,including eicosapentaenoic acid(EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid(DHA),and several studies report that Krill Oil has anti-inflammatory effects and that it decreases serum lipid levels[10–16].Krill Oil has been studied as a bioactive food, but other constituents of Krill have not been studied intensively.In the present study,we investigated the effect of the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill on adipocytes and discovered that this extract prevented triglyceride accumulation in adipocytes by suppressing adipogenesis.
Results
The water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill suppressed triglyceride accumulation in mouse adipocytes
To examine the effect of the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill on adipocytes,we cultured3T3-F442A cells in the presence of10m g/ml of insulin and500m g/ml of the water-soluble extract
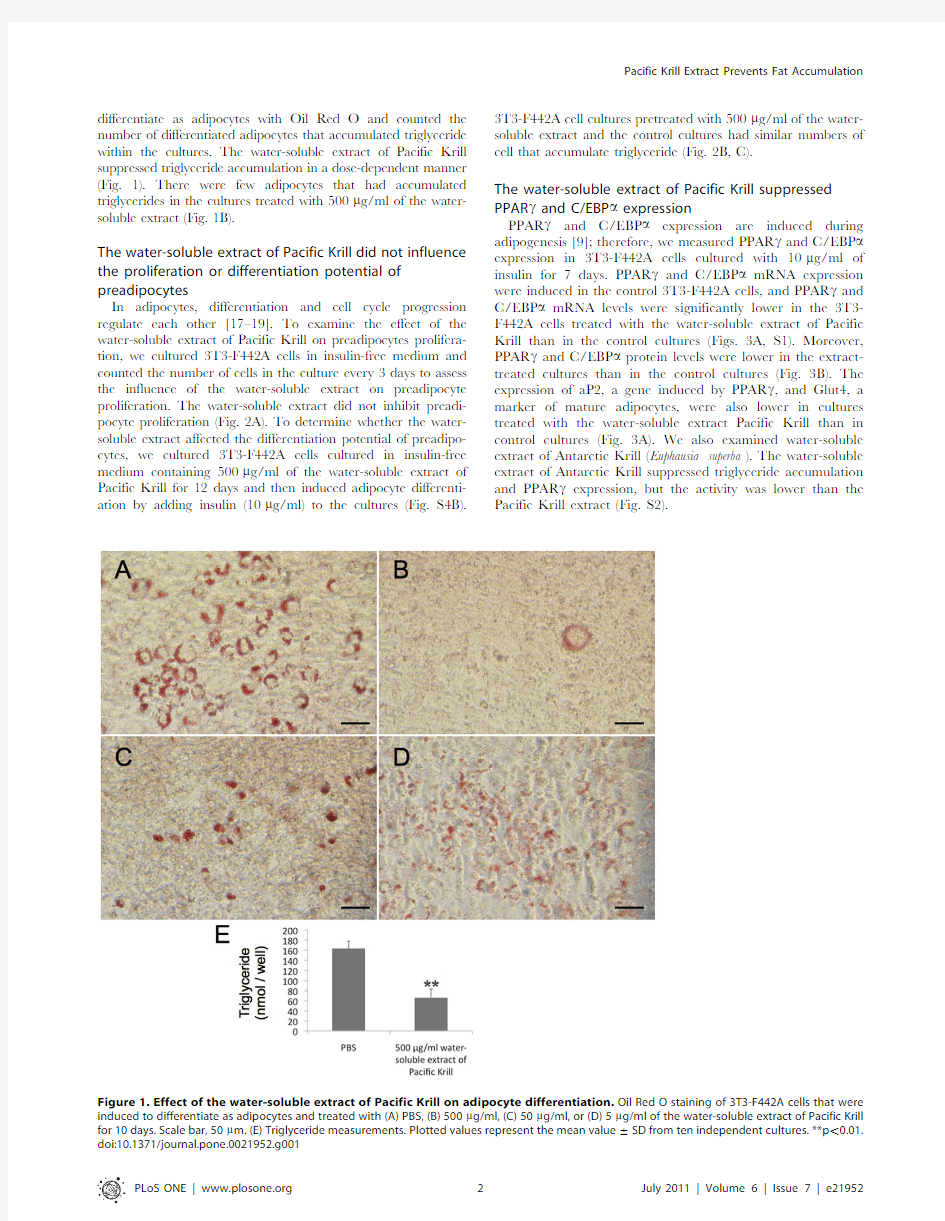
differentiate as adipocytes with Oil Red O and counted the number of differentiated adipocytes that accumulated triglyceride within the cultures.The water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill suppressed triglyceride accumulation in a dose-dependent manner (Fig.1).There were few adipocytes that had accumulated triglycerides in the cultures treated with 500m g/ml of the water-soluble extract (Fig.1B).
The water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill did not influence the proliferation or differentiation potential of preadipocytes
In adipocytes,differentiation and cell cycle progression regulate each other [17–19].To examine the effect of the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill on preadipocytes prolifera-tion,we cultured 3T3-F442A cells in insulin-free medium and counted the number of cells in the culture every 3days to assess the influence of the water-soluble extract on preadipocyte proliferation.The water-soluble extract did not inhibit preadi-pocyte proliferation (Fig.2A).To determine whether the water-soluble extract affected the differentiation potential of preadipo-cytes,we cultured 3T3-F442A cells cultured in insulin-free medium containing 500m g/ml of the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill for 12days and then induced adipocyte differenti-ation by adding insulin (10m g/ml)to the cultures (Fig.S4B).
3T3-F442A cell cultures pretreated with 500m g/ml of the water-soluble extract and the control cultures had similar numbers of cell that accumulate triglyceride (Fig.2B,C).
The water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill suppressed PPAR c and C/EBP a expression
PPAR c and C/EBP a expression are induced during adipogenesis [9];therefore,we measured PPAR c and C/EBP a expression in 3T3-F442A cells cultured with 10m g/ml of insulin for 7days.PPAR c and C/EBP a mRNA expression were induced in the control 3T3-F442A cells,and PPAR c and C/EBP a mRNA levels were significantly lower in the 3T3-F442A cells treated with the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill than in the control cultures (Figs.3A,S1).Moreover,PPAR c and C/EBP a protein levels were lower in the extract-treated cultures than in the control cultures (Fig.3B).The expression of aP2,a gene induced by PPAR c ,and Glut4,a marker of mature adipocytes,were also lower in cultures treated with the water-soluble extract Pacific Krill than in control cultures (Fig.3A).We also examined water-soluble extract of Antarctic Krill (Euphausia superba ).The water-soluble extract of Antarctic Krill suppressed triglyceride accumulation and PPAR c expression,but the activity was lower than the Pacific Krill extract (Fig.
S2).
Figure 1.Effect of the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill on adipocyte differentiation.Oil Red O staining of 3T3-F442A cells that were induced to differentiate as adipocytes and treated with (A)PBS,(B)500m g/ml,(C)50m g/ml,or (D)5m g/ml of the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill for 10days.Scale bar,50m m.(E)Triglyceride measurements.Plotted values represent the mean value 6SD from ten independent cultures.**p ,0.01.
Figure2.Effects of the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill on preadipocytes.(A)Growth curve of preadipocytes cultured with insulin-free medium containing PBS(m)or500m g/ml of the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill(N).The data points represent the mean value6SD from four independent experiments.(B and C)Oil Red O staining of3T3-F442A.These cells were cultured in insulin-free medium containing(B)PBS or(C) 500m g/ml of the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill for12days and then induced to differentiate as adipocytes by adding insulin to the culture medium.Scale bar,50m m.
doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0021952.g002
Figure3.Analysis of PPAR c and C/EBP a mRNA and protein levels in3T3-F442A cells.(A)qRT-PCR analysis of RNA extracts from3T3-F442A cells induced to differentiate as adipocytes for7days.Plotted values represent the mean value6SD from five independent cultures.**p,0.01;
*p,0.05.(B)Protein extracts from3T3-F442A cells induced to differentiate as adipocytes for7days were analyzed by immunoblotting.
The water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill inhibited adipocyte differentiation in human mesenchymal stem cells
We examined whether the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill also inhibited adipocyte differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells(hMSCs).After13days of adipocyte differentiation,we added500m g/ml of the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill to hMSC medium and allowed the cultures to grow.We then measured PPAR c and C/EBP a mRNA expression levels in these hMSCs cultures using qRT-PCR,and we stained hMSCs cultures with Oil Red O.The water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill suppressed PPAR c and C/EBP a expression in hMSC cultures (Fig.4C),and the number of cells that accumulated triglycerides were lower in the extract-treated cultures than in the control cultures(Fig.4A,B).
C/EBP b expression and C/EBP b-mediated transcriptional activation were not affected by the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill
C/EBP b binds to the PPAR c and C/EBP a promoters and activates expression of both genes[20–22].We assumed that the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill decreased the expression of C/EBP b and C/EBP b-mediated transcriptional activation.To test these hypotheses,we measured C/EBP b mRNA expression levels and protein levels in extract-treated and control cultures,but the C/EBP b mRNA and protein levels were similar in control and extract-treated cultures(Fig.5A,B).Next,we performed ChIP analysis and luciferase reporter assays to examine C/EBP b-mediated transcriptional activation.The amount of C/EBP b bound to the PPAR c and C/EBP a promoters was similar in control and extract-treated cells(Fig.5C).The reporter activity of pC/EBP RE-TK hRLuc(F)construct was similar in control and extract-treated cultures(Fig.5D).
The water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill suppressed PPAR c and C/EBP a expression more than a PPAR c antagonist did
The PPAR c antagonists bind to PPAR c selectively and inhibit PPAR c function[23].Because PPAR c and C/EBP a activate each other,the PPAR c antagonists suppress PPAR c and C/EBP a expression.To assess whether the extract functioned as a PPAR c antagonist,we compared the effects of the water-soluble extract with those of a PPAR c antagonist(T0070907).Triglyceride accumulation was suppressed by10m M T0070907(Fig.6C),and 90m M T0070907suppressed the expression of aP2to the levels found in cultures treated with the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill(Fig.6D).However,while the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill suppressed more than95%of PPAR c and C/EBP a expression,T0070907suppressed less than70%of PPAR c and C/EBP a expression(Fig.6D).
Transcriptome analysis of3T3-F442A cells treated with the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill
To identify the genes—other than PPAR c and C/EBP a—that were affected by the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill,we analyzed the transcriptome of3T3-F442A cells using Super SAGE (serial analysis of gene expression).We identified65genes with expression levels that may be affected by treatment with the water-soluble extract by comparing the transcriptome of control3T3-F442A cells with the transcriptome of3T3-F442A cells cultured with the water-soluble extract.We used qRT-PCR to confirm that these65genes were affected by treatment with the extract.
We Figure4.Influence of the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill on adipocyte differentiation in hMSCs.After13days of adipocyte differentiation,(A)PBS or(B)500m g/ml of the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill were added to the cell cultures.(A and B)The Oil Red O staining of UCB TERT-21cells induced to differentiate as adipocytes for22days.Scale bar,50m m.(C)RNA extracts from UCB TERT-21cells induced to differentiate as adipocytes for18days were analyzed by qRT-PCR.Plotted values represent the mean value6SD from four independent cultures. *p,0.05.The p value of C/EBP a was0.059.
identified five genes with expression levels that were increased by the water-soluble extract(Fig.7)and seven genes with expression levels that were decreased(Fig.8).
Discussion
We discovered that the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill prevented triglyceride accumulation by suppressing PPAR c and C/EBP a expression(Figs.1–4).A study of PPAR c+/2mice shows that appropriate reduction in PPAR c expression prevents obesity induced by a high-fat diet[24];therefore,inhibition of PPAR c expression may be an effective way to prevent obesity. However,constitutive or complete elimination of PPAR c results in damage to adipose tissue,and this tissue plays a central role in maintaining lipid homeostasis,energy balance,and producing leptin and adiponectin[25–29].Therefore,suppression,rather than elimination of PPAR c expression,may be a better way to prevent obesity.The water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill did not affect proliferation or differentiation of preadipocytes(Fig.2)and suppressed the expression of PPAR c in adipocytes(Fig.3). Consumption of the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill may be a safe and effective way to prevent obesity.
Decreased C/EBP b expression and DNA binding,inhibition of PPAR c function,and activation of the Wnt/b-catenin pathway suppresses PPAR c and C/EBP a expression[9,23,29–32]. However,the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill did not decrease C/EBP b expression or C/EBP b-mediated transcrip-tional activation(Fig.5),and the extract did not increase the expression of Nr2f2,a gene that acts downstream of Wnt/b-catenin signal to silence PPAR c expression(Fig.S3).Moreover,than the PPAR c antagonist did(Fig.6).These results indicate that the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill was not only a PPAR c antagonist,but that it suppressed the expression of PPAR c and C/EBP a via a pathway other than those mediated by C/EBP b or Wnt/b-catenin.
The water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill induced expression of five genes—Angptl7,Fgf7,Tgfb1,Hgf,and Pak3;and it suppressed expression of seven genes—Fgfr2,Postn,Id1, Pknox2,Gsta4,Ada,and Ldlrad3.FGF signals positively regulate adipocyte differentiation[33–36].While the expression of Fgf7was increased approximately two-fold in cells treated with the extract,the expression of Fgfr2was decreased to approximately one-seventh of the level found in control cells. These findings imply that FGF signaling was blocked in3T3-F442A cells treated with the extract.TGF b signal function is antagonistic to PPAR c,and TGF b induces myoblast differen-tiation[37].We propose that decreased FGF signaling and increased TGF b signaling resulted suppression PPAR c and C/ EBP a expression.
Krill Oil has been identified as a bioactive compound,and its functions have been studied,but other components of the krill have not been studied.This study is the first to report that the water-soluble extract of Krill contains bioactive compound. Furthermore,there are only a few reports that indicate that the water-soluble components extracted from a food can suppress the expression of PPAR c;therefore,the bioactive material contained in the water-soluble extract of Krill is of great interest.Previous studies[10–13,38–42]and the present results indicate that Krill is beneficial to human health because it has anti-inflammatory effects,decreases serum lipid levels,and prevents fat accumulation
Figure5.Effects of the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill on C/EBP b expression and C/EBP b-mediated transcriptional activation.
(A)qRT-PCR analysis of RNA extracts from3T3-F442A cells induced adipocyte differentiation.Plotted values are the mean value6SD from five independent cultures.(B)Protein extracts from3T3-F442A cells induced to differentiate as adipocyte for4days were analyzed by immunoblotting.(C) ChIP analysis of C/EBP b ChIP samples were extracted from the3T3-F442A cells induced to differentiate as adipocyte and cultured with or without 500m g/ml of the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill for4days.Plotted values are the mean value6SD from three independent experiments. Normal Rabbit IgG was used as a negative control.(D)Luciferase reporter assay.The renilla luciferase activity was normalized to firefly luciferase activity.Plotted values are the mean value6SD from eight independent experiments.
doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0021952.g005
Materials and Methods
Water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill
A mixture of Pacific Krill and distilled water(3:1by volume) was homogenized,and the resulting homogenate was centrifuged at8000rpm for30min.The supernatant was filtered and lyophilized.
Cell culture
3T3-F442A cells from a mouse preadipocyte cell line(DS pharma Biomedical Co.,Ltd.,Osaka,Japan)were cultured in DMEM containing10%Fetal Bovine Serum(FBS)and Antibiotic Antimycotic Solution(Sigma-Aldrich,St Louis,MO,USA).3T3-F442A cells were grown until confluent on type II collagen-coated dishes(Corning,Corning,NY,USA),and confluent cells were induced to differentiate into adipocytes with10m g/ml of insulin (Sigma-Aldrich).The culture conditions used in individual experiments are summarized in Figure S4.
UCB TRET-21cells,immortalized human Mesenchymal Stem Cells,(JCRB Cell Bank,Osaka,Japan)were cultured in DMEM containing10%Mesenchymal Stem Cell-qualified FBS(Invitrogen, Carlsbad,CA,USA)and Antibiotic Antimycotic Solution(Sigma-Aldrich).UCB TERT-21cells were induced to differentiate into adipocytes with10m g/ml of insulin,1m M dexamethasone(Wako, Osaka,Japan),200m M indomethasin(Wako),and500m M IBMX, 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine(Wako).The culture conditions used in Quantitative real-time PCR(qRT-PCR)
Total RNA was extracted from3T3-F442A cells or UCB TERT-21cells with an RNeasy kit(QIAGEN,Tokyo,Japan)and used to synthesize cDNA with the PrimeScript RT reagent kit (Takara,Shiga,Japan);all kits were used according to the manufacturers’recommendations.Quantitative real-time PCR was performed with the gene specific primers listed in Tables S1 and S2and Fast SYBER Green master mix(Applied Biosystems). The qRT-PCR data from3T3-F442A cells were normalized to RPLP0.The qRT-PCR data from UCB TERT-21cells were normalized to Actin b.The results are expressed as fold increase compared to non-induced3T3-F442A cells or UCB TRET-21 cells.
Oil Red O Staining
The cells induced to differentiate as adipocytes were fixed with 10%formalin(Wako)at room temperature for10min.Fixed cells were washed with PBS and isopropanol solution and then stained with180mg/ml of Oil Red O for40min.The Oil Red O-stained cells were observed with a Nikon microscope(6400)after washing. An Adipogenesis Assay kit(Bio Vision,Mountain View,CA,USA) was used to measure triglyceride content.
Super serial analysis of gene expression(SAGE)
Super SAGE was performed as previously described[43–45]. Briefly,total RNA was extracted from3T3-F442A cells with an
https://www.360docs.net/doc/5f11830167.html,parison of effects of the water-soluble extract and a PPAR c antagonist on adipocyte differentiation.Oil Red O staining of3T3-F442A cells induced to differentiate as adipocytes and treated with(A)DMSO,(B)500m g/ml of the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill,or(C) 10m M T0070907for10days.Scale bar,50m m.(D)Analysis of mRNA levels in3T3-F442A cells.RNA extracts from3T3-F442A cells induced to differentiate as adipocytes for7days were analyzed by qRT-PCR.Plotted values are the mean value6SD from four independent cultures.**p,0.01. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0021952.g006
biotinated oligo-dT primer and Double-Stranded cDNA Synthesis kit(Invitrogen)from5m g of total RNA.Double-stranded cDNAs were digested with NlaIII(New England Biolabs,Beverly,MA, USA)after purification using a PCR purification kit(QIAGEN). Double-stranded cDNAs digested with NlaIII were bound to Dynabeads M270streptavidin(Invitrogen).Adapter sequence2 containing an EcoP15I restriction site was ligated to the double-stranded cDNAs that were bound to Dynabeads.Double-stranded cDNAs were digested with EcoP15I(New England Biolabs). Double-stranded cDNAs digested with EcoP15I and separated from Dynabeads were tag sequences.Adaptor sequence1 containing index sequence was ligated to tag sequences.Tag sequences were then amplified by PCR and gel purified.Finally, tag sequences were analyzed using a Genome Analyzer II (Ilumina,San Diego,CA,USA).
Super SAGE data analysis
Sorting of sequence reads(35-bases)based on index sequence and the subsequent extraction of26-base reference sequences from reads was conducted using a script written in C++.The reference sequences were compared to the NCBI mouse transcript database using the BLAST program.We searched cDNA sequence,Tags.The total number of analyzed reads and tags are shown in Table S3.
Chromatin immunoprecipitation(ChIP)
ChIP was performed with a ChIP Expression kit(Active motif, Tokyo,Japan).Anti-C/EBP b(Santa Cruz,Santa Cruz,CA,USA) and normal rabbit IgG(Santa Cruz)were used for ChIP.ChIP samples were analyzed by gene-specific quantitative real-time PCR. The primers used to amplify PPAR c promoter sequences were59-CACGCCCCTCACAGAACAGTGAA-39and59-GCACTGTC-CTGACTGAGAGCCA-39.The primers used to amplify C/EBP a promoter sequences were59-ATGCTCCCCACTCACCGCCT-39 59-GCCCCCTGGTGTCCAAACGG-39.The results are present-ed as percent of input DNA.
Plasmids
We used the pC/EBP RE-TK hRluc(F)vector(RIKEN BRC, Ibaraki,Japan),which uses the nucleotide sequence of the C/EBP response element(59-GATCCGCCAATGCCAATGCCAATG-39) found upstream of minimal thymidine kinase(TK)promoter in the renilla luciferase reporter construct.The control vector was pmutant C/EBP RE-TK hRluc(R)vector(RIKEN BRC),which contains the
Figure7.The genes activated by the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill.qRT-PCR analysis of RNA extracts from3T3-F442A cells induced to differentiate as adipocytes and treated with PBS(m)or500m g/ml of the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill(N).Plotted values are the mean value6 SD from four independent cultures.
doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0021952.g007
TATG-39)upstream of minimal thymidine kinase(TK)promoter. The luciferase reporter assay normalization vector pCMV-Luc contains the firefly luciferase gene driven by the cytomegarlovirus promoter.
Luciferase reporter assay
The firefly luciferase normalization vector pCMV-Luc(0.3m g) and the renilla luciferase reporter construct pC/EBP RE-TK hRluc(F)(3m g)were co-transfected using Lipofectamin2000 (Invitrogen)into the3T3-F442A cells that had been induced to differentiate into adipocytes for3days.One day after transfection, the cells were harvested using passive lysis buffer(Promega). Renilla and firefly luciferase activities were determined using a dual luciferase assay system(Promega).
Supporting Information
Figure S1Dose-response curve for the effects of water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill on suppression of PPAR c gene expression.RNA extracts from3T3-F442A cells induced to differentiate as adipocytes and treated with the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill for7days were analyzed by qRT-PCR. (TIFF)
Figure S2Effects of the water-soluble extract of Antarc-3T3-F442A cells that were induced to differentiate as adipocytes and treated with(A)PBS or(B)3mg/ml of the water-soluble extract of Antarctic Krill for10days.Scale bar,50m m.(C)qRT-PCR analysis of RNA extracts from3T3-F442A cells induced to undergo adipocyte differentiation with the water-soluble extract of Antarctic krill for7days.Plotted values are the mean value from three independent cultures.
(TIFF)
Figure S3Influences of the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill on Nr2f2expression.qRT-PCR analysis of RNA extracts from3T3-F442A cells induced to undergo adipocyte differentiation for7days.Plotted values are the mean value6SD from three independent cultures.
(TIFF)
Figure S4Flow chart of culture conditions(A).The culture condition of3T3-F442A cells used to generate the data presented in Figures1,3,5–8.(B)The culture condition of3T3-F442A cells used to generate the data presented in Figure2.(C) The culture condition of UCB TERT-21cells used to generate the data presented in Figure4.
(TIFF)
Table S1The list of primers used for gene expression analysis in3T3-F442A cells.
Figure8.The genes suppressed by the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill.qRT-PCR analysis of RNA extracts from3T3-F442A cells induced to differentiate as adipocytes and treated with PBS(m)or500m g/ml of the water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill(N).Plotted values are the mean value 6SD from four independent cultures.
doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0021952.g008
Table S2The list of primers used for gene expression analysis in UCB TERT-21cells.
(DOC)
Table S3Total number of analyzed reads and tags in the Super SAGE analysis.
(DOC)Author Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments:HY.Performed the experiments: HY.Analyzed the data:HY.Contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools:HY TU AY.Wrote the paper:HY.
References
1.Wakabayashi S,Kishimoto Y,Matsuoka A(1995)Effects of indigestible dextrin
on glucose tolerance in rats.J Endocrinol144:533–8.
2.Han LK,Takaku T,Li J,Kimura Y,Okuda H(1999)Anti-obesity action of
oolong tea.Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord23:98–105.
https://www.360docs.net/doc/5f11830167.html,gouge M,Argmann C,Gerhart-Hines Z,Meziane H,Lerin C,et al.(2006)
Resveratrol improves mitochondrial function and protects against metabolic disease by activating SIRT1and PGC-1alpha.Cell127:1109–22.
4.Mori TA,Bao DQ,Burke V,Puddey IB,Watts GF,et al.(1999)Dietary fish as a
major component of a weight-loss diet:effect on serum lipids,glucose,and insulin metabolism in overweight hypertensive subjects.Am J Clin Nutr70: 817–25.
5.Kao YH,Chang HH,Lee MJ,Chen CL(2006)Tea,obesity,and diabetes.Mol
Nutr Food Res50:188–210.
6.Maeda H,Hosokawa M,Sashima T,Funayama K,Miyashita K(2005)
Fucoxanthin from edible seaweed,Undaria pinnatifida,shows antiobesity effect through UCP1expression in white adipose tissues.Biochem Biophys Res Commun332:392–7.
7.Gesta S,Tseng YH,Kahn CR(2007)Developmental origin of fat:tracking
obesity to its source.Cell131:242–56.
8.Tchoukalova YD,Votruba SB,Tchkonia T,Giorgadze N,Kirkland JL,et al.
(2010)Regional differences in cellular mechanisms of adipose tissue gain with overfeeding.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A107:18226–31.
9.Lowell BB(1999)PPARgamma:an essential regulator of adipogenesis and
modulator of fat cell function.Cell99:239–242.
10.Deutsch L(2007)Evaluation of the effect of Neptune Krill Oil on chronic
inflammation and arthritic symptoms.J Am Coll Nutr26:39–48.
11.Bunea R,El Farrah K,Deutsch L(2004)Evaluation of the effects of Neptune
Krill Oil on the clinical course of hyperlipidemia.Altern Med Rev9:420–8.
12.Zhu JJ,Shi JH,Qian WB,Cai ZZ,Li D(2008)Effects of krill oil on serum lipids
of hyperlipidemic rats and human SW480cells.Lipids Health Dis7:30. 13.Tandy S,Chung RW,Wat E,Kamili A,Berge K,et al.(2009)Dietary krill oil
supplementation reduces hepatic steatosis,glycemia,and hypercholesterolemia in high-fat-fed mice.J Agric Food Chem57:9339–45.
14.Ierna M,Kerr A,Scales H,et al.(2010)Supplementation of diet with krill oil
protects against experimental rheumatoid arthritis.BMC musculoskeletal disorders11:136.
15.Batetta B,Griinari M,Carta G,et al.(2009)Endocannabinoids may mediate the
ability of(n-3)fatty acids to reduce ectopic fat and inflammatory mediators in obese Zucker rats.J Nutr139:1495–1501.
16.Ferramosca A,Conte L,Zara V(2011)A krill oil supplemented diet reduces the
activities of the mitochondrial tricarboxylate carrier and of the cytosolic lipogenic enzymes in rats.Journal of animal physiology and animal nutrition.
17.Guo W,Zhang KM,Tu K,Li YX,Zhu L,et al.(2009)Adipogenesis licensing
and execution are disparately linked to cell proliferation.Cell Res19:216–23.
18.Sarruf DA,Iankova I,Abella A,Assou S,Miard S,et al.(2005)Cyclin D3
promotes adipogenesis through activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma.Mol Cell Biol25:9985–95.
19.Zandbergen F,Mandard S,Escher P,Tan NS,Patsouris D,et al.(2005)The
G0/G1switch gene2is a novel PPAR target gene.Biochem J392:313–24.
20.Zhu Y,Qi C,Korenberg JR,Chen XN,Noya D,et al.(1995)Structural
organization of mouse peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (mPPAR gamma)gene:alternative promoter use and different splicing yield two mPPAR gamma isoforms.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A92:7921–5.
21.Tang QQ,Jiang MS,Lane MD(1999)Repressive effect of Sp1on the C/
EBPalpha gene promoter:role in adipocyte differentiation.Mol Cell Biol19: 4855–65.
22.Christy RJ,Kaestner KH,Geiman DE,Lane MD(1991)CCAAT/enhancer
binding protein gene promoter:binding of nuclear factors during differentiation of3T3-L1preadipocytes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A88:2593–7.
23.Lee G,Elwood F,McNally J,Weiszmann J,Lindstrom M,et al.(2002)
T0070907,a selective ligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma,functions as an antagonist of biochemical and cellular activities.J Biol Chem277:19649–57.
24.Kubota N,Terauchi Y,Miki H,Tamemoto H,Yamauchi T,et al.(1999)PPAR
gamma mediates high-fat diet-induced adipocyte hypertrophy and insulin resistance.Molecular Cell4:597–609.25.Pelleymounter MA,Cullen MJ,Baker MB,Hecht R,Winters D,et al.(1995)
Effects of the obese gene product on body weight regulation in ob/ob mice.
Science269:540–3.
26.Halaas JL,Gajiwala KS,Maffei M,Cohen SL,Chait BT,et al.(1995)Weight-
reducing effects of the plasma protein encoded by the obese gene.Science269: 543–6.
27.Campfield LA,Smith FJ,Guisez Y,Devos R,Burn P(1995)Recombinant
mouse OB protein:evidence for a peripheral signal linking adiposity and central neural networks.Science269:546–9.
28.Yamauchi T,Kamon J,Waki H,Terauchi Y,Kubota N,et al.(2001)The fat-
derived hormone adiponectin reverses insulin resistance associated with both lipoatrophy and obesity.Nat Med7:941–6.
29.Tanaka T,Yoshida N,Kishimoto T,Akira S(1997)Defective adipocyte
differentiation in mice lacking the C/EBPbeta and/or C/EBPdelta gene.
EMBO J16:7432–43.
30.Tong Q,Tsai J,Tan G,Dalgin G,Hotamisligil GS(2005)Interaction between
GATA and the C/EBP family of transcription factors is critical in GATA-mediated suppression of adipocyte differentiation.Mol Cell Biol25:706–15.
31.Rochford JJ,Semple RK,Laudes M,Boyle KB,Christodoulides C,et al.(2004)
ETO/MTG8is an inhibitor of C/EBPbeta activity and a regulator of early adipogenesis.Mol Cell Biol24:9863–72.
32.Okamura M,Kudo H,Wakabayashi K,Tanaka T,Nonaka A,et al.(2009)
COUP-TFII acts downstream of Wnt/beta-catenin signal to silence PPAR-gamma gene expression and repress adipogenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:5819–24.
33.Hutley L,Shurety W,Newell F,McGeary R,Pelton N,et al.(2004)Fibroblast
growth factor1:a key regulator of human adipogenesis.Diabetes53:3097–106.
34.Prusty D,Park BH,Davis KE,Farmer SR(2002)Activation of MEK/ERK
signaling promotes adipogenesis by enhancing peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma(PPARgamma)and C/EBPalpha gene expression during the differentiation of3T3-L1preadipocytes.J Biol Chem277:46226–32.
35.Sakaue H,Konishi M,Ogawa W,Asaki T,Mori T,et al.(2002)Requirement of
fibroblast growth factor10in development of white adipose tissue.Genes Dev 16:908–12.
36.Widberg CH,Newell FS,Bachmann AW,Ramnoruth SN,Spelta MC,et al.
(2009)Fibroblast growth factor receptor1is a key regulator of early adipogenic events in human preadipocytes.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab296:E121–31.
37.Hong KM,Belperio JA,Keane MP,Burdick MD,Strieter RM(2007)
Differentiation of human circulating fibrocytes as mediated by transforming growth factor-beta and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma.J Biol Chem282:22910–20.
38.Tou JC,Jaczynski J,Chen YC(2007)Krill for human consumption:nutritional
value and potential health benefits.Nutrition reviews65:63–77.
39.Gigliotti JC,Smith AL,Jaczynski J,et al.(2011)Consumption of krill protein
concentrate prevents early renal injury and nephrocalcinosis in female Sprague-Dawley rats.Urol Res39:59–67.
40.Bridges KM,Gigliotti JC,Altman S,et al.(2010)Determination of digestibility,
tissue deposition,and metabolism of the omega-3fatty acid content of krill protein concentrate in growing rats.Journal of agricultural and food chemistry 58:2830–2837.
41.Ulven SM,Kirkhus B,Lamglait A,et al.(2011)Metabolic effects of krill oil are
essentially similar to those of fish oil but at lower dose of EPA and DHA,in healthy volunteers.Lipids46:37–46.
42.Kidd PM(2007)Omega-3DHA and EPA for cognition,behavior,and mood:
clinical findings and structural-functional synergies with cell membrane phospholipids.Altern Med Rev12:207–227.
43.Matsumura H,Reich S,Ito A,Saitoh H,Kamoun S,et al.(2003)Gene
expression analysis of plant host-pathogen interactions by SuperSAGE.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A100:15718–23.
44.Matsumura H,Ito A,Saitoh H,Winter P,Kahl G,et al.(2005)SuperSAGE.
Cell Microbiol7:11–8.
45.Matsumura H,Yoshida K,Luo S,Kimura E,Fujibe T,et al.(2010)High-
throughput SuperSAGE for digital gene expression analysis of multiple samples using next generation sequencing.PLoS One5:e12010.
甘油三酯(triglyceride, TG)含量测定试剂盒说明书
货号:MS2408 规格:100管/96样甘油三酯(triglyceride, TG)含量测定试剂盒说明书 微量法 注意:正式测定之前选择2-3个预期差异大的样本做预测定。 测定意义: TG是长链脂肪酸和甘油形成的脂肪分子,不仅是细胞膜的主要成分,也是重要呼吸底物。 测定原理: 用异丙醇抽提取TG,KOH皂化TG后水解生成甘油及脂肪酸,过碘酸氧化甘油生成甲醛,在氯离子存在下甲醛与乙酰丙酮缩合生成黄色物质,在420 nm有特征吸收峰,其颜色的深浅与TG含量成正比。 自备实验用品及仪器: 可见分光光度计/酶标仪、微量石英比色皿/96孔板、水浴锅、可调式移液枪、双蒸水 试剂组成和配置: 试剂一:液体60mL×2瓶,4℃保存。 试剂二:液体5mL×1瓶,4℃保存。 试剂三:液体6mL×1瓶,4℃保存。 试剂四:液体2mL×1瓶,4℃避光保存。 试剂五:液体6mL×1瓶,4℃避光保存。 试剂六:液体6mL×1瓶,4℃避光保存。 标准品:液体1mL×1支,1mg/mL标准甘油三酯溶液,4℃避光保存。 TG的提取: 1、组织中TG的提取:按照组织质量(g):试剂一体积(mL)为1:5~10的比例(建议称取约0.1g组织,加入1mL试剂一)进行冰浴匀浆,8000g,4℃离心10min,取上清,即TG待测液。 2、细胞、细菌中TG的提取:先收集400-500万细胞或细菌到离心管内,弃上清,加1mL试剂一,超声波破碎1min(强度20%,超声2s,停1s),8000g,4℃离心10min,取上清,即TG 待测液。 3、血清(浆)样品:直接测定。 测定操作: 1. 可见分光光度计/酶标仪预热30min,调节波长到420 nm,蒸馏水调零。 15μL,置于新的Ep 管。 3.甘油三酯含量测定: 第1页,共3页
高脂血症的分型和分类
1976年WHO建议将高脂血症分为六型: (1)Ⅰ型高脂蛋白血症:主要是血浆中乳糜微粒浓度增加所致。将血浆至于4℃冰箱中过夜,见血浆外观顶层呈“奶油样”,下层澄清。测定血脂主要为甘油三酯升高,胆固醇水平正常或轻度增加,此型在临床上较为罕见。 (2)Ⅱ型高脂蛋白血症,又分为Ⅱa型和Ⅱb型。 ①Ⅱa型高脂蛋白血症:血浆中LDL水平单纯性增加。血浆外观澄清或轻微混浊。测定血脂只有单纯性胆固醇水平升高,而甘油三酯水平则正常,此型临床常见。 ②Ⅱb型高脂蛋白血症:血浆中VLDL和LDL水平增加。血浆外观澄清或轻微混浊。测定血脂见胆固醇和甘油三酯均增加。此型临床相当常见。 (3)Ⅲ型高脂蛋白血症:又称为异常β-脂蛋白血症,主要是血浆中乳糜微粒残粒和VLDL残粒水平增加,其血浆外观混浊,常可见一模糊的“奶油样”顶层。血浆中胆固醇和甘油三酯浓度均明显增加,且两者升高的程度(以mg/dL为单位)大致相当。此型在临床上很少见。 (4)Ⅳ型高脂蛋白血症:血浆VLDL增加,血浆外观可以澄清也可以混浊,主要视血浆甘油三酯升高的程度而定,一般无“奶油样”顶层,血浆甘油三酯明显升高,胆固醇水平可正常或偏高。 (5)Ⅴ型高脂蛋白血症:血浆中乳糜微粒和VLDL水平均升高,血浆外观有“奶油样”顶层,下层混浊,血浆甘油三酯和胆固醇均升高,以甘油三酯升高为主。 高脂血症的分类 血脂主要是指血清中的胆固醇和甘油三酯。无论是胆固醇含量增高,还是甘油三酯的含量增高,或是两者皆增高,统称为高脂血症。 1、根据血清总胆固醇、甘油三酯和高密度脂蛋白-胆固醇的测定结果,高脂血症分为以下四种类型: (1)高胆固醇血症:血清总胆固醇含量增高,超过5.72毫摩尔/升,而甘油三酯含量正常,即甘油三酯<1.70毫摩尔/升。 (2)高甘油三酯血症:约占20%血清甘油三酯含量增高,超过1.70毫摩尔/升,而总胆固醇含量正常,即总胆固醇<5.72毫摩尔/升。 (3)混合型高脂血症:血清总胆固醇和甘油三酯含量均增高,即总胆固醇超过5.72毫摩尔/升,甘油三酯超过1.70毫摩尔/升。 (4)低高密度脂蛋白血症:血清高密度脂蛋白-胆固醇(HDL-胆固醇)含量降低,<0.9毫摩尔/升。 2、根据病因,高脂血症的分类有: (1)原发性高脂血症:包括家族性高甘油三酯血症,家族性Ⅲ型高脂蛋白血症,家族性高胆固醇血症;家族性脂蛋白酶缺乏症;多脂蛋白型高
孕妇甘油三酯高是怎么回事
孕妇甘油三酯高是怎么回事 妇女在怀孕期间需要注意的事情很多,而且也会因为怀孕而出现一系列的生理现象和疾病,不止会影响到本身,还可能影响到胎儿,所以需要引起重视,甘油三酯高 甘油三酯高的原因在临床上可分为原发性和继发性两种,原发性甘油三酯高常见于遗传,而继发性则可以继发于疾病,如糖尿病,肾病综合征,甲状腺功能减退,透析,胆道阻塞等;也可继发于不良生活习惯,如饮食,烟酒等. 继发性甘油三酯高怎么回事.因疾病导致的甘油三酯高主要是各种原因致使脂肪代谢异常,因不良生活习惯导致的甘油三酯高则是我们每个人生活中必须注意的了. 为什么不良生活习惯也能成为甘油三酯高的原因呢?因为甘油三酯大部分是从饮食中获得的,只有少部分是人体自身合成的.当进食大量脂肪类,尤其是动物脂肪食品后,可测得体内甘油三酯水平明显升高;而过多的碳水化合物,尤其是加工精细的粮食进入体内后,则引起血糖升高,合成更多的甘油三酯.另外,饮酒可以刺激甘油三酯的加速合成。 孕妇甘油三酯高的危害 1、心脏疾病 甘油三酯主要为人体提供和储存能量过多的甘油三酯会导致脂肪细胞功能改变和血液粘稠度增加并增加患心脏动脉硬化、冠心病、心绞痛或心肌梗死、脑卒中、脑中风的危险性。而且血液中甘油三酯过高还会引起脂肪肝、急性胰腺炎。
2、妊娠期糖尿病 妊娠期血脂升高易影响孕妇的糖代谢,导致妊娠期糖尿病及糖耐量降低。糖尿病合并高血脂更容易导致脑中风、冠心病、肢体坏死、眼底病变、肾脏病变、神经病变等。 3、妊娠高血压 妊娠高血压是孕期特有的疾病,由于高血压、高血脂是互相影响的,甘油三酯高的孕妇更容易发生妊娠高血压综合征,出现蛋白尿、水肿等症状。 4、肾脏疾病 甘油三酯高的孕妇更容易因肾动脉硬化而引发尿毒症。 孕妇甘油三酯高怎么做? 1、适量补充蛋白质。特别是大豆及豆制品等植物性蛋白质,也可以补充瘦肉、鸡肉、鸭肉和鱼类等胆固醇低的动物性蛋白质。 2、限制糖的摄入量。饮食中应避免食用蔗糖、果糖、蜂蜜以及含糖的食物,不要在牛奶或豆奶中加糖。 3、限制动物性脂肪摄入量。烹调用油以植物油为主,尽量不要摄入动物性脂肪。 4、限制饮酒。酒精对胎儿的生长发育不利,而且酒还可以使高甘油三酯血症患者甘油三酯含量升高,因此,孕妇更应该避免饮酒。 5、多吃新鲜蔬菜和水果。新鲜蔬菜和水果含丰富的纤维素、维生素和矿物质,在提供能量的同时产生过饱的感觉。 6、适量的运动和锻炼。孕妇不要因为怀孕就经常卧床休息或者长久静坐,适量的体力活动对孕妇和胎儿的身心健康有利。运
甘油三酯测定试剂盒(GPO-PAP法)产品技术要求danda
甘油三酯测定试剂盒(GPO-PAP法) 适用范围:本品用于体外定量测定人血清中甘油三酯的含量。 1.1规格 规格1: (试剂1:20mL;试剂2: 5mL); 规格2: (试剂1:40mL;试剂2:10mL); . 规格3: (试剂1:80mL;试剂2:20mL); 校准品:(选配) 规格1(0.3mL×1;1水平);规格2(0.5mL×1;1水平);规格3(1.0mL×1;1水平); 质控品:(选配) 规格1(0.5mL×2;2水平);规格2(1.0mL×2;2水平)。 1.2组成 试剂盒组成见表1 表1甘油三酯测定试剂盒组成
注:校准品及质控品赋值具有批特异性,每批次浓度详见标签。 2.1试剂 2.1.1外观 试剂盒外观应整洁,文字符号标识清晰;组分齐全,液体无漏液;试剂1为淡黄色透明液体;试剂2为无色透明液体,不得有沉淀和絮状物。 2.1.2装量 每瓶不少于标示值。 2.1.3试剂空白吸光度 用指定的空白样品测试试剂(盒),在光径1cm下,在A546nm处测定试剂空白吸光度A≤0.1。 2.1.4分析灵敏度 在温度37℃,测定2.26 mmol/L样本,吸光度变化在0.10-0.35之间。
2.1.5线性范围 2.1.5.1在[0.2,10.0] mmol/L内,相关系数R≥0.990。 2.1.5.2在[0.2,2.0] mmol/L内,线性绝对偏差不超过±0.2mmol/L;(2.0,10.0] mmol/L内,线性相对偏差不超过±10%。 2.1.6重复性 重复测试(1.1±0.22) mmol/L和(3.0±0.6)mmol/L样本,所得结果的变异系数(CV%)应不大于5%。 2.1.7批间差 测定(1.1±0.22) mmol/L和(3.0±0.6)mmol/L样本,所得结果的批间相对极差(R)应不大于10%。 2.1.8准确度 用国家标准物质GBW09148检测,实测值与标示值的相对偏差在±10%内。 2.2校准品 2.2.1外观 校准品为淡黄色液体。 2.2.2装量 每瓶不少于标示值。 2.2.3准确度 与配套试剂组成测试系统,指标要求同2.1.8。 2.2.4 校准品溯源性 根据GB/T21415-2008的要求,校准品溯源至国家标准物质GBW09148。 2.3质控品
最新对甘油三酯高的认识
对甘油三酯高的认识
高血脂的原因是什么, 原因一:情志刺激。思虑伤脾,脾失健运,或郁怒伤肝,肝失条达,气机不畅,膏脂运化输布失常,血脂升高。 原因二:年老体衰。人老则五脏六腑皆衰,以肾为主,肾主五液.肾虚则津液失其主宰。脾主运化,脾虚则饮食不归正化。肝主疏泄,肝弱则津液输布不利,三者皆使膏脂代谢失常,引起血脂升高。若房劳过度,辛劳忧愁,亦可使人末老而先衰。 原因三:体质禀赋。父母肥胖,自幼多脂,成年以后,形体更加丰腴,而阳气常多不足,津液膏脂输化迟缓,血中育质过多。或素体阴虚阳亢,脂化为育,溶入血中,血脂升高。 原因四:消渴、水肿、胁痛、黄疸、症积等证不愈。消渴证基本病机属阴虚燥热,由于虚火内扰,胃热杀谷,患者常多饮多食,但饮食精微不能变脂而贮藏,人体之脂反尽溶为膏,混入血中,导致血脂升高。 水肿日久,损及脾肾,肾虚不能主液,脾虚失于健运,以致膏脂代谢失常。胁痛、黄疸、症积三者皆属肝、胆之病,肝病气机失于疏泄,影响膏脂的敷布转化,胆病不能净浊化脂,引起血脂升高。 原因五:饮食失当。饮食不节,摄食过度,或恣食肥腻甘甜厚味,过多膏脂随饮食进入人体,输布、转化不及,滞留血中,因而血脂升高。 在了解造成高血脂一系列原因之后,在治疗上我们就会容易的多。砖牌养生茶就可以很好的解决这一问题。砖牌养生茶研发团队在中华养生协会专家的带领下,潜心研究数十载,在我国几千年的“药食同源”养生理论和众多传统保健配方的基础上,结合现代预防医学研究成果,配伍佛禅蔵方,研发出专门针对当代人酸性体质,提高人体免疫力,降低血脂,开创养生茶疗新局面,帮助人们远离高血脂的烦恼,拥有健康幸福。您如果还有什么需要了解的话可以去他们的官方网站看看,网址是:3vv 点 yszcw 点 c0m ,希望能够帮到您。 对于高血脂在饮食方面要注意:(1)宜多食用植物蛋白(如豆制品)及复合碳水化合物(如淀粉等),少吃单纯碳水化合物(如果糖、蔗糖、蜜糖及乳糖等)。(2)宜多吃富含维生素C的食物,因维生素C可促使胆固醇羟基化,从而减少胆固醇在血液和组织中的蓄积。(3)宜多吃高纤维素的食物,因食物纤维不易被人体胃肠道所消化,摄入高纤维食物后可改善大便习惯,增加排便量,使粪便中胆固醇
甘油三酯偏高的诊断及检查方法
甘油三酯偏高的诊断及检查方法 甘油三脂(甘油三酯),又称脂肪,是由食物脂肪与肝脏合成的,它是血液中血脂最重要的一种!它们不溶于水,与蛋白质结合成脂蛋白,在血液中循环运转。甘油二酯与第三个脂酰CoA分子作用生成甘油三酯,起催化作用的酶为甘油二酯转酰基酶,是衡量健康的一个重要指标! 诊断标准 国内一般以成年人空腹血清总胆固醇超过5.72毫摩尔/升,甘油三酯超过1.70毫摩尔/升,诊断为高脂血症。将总胆固醇在5.2~5.7毫摩尔/升者称为边缘性升高。 根据血清总胆固醇、甘油三酯和高密度脂蛋白-胆固醇的测定结果,通常将高脂血症分为以下四种类型: (1)高胆固醇血症:血清总胆固醇含量增高,超过5.72毫摩尔/升,而甘油三酯含量正常,即甘油三酯<1.70毫摩尔/升。 (2)高甘油三酯血症:血清甘油三酯含量增高,超过1.70毫摩尔/升,而总胆固醇含量正常,即总胆固醇<5.72毫摩尔/升。 (3)混合型高脂血症:血清总胆固醇和甘油三酯含量均增高,即总胆固醇超过5.72毫摩尔/升,甘油三酯超过1.70毫摩尔/升。 (4)低高密度脂蛋白血症:血清高密度脂蛋白-胆固醇(HDL-胆固醇)含量降低,<0.9毫摩尔/升。 检查项目: 血脂四项检查 检查高血脂最主要的方法就是血脂四项,包括甘油三酯、总胆固醇、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇和低密度脂蛋白胆固醇。 如果总胆固醇在3-5.2mmol/L属于正常;高于6.2mmol/L就是高血脂了;在5.2~ 6.2mmol/L为临界高血脂甘油三酯只要在1.7mmol/L以下就为正常;高于2.3mmol/L就为高血脂;在1.7~2.3mmol/L之间为临界状态。高密度脂蛋白胆固醇要高于1.04mmol/L,低密度脂蛋白胆固醇要低于3.12mmol/L,否则就不正常。 脂蛋白检查
血脂高的原因及治疗方法
血脂高的原因及治疗方法 血脂高的原因 1.、饮食失当饮食不节,摄食过度,或恣食肥腻甘甜厚味,引起血脂高,过多膏脂随饮食进入人体,输布、转化不及,滞留血中,因而血脂升高。长期饮食失当,或酗酒过度,损及脾胃,致使饮食不归正化,不能化精微以营养全身,反而变生脂浊,混入血中,引起血脂升高。前者为实证,后者为虚中夹实证,这是二者不同之处。 2、喜静少动或生性喜静,贪睡少动;或因职业工作所限,终日伏案,多坐少走,人体气机失于疏畅,气郁则津液输布不利.膏脂转化利用不及,以致生多用少,沉积体内,浸淫血中,故血脂升高。 3、情志刺激思虑伤脾,脾失健运,或郁怒伤肝,肝失条达,气机不畅,膏脂运化输布失常,血脂升高。 4、年老体衰人老则五脏六腑皆衰,引起血脂升高,以肾为主,肾主五液,肾虚则津液失其主宰;脾主运化,脾虚则饮食不归正化;肝主疏泄,肝弱则津液输布不利,三者皆使膏脂代谢失常,引起血脂升高。若房劳过度,辛劳忧愁,亦可使人末老而先衰。 5、体质禀赋父母肥胖,自幼多脂,成年以后,形体更加丰腴,而阳气常多不足,津液膏脂输化迟缓,血中育质过多。或素体阴虚阳亢,脂化为育,溶入血中,血脂升高。
总体来说,要预防血脂高就需要改掉不良生活习惯,多做有氧运动,健康的饮食习惯也必不可少。这样,才能做到预防血脂高的疾病发生。 血脂高的治疗方法 1.保持合适体重,不宜太胖。 肥胖容易引发多种疾病,肥胖的人群平均的血浆胆固醇和三酰甘油水平要明显的高于同龄的体重正常的人。同时一个人身体的脂肪分布是与血浆脂蛋白水平有很大的关系的,特别是对于中心型肥胖者(肚子大,内脏脂肪多),就更容易导致血脂高。资料显示,肥胖的人,在体重减轻后,很多人血脂紊乱都恢复正常了。 2.经常锻炼,有氧运动 经常锻炼的人不仅心肺功能强,保持合适的体重,同时能够改善胰岛素抵抗和葡萄糖耐量,降低血浆三酰甘油和胆固醇水平,升高hdl胆固醇水平。 对于锻炼,也要注意一些问题,避免出现安全问题: (1.运动强度:一般来说,运动后的心率水平可以衡量运动量的大小,衡量一个人的运动强度是否适宜,可以看看心率是否超过了个人最大心率的80%,控制在80%左右为好。运动形式以中速步行、慢跑、游泳、跳绳、做健身操、骑自行车等有氧活动为宜。 (2.运动时间:在运动前要将身体活动开,可以进行5-10分钟的预备活动,使人的心率上升到一定的水平,然后在进行20-30分钟的有氧运动,让身体出一点点汗。运动结束后再进行5-10分钟的放松活动,让身体放松下来。每周可进行3-4次,不宜过于频繁,感觉身体不适可适当休息下。
甘油三酯高、患者饮食
甘油三酯偏高的原因? 甘油三酯偏高的原因在临床上可分为原发性和继发性两种: 1、原发性甘油三酯高常见于遗传。 2、继发性则可以继发于疾病,如糖尿病、肾病综合征、甲状腺功能减退、透析、胆道阻塞等;也可继发于不良生活习惯,如饮食、烟酒等。因疾病导致的甘油三酯高主要是各种原因致使脂肪代谢异常。因不良生活习惯导致的甘油三酯高,因为甘油三酯大部分是从饮食中获得的,只有少部分是人体自身合成的。当进食大量脂肪类、尤其是动物脂肪食品后,可测得体内甘油三酯水平明显升高;而过多的碳水化合物、尤其是加工精细的粮食进入体内后,则引起血糖升高,合成更多的甘油三酯,从而会引起甘油三酯的升高。 高甘油三酯治疗以药物为主,中药类降血脂药在降甘油三酯方面的作用起着越来越重要的做用,如君山第四代降脂宁颗粒因为效果确切,副作用小而在临床上使用的越来越广泛。西药和保健品主要有以下几类:①苯氧芳酸类或称贝特类,如氯贝特、非诺贝特、吉非贝齐、苯扎贝特。但需注意的是,他汀类与贝特类两种降脂药物不能联合应用,否则会有一定几率产生横纹肌溶解的严重并发症。②烟酸及其衍生物,如烟酸、烟酸肌醇酯、阿西莫司。③鱼油制剂,如多烯康胶囊。④抗氧化制剂:如:虾青素、叶黄素、CoQ10、花青素、葡萄籽、灵芝孢子油等,以虾青素最强。
高甘油三酯者:蛋黄,鱼籽,蟹黄等是否该吃?过去的看法:不能吃,过去的看法只是注意到了其中的脂肪(其实有色卵子的脂肪以不饱和脂肪酸为主),但并没有注意到其中的有价值的天然色素成分,如蟹黄和鱼籽以及野生的蛋黄都含有一定的虾青素、叶黄素、b-胡萝卜素等,这些都是很强的抗氧化剂。 甘油三酯高的危害 甘油三酯高的危害最直接体现在动脉粥样硬化上。甘油三酯高的后果是容易造成“血稠”,即血液中脂质含量过高导致的血液粘稠,在血管壁上沉积,渐渐形成小斑块,即我们平时说的动脉粥样硬化。而血管壁上的这些块状沉积会逐渐扩大面积和厚度,使血管内径变小、血流变慢,血流变慢又加速了堵塞血管的进程,严重时血流甚至被中断。这时,甘油三酯高的危害已经相当严重了。除了血流中断,阻塞物脱落还能造成血栓;甘油三酯高的后果无论发生在哪个部位,对人体损伤都很严重。如果在心脏,可引起冠心病、心梗;在大脑,可发生脑卒中、中风;发生在眼底,会导致视力下降、失明;如在肾脏,可引起肾衰;发生在下肢,则出现肢体血流不畅导致坏死。此外,甘油三酯高的危害还包括引发高血压、胆结石、胰腺炎;还能够加重肝炎、致使男性性功能障碍、导致老年痴呆等。研究表明,甘油三酯高的后果还包括一点,它可能导致癌症的发生。
甘油三酯的合成代谢备课讲稿
甘油三酯的合成代谢
甘油三酯的合成代谢? 甘油三酯(Triglyceride),是长链脂肪酸和甘油形成的脂肪分子,是人体内含量最多的脂类,大部分组织均可以利用甘油三酯分解产物供给能量,同时肝脏、脂肪等组织还可以进行甘油三酯的合成,在脂肪组织中贮存。人体可利用甘油、糖、脂肪酸和甘油一酯为原料,经过磷脂酸途径和甘油一酯途径合成甘油三酯。 1. 甘油一酯途径:以甘油一酯为起始物,与脂酰CoA共同在脂酰转移酶作用下酯化生成甘油三酯。 2. 磷脂酸途径:磷脂酸,即3-磷酸-1,2-甘油二酯,是合成含甘油脂类的共同前体。糖酵解的中间产物—类磷酸二羟丙酮在甘油磷酸脱氢酶作用下,还原生成3-磷酸甘油;游离的甘油也可经甘油激酶催化,生成3-磷酸甘油(因脂肪及肌肉组织缺乏甘油激酶,故不能利用激离的甘油)。 3-磷酸甘油在脂酰转移酶作用下,与两分子脂酰CoA反应生成3-磷酸-1,2甘油二酯,即磷脂酸。此外,磷酸二羟丙酮也可不转为3-磷酸甘油,而是先酯化,后还原生成溶血磷脂酸,然后再经酯化合成磷脂酸。磷脂酸在磷脂酸磷酸酶作用下,水解释放出无机磷酸,而转变为甘油二酯,它是甘油三酯的前身物,只需酯化即可生成甘油三酯。 甘油三酯所含的三个脂肪酸可以是相同的或不同的,可为饱和脂肪酸或不饱和脂肪酸。甘油三酯的合成速度可以受激素的影响而改变,如胰岛素可促进糖转变为甘油三酯。由于胰岛素分泌不足或作用失效所致的糖尿病患者,不仅不能很好利用葡萄糖,而且葡萄糖或某些氨基酸也不能用于合成脂肪酸,而表现为脂肪的氧化速度增加,酮体生成过多,其结果是患者体重下降。此外,胰高血糖素、肾上腺皮质激素等也影响甘油三酯的合成。 TCA循环等等重要代谢途径哪些步骤有维生素或其辅酶参与反应?
高脂血症分四大类
高脂血症分四大类 2013年10月11日07:22 《生命时报》 血脂检测已经成为体检的必查项目。血脂报告中的诸多指标该怎么看?这些箭头上上下下,如何才算异常?本期,本版邀请上海交通大学医学院附属仁济医院心内科副主任刘建平、复旦大学附属中山医院心内科副主任医师李清带领广大读者,走近高脂血症。 诊断 不能只看化验单 血浆中的脂类统称为血脂,是供应体内能量的物质,主要由胆固醇和甘油三酯构成。胆固醇又分高密度脂蛋白-胆固醇(HDL-C)、低密度脂蛋白-胆固醇(LDL-C)等。 随着生活水平的改善,血脂异常(俗称高脂血症)的患病率越来越高。通常,血脂检查的化验单上列有4个指标:总胆固醇(TC)、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇和甘油三酯(TG)。它们主要用于诊断以下4种高脂血症。 高胆固醇血症:总胆固醇含量增高,超过5.72毫摩尔/升,而甘油三酯含量正常,即<1.70毫摩尔/升。 高甘油三酯血症:甘油三酯含量增高,超过1.70毫摩尔/升,而总胆固醇含量正常,<5.72毫摩尔/升。 混合型高脂血症:总胆固醇和甘油三酯含量均增高,即总胆固醇超过5.72毫摩尔/升,甘油三酯超过1.70毫摩尔/升。
低高密度脂蛋白血症:高密度脂蛋白-胆固醇(HDL-胆固醇)含量降低,<1.0毫摩尔/升。 诱发高脂血症的原因多种多样。第一,基因决定,尤其是原发性的高脂血症。第二,其他疾病继发的,如肥胖、糖尿病、甲状腺功能减低、肾病综合征以及使用特定药物等,都可能诱发高脂血症。第三,吸烟、过多食用高糖高脂食物,都可能导致胆固醇或甘油三酯升高。 需要提醒的是,有些人看到化验单中上上下下的“箭头”,就以为是高脂血症,然后大量用药,还有人觉得只要不出现箭头,就是正常。这些都是误区。 已有冠心病或糖尿病,或已经发生过心肌梗死、脑卒中者,被视为控制血脂的高危人群。其血脂治疗值和目标值更严格,不能仅靠化验单显示的正常值来判断。40岁以上男性、绝经女性、肥胖、有黄色瘤、有血脂异常及心脑血管病家族史者,也属于“防控重点人群”,其诊断标准也应更严。 因此,每个人情况不同,诊断高脂血症的标准也不一样。患者应该在心内科、内分泌等专科医生指导下,进行风险分层,即分为低危、中危、高危和极高危患者。所谓“极高危”,是指急性冠脉综合征患者、冠心病或脑卒中伴有糖尿病者;高危患者是指冠心病,和其他动脉粥样硬化的患者,如脑卒中、外周血管疾病等。
甘油三脂
甘油三酯高怎么办? 悬赏分:20|解决时间:2010-5-6 17:09|提问者:mengying8866 体检出来我老公的: 甘油三酯为13.66 总胆固醇8.57 极低密度脂蛋白胆固醇6.21 最佳答案 如果甘油三酯和胆固醇都偏高才算是高血脂。血液中的脂肪类物质,统称为血脂。血浆中的脂类包括胆固醇、甘油三酯、磷脂和非游离脂肪酸等,它们在血液中是与不同的蛋白质结合在一起,以“脂蛋白”的形式存在。大部分胆固醇是人体自身合成的,少部分是从饮食中获得的。甘油三酯恰恰相反,大部分是从饮食中获得的,少部分是人体自身合成的。 既然甘油三酯大部分来自食物,那最好的办法当然是从饮食着手。不过一次检查的结果偏高并不一定就偏高,不放心的话可以隔一段时间再查一次。如果还是偏高的话再通过饮食控制。如果饮食已经比较清淡,可考虑饮食中适量增加粗碳水化合物、纤维素和植物蛋白质,少吃糖和甜食,忌烟酒。还可以通过运动改善。 进食大量脂肪类食品后,体内甘油三酯水平明显升高。这是因为,脂肪(特别是动物脂肪)的摄入一方面加速甘油三酯的合成,并且还减慢了甘油三酯的清除,如此双管齐下,血中的甘油三酯会明显增多。 甘油三酯过高的患者还要限制饭量,因为过多的碳水化合物进入体内,可以引起血糖升高,合成更多的甘油三酯,引起高甘油三酯血症。此外,过多的碳水化合物还能使许多促进甘油三酯合成的酶类的生物作用增强,血中的甘油三酯自然增多。 大量的试验已经证明:过多摄入谷类食物,特别是精制加工后的细粮,确实是明显升高血浆甘油三酯的主要原因。所以说,高甘油三酯患者应适当限制饭量,并注意粗粮、细粮合理搭配,这样才有益于甘油三酯水平的控制。 限制饮酒是高甘油三酯患者的重要治疗措施。与其他类型的高脂血症相比,禁酒对高甘油三酯患者来说,有更加重要的意义。为什么这么说呢?因为酒精除了给身体提供更多的热量外,还可以刺激甘油三酯合成,使血中甘油三酯升高;加以大量美味佳肴伴酒助兴,也就意味着更多的热量和脂肪进入体内,为甘油三酯的升高增添了原料。 附:
导致人体的甘油三酯升高的原因
导致人体的甘油三酯升高的原因 甘油三酯高和胆固醇高都是高血脂的一种表现。它是当今社会的常见病;多发病,对人体的损害属于隐匿、危险的类型,甘油三酯偏高的原因在临床上可分为原发性和继发性两种。原发性甘油三酯高常见于遗传,而继发性则可以继发于疾病,如糖尿病、肾病综合征、甲状腺功能减退、透析、胆道阻塞等. 长期甘油三酯高会加速人体动脉硬化的形成,导致冠心病,心肌梗塞,脑血栓等严重的心脑血管疾病,给患者造成的危害是非常大的,严重影响着患者的工作、生活及健康,因此对于高甘油三酯血症人们必须要引起重视,早发现,早治疗。 油三酯升高的主要原主要是过多的饮食、摄取高胆固醇、高脂肪食物过多,吸烟、饮酒等;因此,降低甘油三酯首先要限制进食,不要进食大量碳水化合物,其次,限制糖类,戒烟酒,南京肝病康复网专家指出动物脂肪则最好不吃,少吃或不要吃动物肥肉、奶油、甜点、动物皮类、内脏、鱼子等脂肪含量极高的食物。 甘油三酯升高是一个复杂的过程,因此,患者不仅需要养成良好的生活习惯,而且更需要服用有效的降脂药物及时的进行降脂治疗。甘油三酯高常用的药物是贝特类降脂药,此药降甘油三酯的效果是非常强的,但是经仔细研究发现,此药的副作用很大。安全降甘油三酯可选择纯中药调理,安全性和稳定性都比西药更胜一筹,如君山第四代降脂宁颗粒。
能软化血管,防止血管硬化,恢复血管弹性,增强血管的伸张性,防治血管因硬化而破裂。 治疗高胆固醇型高血脂症:占高血脂症患者的40%,血清总胆固醇含量增高,而甘油三酯含量正常。主要有营养过剩或脂代谢紊乱导致。临床试验证实经过一到三个月的服用,能使此类高血脂患者的总胆固醇和甘油三酯及低密度脂蛋白回归正常水平。并且停药后也不会出现如他汀类降脂药所出现的快速反弹现象。君山第四代降脂宁颗粒也有对心、脑血管有双向调节作用,有效治疗心脑血管供血不足造成的头晕、头昏、头疼、失眠、头脑不清晰、健忘等,它能够软化血管,增强冠状动脉血液循环。对心脑血管阻塞有再通作用,适宜于脑血栓、脑梗塞等闭塞性疾病。
甘油三酯的合成代谢
甘油三酯的合成代谢? 甘油三酯(Triglyceride),是长链脂肪酸和甘油形成的脂肪分子,是人体内含量最多的脂类,大部分组织均可以利用甘油三酯分解产物供给能量,同时肝脏、脂肪等组织还可以进行甘油三酯的合成,在脂肪组织中贮存。人体可利用甘油、糖、脂肪酸和甘油一酯为原料,经过磷脂酸途径和甘油一酯途径合成甘油三酯。 1. 甘油一酯途径:以甘油一酯为起始物,与脂酰CoA共同在脂酰转移酶作用下酯化生成甘油三酯。 2. 磷脂酸途径:磷脂酸,即3-磷酸-1,2-甘油二酯,是合成含甘油脂类的共同前体。糖酵解的中间产物—类磷酸二羟丙酮在甘油磷酸脱氢酶作用下,还原生成3-磷酸甘油;游离的甘油也可经甘油激酶催化,生成3-磷酸甘油(因脂肪及肌肉组织缺乏甘油激酶,故不能利用激离的甘油)。 3-磷酸甘油在脂酰转移酶作用下,与两分子脂酰CoA反应生成3-磷酸-1,2甘油二酯,即磷脂酸。此外,磷酸二羟丙酮也可不转为3-磷酸甘油,而是先酯化,后还原生成溶血磷脂酸,然后再经酯化合成磷脂酸。磷脂酸在磷脂酸磷酸酶作用下,水解释放出无机磷酸,而转变为甘油二酯,它是甘油三酯的前身物,只需酯化即可生成甘油三酯。 甘油三酯所含的三个脂肪酸可以是相同的或不同的,可为饱和脂肪酸或不饱和脂肪酸。甘油三酯的合成速度可以受激素的影响而改变,如胰岛素可促进糖转变为甘油三酯。由于胰岛素分泌不足或作用失效所致的糖尿病患者,不仅不能很好利用葡萄糖,而且葡萄糖或某些氨基酸也不能用于合成脂肪酸,而表现为脂肪的氧化速度增加,酮体生成过多,其结果是患者体重下降。此外,胰高血糖素、肾上腺皮质激素等也影响甘油三酯的合成。 TCA循环等等重要代谢途径哪些步骤有维生素或其辅酶参与反应? 1、乙酰CoA与草酰乙酸的羧基进行醛醇型缩合,柠檬酸转变成异柠檬酸:前者由柠檬酸合成酶催化,后者由顺乌头酸酶催化,均为变构酶,需要维生素B12作为变构酶的辅酶,参与一些异构化作用。 。 2、第一次氧化脱酸:在异柠檬酸脱氢酶作用下,异柠檬酸生成α-酮戊二酸、NADH和CO 2 而第二次氧化脱羧:在α-酮戊二酸脱氢酶系作用下,α-酮戊二酸氧化脱羧生成琥珀酰-CoA、。在过程中,维生素B5是NAD和NADP的组成成分,而它们是脱氢酶的辅酶,NADH·H+和CO 2 参与递氢作用。 3、底物磷酸化生成ATP:在琥珀酸硫激酶的作用下,琥珀酰-CoA的硫酯键水解,释放的自由能用于合成GTP。此时,琥珀酰-CoA生成琥珀酸和CoA。维生素B3是CoA的组成成分,而其又是生物体内转酰基酶的辅酶,参与转酰基作用。 4、琥珀酸脱氢及草酰乙酸再生:前者是在琥珀酸脱氢酶催化作用下,琥珀酸氧化成为延胡索酸。该酶含有铁硫中心和共价结合的FAD。后者则是在苹果酸脱氢酶作用下,苹果酸生成草酰乙酸,NAD+是脱氢酶的辅酶,接受氢成为NADH·H+。在过程中,维生素B2是以FAD与FMN 的形式作为脱氢酶等多种氧化还原酶及递氢体辅基的组成成分,参与生物氧化作用,作为递氢体。维生素B5是NAD和NADP的组成成分,而它们是脱氢酶的辅酶,参与递氢作用。
甘油三酯(triglyceride, TG )含量测定试剂盒说明书
货号: QS2408 规格:50管/48样甘油三酯(triglyceride, TG)含量测定试剂盒说明书 可见分光光度法 注意:正式测定之前选择 2-3个预期差异大的样本做预测定。 测定意义: TG是长链脂肪酸和甘油形成的脂肪分子,不仅是细胞膜的主要成分,也是重要呼吸底物。 测定原理: 用异丙醇抽提取TG,KOH皂化TG后水解生成甘油及脂肪酸,过碘酸氧化甘油生成甲醛,在氯离子存在下甲醛与乙酰丙酮缩合生成黄色物质,在420 nm有特征吸收峰,其颜色的深浅与TG含量成正比。 自备实验用品及仪器: 可见分光光度计、水浴锅、可调式移液枪、1ml玻璃比色皿、双蒸水 试剂组成和配置: 试剂一:液体60mL×2瓶,4℃保存。 试剂二:液体15mL×1瓶,4℃保存。 试剂三:液体30mL×1瓶,4℃保存。 试剂四:液体10mL×1瓶,4℃避光保存。 试剂五:液体30mL×1瓶,4℃避光保存。 试剂六:液体30mL×1瓶,4℃避光保存。 标准品:液体1mL×1支,1mg/mL标准甘油三酯溶液,4℃避光保存。 TG的提取: 1、组织:按照组织质量(g):试剂一体积(mL)为1:5~10的比例(建议称取约0.1g组织, 加入1mL试剂一)进行冰浴匀浆,8000g,4℃离心10min,取上清待测。 2、细胞、细菌:先收集400-500万细胞或细菌到离心管内,弃上清,加1mL试剂一,超声波破碎1min(强度20%,超声2s,停1s),8000g,4℃离心10min,取上清待测。 3、血清(浆)等液体样品:直接测定。 测定操作: 1. 分光光度计预热30min,调节波长到420 nm,蒸馏水调零。 0.15mL,置于新的EP管中。 3.甘油三酯含量测定: 第1页,共2页
高血脂 原因
高血脂原因 高血脂症的病因,基本上可分为两大类,即原发性高血脂症和继发性高血脂症。 原发性高血脂症 1.遗传因素。遗传可通过多种机制引起高脂血症,某些可能发生在细胞水平上,主要表现为细胞表面脂蛋白受体缺陷以及细胞内某些酶的缺陷(如脂蛋白脂酶的缺陷或缺乏),也可发生在脂蛋白或载脂蛋白的分子上,多由于基因缺陷引起。 2.饮食因素。饮食因素作用比较复杂,高脂蛋白血症患者住院中有相当大的比例是与饮食因素密切相关的。 3.血液中缺乏负离子(负氧离子)。临床实验表明:血液中的正常红细胞、胶体质点等带负电荷,它们之间相互排斥,保持一定的距离,而病变老化的红细胞由于电子被争夺,带正电荷,由于正负相吸、则将红细胞凝聚成团,造成血液粘稠。 继发性高血脂症 继发性高血脂症是由于其他中间原发疾病所引起者,这些疾病包括:糖尿病、肝病、甲状腺疾病、肾脏疾病、胰腺、肥胖症、糖原累积病、痛风、阿狄森病、柯兴综合症、异常球蛋白血症等。
1.糖尿病与高脂蛋白血症。在人体内糖代谢与脂肪代谢之间有着密切的联系,临床研究发现,约40%的糖尿病患者可继发引起高脂血症。 2.肝病与高脂蛋白血症。现代医学研究资料证实,许多物质包括脂质和脂蛋白等是在肝脏进行加工、生产和分解、排泄的。一旦肝脏有病变,则脂质和脂蛋白代谢也必将发生紊乱。 3.肥胖症与高脂蛋白血症。本地临床医学研究资料表明,肥胖症最常继发引起血甘油三酯含量增高,部分患者首先血胆固醇含量也可能会增高,大多主要表现为iv型高脂蛋白血症,其次为iib型高脂蛋白血症。 一.合理饮食 人体脂类包括脂肪和类脂两种。高脂血症与饮食的关系最为密切。人体脂肪的积聚和部分类脂的来源,主要来自饮食。只有一部分类脂是在体内合成的,称为内生性类脂。 控制饮食对高脂血症的防治是十分重要的。 1、饮食提倡清淡,基本吃素。 但不宜长期吃素,否则饮食成分不完善,反而可引起内生性胆固醇增高。 2、宜限制高脂肪、高胆固醇类饮食,如动物脑髓、蛋黄、鸡肝、黄油等。
甘油三酯偏高的治疗方法是什么
甘油三酯偏高的治疗方法是什么 三酯增高是指血液中甘油三酯值比正常值偏高。如果只是甘油三酯增高,而其它如胆固醇、低密度脂蛋白等均在正常值范围内,称为单纯性高甘油三酯血症。甘油三酯高是血脂高的一种,其形成与遗传、疾病、饮食习惯多方面因素相关。 甘油三酯增高的主要原因有两方面,一是遗传或先天性,二是继发于代谢性紊乱疾病(糖尿病、高血压、粘液性水肿、甲状腺功能低下、肥胖、肝肾疾病、肾上腺皮质功能亢进),或与其他因素(年龄、性别、季节、饮酒、吸烟、饮食、体力活动、精神紧张、情绪活动)有关。 食疗方法 单纯的甘油三酯增高,一般以合理饮食、适度运动为首选,并长期坚持;其次是消除恶化因素;最后考虑药物治疗。饮食和药物疗法的目的都是延缓和减轻动脉粥样硬化的发生和发展进程。 饮食疗法,最主要的是调节饮食结构,限制总热量摄入,尽量少吃动物脂肪,减少糖的摄入量,适当补充蛋白质。宜食瘦肉、鱼类、鸡、鸭肉(去皮)、牛奶、豆类及豆制品,还有芹菜、大蒜、洋葱、香菇、蘑菇、木耳、苹果、桔子、猕猴桃等富含维生素C、无机盐和纤维素的新鲜蔬菜、水果。 药物治疗 目前临床上治疗甘油三酯高的药物都为处方药,需要到医院开处方,遵医嘱服用。 用于甘油三酯高的药物主要有两大类: 激活脂蛋白代谢酶类药 顾名思义,此类药降甘油三酯的基本原理就是激活脂蛋白代谢酶类,促进甘油三酯水解。很多人问甘油三酯高用什么药时,医生都会推荐这类药物,典型代表为贝特类降脂药,如非诺贝、苯扎贝特、吉非贝齐(诺衡)等;以上皆为口服药物。 阻止脂质在体内合成 这类药物和前一类药物不同,降血脂的基本原理变成了阻止脂质在体内合成。这类药物的典型代表是烟酸类药物。常用的烟酸类药物有烟酸、烟酸肌醇、阿昔莫司等,也是都为口服药。 医院还经常应用他汀类药物。如洛伐他汀(美降脂)、辛伐他汀、普伐他汀、阿托伐他汀等,是以降胆固醇为主、同时也降甘油三酯的药物。
脂肪进行合成代谢的过程
郑州增肥专科医院 来源:河南省现代研究院中医院增肥专科脂肪是怎样消耗的——脂肪分解的“三大环节” 为了方便大家理解这个相对专业的生化反应过程,我画了一张图(如下),我就按图解说了。 建议大家先仔细阅读一下图,再接着看下文—— 第一环节:脂肪动员 我们的脂肪主要以“甘油三酯(TG)”的形式储存在脂肪组织内,另外,心肌、骨骼肌、血浆中也有少量甘油三酯存在。对于减肥瘦身来说,主要是将脂肪组织内的甘油三酯动员起来用于供能,才能达到理想的效果。如果一个人脂肪动员的能力较低,就更容易产生肥胖,或者更不容易减肥。 一些特定的食物也能促进脂肪动员,如茶(茶多酚、咖啡碱)、咖啡、辣椒,以及瓜拉那等草本提取物,同时伴有心跳加速、血压增高的反应,因此需慎重使用。 第二环节:活性脂酸转移 当脂肪酸从脂肪组织中分解出来进入血浆后,在血浆蛋白的帮助下运送到全身各处的活动细胞内,开始了它的第二个环节——活化。只有被活化的脂肪酸才能进入被称作“细胞内动力工厂”的“线粒体”内,进一步被氧化分解。这个进入过程就是第三环节:活性脂酸转移。 脂肪酸被活化是受一系列酶的催化作用完成的,因此,这些酶的活性成为脂肪分解的一个限制因素。当然,这个因素主要受遗传决定,同时也受特定的代谢物质(如共轭亚油酸,CLA)影响。 第三环节:脂肪酸β氧化 这是脂肪酸在线粒体内最后被分解成二氧化碳和水,并产生能量的过程,受一系列酶和其他代谢反应影响。值得重视的是,脂肪酸的β氧化和糖的氧化在最后阶段都必须进入一个叫“三羧酸循环”的生化反应过程,才能最终分解成二氧化碳和水,最大限度地释放能量。
如果脂肪分解过程中,糖供应不足,导致三羧酸循环不能顺利进行,脂肪分解也会受到抑制,从而产生“酮体”。高浓度的酮体对人体是有害的,可能造成“酮中毒”。
甘油三酯偏高的原因与治疗方法
甘油三酯偏高的原因与治疗方法 如果甘油三酯超过了正常值。并伴随头晕、胸闷、气 短肢体麻木等症状,就可能会引起动脉粥样硬化,造成血管堵塞形成血栓等... 请来详细了解下甘油三酯偏高的原因。 甘油三酯高和大家熟知的高胆固醇都是高血脂的一种,对人体的损害属于隐匿但危险的类型,直接损害就是加速全身动脉硬化,最终引起脑卒中、冠心病、心梗、肾衰等严重疾病。甘油三酯偏高的原因在临床上可分为原发性和继发性两种,原发性甘油三酯高常见于遗传,而继发性则可以继发于疾病,如糖尿病、肾病综合征、甲状腺功能减退、透析、胆道阻塞等;也可继发于不良生活习惯,如饮食、烟酒等。遗传性甘油三酯高我们暂不讨论,来看看继发性甘油三酯高怎么回事。因疾病导致的甘油三酯高主要是各种原因致使脂肪代谢异常,因不良生活习惯导致的甘油三酯高则是我们每个人生活中必须注意的了。为什么不良生活习惯也能成为甘油三酯高的原因呢?因为甘油三酯大部分是从饮食中获得的,只有少部分是人体自身合成的。当进食大量脂肪类、尤其是动物脂肪食品后,可测得体内甘油三酯水平明显升高;而过多的碳水化合物、尤其是加工精细的粮食进入体内后,则引起血糖升高,合成更多的甘油三酯。另外,饮酒可以刺激甘油三酯的加速合成。甘油三酯高怎么回事?排除了
疾病和遗传,就要从饮食习惯上找原因啦!了解了甘油三酯高的原因,就要注意健康饮食了,不要忽略身体敲响的警钟。属于高甘油三酯型高血脂!建仪你吃西药!要吃贝特类降酯药.还要调整饮食结构:1.少吃高脂食物如肥肉,油,奶油,花生等;2少吃高胆固醇食物如动物内脏,脑髓,蛋黄,松花蛋等;3.少吃高热量食物,如面粉,大米,巧可力,白糖,油脂等.4.多吃降脂食物如玉米,燕麦,洋葱,大蒜,茄子,芹莱,木耳,海带,香菇,鱼等.5.可经常用山楂,菊花,绞股兰泡水喝.6.要加强锻练或减肥. 平时注意合理运动,低脂肪,低胆固醇饮食,多食蔬菜水果,多喝水等。可以在当地医生指导下口服:绞股蓝总甙片和辛伐他丁片治疗. 在饮食中,动物性脂肪、动物的脑、肝、肾、鸡蛋黄、鸭蛋黄、鹅蛋黄、松花蛋、虾子、蟹黄等食物,胆固醇含量很高,应控制食用量。以人们常吃的鸡蛋为例,每个蛋黄约含有320毫克胆固醇,每天只吃一个鸡蛋为宜;如果不是血脂过高,也不必只吃蛋清不吃蛋黄。控制纯糖和脂肪有利于降低甘油三酯。含胆固醇较低或有降低胆固醇作用的食物,比如谷类、瘦肉、鸡鸭肉、鱼类(尤其是海产鱼)、海参、海带、薯类、香蕉等食品,以及植物油(尤其是芝麻油、花生油、玉米油),应在日常膳食中适量增加。摄入牛奶、豆类或其制品还可补钙,也有利于控制胆固醇。喝茶,尤其是绿茶也有降血脂作用。已经发现,大蒜有升高血液中高密度脂蛋白、增强胆固醇分解、
甘油三酯
甘油三酯是被储藏起来的热量源。如同其名称一样,甘油三 酯是人体的脂肪成分,如果以猪肉或牛肉为例,那么甘油三酯就 是白色的肥肉部位。皮下脂肪就是甘油三酯所蓄积而成的。 甘油三酯是由三分子脂肪酸与一分子甘油结合而成的,一般 情况下会成为脂肪酸的贮藏库,根据身体所需会被分解。被分解 后的脂肪酸会被作为我们生命活动的热量源来加以利用。从甘油 三酯中脱离的脂肪酸便是游离脂肪酸,是一种能够迅速用于生命 活动的高效热量源。 此外,皮下脂肪还有保持的体温、保护身体免受寒冷袭击的 类似隔热材料的功能,以及保护身体免受外来袭击的缓冲材料的 功能。 也就是说,甘油三酯在人类进化的过程中,为适应严酷的自然以求生存下来发挥了重要的作用。但是,在拥有舒适的环境与丰富食用材料的现代生活中,甘油三酯却面临着愈加过剩蓄积的危险。 甘油三酯偏高的原因在临床上可分为原发性和继发性两种: 1、原发性甘油三酯高常见于遗传。 2、继发性则可以继发于疾病,如糖尿病、肾病综合征、甲状腺功能减退、透析、胆道阻塞等;也可继发于不良生活习惯,如饮食、烟酒等。 因疾病导致的甘油三酯高主要是各种原因致使脂肪代谢异常。因不良生活习惯导致的甘油三酯高,因为甘油三酯大部分是从饮
食中获得的,只有少部分是人体自身合成的。当进食大量脂肪类、尤其是动物脂肪食品后,可测得体内甘油三酯水平明显升高;而过多的碳水化合物、尤其是加工精细的粮食进入体内后,则引起血糖升高,合成更多的甘油三酯,从而会引起甘油三酯的升高。 高甘油三酯的治疗 通常,对于仅血甘油三酯含量增高,而胆固醇含量正常的患者,应改变饮食结构,控制体重。另外还要适当参加体力活动或运动。 高甘油三酯血症治疗阶段,在饮食方面,应该减少脂肪酸和胆固醇的摄入,限制饮酒。每日摄入的脂肪应控制在总热量的30%以下,其中饱和脂肪酸控制在7%以下。对高甘油三酯血症患者而言,少量饮酒也可以导致血清甘油三酯水平的明显升高,所以要限制饮酒。 肥胖时,机体对游离脂肪酸的动员利用减少,血中游离脂肪酸水平上升,导致血清中甘油三酯水平升高,而减轻体重可以使肥胖患者血清甘油三酯水平下降。 运动和体力活动可以使甘油三酯水平明显下降。因此,高甘油三酯血症患者也应进行长期、规则的体育锻炼或体力劳动。 当血清甘油三酯水平升高合并有导致动脉粥样硬化的脂质紊乱如家族性复合型高脂血症时,应该采用药物治疗。在药物的选择方面,可以选用烟酸或烟酸的衍生物,如乐脂平。对血清甘油三酯水平极度升高的患者,可以使用纤维酸衍生物或烟酸来治疗。
甘油三脂(TG)检测试剂盒(GPO-PAP单试剂微板法)
甘油三脂(TG)检测试剂盒(GPO-PAP 单试剂微板法) 简介: 甘油三酯(Triglyceride ,TG )又称三酰甘油,是3分子长链脂肪酸和甘油形成的脂肪分子,是人体内含量最多的脂类,大部分组织均可以利用甘油三酯分解产物供给能量,同时肝脏、脂肪等组织还可以进行甘油三酯的合成。 Leagene 甘油三脂(TG)检测试剂盒(GPO-PAP 单试剂微板法)又称磷酸甘油氧化酶法或磷酸甘油氧化酶-过氧化物酶偶联法等,甘油三脂被LPL 水解为甘油和脂肪酸,再经过氧化物酶(POD)催化,使4-氨基安替比林与酚(三者合称PAP)反应,生成红色苯醌亚胺(Trinder 反应)。酶标仪在500~520nm 处进行比色测定。本试剂盒用于人或动物的血清、血浆、脑脊液、细胞、组织等样本中的甘油三脂含量定量测定。本试剂盒仅用于科研领域,不宜用于临床诊断或其他用途。 组成: 操作步骤(仅供参考): 1、 样本处理: ①血清、血浆、脑脊液样本:从待测样本中分理出的血清或血浆不应有溶血,直接检测,如超过线性范围,用生理盐水稀释后检测。 ②细胞样本: a 、取适量的细胞(一般推荐>106以上),弃上清,留取沉淀。 b 、用PBS 或生理盐水清洗1~2次,弃上清,留取沉淀。 c 、加入200~300μl 的PBS 或生理盐水匀浆,冰浴条件下超声破碎细胞,功率300W ,每次3~5s ,间隔30s ,重复3~5次。亦可手动匀浆,制备好的匀浆液不可离心,待用。 d 、③组织样本:准确称取适量组织样本,按质量(g):生理盐水或PBS(ml)=1:9的比例, 编号 名称 TC1241100T Storage 试剂(A): GPO-PAP 工作液 Tris-HCl buffer 30ml -20℃ 避光 LPL 、GK 4-氨基安替比林 对氯酚 试剂(B): Glycerol 标准(1.7mmol/L) 1ml RT 试剂(C): ddH 2O 1ml RT 使用说明书 1份
