直接引语与间接引语变化的一般规律

1. 直接引语与间接引语变化的一般规律
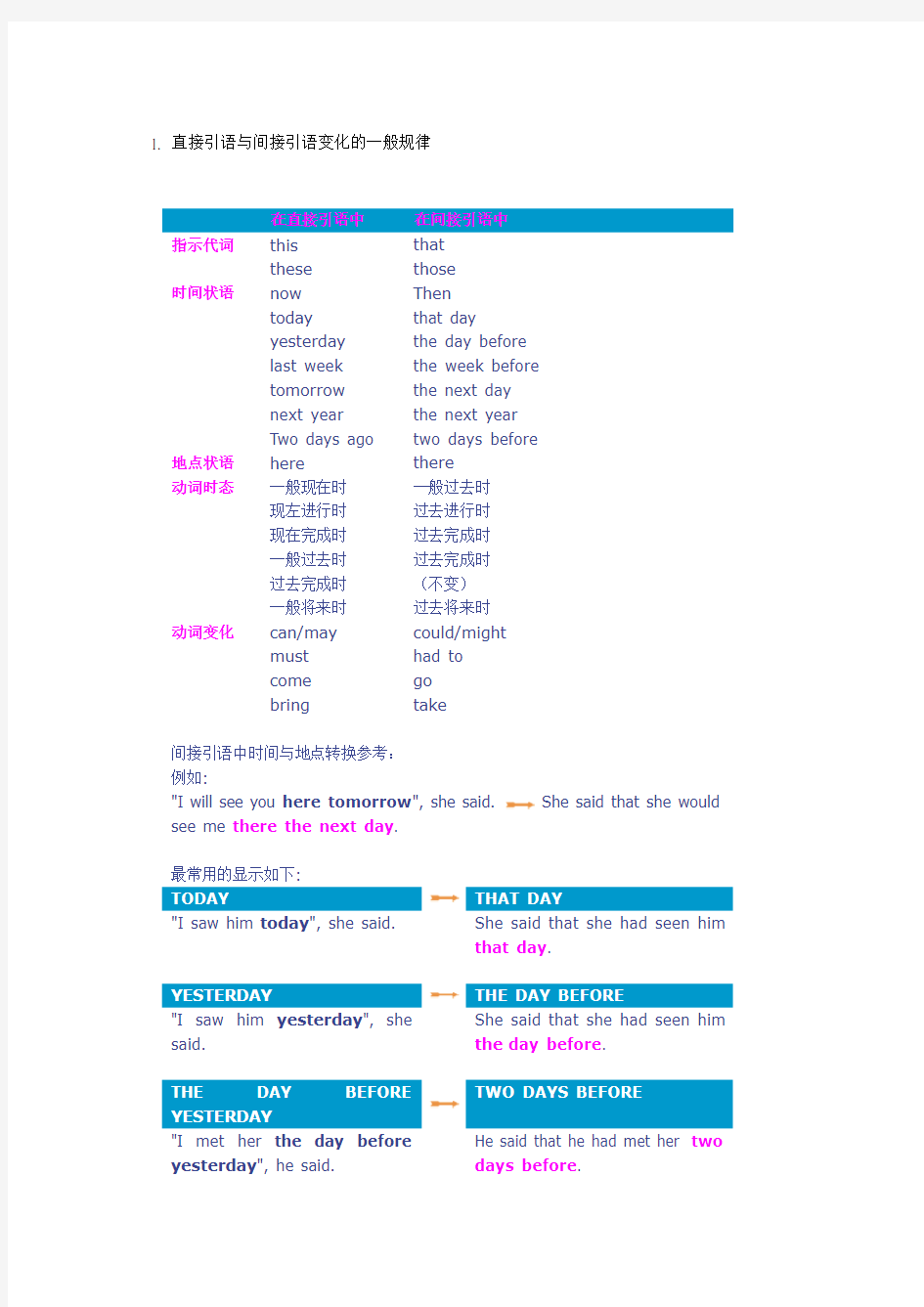
在直接引语中在间接引语中
指示代词this
these that those
时间状语now
today
yesterday
last week
tomorrow
next year
Two days ago Then
that day
the day before the week before the next day the next year two days before
地点状语here there
动词时态一般现在时
现左进行时
现在完成时
一般过去时
过去完成时
一般将来时一般过去时过去进行时过去完成时过去完成时(不变)过去将来时
动词变化can/may
must
come
bring could/might had to
go
take
间接引语中时间与地点转换参考:
例如:
"I will see you here tomorrow ", she said. She said that she would see me there the next day.
最常用的显示如下:
TODAY THAT DAY
"I saw him today", she said. She said that she had seen him
that day.
YESTERDAY THE DAY BEFORE
"I saw him yesterday", she said. She said that she had seen him the day before.
THE DAY BEFORE
YESTERDAY
TWO DAYS BEFORE
"I met her the day before yesterday", he said. He said that he had met her two days before.
TOMORROW THE NEXT/FOLLOWING DAY
"I'll see you tomorrow", he said He said that he would see me the next day.
THE DAY AFTER TOMORROW IN TWO DAYS TIME/ TWO DAYS LATER
"We'll come the day after tomorrow", they said. They said that they would come in two days time/ two days later.
NEXT WEEK/MONTH/YEAR THE FOLLOWING
WEEK/MONTH/YEAR
"I have an appointment next week", she said. She said that she had an appointment the following week.
LAST WEEK/MONTH/YEAR THE
PREVIOUS/WEEK/MONTH/ YEAR
"I was on holiday last week", he told us. He told us that he had been on holiday the previous week.
AGO BEFORE
"I saw her a week ago," he said. He said he had seen her a week before.
THIS (FOR TIME) THAT
"I'm getting a new car this week", she said. She said she was getting a new car that week.
THIS/THAT (形容词) THE
"Do you like this shirt?" he
asked
He asked if I liked the shirt.
HERE THERE
He said, "I live here". He told me he lived there.
别的变化:
通常来说, 第一人称代词转为第三人称单数或复数(除非讲话者在引用自己的话): I/me/my/mine, you/your/yours him/his/her/hers
we/us/our/ours, you/your/yours they/their/theirs:
He said: "I like your new car." He told her that he liked her new car.
I said: "I'm going to my friend's house." I said that I was going to
my friend's house.
通常来说,转换成间接引语时,要比直接引语时间上提前一个时态: She said, "I am tired." She said that she was tired.变化如下:
一般现在时一般过去时
"I always drink coffee", she said She said that she always drank coffee.
现在进行时过去进行时
"I am reading a book", he explained. He explained that he was reading a book
一般过去时过去完成时
"Bill arrived on Saturday", he said. He said that Bill had arrived on Saturday
现在完成时过去完成时
"I have been to Spain", he told me. He told me that he had been to Spain
过去完成时过去完成时
"I had just turned out the light," he explained. He explained that he had just turned out the light.
现在完成进行时过去完成进行时
They complained, "We have been waiting for hours". They complained that they had been waiting for hours.
过去进行时过去完成进行时
"We were living in Paris", they told me. They told me that they had been living in Paris.
一般将来时过去将来时
"I will be in Geneva on Monday", he said He said that he would be in Geneva on Monday.
将来进行时过去将来进行时
She said, "I'll be using the car next Friday". She said that she would be using the
car next Friday.
2. 直接引语与间接引语变化中的三要素
我们要很好地掌握直接引语变间接引语这一语法项目,关键要掌握下列“三要素”。
要素一:陈述句的间接引语——连接词用that,在口语中可省略。引述动词用said, told, 等。例如:
1) He said: “I’ve left my book in my room.”→
He told me that he had left his book in his room.
2) She said: “He will be busy.”→
She said that he would be busy.
要素二:疑问句的间接引语。一般疑问句后连接词用if或whether,而引述选择疑问句时只能用whether,引述动词用asked,没有间接引语的可以加一个间接宾语me, him等,例如:
She said to Tom, “Can you help me?”→
She asked Tom if /whether he could help her.
1) She asked, “Is this book yours or his?”→
She asked me whether that book was mine or his.
2) 特殊疑问句用原句中的疑问词作连接词,改为陈述语序。例如:
The teacher asked, “how did you repair it?”→
The teacher asked me how I had repaired it.
要素三:祈使句的间接引语——采用“动词+宾语+不定式”结构。
told
即asked sb. (not) to do sth.
ordered
warned
注意:引语中的呼语可改成宾语。引语中的please 去掉,动词改为ask
1) The teacher said to the students, “Don’t waste your time.”→
The teacher told the students not to waste their time.
2) The mother said,“Tom, get up early, please.”→
The mother asked Tom to get up early.
3. 直接引语与间接引语变化中需要注意的“五不变”
在直接引语变间接引语时,还要注意以下五种不变的特殊情况。
1.直接引语如果是客观真理,谚(习)语,变间接引语时时态不变。例如:The teacher said, “The earth goes round the sun.”→
The teacher said that the earth goes round the sun.
My father said, “Practice makes perfect.”→
My father said practice makes perfect.
2. 直接引语中被引述的部分是反复出现的,习惯性的动作或说话时情况仍然存
在的,变间接引语时,时态保持不变,例如:
The boy said to us, “ I usually get up at six every day.”→
The boy told us he usually gets up at six every day.
He said, “We are still students.’→
He said they are still students.
3.直接引语如果有明确的表示过去的时间状语,时态不变。例如:
He said to me, “I was born in 1978.”→
He told me that he was born in 1978.
The engineer said, “I was at college in 1967.”→
The engineer said he was at college in 1967.
4.直接引语中凡有When,since,while 引导的从句,在变为间接引语时,只改变主句时态,从句的时态不变。例如:
He said, “I have studied English since I was a boy.”→
He said he had studied English since he was a boy.
She said, “I read the book while I was waiting for a bus.→
She said she had read the book while she was waiting for a bus.
Mr. Green said to them, “Joe told me all about his story when he asked for a job.”→
Mr. Green told them Joe had told him all about his story when he asked for a job.
5.如果直接引语中引述部分含有insist, suggest, demand等引导的虚拟宾语从句,变间接引语时,引语中的主从句时态都不变。例如:
He said, “We insisted that she start immediately.→
He said they (had) insisted that she start immediately.
She said, “He demanded that the girl leave at once.”→
She said he demanded that the girl leave at once.
另外,如果说话人转述自己的话,人称则可不变. 例如:
I said to him, “I have finished it.”→I told him I had finished it.
如果就在当地转述, here不必变为there,come不必改为go,如果就在当天转述,则today, yesterday, tomorrow等状语也不必变化。例如:She said to us, I’ll come here tomorrow.”→
She told us she would come here tomorrow.
1.3 名词复数的不规则变化
1)一些特殊变化
单数复数
woman women
man men
child children
tooth teeth
foot feet
person people
leaf leaves
half halves
knife knives
wife wives
life lives
loaf loaves
potato potatoes
cactus cacti
focus foci
fungus fungi
nucleus nuclei
syllabus syllabi/syllabuses
analysis analyses
diagnosis diagnoses
oasis oases
thesis theses
crisis crises
phenomenon phenomena
criterion criteria
datum data
注意:由一个词加 man 或 woman构成的合成词,其复数形式也是 -men 和-women,如an Englishman,two Englishmen。但German不是合成词,故复数形式为Germans;Bowman是姓,其复数是the Bowmans。
2)2)单复同形,如deer,sheep,fish,Chinese,Japanese 等。但除人民币的元、角、分外,美元、英镑、法郎等都有复数形式。如:a dollar, two dollars; a meter, two meters。
单数复数
sheep sheep
fish fish
species species
aircraft aircraft
3)集体名词,以单数形式出现,但实为复数。例如:
people police cattle等本身就是复数,不能说 a people,a police,a cattle,但可以说 a person,a policeman,a head of cattle, the English,the British,the French,the Chinese,the Japanese,the Swiss 等名词,表示国民总称时,作复数用
如The Chinese are industries and brave. 中国人民是勤劳勇敢的。
4)以s结尾,仍为单数的名词,如:
a. maths,politics,physics等学科名词,一般是不可数名词,为单数。
b. news 为不可数名词。
c. the United States,the United Nations应视为单数。
The United Nations was organized in 1945. 联合国是1945年组建起来的。
news The news is on at 6.30 p.m.
athletics Athletics is good for young people.
linguistics Linguistics is the study of language.
darts Darts is a popular game in England.
billiards Billiards is played all over the world.
d. 以复数形式出现的书名,剧名,报纸,杂志名,也可视为单数。例如:
"The Arabian Nights"is a very interesting story-book. 《一千零一夜》是一本非常有趣的故事书。
5)5)表示由两部分构成的东西,如:glasses(眼镜)trousers, clothes 等,若表达具体数目,要借助数量词pair(对,双); suit(套); a pair of glasses; two pairs of trousers等。
trousers My trousers are too tight.
jeans Her jeans are black.
glasses Those glasses are his.
6)另外还有一些名词,其复数形式有时可表示特别意思,如:goods 货物,waters 水域,fishes(各种)鱼。
直接引语和间接引语用法讲解资料
直接引语和间接引语用法讲解 一、概述 引用或转述别人说的话时有两种方法:直接引述别人的原话,这叫做直接引语(direct speech)。用自己的话转述别人的话,叫间接引语(indirect speech)。一般地讲,直接引语前后要加引号,间接引语不用引号,而用宾语从句来表达。 Mr. Black said, “I'm busy.”布菜克先生说:“我很忙”。(直接引语) Mr. Black said that he was busy.布菜克先生说他很忙。(宾语从句是间接引语)从上例看来,直接引语改为间接引语时,除将直接引语改为宾语从句之外,还须对直接引语中的人称和时态进行相应的变化,如上例直接引语中的I改成了he, am则改成了was。现将由直接引语改为间接引语时应注意的问题,分述如下: 二、直接引语是陈述句时 直接引语如果是陈述句,变为间接引语时,用连词that引导(that在口语中常省去),that从句之前用say、tell等动词,从句中的人称、时态、指示代词、时间状语、地点状语等要作相应的变化。 1、人称的变化 直接引语改为间接引语人称要相应的变化,把直接引语中的第一人称(如:I,me,my,mine,we,us,our,ours)变为与主句的主语相一致的人称。把直接引语中的第二人称(you,your,yours)变为和主句的间接宾语(即听话人,如无听话人,可根据上下文的体会人为确定一个人称)相一致的人称。直接引语中的第三人称(he,him,his,she,her,hers,it,its,they,their,theirs,them)变为间接引语时,人称不变。 He said , “I like it very much.” 他说:“我非常喜欢它”。 →He said that he liked it very much. 他说他非常喜欢它。(I改为he, it不变) He said, “You told me this story.”他说:“你给我讲过这个故事。”
直接引语和间接引语句子训练
直接引语和间接引语句子训练(转述句和陈述句): 1.直接引语是直接引用别人的话,而间接引语则是转达别人说的话,因此,直接引语改为间接引语时,说话人即第一人称“ 我”要改为第三人称“ 他” 或“ 她”。如:张童对我说:“我一定要坚持长跑锻炼。” 改:张童告诉我,他一定要坚持长跑锻炼。 2.当转述内容涉及其他人称时的改法。如:姐姐对我说:“ 你说得对,我就这样做。” 改:姐姐告诉我,我说得对,她就这样做。上面的例句中涉及了第二人称,在改为转述句时就应改为第一人称。还应注意,冒号和引号前的内容不变。 3.间接引语改为直接引语,第三人称“ 他” 或“ 她”应改为第一人称“ 我”,说话内容涉及第一人称应改为第二人称。如:老班长告诉我们,他没有完成任务,没把我们照顾好。改:老班长对我们说:“ 我没有完成任务,没把你们照顾好。” 特例: 1.小华对小强说:“你明天把钢笔还给我。” 小华对小强说,他明天把钢笔还给小强。 2.妹妹对爸爸说:“哥哥让我转告你,它晚上有事不回来吃饭了。” 妹妹告诉爸爸,哥哥说他晚上有事不回来吃饭了。 3.老师对小丽说:“你知道自己表现得最出色吗?” 老师对小丽说,她的表现很最出色。 1. 小红军对陈赓说:“我还要等我的同伴呢。” 2. 老师对我说:“我教你怎么写。” 3. 雨来摇摇头说:“我在屋里什么也没看见。” 4. 李楠小声告诉我:“我家在少年宫附近。” 5. 小姑娘说:“我要去北京,我要去看看北京的名胜古迹。” 6. 老师对王芳说:“学校让你明天出席区小学生座谈会。” 7. 罗蒙诺索夫摇摇头对爸爸说:“我也要一本书!” 8. 雷锋对大嫂说:“我送你一程吧!” 9. 小鸟对青蛙说:“朋友,不信请你跳出井口看一看!” 10. 有一家外国报纸轻蔑地说:“能在南口以北修筑铁路的中国工程师还没有出世呢!” 11. 老师说:“你今天放学之前必须完成作业。” 12. 有句俗话说:“磨刀不误砍柴工。” 13. 楚王瞅了他一眼,冷笑一声,说:“难道齐国没有人了吗?” 14. 他惊讶地说:“原来是你!” 15. 妈妈对我说:“你今天晚上不能看电视。” 1 6. 爸爸说:“今天晚上你和妈妈先吃饭,我有事。” 17. 一个同学对我说:“借我一只笔。” 18. 外婆问我:“你在干什么?”
直接引语改为间接引语的变化
直接引语改为间接引语的变化 1.人称的变化。其规律为:一从主,二从宾,三不变。具体为: (1)如果直接引语的主语是第一人称,变化时,该人称与主句的主语保持一致。 如:Mary said, “I want to forget the past.”→ Mary said (that)she wanted to forget the past. (2)如果直接引语的主语是第二人称,变化时,该人称与主句的宾语保持一致。 如:He said to me,“Do you want to ask about the lab?” → He asked me if I wanted to ask about the lab. (3)如果直接引语的主语是第三人称,变化时,该人称保持不变。 如:Jim said ,“They are going to do their homework..”→ Jim said (that) they were going to do their homework. 2.时态的变化。 (1)如果主句是一般现在时,宾语从句原有时态保持不变。 如:Mary says,“I w ent to see the movie yesterday.” →Mary says that she went to see the movie yesterday.” (2)如果主句是一般过去时,宾语从句的时态会有以下变化(科学事实、自然规律除外)。 a.一般现在时→一般过去时 b.一般将来时→过去将来时 c.现在进行时→过去进行时 d.一般过去时→过去完成时 e.现在完成时→过去完成时。也就是说要落后一个时态。 3.直接引语变间接引语时,指示代词、时间状语、地点状语及动词都会发生相应的变化,变化见下表。 4.各种句型的直接引语改为间接引语的方法。 (1).陈述句改为间接引语时,常用动词said, told,连词that,多被省略。 如:Ben said, “I won’t go to Marcia’s house on Friday night.”→ Ben said (that)he wouldn’t go to Marcia’s house on Friday night. Lana said to me,“I’m not mad at you anymore.” → Lana told me(that)she wasn’t mad at me anymore.
高中必修一直接引语变间接引语详解
直接引语变间接引语(宾语从句) 一.直接引语和间接引语的定义。 直接引语:直接引用别人的话叫直接引语, 间接引语:用自己的话转述别人的话叫间接引语。 直接引语前后加引号;间接引语不必加引号。 He said, “ I’m a student.” (直接引语)→He said that he was a student. (间接引语) 主句从句主句从句 二.当直接引语为特殊疑问句变间接引语形成宾语从句时,首先要注意用特殊疑问词, 其后用陈述语序的句子,同时注意人称、时态、时间状语,连接词,语序的变化. (一)人称的变化规则:一随主,二随宾,第三人称不更新。
★(二).时态变化 宾语从句时态变化规则:主现从不限;主过从四过(即4种过去的
时态:一般过去时;过去进行时;过去将来时;过去完成时);客观真理,只用一般现在时。 1.主句一般现在时,从句可用任意时态。 2.主句过去时,从句用相应的过去时态。即一般现在时改成一般过去时;现在进行时改成过去进行时;一般将来时改成过去将来时;一般过去时、现在完成时、过去完成时改成过去完成时。 3.主句过去时,从句是客观真理时,只用一般现在时。 Teacher told us:" The moon moves round the earth." Teacher told us the moon moves round the earth.
(三).时间状语变化
★(四).连接词 1.从句为陈述句,常选择连接词that或将that省略,直接与主句相连。 2.从句为一般疑问句,常选择连接词if或whether。 3.从句为特殊疑问句,常选择what,when,where,which,who,how 等的疑问代、副词作连接词。 注意:当who为主语时,句式为:who+谓语+其他
间接引语详解
人称、时间、地点等方面作相应的变化。 1、引语转换时的句式变化 不同的直接引语句式,如:陈述句、疑问句、祈使句和感叹句,转换成间接引语时要遵循一定的句式转换规则,还要注意根据句意,使用适当的引述动词。(1)陈述句的间接引语 将陈述句转换为间接引语,通常用that引导的宾语从句来表达。连词that 在不引起歧义的情况下可以省略。引述分句的动词常见的有say 和tell等。 He s aid, “I caught[k?:t] a cold yesterday.” 他说:“我昨天感冒了。” →He said (that) he had caught a cold the day before. 他说他前天感冒了。 Helen said to me, “I’m tired of taking such exams[iɡ’z?m].” 海伦说:“我讨厌参加这种考试。” →Helen told me (that) she was tired of taking such exams. 海伦说她讨厌参加这种考试。 He said (that) the book was very interesting and that(不省略) all the children like to read it.他说那本书很有趣,所有小孩都喜欢读。
例题: He says,“I like singing and I want to be a singer.” 他说:“我喜欢唱歌,我想当歌手。” →He says that he likes singing and that he wanted to be a singer.他说他喜欢唱歌,想当歌手。 在此种情况下,引导第一个宾语从句的that有时可以省略,但引导第二个宾语从句的that通常不省略,以免误解。 (2)疑问句的间接引语 直接引语如果是疑问句,变成间接引语后,叫做间接问句。引述的动词常用ask, wonder, want to know等。间接问句的词序一般都用正常词序,句末不用问号,用句号。 ①一般疑问句的间接引语 直接引语为一般疑问句时,用连词whether或if 引导。 I asked him, “Are you satisfied[’s?t?s'fa?d]with the results[ri'z ?lt]?” 我问他:“你对这结果满意吗?” I asked him whether / if he was satisfied with the results. 我问他对这结果是否满意。 “Did you go to the British ['br?t??]Museum yesterday?” asked Kate. 凯特问:“你昨天有没有去大英博物馆?” Kate asked me whether / if I had gone to the British Museum the day before. 凯特问我昨天有没有去大英博物馆。 The old man said to a passer-by, “Will you tell me the way to get to the Great Wall Hotel?” 那位老人跟一位过路人说:“请问到长城饭店的路怎么走。” The old man asked a passer-by to tell him the way to the Great Wall Hotel. 那位老人请一位过路人告诉他去长城饭店的路。 ②选择疑问句的间接引语
直接引语改为间接引语
直接引语改为间接引语 一、直接引语(也叫“直述句”)改为间接引语(也叫“转述句”)的两个特点直接引语改为转述句,从它的形式上来看,有比较明显的两个特点:一、标点符号的改变引述句改为转述句,冒号要改为逗号,双引号要去掉。转述句改引述句,要加上冒号和引号。 二、人称的变化 1、引述是直接别人的话,而转述则是转达别人说的话,因此,引述句改为转述句时,说话人即第一人称“我”要改为第三人称“他”或“她”。 如:小明说:“我一定要努力学习。” 改:小明说,他一定要努力学习。 2.当引述内容涉及其他人称时的改法。 如:姐姐对我说:“你说得对,我就这样做。” 改:姐姐对我说,我说得对,她就这样做。 上面的例句中涉及了第二人称,在改为转述句时就应改为第一人称。应注意,冒号和引号前的内容不变。 3.转述句改为引述句,第三人称“他”或“她”应改为第一人称“我”,说话内容涉及第一人称应改为第二人称。 如:老班长说,他没有完成任务,没把我们照顾好。 改:老班长说:“我没有完成任务,没把你们照顾好。” 二、直接引语和转述句的类型 (一)从转述的那个人或者向谁转述上来分析有大致两种情况: 1、第二个人转述(转给第三个人):A对B说话,然后B转述给第三个人听。 【例如】妈妈..对我说:“我.明天还要去开会。” 【改为】妈妈..对我说,她.明天还要去开会。 2、第三个人转述(转给第四个人):A对B说话,然后C转述给第四个人听。 【例1】妈妈..对爸爸说:“我.明天要去开会。” 【改为】妈妈..对爸爸说,她.明天要去开会。 【例2】军官对夜莺说:“要是路带对了,我就把这.东西送给你。” 【改为】军官对夜莺说,要是路带对了,他就把那.东西送给夜莺。 (二)从被转述的人(说话的那个人)来分析大致有三种情况。 1、直接引语提示语在前面。 【例如】妈妈说:“我明天还要去开会。” 【改为】妈妈说,她明天还要去开会。 2、直接引语提示语在中间。(改后说话人都放在前面) 【例如】“工作太多了。”妈妈说,“我明天还要去开会。” 【改为】妈妈说,工作太多了,她明天还要去开会。 3、直接引语提示语在后面。(改后说话人都放在前面) “我明天还要去开会。”妈妈说。改为:妈妈说,她明天还要去开会。 三、直接引语和转述句的代词响应变化的分析 1、第二个人转述(转给第三个人)中的人称代词的变化。 【例1】妈妈对我说:“我明天要去开会。” 【改为】妈妈对我说,她明天要去开会。 【例2】妈妈对我说:“你要好好学习。”
直接引语变间接引语的用法
2014望子成龙学校暑假班八年级英语讲义 直接引语变间接引语的用法 She said. "My brother wants to go with me."(直接引语,即直接用“”把说话者所说的话引用) She said her brother wanted to go with her.(间接引语,即通过说话人与听话人之外的人称也就是第三人称转述成一个宾语从句) 一、如何变人称:下面有一句顺口溜“一随主、二随宾、第三人称不更新”。 He said to me . "My brother wants to go with me."(He said .为主句,he 为主句的主语;me 为主句的宾语,"My brother wants to go with me."为直接引语,将要变成间接引语即宾语从句) “一随主”是指在直接引语中有第一人称的人称代词、物主代词或反身代词时,变成间接引语要变成与主句中主语的人称相应的代词。如: He said. "My brother wants to go with me ." →He said his brother wanted to go with him. 说明:①my 是直接引语中的一人称单数的形容词性物主代词,所以变成间接引语要变成与主句he said 中的主语he 相一致的形容词性物主代词,即his;②me 是直接引语中的一人称单数的人称代词宾格,所以变成间接引语时要变成与主句he said 中的主语he 一致的人称代词宾格,即him “二随宾”是指直接引语中有第二人称的人称代词、物主代词或反身代词时,变成间接引语要变成与主句中宾语的人称相应的代词。如: He says to Kate. "I am your sister ?" →He tells Kate he is her sister 。 说明:①I 是直接引语中的一人称单数的人称代词主格,所以变成间接引语时要变成与主句he says to Kate 中的主语he 相一致的人称代词主格,即he;②your 是直接引语中的二人称单数的形容词性物主代词,所以变成间接引语时要变成与主句he says to Kate 中宾语Kate 一致的形容词性物主代词,即her. “第三人称不更新”是指直接引语中的三人称的代词变成间接引语时不需要改变人称。如: Mr. Smith said: "Jack is a good worker 。"→Mr. Smith said Jack was a good worker 。(Jack 是三人称,变成间接引语时依然是Jack 。) 二、如何变时态: 1、当主句为一般现在时,直接引语变成间接引语的时态不变,依然用直接引语的时态。如: Lily says to us,"I will go to America with you "→Lily tells us that she will go to America with us. 2、当主句为一般过去时,直接引语变成间接引语的时态要做相应的调整,用成相应的过去时态。如: 1) She said. "I have lost a pen." →She said she had lost a pen. 2) She said. "We hope so." →She said they hoped so.
英语语法 如何把直接引语转换为间接引语
如何把直接引语转换为间接引语 引述别人的话时,一般采用两种方式:一是引用别人的原话,把它放在引号内,称为直接引语;二是用自己的话加以转述,被转述的话不放在引号内,称为间接引语。间接引语在大多数情况下是一个宾语从句。直接引语变成间接引语时,要注意以下几点:人称变化、时态变化、宾语从句要用陈述句语序。 1. 直接引语是陈述句,变成间接引语时,由连词that ....引导,很多时候可省略that。例如:She said, "I am very happy to help you." →She said she was very happy to help me. She said, “I will go to Guangzhou tomorrow.” →She said that she would go to Guangzhou the next day/the following day. She said, “I have lived in Foshan for several years.” →She said that she had lived in Foshan for several years. She said, “ I am reading a book now.” →She said that she was reading a book at that time/moment. John said, “I am leaving for Paris on Wednesday” →John said that he was leaving for Paris on Wednesday. 2. 直接引语是一般疑问句,变成间接引语时,由连词whether .......或if..(是否)引导。先把直 接引语变为陈述句语序,再放在whether或if后面。例如: He asked me, "Do you like playing football?" → →He asked me whether/if I liked playing football. He asked Mary, “Will you come to my birthday party?”
直接引语与间接引语相互转换的方法指导及练习题
直接引语与间接引语相互转换的方法指导及练习题 方法: 直接引语是直接引用别人的话,而间接引语则是转达别人说的话。“直接引语变间接引语”就是要求把别人说的原话进行转述。 一、只改变引语部分,提示语不变; 例如:妈妈说:“我今天加班。”需要改变的只是:“我今天加班。”这一部分。 二、标点符号要作相应改变,即把冒号、前引号(:“)变成逗号(,),后引号(”)删除; 三、引语中,人称要变成相应的指代者:说话人即第一人称“我” 、“我们”要改为第三人称“他”、“她”或“他们”; 例如:妈妈说:“我今天加班。”其中“我”指代的是妈妈。所以,要变成“她”。改后为:妈妈说,她今天加班。 当转述内容涉及其他人称时也要发生相应变化。 如:姐姐对我说:“你说得对,我就这样做。” 改:姐姐告诉我,我说得对,她就这样做。 上面的例句中涉及了第二人称,在改为转述句时就应改为第一人称。 四、有称呼语的,称呼语要去掉; 例如:老红军说:“小鬼,你骑上我的马吧!”其中,“小鬼”要删除。变后为:老红军说,小鬼骑上他的马吧! 五、引语是疑问句的,要变成陈述的语气。 例如:明明问我:“今天放学后,到我家写作业,行吗?”变后为:明明问我,今天放学后,到他家写作业,行不行。 六、间接引语改为直接引语的方法正好相反,上面的五点都适用,如第三人称“他”或“她”应改为第一人称“我”,说话内容涉及第一人称应改为第二人称。 如: 1. 小华对小强说,他明天把钢笔还给小强。 2. 妹妹告诉爸爸,哥哥说他晚上有事不回来吃饭了。 3. 老师对小丽说,她的表现最出色。
4.老班长告诉我们,他没有完成任务,没把我们照顾好。 练习题一:把直接引语变成间接引语。 1.老师对我说:“我教你毛笔字的写法。” 2.梅花兴奋地说:“我是中国人,我怎么能忘掉祖国的语言呢?” 3.他站起来对大家说:“孩子们,我要去开会了。你们要听话。” 4.奶奶问我:“今天我还给你送饭吗?” 5.妈妈说:“小明,今晚我加班,你自己做饭吃!” 6.诸葛亮对鲁肃说:“你借给我二十条船,我自有妙用。” 7.小红军对陈赓说:“将军,我还要等我的同伴呢!” 8.妈妈气喘吁吁地说:“我今晚有急事,你去姥姥家。” 9.江姐回答说:“上级的姓名地址,我知道,下级的姓名地址,我也知道。” 10.小明和小红在一起写作业,小明对小红说:“你能教我怎样写作文吗?” 11.父亲坚决地对母亲说:“不是常对你说吗?我是不能轻易离开北京的。你要知道现在是什么时候,这里的工作多么重要。我哪能离开呢?” 12.妈妈对小红说:“你这么小,一个人出门我不放心?” 13.鲁肃对诸葛亮说:“都是你自己找的,我怎么帮得了你的忙?”
直接引语变间接引语专项练习题(答案)
直接引语变间接引语专项练习题 一、将所给直接引语变为间接引语,每空一词: 1. “I am having supper,” he said. He said that _______ _______ having supper. 2. “I’ve seen the film,” Gina said to me. Gina _______ me that she _______ _______ the film. 3. “I went home with my sister,” she said. She said that _______ _______ _______ home with her sister. 4. The teacher said, “The sun is bigger than the moon.” The teacher said that the sun _______ bigger than the moon. 5. “I met her yesterday,” he said to me. He told me that he _______ met her the day _______. 6. “You must come here before five,” he said. He said that I _______ to go _______ before five. 7. “I bought the computer two weeks ago,” she said. She said that she _______ bought the computer two weeks _______. 8. “Did you read the book last week?” he said. He _______ _______ I had read the book the week _______. 9. He said, “You can sit here, Jim.” He _______ Jim that he _______ sit there 10. He asked, “How did you find it, mother?” He asked her mother _______ _______ _______ found it. 11. “Where have you been these days?” he a sked. He asked me _______ _______ _______ been _______ days. 12 “Do you know where she lives?” he asked. He asked _______ _______ knew where she _______. 13. “Keep quiet, children.” he said. He _______ the children _______ _______ quiet. 14. “Don’t look out of the window,” she said. She told me _______ _______ _______ out of the window. 15. “Are you interested in this?” he said. He _______ _______ I was interested in _______.
直接引语和间接引语讲解及练习培训讲学
直接引语和间接引语讲解及练习
Unit1 语法核心突破: 直接引语变间接引语 这两种引语都是宾语从句,但是直接引语放在引号内,不用连词联接;间接引语不用引号,通常用连接词与主句联接 一、直接引语变间接引语时句式的变化 例:He said, “I'm very glad.” → He said he was very glad. 例:He said, “Can you come this afternoon, John?” →He asked John could come that afternoon. 例 : He said, “Where is Mr. Wang?” → He asked where Mr. Wang was. Tom says to me, “what food do you like best”. → Tom asks me food I like best Our parents told us“Learn English well!”我们的父母告诉我们:“把英语学好啊!” ?Our parents told us English well. 我们的父母告诉我吗要把英语学好。 The teacher said to me, “Don’t read that novel!” ? The teacher asked/ told me that novel. Our parents told us, “ Never do wrong!” 父母告诉我们:“不要做错事!” Our parents told us never to do wrong. 我们的父母告诉我们不要做错事。
语法大全:直接引语变间接引语用法(经典版)
直接引语变间接引语的用法 一、如何变人称; 下面有一句顺口溜“一随主。二随宾,第三人称不更新”。“一随主”是指在直接引语变间接引语时,如果从句中的主语是第一人称或被第一人称所修饰。从句中的人称要按照主句中主语的人称变化如: She said. "My brother wants to go with me." →She said her brother wanted to go with her. “二随宾”是指直接引语变间接引语时,若从句中的主语及宾语是第二人称。或被第二人你所修饰。从句中的人称要跟引号外的主句的宾语一致。如果引号外的主句没有宾语。也可以用第一人称,如: He said to Kate. "How is your sister now?" →He asked Kate how her sister was then。 “第三人称不更新”是指直接引语变间接引语时。如果从句中的主语及宾语是第三人称或被第三人称所修饰从句中的人称一般不需要变化如: Mr. Smith said: "Jack is a good worker。"→Mr. Smith said Jack was a good work er。 二、如何变时态: 直接引语在改为间接引语时、时态需要做相应的调整。 现在时它需改为过去时态;过去时态改为完成时;过去完成时则保留原来的时态。如: 1) She said. "I have lost a pen." →She said she had lost a pen. 2) She said. "We hope so." →She said they hoped so. 3) She said. "He will go to see his friend。"→She said he would go to see his friend。 但要注意在以下几种情况下。在直接引语变为间接引语时,时态一般不变化。 ①直接引语是客观真理。 "The earth moves around the sun and the moon moves around the earth, the teacher told me. → The teacher told me the earth moves around the sun and the moon moves around the earth。 ②直接引语是过去进行时,时态不变。如: Jack said. “John, where were you going when I met you in the street?” →Jack asked John where he was going when he met him in the street。 ③直接引语中有具体的过去某年、某月、某日作状语,变为间接引语时,时态不变。如: Xiao Wang said. "I was born on April 20, 1980。" →Xiao Wang said he was born on April 20, 1980。 ④直接引语如果是一般现在时。表示一种反复出现或习惯性的动作,变间接引语,时态不变。如: He said, "I get up at six every morning。" →He said he gets up at six every morning。 ⑤如果直接引语中的情态动词没有过去时的形式(例:ought to,had better, used to)和已经是过去时的形式时,(例:could, should, would, might)不再变。如:Peter said. "You had better come have today。" →Peter said I had better go there that day。 三、如何变状语:
直接引语变间接引语规则
直接引语变间接引语规则 (一)时态的变化:主句中的谓语动词如果是过去时态,直接引语中的谓语动词的时态须做下列变化: 一般现在时变为一般过去时 (但直接引语是客观事实、永恒真理,变成间接引语时,时态不变。 例如:They told their son :”The earth goes round the sun.” They told their son that the earth goes round the sun.。 (二)人称的变化:要根据句子 意思改变人称,如:I--he,she; we--they等等。 “一随主。二随宾,第三人称不更新”。 “一随主”是指在直接引语变间接引语时,如果从句中的主语是第一人称或被第一人称所修饰。从句中的人称要按照主句中主语的人称变化如:She said. "My brother wants to go with me. "→She said her brother wanted to go with her. “二随宾”是指直接引语变间接引语时,若从句中的主语及宾语是第二人称。或被第二人你所修饰。从句中的人称要跟引号外的主句的宾语一致。如果引号外的主句没有宾语。也可以用第一人称,如: He said to Kate. "How is your sister now?"→He asked Kate how her sister was then。 “第三人称不更新”是指直接引语变间接引语时。如果从句中的主语及宾语是第三人称或被第三人称所修饰从句中的人称一般不需要变化如: Mr Smith said。 "Jack is a good worker。"→Mr Smith said Jack was a good worke (三)指示代词、时间状语、地点状语的变化,动词变化: this--that; these--those; now--then; yesterday--the day before; today--that day; tomorrow--the next day; next week(month, year)--the next week(month,year); ago--before; here—there; brig—take; come--go.
初中语法-直接引语转换间接引语讲解-附练习题及答案
直接引语与间接引语 直接引语:一字不改的引用或复述别人的话,被引用或复述的部分即为直接引语。一般前后用引号,首字母大写。间接引语:用自己的话转述别人的话,被转述的部分即为间接引语。通常以宾语从句的形式出现,不用引号。直接引语变为间接引语时,要注意人称、时态、连接词、语序以及时间状语、地点状语、指示代词及方向性动词的变化。 一、人称变化 直接引语是第一人称变为间接引语时,一般要变为第三人称;第二人称变为与主句的间接宾语相一致的人称(如果没有间接宾语,可根据上下文的体会确定一个人称);第三人称一般不改变。例如He told me,"I’ll give you a book when I meet you again."—He told me he would give me a book when he met me again. 二、时态的变化 如果主句是过去式态,变为间接引语时应向前推一个时态。即一般现在时---一般过去式,现在进行时---过去进行时,现在完成时---过去完成时,一般过去时---过去完成时,过去进行时---过去进行时,一般将来时---过去将来时,现在完成进行时---过去完成进行时,过去完成时---过去完成时,过去完成进行时---过去完成进行时。等。例如 She wondered:"When will the meeting begin."—She wondered when the meeting would begin.但在以下几种情况下,间接引语的时态不用变化。 1、当直接引语表示的是客观真理或经常性的特点时。例如She said,"The earth goes around the sun".--She said that the earth goes around the sun. 2、当直接引语中有绝对具体的过去时间作状语时,保持原来的一般过去时。例如He said,"I left home in 1942.—He said he left home in 1942. 注:间接引语中的谓语动词有时需要适当的调整。Say后的直接引语表示陈述或命令时可变为ask; say后的直接引语表示请求或询问时可变为ask.例如The teacher said to me,"I have seen your book.."—The teacher told me that she had seen my book. 三、连接词的选择 1、陈述句陈述句转化为间接引语时用that引导,也可省略that。主句谓语动词可用直接引语中的said,也可用told来代替,可以说said that,said to sb. that, told sb. that, 不可以直接说told that.主句中的谓语还常有repeat, answer, reply, explain, announce, declare, think, 等。例如 Danny said,"I come from Canada."—Danny said that he came from Canada. 2、疑问句直接引语是疑问句变为间接引语时要用陈述语序。主句的动词常用ask,wonder,want to know等。 1)、一般疑问句直接引语为一般疑问句时变为间接引语须用if或whether引导。例如 She asked me,"Is he a teacher?"—She asked me if/whether he was a teacher. 2}、选择疑问句或反意疑问直接引语是选择疑问句需用or;反意疑问句需用or not变为间接引语时要用whether而不用if.例如 My brother asked me,"Is Tom tall or short?"—My brother asked me whether Tom was tall or short."You are reading,aren’t you"he said to me.—He asked me whether I was reading or not. 3)、特殊疑问句当直接引语为特殊疑问句变为间接引语时,常变成与疑问句同形的连接词引导的宾语从句,用陈述语序,问号变句号。例如"What do you want to eat?"he asked me.—He asked me what I wanted to eat. 3、祈使句直接引语是祈使句变为间接引语时,要用不定式表示,使其成为 ask /tell /order sb (not) to do sth 句型。例如"Don’t open the d oor."he said to her.—He asked her not to open the door. 4、感叹句感叹句变为间接引语时可用 what或how引导,也可用that引导。例如 He said,"What a lovely day it is!"—He said what a lovely day it was.—He said that it was a lovely day.
最新全面归纳直接引语改间接引语
引语四点变化1时态变化 2如何变句型 3人称变化 4 注丿意 1、直接引语如果表示客观真理,变间接引语时,时态不变。 2、直接引语若有明确的表示时间的词语,变间接引语时,时态不变。 3、若直接引语中含有could, must, should 等情态动词,变间接引语时,时态不变。 4、直接引述别人的原话,叫直接引语。 5、用自己的话转述别人的话,叫间接引语 时态变化 : 如果直接引语中的情态动词没有过去时的形式(例:ought to,had better, used to ,must, need)和已经是过去时的形式时,(例:could, should, would, might )不再变。 2时间状语,地点状语,指示代词、动词 直接引语变为间接引语时,有些时间状语,地点状语,指示代词和动词也要作相应的变动。
注:直接引语转换成间接引语时的变化应视实际情况而定。假如就在当天转述,today ,yesterday,tomorrow 等就不需改变;如果在当地转述,here也不必改为there,come 也不必改为go。另外,直接引语中有具体的过去某年、某月、某日作状语,变为间接引语时,时态不变。 如何变句型 ①直接引语如果是陈述句,间接引语应改为由that引导的宾语从句。如: She said, "Our bus will arrive in five minutes." f She said that their bus would arrive in five minu tes. ②直接引语如果是反意疑问句、选择疑问句或一般疑问句,间接引语应改为由whether 或if引导的宾语从句? 如: He said, "Ca n you swim, Joh n?" f He asked Joh n if he could swim. "You have fini shed the homework, have n ‘ t you?" my mother asked. f My mother asked me whether I had fini shed the homework. "Do you go to school by bus or by bike?" f He asked me if I went to school by bus or by bike. ③直接引语如果是特殊问句,间接引语应该改为由疑问代词或疑问副词引导的宾语从句 (宾语从句必须用陈 述句语序)。
2直接引语改为间接引语
直接引语改为间接引语 一、要点 基本方法:“二变一不变”,即:人称变,符号变,但原意不变。 其他细节: (1)改好之后,语气是陈述语气。换句话说,改为间接引语后,句子都是句号结尾的,疑问句、反问句、感叹句、祈使句都要改成陈述句。 (2)改好之后,只有一句话。换句话说,改为间接引语后,原来人物说的话如果有好几句,要把中间的句号都改为逗号。 (3)“对某人说”一般来说可以改为“告诉某人”,但如果保持“对某人说”也可以。 例如从阅读题《绿手指》里拿来的题目 女儿说:“你根本不懂植物遗传学。专家都做不到的事,你这么大年纪了,怎么能做到呢?” 女儿说,老奶奶根本不懂植物遗传学,专家都做不到的事,她这么大年纪了,是不能做到的。 (1)前后两处引号去除 (2)冒号改为逗号 (3)原句中间的句号改为逗号 (4)人称改掉,因为这是从阅读题里拿来的例题,联系上下文,知道“你”是指“老奶奶”。 (5)反问语气改为陈述语气 如果这道例题你弄懂了,那这类题目基本上难不倒你。现在我们来试试身手。 1、妈妈严肃地对我说:“马上就要期末考试了,你一定要认真复习,不要辜负老师和我对你的一片期望。” 以下两种都可以:
妈妈严肃地告诉我,马上就要期末考试了,我一定要认真复习,不要辜负老师和她对我的一片期望。 妈妈严肃地对我说,马上就要期末考试了,我一定要认真复习,不要辜负老师和她对我的一片期望。 关键在于“你”改成“我”,“我”改成“她”,代词改好,句子保持愿意不变。 2、熊猫问海豚:“海豚姐姐,你的身材这么好,是不是有减肥秘诀?” 最佳答案: 熊猫问海豚姐姐,她的身材这么好,是不是有减肥秘诀。 思考过程: (1)原来的“提示语”部分“熊猫问海豚”不完整,参考“说的话”,把提示语补充完整,成为“熊猫问海豚姐姐”。 (2)既然“提示语”已经写完整了,那么原来熊猫话语中打招呼的“海豚姐姐”就可以简化为“她”。 (3)我们说过通常可以用“是否”一词来帮助把疑问语气改为陈述语气。例如:你今天去小李家玩吗?改为:你今天是否去小李家玩。但是现在句中已有“是不是”,不必动用“是否”,只要把问号改成句号就行。 3、小明赞叹道:“香港迪士尼乐园真不错!” 小明赞叹说,香港迪士尼乐园很不错。 思考过程: (1)把“道”改成“说”,使语句更通顺。 (2)把“真”改成“很”,使语气变得平和,即陈述语气。当然,“!”改成“。”你已经懂了吧。 4、“妈!给我倒杯水!”我大声喊。 我大声喊妈妈,让她给我倒杯水。 思考过程:
