辅助精神病专家(SVESTAP)的智能虚拟专家系统(IJITCS-V10-N1-7)

I.J. Information Technology and Computer Science, 2018, 1, 59-67
Published Online January 2018 in MECS (https://www.360docs.net/doc/54728686.html,/)
DOI: 10.5815/ijitcs.2018.01.07
Smart Virtual Expert System to Assist
Psychiatrists (SVESTAP)
Udara Srimath S. Samaratunge Arachchillage
Faculty of Computing, Department of Software Engineering, Sri Lanka Institute of Information
Technology (SLIIT), Malabe, Sri Lanka,
E-mail: samaratunge@https://www.360docs.net/doc/54728686.html,
Received: 29 July 2017; Accepted: 07 November 2017; Published: 08 January 2018
Abstract—Psychological issues in the world are exponentially growing and the treatment gap is also comparatively high. The main reason would be the shortage of expertise and time-consuming in conventional diagnose process. The main objective of this research is to lower the mental issues treatment gap of professionals or apprentices in the field by creating a virtual expert system to assist psychiatrists. This system diagnoses most common mental disorders such as Depression Disorder, Anxiety Disorder, and Dementia. The proposed expert system can communicate with patients, to identify the current state of the illness. During the conversation, a standard questionnaire is given for the disease verification purpose. The experienced mental health professionals can use this expert system to assist in diagnosing process and the apprentices of the psychology can use this expert system as a training asset.
Index Terms—Psychiatrists, Expert System, Knowledge base, Ontology, Natural Language Understanding (NLU), Natural Language Generation (NLG), Anxiety, Dementia.
I.I NTRODUCTION
Health is considered as one of the most vital factors to measure the development of the society, and mental health is significant among them. According to the current statistics, the healthcare industry is one of the top most profitable industries in the world [1]. With the evolution of this scientific knowledge, the healthcare field emerged in areas of medical drugs, treatment methods, and medical equipment and involved with performing research and development activities globally. Even though the knowledge in medicine has been expanding with the time, the patients diagnose process remains as it is since the last couple of years. When diagnosing most mental diseases of patients, the experts would provide a key contribution to determine the exact disease [2]. Based on the gained experience, experts can diagnose mental disorder conditions precisely before proceeding to treatments.
The one major problem in this field is the comparatively low availability of those professional experts and scarce finding them from hospitals in rural areas. Therefore, it would be a challenging task to determine the exact mental disorder for psychiatrists who are newly appointed for the field. Furthermore, erroneously diagnose illnesses of the patient and proceed with treatments would detrimentally impact for the patient and eventually, the whole effort would be in vain. Hence, it is impelled to develop virtual expert system in purpose of assisting for the psychiatrist is key concern. Consequently, construct knowledgebase specific to the psychological diseases can be utilized to pinpoint the exact mental illness.
II.R ELATED WORKS
There have been many types of researches and experiments were conducted to develop decision support systems as an attempt to enhance the productivity and efficacy during disease diagnose. Since healthcare domain is a vast area considering immense clinical terms it comprises, and many symptoms and diseases need to be identified, analyzed, and categorized before moving towards treatments. Mainly virtual experts use fed rules and factors to analyze the situation and make decisions but, the accuracy of the decision is the crucial factor to be considered. When analyze the existing expert systems their behavior, and implemented focus is categorically different.
A. MYCIN expert system
MYCIN was an early expert system that used artificial intelligence to identify severe infections, such as bacteremia and meningitis, and to recommend antibiotics, with the dosage adjusted for patient's body weight [3]. Furthermore, MYCIN operated using a simple inference engine, and the knowledge base embedded with rules [4]. MYCIN is one of the well-known programs that embody intelligence and provide data to behave in an intelligent manner. Compared to other artificial intelligent (AI) programs, it was slow in progress and not always in forwarding direction [3].
B. DXplain decision support system
Apart from that, DXplain is a decision support system that developed at the laboratory of computer science at the Massachusetts General Hospital, which has the characteristics of both electronic medical textbook and a
medical reference system [5]. DXplain can provide a list of clinical manifestations such as signs, symptoms, and laboratory examinations for approximately 2000 diseases [5]. Moreover, it provides justifications for each of these diseases and suggests what further clinical information should be collected pertaining to each disease. C. CADUCEUS medical expert system
In addition to that, CADUCEUS was a medical expert system completed by Harry Pople in University of Pittsburgh in 1980, which took around ten years to build the knowledge base having ability to diagnose up to 1000 different diseases [6]. Both expert systems (CADUCEUS and MYCIN) were developed using the concept of inference engine and incorporate abductive reasoning to deal with additional complexity of internal diseases [6,7]. It is hard to find the expert systems which diagnose most mental illnesses and the above-mentioned expert systems (CADUCEUS, Mycin, DXplain) are not strong enough to recognize patient’s symptoms and determine the disease exactly.
D. Mental Health Diagnostic Expert System (MeHDES) This is AI rule-based reasoning (fuzzy based reasoning) system developed using techniques such as fuzzy logic and fuzzy genetic algorithm [8], [9], [10]. This fuzzy based reasoning is one approach to construct domain knowledge. It is extended version of semantic web rule and it does not create any inconsistencies for the knowledgebase. Nevertheless, describe the ontology in fuzzy knowledgebase has limited use and fuzzy inference is limited to rules only [11]. As well this MeHDES does not support question and answering approach and system did not act as a separate human counterpart to identify the situation in a conversational manner.
Therefore, the system needs to be more dynamic and it should be further enhanced to response dynamic questions. Hence it is obvious, to develop virtual expert system rule-based reasoning is not only sufficient, whereas understanding user’s question and generate suitable answer is another essential part of it. Therefore, the proposed system fulfills the research goal by performing the role of the virtual human counterpart. Furthermore, it uses the conversational approach to diagnose the patient and its behavior is highly dynamic when making the decision ba sed on the patient’s response.
III. R ESEARCH M ETHODOLOGY
How this proposed system fulfills the key idea of the research goal is significantly considered during the system design stage. Designing smart virtual expert system is the main research problem and this can be decomposed into four substantial research questions. Refer the following Table 1 represents the defined approach that addresses each research question.
Table 1. Research based question map with defined approach
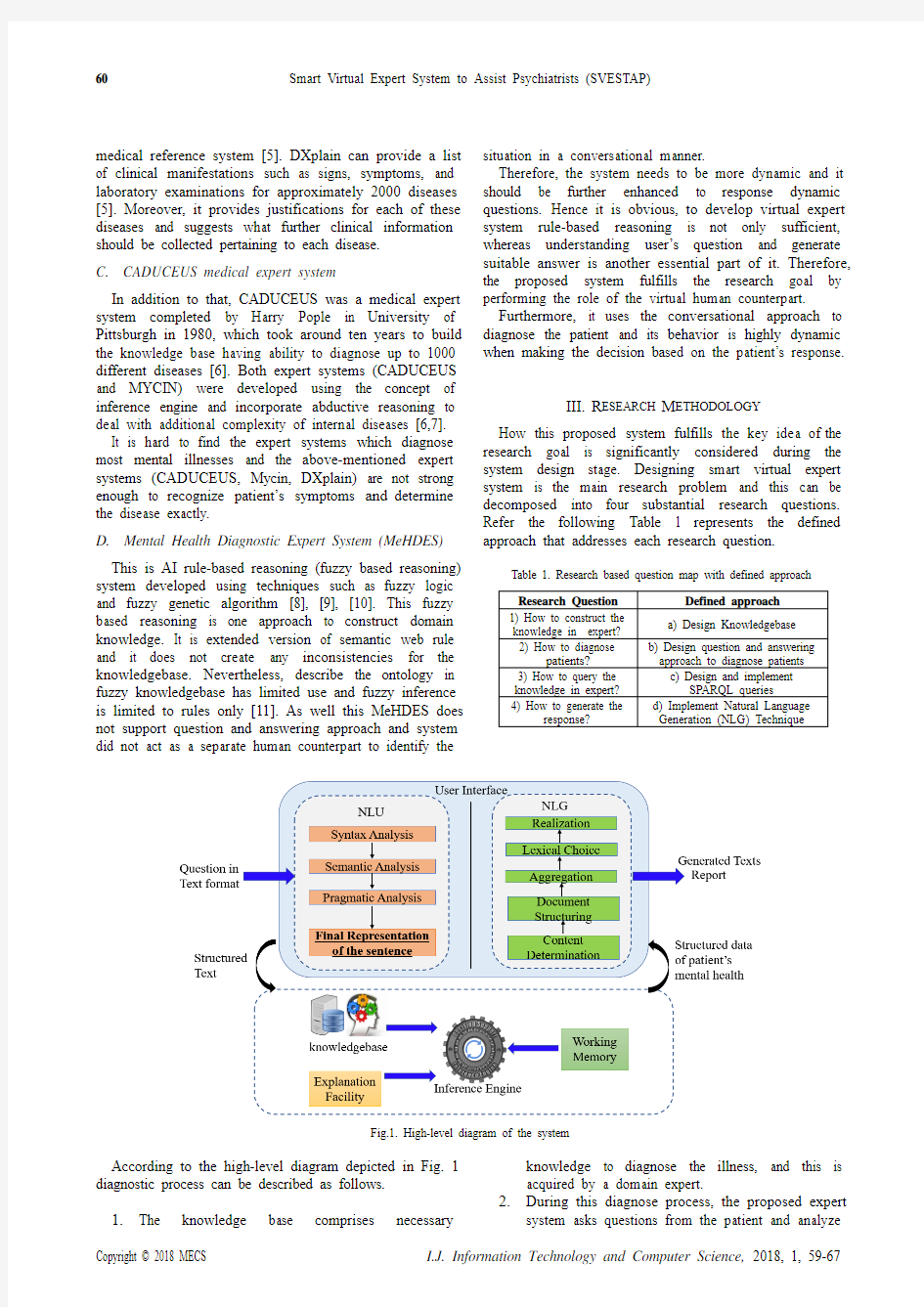
Fig.1. High-level diagram of the system
According to the high-level diagram depicted in Fig. 1 diagnostic process can be described as follows.
1. The knowledge base comprises necessary knowledge to diagnose the illness, and this is acquired by a domain expert.
2. During this diagnose process, the proposed expert
system asks questions from the patient and analyze
the patient ’s response using natural language understanding (NLU) technique.
3. This NLU technique analyzes those responses
(language: English) and extracts keywords to query the knowledge base.
4. SPARQL queries are used to query the
knowledgebase and extracts information based on the given keywords in step 3. Then find most
probable disease and send those results to the response formation process.
5. Natural language generation (NLG) technique is
used to form the response in human understandable manner.
The Fig. 2 represents interactions of each component in this proposed system.
Fig. 2. Interactions of each component in SVESTAP
A. Knowledgebase Construction for SVESTAP
The knowledgebase is the most important part in this SVESTAP to diagnose illnesses. The knowledgebase is constructed by mapping domain experts’ knowledge into an ontology [12]. For this, knowledge acquisition session is conducted with real human experts. Furthermore, to accomplish this knowledge acquisition process professional psychiatrist or panel of psychiatrists need to be interviewed through a questionnaire. This questionnaire should be meticulously planned to fully elicit the knowledge and experience of these experts. Especially, this diagnose process and judgment of diseases based on the symptoms, are performed during the discussion with patients. According to the symptoms of the patient, inference engine infers new knowledge using the embedded knowledge in the knowledge base. Ontology comprises the logical structure of data in Extensible Markup Language (XML) format and all rules pertaining to that domain can be stored as Semantic Web Rule Language (SWRL) rules [13]. During this construction process classes, object/data properties,
instances (individuals) and rules should be designed [14]. Standard books referred by psychiatrists (Eg. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorder/ Mental State Examination) are used to map those details to Ontology. Fig. 5 illustrates, how classes are linked with properties to construct relationships in the knowledgebase. To implement the ontology Protégé IDE is used and Fig. 3 depicts class hierarchy related to three mental diseases. It can be visualized Onto Graph view as represented in Fig. 4.
Fig.3. Class hiarachy in domain knowledge
Fig.4. Class hiarachy in Onto Graph view
Fig.5. Ontology relationships among classes and properties
B. Understand the Query Using NLU Technique NLU technique is used to understand the answer given by the user as depicted in Fig. 6. This can be further divided into sub-processes such as (Morphology, Syntax analysis, Semantic analysis, Pragmatics and Discourse analysis) [15, 16]
Fig.6. NLU Process
1. Morphology : Initially, the system breaks the long
natural language sentence into sub-sentences to derive the meaning of it.
2. Syntax analysis : In this process, it realizes the
relationships in between sentences through syntaxes. And mainly consider how words are put together to form the correct sentences and what structural role each word has.
3. Semantics analysis : In this step, consider how
these words are combined to derive the meaning of the sentence. Hence, the system can highlight which keyword is put through the knowledgebase. 4. Pragmatics: Sometimes the sentence gives
different meaning based on the context. As a result, in this step system considers how sentences are used in different situations and how it affects the interpretation of the sentence.
5. Discourse: In here, it considers how current
sentence affects to the interpretation of the next sentence. Therefore, the system can keep track of the next sentence to match ordinary keywords which are coming from the user ’s response.
NLU sub processes perform the following tasks to
elicit keywords from the sentence.
1. Split the sentence into words (Use the delimiter of
space to split the sentence into words).
2. Identify the tag of the words (e.g. noun phrases,
nouns, verb phrases, verbs, adjective, etc.).
3. Develop a method to identify keywords of the
sentence and negation of the sentence.
4. Develop a method to identify the synonyms of
keyword related to the answer (when keywords are not matched with the given context).
5. Develop a method to check whether any spellings
or grammatical mistakes in the sentence.
6. Send extracted keywords of the sentence to
knowledgebase querying process. C. Query the Knowledgebase and Diagnosing
Keywords are extracted from above section B stage (Understand the user’s question using NLU technique) and it is used to query the constructed domain knowledge to derive the correct disease. Query answering is important in semantic web and several query languages were designed for this purpose such as Resource Description Framework Data Query Language (RDQL), Second generation Resource Description Framework Query Language (SeRQL), and most recently used SPARQL [17]. SPARQL queries can be used across diverse data sources, to verify whether the data is stored natively as RDF or viewed as RDF via middleware [18]. SPARQL contains capabilities for querying required and optional graph patterns along with their conjunctions and disjunctions. The output of SPARQL queries can be results-sets or RDF graphs [18, 19].
E.g. Data in turtle format can be represented as below.
@prefix svestap:
Use following query to extract data
PREFIX svestap:
?x svestap:disease ?disease ?x svestap:symptom ?symptom
}
SPARQL uses “?” to define variables and SELECT clause define return ing variables as “?symptom” and “?disease” and WHERE clause define matching criteria. Fig. 7 illustrates sample query that retrieves disease by giving the set of symptoms. In here, there are four results sets fulfilling above criteria and following datasets are given as result set in Table 2.
Table 2. SPARQL Results set of matching criteria
Fig.7. SPARQL query to select disease from symptoms
During the conversation, the proposed expert system asks few questions from the patient and analyze patient’s responses to extract symptoms. From the NLU technique, symptoms were extracted and proceed to the next step of identifying disease category those symptoms belong to. Identify the exact disease based on the given symptoms is another key concern. This goal is accomplished in two stages as follows.
1.
First execute SPARQL queries separately for each
symptom and fetch all probable diseases for given symptom and categorize them as depicted in Fig. 8.
Fig.8. Sets of Diseases
E.g. Diseases ∈ {A, B, C, D} and Symptoms ∈ {X, Y, Z}, then diseases for symptoms are as follows,
Symptom X ∈ {Disease A, Disease B, Disease C}, Symptom Y ∈ {Disease C, Disease A, Disease D}, Symptom Z ∈ {Disease E, Disease C}.
2. Then find intersection of disease sets to find most
probable disease. Refer the Fig. 9 for interaction of diseases.
Symptom X ∩ Symptom Y = {Disease C},
Symptom X ∩ Symptom Z = {Disease C, Disease E}, Symptom Y ∩ Symptom Z = {Disease C},
Symptom X ∩ Symptom Y ∩ Symptom Z = {Disease C}.
Fig.9. Interaction of Diseases
If there is no disease which has all given symptoms, then proposed system get the disease with maximum number of matching diseases. Then the result will be passed to the NLG process to generate the response familiar to user.
D. Response Formation Using NLG Technique
Response formation is the final stage in the proposed system, after querying the knowledgebase (using SPARQL queries) the new inferred knowledge is given as set of keywords. To comprehend the final results, these keywords must be organized in a human-readable manner [20]. As depicted in Fig. 10, NLG process achieves this by converting keywords into human readable natural language sentences.
Fig.10. NLG Overview
Fig.11. Subprocess of NLG
NLG technique is implemented using Java language and separate library called “SimpleNLG” needs to be imported. This comprises inbuilt functions to accomplish the tasks depicted in Fig. 11 (Text planning, microplanning and realization) [22]. Sentence generation can be summarized as per the below three steps:
1. Develop a method to retrieve symptom keywords
from the knowledgebase.
2. Develop a method to include required words and
form meaningful phrases.
3. Develop a method to generate full sentence based
on small sentence-phrases using previously mentioned method.
To generate symptoms in question format for the user, separate xml document has been used to refer them as lexicons. The words in this xml document contains nouns, verbs, and complements (adjectives) refer Fig. 12. Then
keys are extracted from xml file using Xpath statements and “SimpleNLG” technique assists you to write a program which generates grammatically correct English sentences as illustrated in Fig. 13.
Fig.12. Lexicon keywords xml
Fig.13. Sentence Generation
After diagnosing the patient, the proposed system conducts a separate patient evaluation process to determine the intensity of the detected disease. This evaluation is performed by giving a Hypomania Checklist (HCL-32) standard questionnaire [21]. The intensity of the disease can be determined based on the
responses given for the questionnaire. In here, system acts as a separate human-counterpart and provides responses for the user’s questions.
IV. R ESULTS AND O UTCOME
This proposed system gives ten questions for the patient to answer and patient can answer them by using natural language sentences as shown in Fig. 14. The given response will be processed by the system and it elicits all symptoms from the response of patient to diagnose the disease. Then based on the given symptoms, it identifies the exact disease that patient is suffering from and formulate it as the response. The Fig. 15 represents, how it generates the response by inferring new knowledge.
Fig.14. Sample Q&A process with SVESTAP and Patient
Fig.15. Infer the disease based on symptoms
SVESTAP system was evaluated considering the factors such as understanding of the application, features included, usage of application, and willingness to use the application. From this evaluation positive and negative feedbacks were taken as illustrated in Table 3.
Table 3. User feedback summary
According to the chart depicted in Fig. 16 more than 80% of feedbacks were postive regarding the system usability and willingness to use the application is comparatively high.
Fig.16. User evaluation outcome of SVESTAP application
V. S UMMARY /C ONCLUSION
Nowadays the availability of experts to provide services symultaneously for multiple users would be a challenging task. To fullfill this problem, experimental analysis are conducted in many fields in developing similar virtual expert systems. Development of virtual experts would be an ideal solution but, validity of the made decision is questionable before applying them to real environment. Specially in medical domain, accuracy is the most decisive factor to be considered. As a result, development of expert system to assist real human expert would reduce upcoming risk in the medical domain. As the initial step, I would like to suggest a system that works with a real human expert, which maximizes accuracy factor of the made decision. Therefore, the decisions of disease judgement should always be aligned with actual psychiastrist and the end system response should be frequently evaluated. This system can be utilized for apprentices in the medical field to validate made disease judgement and to identify the root cause before proceeding for treatment.
R EFERENCES
[1] H. P. Selker and A. J. J. Wood, “Industry Influence on
Comparative-Effectiveness Research Funded through Health Care Reform,” New England Journal of Medicine ,
vol. 361, pp. 2595-2597, Dec 2009.doi:
10.1056/NEJMp0910747.
[2] A. Demirhan, "Pattern analysis for the neuroimaging
based diagnosis of schizophrenia," 2017 25th Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU), Antalya, Turkey, 2017, pp. 1-4.
[3] D. E. Heckerman, E. H. Shortliffe, “From certainty factors
to belief networks,” Artificial Intelligentce in Medicine, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 35-52, Feb 1992.
[4] C. WenBin, L. XiaoLing, L. YiJun and F. Yu, "A machine
learning algorithm for expert system based on MYCIN model," 2010 2nd International Conference on Computer Engineering and Technology, Chengdu, 2010, pp. V2-
262-V2-265.
[5]G. Barnett, J.J. Cimino, J.A. Hupp and E. P. Hoffer,
“Dxplain: An evolving diagnostic decision-support system,” Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), vol. 258, no. 1, pp. 67-74 1987.
[6]O. J. Ayangbekun, A. I. Olatunde and F. O. Bankole, “An
Expert System for Diagnosis of Blood Disorder,”
International Journal of Computer Applications (IJCA), vol. 100, no. 7, pp. 37-40, Aug 2014.
[7] C. V. D. Schatz and F. K. Schneider, “Intelligent and
Expert Systems in Medicine – A Review,”XVIII Congreso Argentino de Bioingeniería SABI 2011 - VII Jornadas de Ingeniería Clínica Mar del PlataSara, pp. 28 – 30, September, 2011, pp. 326-331.
[8] A. T. Owoseni, I. O. Ogundahunsi,"Mobile-Based Fuzzy
Expert System for Diagnosing Malaria (MFES)", International Journal of Information Engineering and Electronic Business(IJIEEB), Vol.8, No.2, pp.14-22, 2016.
DOI: 10.5815/ijieeb.2016.02.02.
[9]V. Jain, S. Raheja, "Improving the Prediction Rate of
Diabetes using Fuzzy Expert System", International Journal of Information Technology and Computer Science (IJITCS), no. 10, pp. 84 - 91, 2015. DOI: 10.5815 / ijitcs.
2015.10.10.
[10]T. W. Wlodarczyk, M.O'Connor, C. Rong, M. Musen,
"SWRL-F -A Fuzzy Logic Extension of the Semantic Web Rule Language"Available:https://www.360docs.net/doc/54728686.html,/ursw/2010/papers
/URSW2010_P1_WlodarczykEtAl.pdf.
[11]T. W. Wlodarczyk, M. O'Connor, C. Rong, M. Musen,
"SWRL-F-A Fuzzy Logic Extension of the Semantic Web Rule Language" Available: https://www.360docs.net/doc/54728686.html,/ursw/2010/papers/URSW2010_P1_Wl
odarczykEtAl.pdf.
[12]K. Balachandran and S. Ranathunga, "Domain-Specific
Term Extraction for Concept Identification in Ontology Construction," 2016 IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference on Web Intelligence (WI), Omaha, NE, 2016, pp. 34-41.
[13] B. Jafarpour, S. R. Abidi and S. S. R. Abidi, "Exploiting
Semantic Web Technologies to Develop OWL-Based Clinical Practice Guideline Execution Engines," in IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, vol. 20, no.
1, pp. 388-398, Jan. 2016. doi:
10.1109/JBHI.2014.2383840
[14]S. Sitthithanasakul and N. Choosri, "Application of
software requirement engineering for ontology construction," 2017 International Conference on Digital Arts, Media and Technology (ICDAMT), Chiang Mai, 2017, pp. 447-453. [15]M. Bates, “Models of natural language
understanding,”Proceedings of the National Academy of
Sciences, vol. 92, pp. 9977-9982, Oct 1995.
[16]W. G. Lehnert, M. H. Ringle, “Strategies for natural
language processing,” New York, Psychology Press, 2014.
[17]S. Im, M. Sohn, S. Jeong and H. J. Lee, "Keyword-Based
SPARQL Query Generation System to Improve Semantic
Tractability on LOD Cloud," 2014 Eighth International
Conference on Innovative Mobile and Internet Services in
Ubiquitous Computing, Birmingham, 2014, pp. 102-109.
doi: 10.1109/IMIS.2014.95
[18]I. Abdelaziz; M. R. Al-Harbi; S. Salihoglu; P. Kalnis,
"Combining Vertex-centric Graph Processing with
SPARQL for Large-scale RDF Data Analytics," in IEEE
Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, vol. PP, no. 99, pp. 1-1.
[19] A.Merazi, M. Malki, "SQUIREL: Semantic Querying
Interlinked OWLS traveling Process Models",
International Journal of Information Technology and
Computer Science (IJITCS), No. 12, pp. 30 –39, 2015.
DOI: 10.5815 / ijitcs. 2015.12.04.
[20]S. Puls, D. Lemcke and H. Worn, "Context-sensitive
natural language generation for human readable event logs
based on situation awareness in human-robot
cooperation," 2014 11th International Conference on
Ubiquitous Robots and Ambient Intelligence (URAI),
Kuala Lumpur, 2014, pp. 350-355.
[21]J. Angst et al, “The HCL-32: Towards a self-assessment
tool for hypomanic symptoms in outpatients,” Journal of
Affective Disorders, vol. 88, no. 2, pp. 217-233, Oct
2005.
[22]N. Dethlefs, "Domain Transfer for Deep Natural
Language Generation from Abstract Meaning
Representations," in IEEE Computational Intelligence
Magazine, vol. 12, no. 3, pp. 18-28, Aug. 2017. doi:
10.1109/MCI.2017.2708558.
Authors’ Profiles
Udara Srimath S. Samaratunge
Arachchillage received the M.Sc. degree
in Enterprise Application Development
from Sheffield Hallam University (SHU) in
Sheffield, UK and won the best performer
award in 2014. He received his B.Sc.
Special honour degree in field of
Information Technology (IT) from Sri Lanka Institute of Information Technology (SLIIT) in Sri Lanka in 2010 and B.Sc. degree in IT from Curtin University of Technology, Bentley, Perth, Western Australia in 2009.
He is a Researcher, Lecturer and Software Engineer and currently works as Research Engineer in Department of Software Engineering, Institute of Cybernetics, National Research Tomsk Polytechnic University, Russia and Lecturer in Faculty of Computing, Department of Software Engineering, Sri Lanka Institute of Information Technology (SLIIT) in Sri Lanka. His research interests are Semantic Web, Expert System, Knowledgebase construction, Natural Language Processing, Software Engineering, Human Computer Interaction, Wireless Communication.
He is a member of Computing Society of Sri Lanka (CSSL) and manuscript reviewer in IEEE.
How to cite this paper:Udara Srimath S. Samaratunge Arachchillage, "Smart Virtual Expert System to Assist Psychiatrists (SVESTAP)", International Journal of Information Technology and Computer Science(IJITCS), Vol.10, No.1, pp.59-67, 2018. DOI: 10.5815/ijitcs.2018.01.07
《人工智能与专家系统》试卷
《人工智能与专家系统》试卷 (1)参考答案与评分标准 问答题(每题5分,共50分)1.人工智能是何时、何地、怎样诞生的?(5分)答:人工智能于1956年夏季在美国达特茅斯(Dartmouth)大学诞生。(3分)1956年夏季,美国的一些从事数学、心理学、计算机科学、信息论和神经学研究的年轻学者,汇聚在Dartmouth大学,举办了一次长达两个月的学术讨论会,认真而热烈地讨论了用机器模拟人类智能的问题。在这次会议上,第一次使用了“人工智能”这一术语,以代表有关机器智能这一研究方向。这是人类历史上第一次人工智能研讨会,标志着人工智能学科的诞生,具有十分重要的意义。(2分) 2.行为主义是人工智能的主要学派之一,它的基本观点是什么?(5分)答:行为主义,又称进化主义或控制论学派。这种观点认为智能取决于感知和行动(所以被称为行为主义),它不需要知识、不需要表示、不需要推理。其原理是控制论和感知——动作型控制系统。 3.什么是知识表示?在选择知识表示方法时,应该考虑哪几个因素?(5分)答:知识表示是研究用机器表示知识的可行性、有效性的般方法,是一种数据结构与控制结构的统一体,既考虑知识的存储又考虑知识的使用。知识表示实际上就是对人类知识的一种描述,以把人类知识表示成计算机能够处理的数据结构。对知识进行表示的过程就是把知识编码成某种数据结构的过程。
(3分) 在选择知识表示方法时,应该考虑以下几个因素:(1)能否充分表示相关的领域知识;(2)是否有利于对知识的利用;(3)是否便于知识的组织、维护和管理;(4)是否便于理解和实现。(2分)4.框架表示法有什么特点?(5分) 答:框架表示法有如下特点:结构性、继承性、自然性。(5分)5.何谓产生式系统?它由哪几部分组成?(5分) 答:把一组产生式放在一起,让它们相互配合,协同作用,一个产生式生成的结论可以供另一个产生式作为已知事实使用,以求得问题的解,这样的系统称为产生式系统。(2分) 产生式系统一般由三个基本部分组成:规则库、综合数据库和推理机。(3分)6.产生式系统中,推理机的推理方式有哪几种?请分别解释说明。(5分)答:产生式系统推理机的推理方式有正向推理、反向推理和双向推理三种。正向推理:正向推理是从己知事实出发,通过规则库求得结果。反向推理:反向推理是从目标出发,反向使用规则,求证已知的事实。双向推理:双向推理是既自顶向下又自底向上的推理。推理从两个方向进行,直至在某个中间界面上两方向结果相符便成功结束;如两方衔接不上,则推理失败。
人工智能与专家系统复习
人工智能与专家系统复习尹朝庆,尹皓中国水利水电出版社 第一章 【P1】1.1何谓人工智能?人类智能主要包括哪些能力? 答:人工智能是研究、设计和应用智能机器或智能系统,来模拟人类智能活动的能力、以延伸人类智能的科学。 四种能力: 认识和理解外界环境的能力; 进行演绎和归纳推理、作出决策的能力; 学习的能力; 自适应的能力。 【P6-8】1.4人工智能有哪几个主要学派?各学派的基本理论框架和研究方法有何不同?答:(1)符号主义学派的框架: 知识是智能的基础,人工智能的核心问题是知识表示和知识推理,可以用一个符号系统在计算机上形式化的描述和模拟人的思维活动过程。 研究方法:功能模拟方法,力图用数理逻辑方法来建立人工智能的统一理论体系。 (2)联接主义学派的框架: 利用人工神经网络模仿人类智能,认为人的智能的基本单位是神经元,由人工神经元联接起来的人工神经网络可以具有学习和自适应能力。 研究方法:结构模拟。 (3)行为主义学派的框架: 提出智能行为的“感知-动作模式”。 研究方法:行为模拟方法。 【P8-9】1.5人工智能的近期研究目标和远期研究目标分别是什么? 近期:建造智能计算机。 远期:研究人类智能和机器智能的基本原理,用智能机器来模拟人类的思维过程和智能行为。 【P9-12】1.6人工智能主要的研究应用领域? 十条:定理证明;专家系统;机器学习;自然语言理解;智能检索;机器人学;自动程序设计;组合调度问题;模式识别;机器视觉。 第二章 【P19】2.2简述谓词逻辑中的下述推理规则: (1)P规则:在推理的任何步骤上都可引入前提; (2)T规则:在推理时,如果前面步骤中有一个或多个公式永真蕴含公式S,则可把S引入推理过程中; (3)CP规则:如果能从R和前提集合中推出S来,则可从前提集合推出R→S。 (4)反证法规则:P=>Q,当且仅当P∧┑Q<=>F。即Q为P的逻辑结论,当且仅当P∧┑Q是不可满足的。 【P20-21】2.3一阶谓词逻辑表示法适合于表示哪种类型的知识?它有主要哪些特点? 答:谓词逻辑适合于表示事物的状态、属性、概念等事实性的知识,也可以用来表示事物间确定的因果关系,即规则。
人工智能专家系统论文
人工智能专家系统概述 摘要:人工智能(Artificial Intelligence) ,英文缩写为AI。它是研究、开发用于模拟、延伸和扩展人的智能的理论、方法、技术及应用系统的一门新的技术科学。人工智能是计算机科学的一个分支,它企图了解智能的实质,并生产出一种新的能以人类智能相似的方式做出反应的智能机器,该领域的研究包括机器人、语言识别、图像识别、自然语言处理和专家系统等。 专家系统是人工智能应用研究的主要领域。专家系统是一个具有大量的专门知识与经验的程序系统,它应用人工智能技术和计算机技术,根据某领域一个或多个专家提供的知识和经验,进行推理和判断,模拟人类专家的决策过程,以便解决那些需要人类专家处理的复杂问题,简而言之,专家系统是一种模拟人类专家解决领域问题的计算机程序系统。 关键词:人工智能,专家系统。 Abstract: The artificial intelligence (Artificial Intelligence), English abbreviation is AI. It is the research, the development uses in simulating, extending and expands human's intelligence theory, the method, technical and an application system new technical science. The artificial intelligence is a computer science branch, it attempts the understanding intelligence the essence, the parallel intergrowth delivers one kind newly to be able to make the response by the human intelligence similar way the intelligent machine, this domain research including robot, language recognition, pattern recognition, natural language processing and expert system and so on. An expert system is artificial intelligence application research of the main fields. An expert system is a has a large number of specialized knowledge and experience of the program system, it used artificial intelligence technology and computer technology, according to a field one or more experts to provide the knowledge and experience, reasoning and judgment, simulation of human experts decision-making process, so as to solve the need to deal with complicated problems of human experts, in short, the expert system is a kind of simulation to solve the problem domain experts human
医疗专家系统方法
医生一般是 ①通过询问病史、体格检查、实验室检查和辅助检查手段搜集临床资料;②整理、分析、评价资料;③提出诊断;④给出治疗处理。 医学专家系统的推理方法: 1.基于规则推理 基于规则的推理是从领域专家那获取问题求解的知识,概括、转化为易于被计算机表示和推理的形式,然后以知识库中已有知识构成的规则为基础,将初始证据与知识库中的规则进行匹配的推理技术。而当知识库中的规则太多时会导致系统推理前后产生矛盾,另外,自学习能力很弱。 2.基于案例推理 基于案例的推理是通过查找知识库中过去同类问题的解决方案从而获得当前问题解决的一种推理模式,这一过程与医生看病采取的方法很相似。然而这种系统也有局限性:怎样有效地表示病例以及如何在大型病例库中快速有效地检索相似病例等问题。 3.模糊数学推理 模糊推理是运用模糊数学的理论建立模型,对不明确的信息进行分类,解决用一般数学模型难以描述的高度复杂和非线性的问题。 4.基于规则的神经网络推理 在许多疾病的诊断中,由于获得的临床信息可能不完整又含有假象,经常遇到不确定性信息,决策规则可能相互矛盾,有时表现无明显的规律可循,这给传统推理方法的专家系统应用造成极大困难。人工神经网络(artificial neural network,ANN)能突破这些障碍。但也存在缺点:①仅适用于解决一些规模较小的问题;②系统的性能在很大程度上受训练数据集的限制,难以解决异类数据源的融合和共享;③知识提取过程繁杂而低效。④得出结论的“黑箱”特征也限制了系统对诊断结果的解释功能。
医学专家系统的发展趋势 医学专家系统可借鉴数据库关于信息存贮、共享、并发控制和故障恢复技术,对知识库的管理、设计以及大型知识库、共享知识库和分布式知识库提供帮助,改善专家系统的特性,扩大规模。 将多媒体技术应用于医学专家系统,可集多种知识表达形式为一体(文字、图形、图像、影像及声音);能够充分发挥其高速处理综合问题的特点,提高系统识别速度,有效地模拟医生在临床诊断中用的直觉和模拟诊断功能;并具有友好的用户界面,系统将能以类似人类专家的方式来传播信息,与用户深入沟通,用户可向系统寻求解释、咨询、谈话;利用多媒体专家系统的知识获取模块,采用图像扫描器,可直接将医学图像及精确的解剖位置转化为系统内部知识表示,也可由人类专家用话筒直接向系统传授知识,从而使知识获取更方便。 将网络技术用于医学专家系统,一是可采用分布式知识库结构,将知识按其专业和特点分为若干个相关的知识库,提高数据的安全性,方便用户访问数据;二是可采用分布式推理机制,改善应用环境的系统运行能力,提高专家系统推理的速度和灵活性;三是可采用分布式结构,在一个网络运行多个专家系统,为疑难杂症诊断提供多种途径;四是远程医疗的蓬勃发展和网上医疗站的出现。 ⑴医学专家系统应以解决一些特殊的问题为目的。这些特殊的问题在计算机视觉和人工智能方面没有被研究过。人类对可视图案的认识不同于常规的推理, 并且代表明确的领域知识常常在视觉认识过程中下意识地忽略了被用到的那些因素。 ⑵医学专家系统的模型可能会是以多种智能技术为基础, 以并行处理方式、自学能力、记忆功能、预测事件发展能力为目的。目前发展起来的遗传算法、模糊算法、粗糙集理论等非线性数学方法, 有可能会跟人工神经网络技术、人工智能技术综合起来构造成新的医学专 家系统模型。
人工智能小型专家系统的设计与实现解读
人工智能技术基础实验报告 指导老师:朱力 任课教师:张勇
实验三小型专家系统设计与实现 一、实验目的 (1)增加学生对人工智能课程的兴趣; (2)使学生进一步理解并掌握人工智能prolog语言; (3)使学生加强对专家系统课程内容的理解和掌握,并培养学生综合运用所学知识开发智能系统的初步能力。 二、实验要求 (1)用产生式规则作为知识表示,用产生系统实现该专家系统。 (2)可使用本实验指导书中给出的示例程序,此时只需理解该程序,并增加自己感兴趣的修改即可;也可以参考该程序,然后用PROLOG语言或其他语言另行编写。 (3)程序运行时,应能在屏幕上显示程序运行结果。 三、实验环境 在Turbo PROLOG或Visual Prolog集成环境下调试运行简单的PROLOG程序。 四、实验内容 建造一个小型专家系统(如分类、诊断、预测等类型),具体应用领域由学生自选,具体系统名称由学生自定。 五、实验步骤 1、专家系统: 1.1建造一个完整的专家系统设计需完成的内容: 1.用户界面:可采用菜单方式或问答方式。
2.知识库(规则库):存放产生式规则,库中的规则可以增删。 3.数据库:用来存放用户回答的问题、已知事实、推理得到的中 间事实。 4.推理机:如何运用知识库中的规则进行问题的推理控制,建议 用正向推理。 5.知识库中的规则可以随意增减。 1.2推理策略 推理策略包括:正向(数据驱动),反向(目标驱动),双向 2、动物分类实验规则集 (1)若某动物有奶,则它是哺乳动物。 (2)若某动物有毛发,则它是哺乳动物。 (3)若某动物有羽毛,则它是鸟。 (4)若某动物会飞且生蛋,则它是鸟。 (5)若某动物是哺乳动物且有爪且有犬齿且目盯前方,则它是食肉动物。(6)若某动物是哺乳动物且吃肉,则它是食肉动物。 (7)若某动物是哺乳动物且有蹄,则它是有蹄动物。 (8)若某动物是有蹄动物且反刍食物,则它是偶蹄动物。 (9)若某动物是食肉动物且黄褐色且有黑色条纹,则它是老虎。 (10)若某动物是食肉动物且黄褐色且有黑色斑点,则它是猎豹。 (11)若某动物是有蹄动物且长腿且长脖子且黄褐色且有暗斑点,则它是长颈鹿。 (12)若某动物是有蹄动物且白色且有黑色条纹,则它是斑马。 (13)若某动物是鸟且不会飞且长腿且长脖子且黑白色,则它是驼鸟。
疾病诊断专家系统
目录 摘要............................................... 错误!未定义书签。Abstact............................................ 错误!未定义书签。第一章绪论........................................ 错误!未定义书签。 1.1引言........................................ 错误!未定义书签。 1.2问题的提出.................................. 错误!未定义书签。 1.3可行性分析.................................. 错误!未定义书签。 2.1专家系统概述................................ 错误!未定义书签。 2.1.1什么是专家系统........................ 错误!未定义书签。 2.1.2专家系统的组成........................ 错误!未定义书签。 2.1.3专家系统的应用领域.................... 错误!未定义书签。 2.2 知识库..................................... 错误!未定义书签。 2.3推理原理.................................... 错误!未定义书签。 2.3.1推理概念及分类........................ 错误!未定义书签。第三章鸡疾病诊断专家系统知识库的研究............. 错误!未定义书签。 3.1鸡疾病诊断专家系统介绍...................... 错误!未定义书签。 3.2鸡疾病诊断专家系统设计...................... 错误!未定义书签。 3.2.1系统功能.............................. 错误!未定义书签。 3.2.2 鸡疾病诊断专家系统知识开发的技术流程.. 错误!未定义书签。 3.2.3 鸡疾病诊断专家系统知识库的设计........... 错误!未定义书签。 3.3.1 知识表示.............................. 错误!未定义书签。第四章系统调试................................... 错误!未定义书签。 4.1 Prolog软件介绍............................. 错误!未定义书签。 4.1.1 Prolog语言的特征..................... 错误!未定义书签。 4.1.2 Prolog语言基本语句................... 错误!未定义书签。 4.2 程序调试................................... 错误!未定义书签。 4.2.1 推理机的概述.......................... 错误!未定义书签。 4.2.2 推理机的使用.......................... 错误!未定义书签。 4.2.2 调试结果.............................. 错误!未定义书签。第五章毕业设计小结................................ 错误!未定义书签。 5.1论文小结.................................... 错误!未定义书签。 5.2 知识库发展的趋势........................... 错误!未定义书签。致谢............................................... 错误!未定义书签。参考文献........................................... 错误!未定义书签。附录一源程序...................................... 错误!未定义书签。
鱼病诊断专家系统设计
中国农业大学学报 2000,5(6):94~97 Journal of Ch ina A gricultural U niversity 鱼病诊断专家系统设计① 郑育红① 傅泽田 张小栓 (中国农业大学农业工程研究院) 摘 要 叙述了智能化鱼病诊断专家系统的总体设计思路与设计方法、关键技术及系统工作流程。重点阐述了智能化鱼病诊断的过程、基本内容以及推理机的基本原理。 关键词 专家系统;鱼病诊断;推理机 分类号 T P182;S942 D esign of An Expert System for F ish D isea se D i agnosis Zheng Yuhong Fu Zetian Zhang X iao shuan (A gricultural Engineering Institute,CAU) Abstract System specialty,design m ethod,co llectively design though t,system w o rk ing p rocess of fish disease expert system and key techno logy of the expert system are discu ssed. P rocess and basic con ten t of fish disease diagno sis,basic p rinci p le of rati ocinati on are in troduced. Key words expert system;fish disease diagno sis;rati ocinati on 智能化鱼病诊断专家系统是国家863重点资助项目“智能化水产养殖信息系统”的子系统,本系统以系统工程思想为指导,利用人工智能技术将水产领域专家知识加以归纳整理,使其系统化和形式化,从而为生产管理部门、鱼病医院提供鱼病诊断与防治的辅助决策工具,为广大养鱼专业户提供鱼病识别和防治等技术指导[1]。 1 鱼病诊断专家系统的主要内容及工作流程 111 主要内容 鱼病诊断专家系统由现场调查、目检、深层判断、镜检、解释机制多个模块集成,各模块主要内容如下。 现场调查模块包括对鱼类名称、生长阶段、发病时间、特殊表现、水质调查等项目的调查记录。 目检模块包括对体表、头部、鳃部、腹部、鳞片、鱼鳍、肌肉、内脏等8个项目的观察诊断。其中,体表具有22种不同的症状,头部有12种,鳃部18种,腹部4种,鳞片6种,鱼鳍9种,肌肉5种,内脏17种,共93种症状描述,186张图片。对应每种不同的症状,具有相应的图片描述。 深层判断模块是对应目检得出的多种结果而进行的。进行深层判断时,根据目检结果,判 收稿日期:20000414 ①国家863计划306主题重点资助项目 ②郑育红,北京清华东路17号中国农业大学(东校区)121信箱,100083
医疗诊断专家系统研究进展
收稿日期:2001-08-24 作者简介:邵 虹,博士研究生,讲师.目前主要从事医学图像检索、图像处理和专家系统等研究.E-mail:shaoh @neusoft .com 崔文成,硕士研究生.助理研究员,研究方向为数据挖掘、网络等.张继武,博士.教授,博士生导师.研究方向为医学多媒体信息处理及通信技术等.赵 宏,教授,博士生导师,研究方向为分布式多媒体信息系统及多媒体网络技术. 医疗诊断专家系统研究进展 邵 虹1,2 崔文成2 张继武3 赵 宏1 1( 东北大学软件中心,辽宁沈阳110179) 2( 沈阳工业大学,辽宁沈阳110023) 3(中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所,陕西西安710068) 摘 要:专家系统是人工智能领域的重要分支,医疗诊断专家系统可以作为医生诊断的一种辅助工具.本文从医疗诊断专家系统中的知识表示、推理机制等理论知识和实践研究两方面,对其研究现状进行了回顾.关键词:专家系统;医疗诊断 中图分类号:T P 391 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1000-1220(2003)03-0509-04 Research Advances on Medical Diagnosis Expert System SHAO Hong 1,2,CU I Wen-cheng 2,ZHA NG Ji-w u 3,ZHA O Ho ng 1 1( S ef tw are Center ,N or theaster n Univer sity ,S heny ang 110179,China ) 2( She nyang Unive rsity of T echnology ,S henyang 110023,China ) 3 (X i an Institute of Op tics &P recision M echanics ,S inic Ac ad emy of S cience ,X i an 710068,China ) Abstract :Expert sy stem is an impor tant embra nchment of ar tifical intellig ent ,medical diag no sis exper t system may be assistant to ol for docto r s dia gnosis .T his paper r ev iew s resear ch adva nces on m edical diag no sis practice and theo ries including know ledg e repr esentat ion,inference,etc.Key words :exper t system ;medical diag no sis 1 引 言 专家系统是当前人工智能研究中最活跃的分支之一,它实现了人工智能从理论研究走向实际应用,从一般思维方法探讨转入专门知识运用的重大突破.从20世纪70年代开始,人们着手进行“医疗诊断专家系统”的研究工作,美国斯坦福大学最先于1974年开发出了性能较高、功能较全的M Y CIN 系统,用于帮助内科医生诊治感染性疾病.在这之后将近三十年的时间内,国内外都投入了巨大的力量进行研究与开发,有了一定的进展,但真正能为医生所接受并投入实际临床使用的为数极少. 能够诊断疾病的专家系统可以帮助医生解决复杂的医学问题,可以作为医生诊断的辅助工具,可以继承和发扬医学专家的宝贵理论以及丰富的临床经验,特别是对那些年轻无经验的医生,能够帮助他们提高诊断技能,为患者提供最佳的诊断方案.医疗诊断领域是信息处理技术的一个前景十分广阔的应用领域.但是,要想在该领域内取得真正有意义的发展,必须认真研究过去的医疗专家系统.下面将从理论和实践两方面对医疗诊断专家系统进行回顾. 2 医疗诊断专家系统的理论研究 知识表示和推理机制是人工智能的重要研究课题,是专家系统的核心.2.1 医学知识的表示 所谓知识表示是指将问题领域的知识和专家的经验知识用适当的结构表示出来,且便于在计算机中存储、检索和修改,知识表示是知识处理中最基本的问题,因为各种领域的知识必须表示成某种形式才能被记录下来,没有知识表示就谈不上知识使用.目前,已经提出了许多较为成熟而又针对特定领域的知识表示方法,常用的有:谓词逻辑表示法,产生式系统,框架理论,语义网络等.下面介绍在医疗诊断专家系统中所用到的几种知识表示方法. 产生式规则是目前应用最为广泛的一种知识表示方法.规则描述的是事物间的因果关系,规则的产生式表示形式常称为产生式规则,简称为产生式,或规则.产生式表示法易于理解,能充分表示与问题有关的推理规则和行为,较好地体现了动态知识即专家的经验知识.其基本形式是“IF a T HEN b ”,IF 部分称为前提,T HEN 部分称为操作.它说明在产生式系统的执行过程中,如果某条规则的条件部分被满足,那么这条规则就可以被应用,即可以给出结论或触发另一条规则.这种方法的缺点是:由于疾病的种类繁多,症状各异,因而需要的规则很多. 第24卷第3期 2003年3月 小型微型计算机系统M IN I -M ICR O SY ST EM S V ol .24N o .3 M ar .2003
远程农作物病虫害诊断专家系统的设计与实现
摘要 本文论述了集成农作物种植理论和实用技术、远程农作物病虫害诊断专家系统的构建和实现。在比较国内外农业专家系统构思的基础上,论证了本系统实施的方案,实现了农作物病虫害诊断专家系统的网络化,扩大了农作物病虫害诊断专家系统应用的空间范围。文中主要以病害诊断为例着重介绍了规则库的建立、推理机的设计。论文前半部分首先对农作物病虫害诊断专家系统研究的背景、课题的研究内容、农业专家系统在国内外的研究、专家系统概况作了较全面的介绍和阐述,说明了本课题的研究目的和意义,接着对本课题专家系统的核心部分——知识表示和推理机的设计进行了阐述。论文后半部分是对于专家系统的总体设计、数据库设计以及界面功能进行了详细论述,并用其设计专家系统开发平台的框架模型。 关键词:农业专家系统推理机病虫害
Abstract This paper discusses the structure and achievement of the theory of integrated crop planting, practical technology and the expert system of remote crop diseases and insect pests diagnosis. Contrast of the domestic and foreign agricultural expert system conception, it demonstrates the system of the implementation of the scheme that realizing the network of the expert system of remote crop diseases and insect pests diagnosis and enlarging the spatial dimension.It introduces the establishment of rule-base and the design of the inference engine which takes disease screening as example.The preceding half part of thesis stresses the background and content of expert system of remote crop diseases and insect pests diagnosis, also states of research both at home and broad and general situation of expert system. Then introduce the main part that is the design of the inference engine.The last part of the thesis analyzes the overall design of expert system, base design and Interface and Function in order to apply to the model. Key words:Agricultural expert system,inference engine,diseases and pests
人工智能专家系统论文
人工智能专家系统论文 摘要:人工智能是研究、开发用于模拟、延伸和扩展人的智能的理论、方法。 技术及应用系统的一门新的技术科学。该领域的研究包括机器人、语言识别、图像识别、自然语言处理和专家系统等。其中专家系统是一种模拟人类专家解决领域问题的计算机程序系统。它应用人工智能技术和计算机技术,根据某领域一个或多个专家提供的知识和经验,进行推理和判断,模拟人类专家的决策过程,求解需要专家才能解决的困难问题。 关键词:计算机,人工智能,专家系统 引言: 人工智能(Artificial Intelligence) ,英文缩写为AI。它是研究、开发用于模拟、延伸和扩展人的智能的理论、方法、技术及应用系统的一门新的技术科学。从基础理论的角度出发,其研究基本内容包括:知识表示、自动推理和搜索方法、机器学习和知识获取、知识处理系统、自然语言理解、计算机视觉、智能机器人、自动程序设计等方面。 人工智能系统的开发和应用,已为人类创造出可观的经济效益,专家系统就是一个例子。随着计算机系统价格的继续下降,人工智能技术必将得到更大的推广,产生更大的经济效益。 专家系统(expert system)是一个智能计算机程序系统,其内部含有大量的某个领域专家水平的知识与经验,能够利用人类专家的知识和解决问题的方法来处理该领域问题。也就是说,专家系统是一个具有大量的专门知识与经验的程序系统,它应用人工智能技术和计算机技术,根据某领域一个或多个专家提供的知识和经验,进行推理和判断,模拟人类专家的决策过程,以便解决那些需要人类专家处理的复杂问题,简而言之,专家系统是一种模拟人类专家解决领域问题的计算机程序系统。 专家系统属于人工智能的一个重要发展分支,并且应用于数学、物理、医疗、军事、地质勘探、气象、农业、法律、教学、化工、机械、艺术以及计算机科学本身,甚至渗透到政治、经济、军事等重大决策部门,产生了巨大的经济效益和社会效益。现在,专家系统已成为人工智能领域中最活跃、最受重视的领域。[1].[2] 一、专家系统 1.1 专家系统的特点 (1).具有专家水平的专业知识:专家系统中的知识按其在问题求解中的作用可分为三个层次,既数据级、知识库级、控制级。数据级知识是指具体问题所提供的初始事实及在问题求解过程中所产生的中间结论、最终结论。数据级知识通常存放与数据库中。知识库知识是指专家的知识。这一类知识是构成专家系统的基础。控制级知识也称为元知识,是关于如何应用前两种知识的知识,如在问题求解中的搜索策略、推理方法等。具有专家专业水平是专家系统的最大特点。专家系统具有的知识越丰富,质量越高,解决问题的能力就越强。 (2).能进行有效的推理:专家系统要利用专家知识来求解领域内的具体问题,必须有一个推理机构,能根据用户提供的已知事实,通过应用知识库中的知识,进行有效的推理,以实现问题的求解。 (3).启发性:专家系统能利用经验的判断知识来对求解的问题作出多个假设。依据某些条件选定一个假设,是推理继续进行。
人工智能习题&答案-第6章-专家系统
第六章专家系统 6-1 什么叫做专家系统?它具有哪些特点与优点? 专家系统是一种模拟人类专家解决领域问题的智能计算机程序系统,其内部含有大量的某个领域专家水平的知识与经验,能够利用人类专家的知识和解决问题的方法来处理该领域问题。也就是说,专家系统是一个具有大量的专门知识与经验的程序系统,它应用人工智能技术和计算机技术,根据某领域一个或多个专家提供的知识和经验,进行推理和判断,模拟人类专家的决策过程,以便解决那些需要人类专家处理的复杂问题。 特点: (1)启发性 专家系统能运用专家的知识与经验进行推理、判断和决策 (2)透明性 专家系统能够解释本身的推理过程和回答用户提出的问题,以便让用户能够了解推理过程,提高对专家系统的信赖感。 (3) 灵活性 专家系统能不断地增长知识,修改原有知识,不断更新。 优点: (1) 专家系统能够高效率、准确、周到、迅速和不知疲倦地进行工作。 (2) 专家系统解决实际问题时不受周围环境的影响,也不可能遗漏忘记。 (3) 可以使专家的专长不受时间和空间的限制,以便推广珍贵和稀缺的专家知识与经验。 (4) 专家系统能促进各领域的发展,它使各领域专家的专业知识和经验得到总结和精炼,能够广泛有力地传播专家的知识、经验和能力。 (5) 专家系统能汇集多领域专家的知识和经验以及他们协作解决重大问题的能力,它拥有更渊博的知识、更丰富的经验和更强的工作能力。 (6) 军事专家系统的水平是一个国家国防现代化的重要标志之一。 (7) 专家系统的研制和应用,具有巨大的经济效益和社会效益。 (8) 研究专家系统能够促进整个科学技术的发展。专家系统对人工智能的各个领域的发展起了很大的促进作用,并将对科技、经济、国防、教育、社会和人民生活产生极其深远的影响。
诊断专家系统
诊断专家系统 【摘要】 人工智能是研究、开发用于模拟、延伸和扩展人的智能的理论、方法。技术及应用系统的一门新的技术科学。该领域的研究包括机器人、语言识别、图像识别、自然语言处理和专家系统等。其中专家系统是一种模拟人类专家解决领域问题的计算机程序系统。它应用人工智能技术和计算机技术,根据某领域一个或多个专家提供的知识和经验,进行推理和判断,模拟人类专家的决策过程,求解需要专家才能解决的困难问题。 【关键词】计算机,人工智能,专家系统 引言 随着科学技术的发展,装备的结构越来越复杂,功能也越来越完善,自动化程度越来越高,不但同一设备的不同部分之间相互关联,紧密耦合,而且不同设备之间也存在着紧密的联系,在运行过程中形成一个整体。一处故障可能引起一系列连锁反应,导致整个过程不能正常运行,甚至会造成重大的损失。因此,对故障诊断的要求也越来越高。另一方面,人工智能技术近年来得到很大发展,基于知识的故障诊断专家系统已成为当前研究和应用的一个热点。 人工智能又称机器智能,是计算机科学中新兴的一门边缘科学技术,利用计算机模拟人的智能行为、完成能表现出人类智能的任务。故障诊断专家系统是将人类在故障诊断方面的多位专家具有的知识、经验、推理、技能综合后编制成的大型计算机程序,它可以利用计算机系统帮助人们分析解决只能用语言描述、思维推理的复杂问题,扩展计算机系统原有的工作范围使计算机系统有了思维能力,能够与决策者进行“对话”,并应用推理方式提供决策建议,专家系统在故
障诊断领域的应用非常广泛,故障检测与诊断技术与专家系统相结合,使工程的安全性与可靠性得到保证。 1故障诊断专家系统简介 故障诊断专家系统,是指计算机在采集被诊断对象的信息后,综合运用各种规则(专家经验),进行一系列的推理,必要时还可以随时调用各种应用程序,运行过程中向用户索取必要的信息后,可快速地找到最终故障或最有可能的故障,再由用户来证实。专家系统故障诊断方法 可用下图的结构来说明:它由数据库、知识库、人机接口、推理机等组成。其各部分的功能为: 图1:故障诊断专家系统结构图 (1)数据库数据库通常由动态数据库和静态数据库两部分构成。静态数据库是相对稳定的参数,如设备的设计参数、固有频率等;动态数据库是设备运行中所检测到的状态参数,如工作转速、介质流量、电压或电流等。 (2)知识库存放的知识可以是系统的工作环境、系统知识(反映系统的工作机理及系统结构知识)、设备故障特征值、故障诊断算法、推理规则等,反映系统的因果关系,用来进行故障推理。知识库是专家领域知识的集合。 (3)人机接口人与专家系统打交道的桥梁和窗口,是人机信息的交接点。 (4)被诊断对象 人机接口 数据库 人机推理 结果 知识库
奶牛疾病诊断专家系统的设计说明
奶牛疾病诊断专家系统(人工智能期中作业) 学号:2007117019 班级:07级计科二班 姓名:陈青
奶牛疾病诊断专家系统 1.前言 专家系统是一个只能的计算机程序,它利用专家知识和经验解决领域难题。在过去的几十年发展中,专家系统已经成功地应用于各个领域,特别是疾病诊断领域专家系统的研究与应用更是呈现出蓬勃发展的景象,动物疾病诊断专家系统也位于其列。本文就奶牛疾病诊断专家系统的开发,对系统中的表示方法,知识库的监理方法,推理机的设计和实现以及推理过程作了全面的 阐述和讨论。2.正文 一、专家系统的任务与目标 1.奶牛疾病诊断知识的获取 2.奶牛疾病诊断专家系统推理机的研制 3.奶牛疾病诊断专家系统原型机实现 专家系统总体结构 二、专家系统的整体结构个部分:知识库、综合数据库、推理机、解释部分、专家系统基本结构一般包括以下6人机接口和知识获取机。(1) 用户界面统提供用户界面是用户同系统交流的通信机制。通过用户界面,用户选择系 的事实(问题的答案),回答系统提问,完成奶牛疾病诊断;查看相关资料和信息,进行有关知识咨询;系统为用户提供相关信息,进行有关知识咨询;系统为用户提供相关信息。 (2)解释机
基于规则的系统的一个最大特色就是具有解释功能,可以向用户解释系统为什么采用了一条规则,得出结论的依据是什么以及为什么向用户提问一定的问题等。 (3)推理机 推理机是系统根据用户提供的信息进行推理,最终得出结论的模块。 (4)其他数据库 该库由3个主要数据库组成。 动态数据库是系统在运行期间产生的一个临时数据库,用于存储用户提供的事实、系统激活的规则、系统产生的中间解以及系统中断的推理过程等。 多媒体数据库是为适应信息及其相关技术的迅速发展和应用而添加于专家系统中的辅助诊断信息库,它提供了与奶牛疾病诊断和治疗有关的图片、声音、影像和动画等资料。 防治措施库是存放防治措施和其他有关奶牛疾病相关的文字内容的数据库。 (5)知识库 该系统中采用了将事实库作为知识库的一部分的构造方法,因为奶牛疾病诊断知识的特殊性,把事实库中的事实作为界面上位用户提供的供选答案,因此,实时库中的所有事实都会在规则库中有完全匹配的规则,其实际作用相当与规则的前件。规则库是存放规则的所在。(6)知识编辑器 该系统采用了基于数据库的系统构建模式,系统中的知识库和所有数据库都是完全独立于系统的其他模块之外,知识编辑器是一个实施知识库的修改、删除、增加、检验的模块。 1.知识的获取与知识库的建立 奶牛疾病诊断知识的结构(1)对奶牛疾病诊断知识进行分析,并且完成对知识结构的划分,设计推理策略和建立知识库的前提条件。根据奶牛疾病诊断知识的特点,从3个方面对知识进行了从层次结构上的详尽描述。. ①以疾病为对象的分析 利用面向对象的思想,把对精兵的诊断知识进行面向对象的表示。 例如: 疾病=“炭疽”; 表现型数量=3; 表现型={最急性炭疽;急性炭疽;亚急性炭疽}; 表现性名称={急性炭疽}; 一般信息=“急性炭疽一般信息”; { 发病年龄=“犊牛成牛均发”; 发病季节=“夏秋季多发”; 饲喂方式=“放牧”; 放牧环境=“潮湿低洼地”; }; 症状=“急性炭疽症状” { 体温=“升高”; 精神=“兴奋不安、嚎叫或沉郁”; 呼吸=“呼吸促迫”; 可视粘膜变化=“发绀”; 食欲=“减退或停止”;
人工智能第六章_专家系统_的要点
1什么是专家系统。有什么特点和优点? 专家系统是一个具有大量的专门知识与经验的程序系统 专家系统是一种模拟人类专家解决领域问题的计算机程序系统特点: 启发性,能够运用专家的知识进行推理判断与决策 透明性,能够解释推理过程和回答用户问题 灵活性,能不断增长知识,更新知识库 专家系统的优点,自己课后了解一下。 2专家系统由哪些部分构成?各部分的作用? 知识库;综合数据库;推理机;解释器;接口 知识库,存储各领域专家的专门知识。静态。硬盘 综合数据库,存储初始问题数据和推理过程的中间数据。内存推理机,根据知识进行推理并导出结论。CPU 接口,用户界面,和用户进行交互。向用户提问,回答用户问题,并进行必要的解释。
知识获取机制是将专业知识转换成机器能理解的表达形式。 解释机制向用户解释以下问题:系统为什么要向用户提出该问题(Why)?计算机是如何得出最终结论的(How)? 3专家系统的分类,自己课下了解。 4建造专家系统的关键步骤。 专家系统团队关系图
是否拥有大量知识是专家系统成功与否的关键。因此知识表示是设计专家系统的关键 一.设计初始数据库 二.原型机的开发与实验 三.知识库的改进与归纳 建立专家系统的步骤图6.3P156页 5基于规则的专家系统
知识库:包含解决问题用到的领域知识,知识表达成为一序列规则。每个规则使用IF(条件)THEN(动作)结构指定的关系。当满足规则的条件部分时,便激发规则,执行动作部分。 数据库:包含一序列事实(一个对象及其取值构成了一个事实),所有的事实都存放在数据库中,用来和知识库中存储的规则的IF(条件)部分相匹配。 3. 基于规则的专家系统的推理机制 推理机制分为两大类:前向连接和后向链接 前向链接就是根据已有事实推断出新的事实。例如已知事实A is x,根据规则IF A is x THEN B is y。获得B is y。然后将B is y加入数据库。再寻找新的规则,即IF B is y THEN ….。
农作物病虫害诊断专家系统
农作物病虫害诊断专家系统 农业专家系统是农业信息技术中的一项重要技术、它是运用人工智能的专家系统技术,结合农业特点发展起来的一门高新技术。目前国际上的农业专家系统,广泛应用于作物生产管理、灌溉、施肥、品种选择、病虫害控制、温室昔理、家禽饲料配方、水上保持、食品加工、财务分析等许多方面。 1、专家系统体系结构 专家系统由知识库、知识的获取、推理机、综合数据库、解释程序、人机接口六个部分组成。 1.1知识库 知识库用以存放领域专家提供的专门知识、这此专门知识包括与领域相关的书木知识、常识性知识以及专家凭经验得到的试探性知识、专家系统的问题求解是运用专家提供的专门知识来模拟专家的思维方式进行的、知识库中拥有知识的数量和质量成为一个专家系统中系统性能和问题求解能力的关键因素。因此,知识库的建立是建造专家系统的中心任务。 1.2知识获取 知识获取部分负责对知识库进行昔理和维护,包括知识的输入、修改、删除和查询等昔理功能及知识的一致性、冗余性和完整性检查等维护功能。这些功能为领域专家提供了很大方便,使得他们不必知道知识库中的知识表示形式即可建立知识库并对其进行修改和扩充,大大提高了系统的可扩充性。 1.3推理机 推理机是专家系统的思维机构,是构成专家系统的核心部分,因为推理是专家系统解决问题的基木技术。它能够根据当前已知的事实利用知识库中的知识按一定的推理方法和控制策略进行推理求得问
题的解答或证明某个假设的正确性;在一定的控制策略下针对综合数据库中的当前信息,识别和选取知识库中对当前问题求解有用的知识进行推理。 1.4综合数据库 主要存放与专家系统推理相关的数据,包括用户输入的信息、推理过程产生的新信息以及推理所得到的结了等。 1.5解释程序 解释机由一组程序组成,跟踪并记录推理过程,当用户提出“为引一么?”“结论是如何得出的?”等询问需要解释时,它将根据问题的要求分别做出相应的处理,最后把解答用约定的形式通过用户界面输出给用户,便于用户理解系统的问题求解,增加用户对求解结果的信任程度、在知识库的完善过程中便于专家或知识工程师发现和定位知识库中的错误,便于领域的专业人员或初学者能够从问题的求解过程中得到直观学习。 1.6人机接口 人机接口是专家系统与用户的接口,用于完成输入输出工作。领域专家或知识工程师通过它输入知识、更新、完善知识库;一般用户通过它查询欲求解的问题以及向用户索取更多的事实。它可以将专家或用户的输入信息翻译为系统可接受的内部形式,把系统向专家或用户输出的信息转换成人类易于理解的外部形式。 2、农作物病虫害诊断专家系统设计 2.1知识获取 知识的获取分为两大类:一是应用领域的基木原理和常识;二是领域专家求解问题的经验知识。前者构成专门知识的主部,可以精确地定义和使用。这类知识尽昔是求解问题的基础,但并不与求解的问题紧密结合,加之知识量大和推理步小,不能高效地支持问题求解。
