情态动词+被动语态
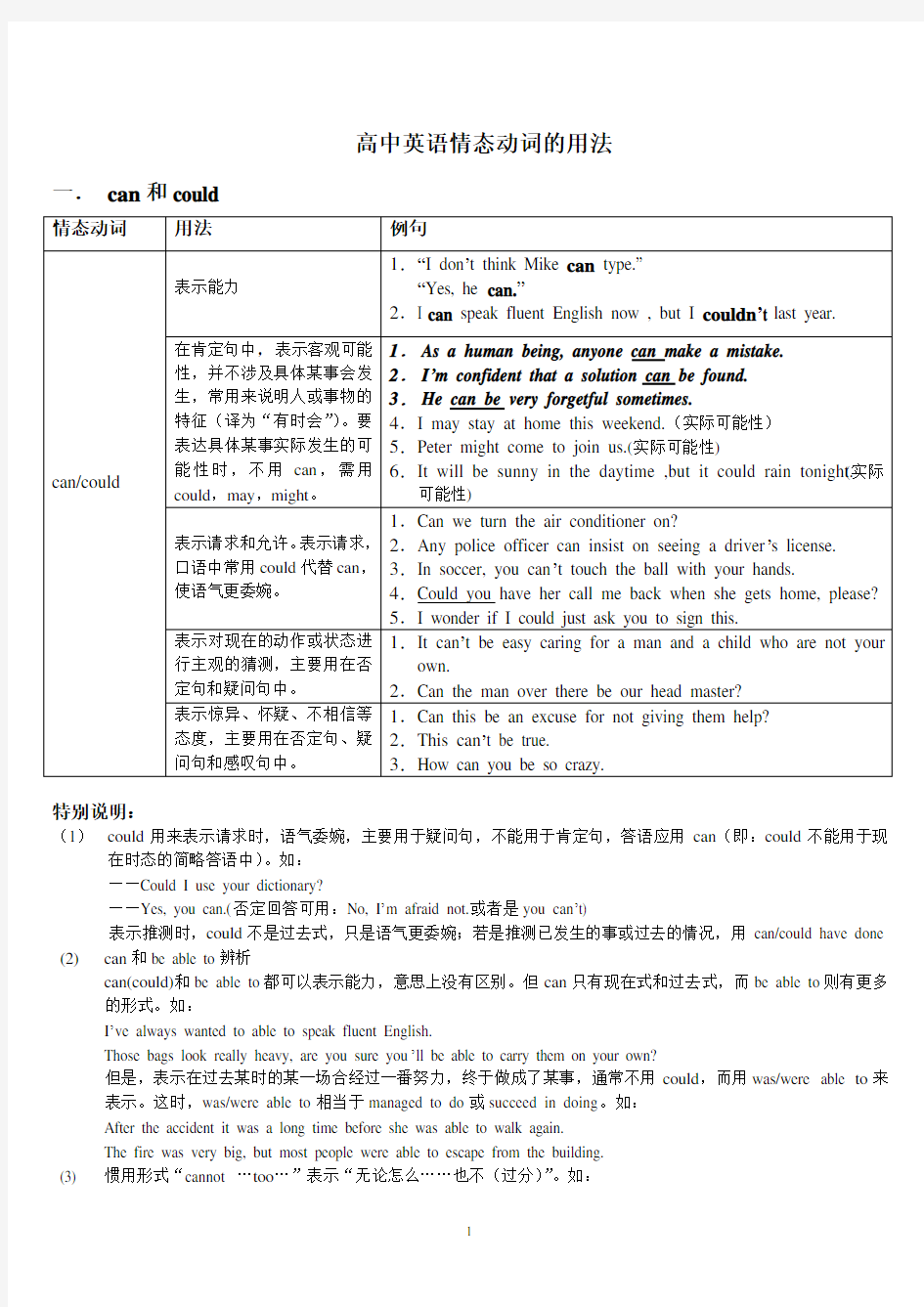

高中英语情态动词的用法一.can和could
情态动词用法例句
can/could 表示能力
1.“I don?t think Mike can type.”
“Yes, he can.”
2.I can speak fluent English now , but I couldn’t last year.
在肯定句中,表示客观可能
性,并不涉及具体某事会发
生,常用来说明人或事物的
特征(译为“有时会”)。要
表达具体某事实际发生的可
能性时,不用can,需用
could,may,might。
1.As a human being, anyone can make a mistake.
2.I’m confident that a solution can be found.
3.He can be very forgetful sometimes.
4.I may stay at home this weekend.(实际可能性)
5.Peter might come to join us.(实际可能性)
6.It will be sunny in the daytime ,but it could rain tonight.(实际
可能性)
表示请求和允许。表示请求,
口语中常用could代替can,
使语气更委婉。
1.Can we turn the air conditioner on?
2.Any police officer can insist on seeing a driver?s license.
3.In soccer, you can?t touch the ball with your hands.
4.Could you have her call me back when she gets home, please?
5.I wonder if I could just ask you to sign this.
表示对现在的动作或状态进
行主观的猜测,主要用在否
定句和疑问句中。
1.It can?t be easy caring for a man and a child who are not your
own.
2.Can the man over there be our head master?
表示惊异、怀疑、不相信等
态度,主要用在否定句、疑
问句和感叹句中。
1.Can this be an excuse for not giving them help?
2.This can?t be true.
3.How can you be so crazy.
特别说明:
(1)could用来表示请求时,语气委婉,主要用于疑问句,不能用于肯定句,答语应用can(即:could不能用于现在时态的简略答语中)。如:
——Could I use your dictionary?
——Yes, you can.(否定回答可用:No, I?m afraid not.或者是you can?t)
表示推测时,could不是过去式,只是语气更委婉;若是推测已发生的事或过去的情况,用can/could have done (2)can和be able to辨析
can(could)和be able to都可以表示能力,意思上没有区别。但can只有现在式和过去式,而be able to则有更多的形式。如:
I?ve always wanted to able to speak fluent English.
Those bags look really heavy, are you sure you?ll be able to carry them on your own?
但是,表示在过去某时的某一场合经过一番努力,终于做成了某事,通常不用could,而用was/were able to来表示。这时,was/were able to相当于managed to do或succeed in doing。如:
After the accident it was a long time before she was able to walk again.
The fire was very big, but most people were able to escape from the building.
(3) 惯用形式“cannot …too…”表示“无论怎么……也不(过分)”。如:
You cannot be too careful.你越小心越好。
惯用形式“cannot but+ 不定式(不带to)”表示“不得不,只好”。如:
I cannot but admire her determination.我不得不钦佩你的决心。二.may和might
情态动词用法例句
may/might 表示允许、许可。否定回答一般用must not/mustn?t,
表示“禁止、阻止”之意,但也可以用had better not
(最好别)或may not(不可以),语气较为委婉。
1.May I come in and wait?
2.——May I smoke here?
——No, you mustn?t(或No, you?d better not.)
在表示请求、允许时,might比may语气更委婉
些。用May I征询对方许可在文体上比较正式,
在口气上比较客气,在日常用语中,用Can I征询
对方意见更为常见。
1.Might I borrow your pen?
2.I wonder if I might speak to your son.
表示可能性的推测,通常用在肯定句和否定句中,
含有“或许”“大概”“可能”之意;用might代
替may时,则语气显得更加不肯定。
1.It may rain this afternoon.
2.She might come to join us this afternoon.
3.I suppose he might have missed the train.
may用于祈使句表示祝愿
1.May you succeed.
2.May you live happily!
3.May she rest in peace.愿她安息。
惯用句式:
“may as well或might(just)as well+动词原形”意
为“最好,满可以,倒不如”,相当于“had better
或there is no reason to do anything else.
1.There is nothing to do, so I may as well go to bed.
2.You may as well tell us now, we?ll find out sooner or
later.
3.I suppose we might as well go home.
4.And if you have to plough the field anyway, you
might as well plant it at the same time.
二.must和have to
情态动词用法例句
must 表示“必须,应该”之意,语气比should,ought to
强烈。其否定形式mustn?t表示“不准,不应该,禁
止”等意
1.You must come to school on time.
2.Everybody must obey the law.
3.You mustn?t drive so fast in the street.
4.We mustn?t waste any more time.
在回答带有must的问句时,否定回答常用needn?t
或don?t have to,表示“不必”,而不用mustn?t
1.—Must I come back before ten?
—Yes,you must.
----No, you needn?t(No, you don?t have to) 表示有把握的推测,意为“一定、准是、相必”,只
用于肯定句中
1.It must be my mother.
2.You must be hungry after a walk.
3.There must be a hole in the wall.
have to “必须,不得不”,意义与must相近。但must表示的是说话人的主观看法,而have to则往往强调客观
需要。1.The film is not interesting. I really must go now. 2.I have to go now, because my mother is in hospital.
must只有一种形式,即现在式与过去式都是一种形式,而have to则涉及各种人称、时态等方面的变化形式。1.I had to work hard when I was your age.
2.I will have to learn how to use a computer.
3.In order to take the exam, we?ll have to finish the
whole book by the end of this month .
两者的否定意义不同,mustn?t表示“禁止,不许”,don?t have to表示不必。1.You mustn?t go there. 2.You don?t have to go there.
注意:表示”偏要,硬要做某事
-how old are you, madam?
-if you must know, I?m twice my son?s age(如果你非得知道,是我儿子年龄的两倍) 四.shall和should
情态动词用法例句
shall 用于第一、三人称构成的疑问句,表示征求对方意见或请求指示,其意为“要不要”、“…好吗”:1.Shall I open the window? 2.Shall we say 6 o?clock, then? 3.Shall he come to see you?
1 用于第二、三人称陈述句中,表示说话人给对方的命令、警告、允诺、威胁、命令、规定、必然性等
2表示强制,用于法令、条约、规章中,意为“必须,应该”。1.Don?t worry, you shall get the answer this afternoon.(允诺)
2.He shall be sorry for it one day, I tell you. (警告)3.You shall do as I say. (命令)
4.If you children don?t do as I tell you, you shall not go to the party. (威胁)
5.The Persons under 18 shall not be employed in night work.不满十八岁的人不得雇佣干夜间工作。(表规定)
6.That day shall come(表必然性) 7.Candidates shall remain in their seats until all the papers have been collected.
试卷完全收回后,应试人才能离开座位。
should 表示劝告或建议,意为“应该”1.What should I do?
2.Should I trust him?
3.You should read his new book.
表示推测,用在肯定句中,对现在的情况或可能发生的事的主观推测或期待。意为“想必,大概,或许”。
【注】should表示推断时,语气较肯定,通常是指非常可能的事(因为暗示有一定的事实依据或合乎常理),而may, might, could等表示推测时,则语气较不肯定,尤其是might, could。1.It should be a nice day tomorrow.
2.It …s nearly 7 o?clock .Jack should speak in such a way.
3.He should be around sixty years old.
还可以用在if引导的条件句中,表示一件事听起来可能性很小,但也不是完全不可能,相当于“万一”的意思。从句谓语用should+动词原形构成,主句都一定用虚拟语气1.Ask Tom to ring me up if you should see him. (你万一见到汤姆,请让他给我打个电话) 2.Should I be free tomorrow, I?ll come. (万一我明天有时间,我就过来)
3.If things should change suddenly, please let me know. (万一情况突变,请通知我)
1should表示意外或惊讶1.It’s strange that he should come so late.
2用于疑问句或感叹句中,表示意外、惊异的情绪,意为“竟会”,与why,what,how,who连用,如果是疑问句,则不需要回答。
他竟然来这么迟真是奇怪。
2.I’m sorry that this should have happened. 我很遗憾竟然发生这种事。3.I’m surprised that he should say so. 他竟这样说,这使我很惊讶。
4.Why should anyone want to marry Tony?
5.Don?t ask me. How should I know?
五.will和would
情态动词用法例句
will/would 用于表示意志或意愿或决心。will指现在,
would指过去。1.He is the man who will go his own way. (他首歌自行其是的人。)
2.They said they would meet us at 10:30 at the station.
表示请求、建议等和you连用,用would比用will委婉、客气。1.Will you please take a message for him? 2.Would you please tell me your telephone number?
表示习惯或倾向,意为“总是,惯于”。will 至现在,would指过去。1.Fish will die without water.
2.People will talk. (人们总会说闲话。)
3.When we worked in the same office, we would often have coffee together.
表示推测,意为“很可能,大概”。will表示推测比should把握大,比must把握小。1.These things will happen.
2.That will be the messenger ringing.
3.It would be about ten o?clock when he left home.
表示功能,意为“能,行”。惯用形式:will do/would do表示“解决问题”、“就行”。1.That will be all right.
2.Either pen will do.
3.It would not do to work too late.(工作太晚不行。)
用于否定句中,意为“不肯”、“不乐意”1.I won?t listen to your nonsense.
2.No matter what I said, he wouldn?t listen to me.
特别说明:would与used to辨析
would可用来表示过去反复出现的动作,但不能表示过去存在的状态,所以我们不能说:“she would be a quiet girl.”另外,would强调过去某种特定情况下的活动,是完全过去的事情,同现在没有联系。而used to则着眼于过去和现在的对比,隐含现在已不存在,动作或状态都可表示。Would可以表示不规则的习惯,used to则不可。如:He used to be a naughty boy and cause trouble.
I used to get up at six in the morning.
Sometimes she would take a walk in the neighboring woods.
In those days, whenever I had difficulties, I would go to Mr. Chen for help.
六.need和dare
情态动词用法例句
用于表示“需要,必要”之意。做情态动词时,仅用于否定句和疑问句,只有现在时,过去式要用needn't have,疑问式用need+人称?,否定式用need not(即needn't),1.—Need we leave soon?
—Yes, you must.(No, you needn't, or don?t have to) 2.You needn't have hurried.
(=It was not necessary for you to hurry,but you did).你当时不必这么匆忙。
need 做实义动词时,其变化与一般的实义动词相同,
后接带to的不定式(need doing = need to be
done ),过去式用needed、did you need?和
didn't need,肯定式用needs/needed/need,疑问
式用do、does、did提问,否定式要在前面加
don't、doesn't、didn't
1. A job like nursing needs patience and
understanding.(need+名词,need understanding=need to
be understood,需要被理解)
2.He needs to see a doctor.(need to do)
3.Do you still need volunteers to help clean up after the
party?(need somebody to do something)
4.They didn't need to start so early.(do not need to do)
dare 用于表示“敢于”之意。做情态动词,没有人称和数的变化,主要用于否定句、疑问句和条
件状语从句中1.—Dare you tell her the truth?
—Yes, I dare. /No, I daren?t. 3.How dare you accuse me of lying! 4.He daren?t admit this.
用作实义动词时,其变化与一般的实义动词相同。在肯定句中,dare后接带to的不定式;否定句中,dare后既可接带to的不定式,也可接不带to的不定式。1.Only a few journalists dared to cover the story. 2.He doesn?t dare (to) go there alone.
3.Don?t you dare (to) touch it?
七.ought的用法:
情态动词用法例句
ought to do 表示“应该”之意1.You ought to take care of him.
2.—Ought I go now?
—Yes, you ought to. /No, you oughtn?t to.
表示推测。注意与must表示推测是的区别1.He must be home by now. (断定他已到家)
2.He ought to be home by now. (不十分肯定)
3.This is where the oil must be. (比较直率)
4.This is where the oil ought to be. (比较含蓄)
说明:should与ought to 表示“应该”时的区别
should 表示自己的主观看法,而ought to的语气中,含有“按道理应该……”之意。若要反映客观情况或涉及法律义务和规定,一般用ought to。如:
You should help them with their work.
You are his father. You ought to get him to receive good education.
八.“情态动词+have done”用法
情态动词+have done 用法例句
must have done 表示主观上对过去已经发生的行为进行
推测,意为“想必,准是,一定做了某事”1.She must have gone through a lot. 2.He must have visited the White House during his stay in the United States.
may/might have done 表示对过去已发生行为的推测,意为“也
许/或许已经(没有)……“。一般用于肯
定句或否定句中,不用于疑问句。用might
则表示语气更加不肯定。1.You may have learnt the news. 2.He may not have heard his name called.
3.Sorry I?m late. I might have turned off the alarm clock and gone back to
sleep again.
can…have done cannot have done 表示对过去发生的行为的怀疑和不肯定,
通常用在否定句和疑问句中。(can换成
could时语气委婉)
1.Where can she have gone?
2.Could he have done such a foolish
thing?
3.The boy can?t have finished reading
the book so soon because it is
difficult even to an adult.
could have done 可用于肯定句中,表示“可能已经……”
之意,此外,还可以表示过去能做而没做
的事,有一种对过去为付诸实施的事情的
惋惜。1.He could have killed himself driving at a dangerous speed.
2.You could have been more considerate.
3.You could have done better, but you were too careless.
might have done 表示“本来可能……,但实际上没有发生
的事情”。另外,还可以表示“本来应该
或可以做某事”之意,含有轻微的责备语
气。1.You should not swim in that sea. You might have been eaten by a shark. 2.He might have given him more help, thought he was busy.
should/ought to have done 用于肯定句时,表示本该做某事,而实际
上未做;用于否定句时,则表示不该做的
事反而做了。1.He should have known that the police would never allow this sort of thing.
2.You shouldn?t have done it so carelessly.
3.You ought to have returned the book earlier.
4.You ought not to have refused his offer.
needn?t have done 表示做了本来不必去做的事。注意:didn?t
need to do表示“没必要做而实际上也没
有做某事”1.You needn?t have watered the plants, for it is going to rain.
2.I didn?t need to buy the dictionary. I had a copy at home.
had better have done 用于事后的建议,含轻微责备的口吻,意
为“当时最好做了某事”,其否定式had
better not have done表示相反的含义。1.You had better have started earlier. 2.You had better not have scolded her.
would rather have done 表示“当时宁愿做了某事”,其否定式
would rather not have done表示相反的含
义,两者都表示“后悔”之意。1.I would rather have taken his advice. 2.I would rather not have told him the truth.
被动语态
1. 被动语态的基本时态变化
被动语态通常为十种时态的被动形式, 被动语态由be+过去分词构成,be随时态的变化而变化。以do为例,各种时态的被动语态形式为:
1) am/is/are +done (过去分词) 一般现在时
例Visitors are requested not to touch the exhibits.
2)has /have been done 现在完成时
例All the preparations for the task have been completed, and we're ready to start.
3)am/is /are being done 现在进行时
例A new cinema is being built here.
4)was/were done 一般过去时
例I was given ten minutes to decide whether I should reject the offer.
5)had been done 过去完成时
例By the end of last year, another new gymnasium had been completed in Beijing.
6)was/were being done 过去进行时
例A meeting was being held when I was there.
7)shall/will be done/ be going to be done/ be about to be done/ be to be to done一般将来时
例Hundreds of jobs will be lost if the factory closes.
8)should/would be done/ was\were going to be done/ was\were about to be done/was\were to be to done过去将来时
例The news would be sent to the soldier's mother as soon as it arrived.
9)shall/will have been done 将来完成时(少用)
例The project will have been completed before July.
10)should/would have been done 过去将来完成时(少用)
例He told me that his new clothes would have been made very soon.
2. 被动语态的特殊结构形式
1)带情态动词的被动结构。其形式为:情态动词+be+过去分词。
例The baby should be taken good care of by the baby-sitter.
2) 有些动词可以有两个宾语,在用于被动结构时,可以把主动结构中的一个宾语变为主语,另一宾语仍然保留在谓语后面。通常变为主语的是间接宾语。
例His mother gave him a present for his birthday.
可改为He was given a present by his mother for his birthday.
3) 当“动词+宾语+宾语补足语”结构变为被动语态时,将宾语变为被动结构中的主语,其余不动。
例Someone caught the boy smoking a cigarette.
可改为The boy was caught smoking a cigarette.
4)在使役动词have, make, get以及感官动词see, watch, notice, hear, feel, observe等后面不定式作宾语补语时,在主动结构中不定式to要省略,但变为被动结构时,要加to。
例Someone saw a stranger walk into the building.
可改为A stranger was seen to walk into the building.
5) 有些相当于及物动词的动词词组,如“动词+介词”,“动词+副词”等,也可以用于被动结构,但要把它们看作一个整体,不能分开。其中的介词或副词也不能省略。
例The meeting is to be put off till Friday.
3. 非谓语动词的被动语态
v.+ing 形式及不定式to do 也有被动语态(一般时态和完成时态) 。
例I don't like being laughed at in the public.
二、It is said that+从句及其他类似句型
一些表示“据说”或“相信”的动词如believe, consider, expect, report, say, suppose, think等可以用于句型“It+be+过去分词+that从句”或“主语+be+过去分词+to do sth.”。有:
It is said that… 据说,It is reported that…据报道,It is believed that…大家相信,
It is hoped that…大家希望,It is well known that…众所周知,
It is thought that…大家认为,It is suggested that…据建议。
例It is said that the boy has passed the national exam.
(=The boy is said to have passed the national exam. )
三、谓语动词的主动形式表示被动意义
1.英语中有很多动词如break,catch,clean,drive,lock,open,sell,read,write,wash等,当它们被用作不及物动词来描述主语特征时,常用其主动形式表达被动意义,主语通常是物。
例This kind of cloth washes well.
注意:主动语态表被动强调的是主语的特征,而被动语态则强调外界作用造成的影响。
试比较:The door won't lock.(指门本身有毛病)
The door won't be locked.(指不会有人来锁门, 指“门没有锁”是人的原因)
2. 表示“发生、进行”的不及物动词和短语,如:happen, last, take place, break out, come out, come about, come true, run out, give out, turn out等以主动形式表示被动意义。
例How do the newspapers come out? 这些报纸是如何引出来的呢?
3. 系动词没有被动形式, 但有些表示感受、感官的连系动词feel, sound, taste, book, feel等在主系表结构中常以主动形式表示被动意义。
例Your reason sounds reasonable.
四、非谓语动词的主动形式表被动意义
在某些句型中可用动名词和不定式的主动形式表被动意义。
1.在need,want,require, bear等词的后面,动名词用主动形式表示被动意义,其含义相当于动词不定式的被动形式。The house needs repairing(to be repaired).这房子需要修理。
2.形容词worth后面跟动名词的主动形式表示被动含义,但不能跟动词不定式;而worthy后面跟动词不定式的被动形式。
例The picture-book is well worth reading.(=The picture-book is very worthy to be read.)
3. 动词不定式在名词后面作定语,不定式和名词之间有动宾关系时,又和句中另一名词或代词构成主谓关系, 不定式的主动形式表示被动含义。
例I have a lot of things to do this afternoon.(to do与things是动宾关系,与I是主谓关系。) 试比较:I?ll go to the post office. Do you have a letter to be posted? ( 此处用不定式的被动语态作定语表明you不是post动作的执行者。)
4. 在某些“形容词+不定式”做表语或宾语补足语的结构中,句子的主语或宾语又是动词不定式的逻辑宾语时,这时常用不定式的主动形式表达被动意义。这些形容词有nice,easy,fit,hard,difficult,important,impossible,pleasant,interesting等。
例This problem is difficult to work out .(可看作to work out省略了for me).
5.在too… to…结构中,不定式前面可加逻辑主语,所以应用主动形式表示被动意义。
例This book is too expensive (for me) to buy.
6. 在there be…句型中,当动词不定式修饰名词作定语时,不定式用主动式作定语,重点在人,用被动形式作定语,重点在物。
例There is no time to lose(to be lost).(用to lose可看成for us to lose;用to be lost,谁lost time 不明确。)
7. 在be to do结构中的一些不定式通常应用主动表主动, 被动表被动。然而,由于古英语的影响,下列动词rent,blame,let等仍用不定式的主动形式表示被动意义。
例Who is to blame for starting the fire?
五、介词in, on, under等+名词构成介词短语表被动意义
表示方位的介词与含动作意义的名词合用,含被动之义,其意义相当于该名词相应动词的被动形式,
名词前一般不用冠词。
1. “under +名词”结构,表示“某事在进行中”。常见的有:under control(受控制), under treatment (在治疗中), under repair(在修理中), under discussion(在讨论中), under construction(在施工中)。
例The building is under construction( is being constructed).
2.“beyond+名词”结构,“出乎……胜过……、范围、限度”。常见的有:beyond belief (令人难以置信),beyond one’s reach(鞭长莫及),beyond one’s control(无法控制),beyond our hope.我们的成功始料不及。
例The rumour is beyond belief(=can?t be believed).
3.“above+名词”结构, 表示“(品质、行为、能力等) 超过……、高于……”。
例His honest character is above all praise.=His honest character cannot be praised enough.4.“for+名词”结构,表示“适于……、为着……”。如:for sale(出售), for rent(出租)等。
例That house is for sale. (= That house is to be sold).
5.“in+名词”结构,表示“在……过程中或范围内”常见的有:in print(在印刷中),in sight(在视野范围内),等。
例The book is not yet in print.(=is not yet printed)
6.“on+名词”结构, 表示“在从事…… 中”。常见的有:on sale(出售),on show(展出), on trial(受审)。
例Today some treasures are on show in the museum (= are being showed).
7.“out of+名词”结构;表示“超出…… 之外“,常见的有:out of control (控制不了),out of sight (超出视线之外),out of one’s reach(够不着), out of fashion(不流行)等。
例The plane was out of control (can?t be controlled).。
8.“within+名词”结构,“在……内、不超过……”。
例He took two days off within the teacher's permission.
六、被动语态与系表结构的区别
当“be+过去分词”作被动语态时表示主语承受的动作;作系表结构时表示主语的特点或所处的状态时,be后面的过去分词是表语,相当于形容词。其区分办法如下:
1.如果强调动作或句中有介词by引导出动作的执行者,该句一般为被动语态,否则为系表结构。
例The glass is broken.(系表结构)
The glass was broken by the boy.(被动语态)
2.如果句中有地点、频率或时间状语时,一般为被动语态。
例The door is locked.(系表结构)
The door hasalready/just been locked.(被动语态)
3.被动语态除用于一般时态和完成时态外,还可以用于其他各种时态,而系表结构中的系动词be 只有一般时态和完成时态。
例The machine is being repaired.
将主动语态变被动语态的基本方法为
1)划分句子的主语和宾语,区分动作的执行者和承受者,并将主动语态的宾语作被动语态的主语;
2)谓语动词变为“be+及物动词的过去分词”,并通过be的变化来表达出不同的时态;
3)主动语态的主语变为介词by的宾语,组成介词短语放在被动结构中的谓语动词之后。(有时by短语可以省略)
中考英语专题练习-含情态动词的被动语态(含解析)
中考英语专题练习-含情态动词的被动语态(含解析) 一、单选题 1.-- When should I hand in my paper? -- Your paper must as soon as the bell . A. hand in; rings B. hand in; will ring C. be handed in; rings 2.Which things ______ by common people to protect the environment? A. can be B. can do C. can be done D. can be do 3.Children to watch thrillers. They may have a bad influence on children. A. shouldn't allow B. should allow C. shouldn't be allowed D. should be allowed 4.Your bedroom is so dirty, It should every day. A. clean B. is cleaned C. cleans D. be cleaned 5.Waste paper everywhere. It's our duty to keep the school clean. A. throws B. are thrown C. shouldn't be thrown 6.—It's difficult for village children to cross the river to school. —I think a bridge _________ over the river. A. should be built B. will build C. is built D. was built 7.Don't put off today's work for tomorrow. I mean, today's work______ today. A. may do B. must do C. may be done D. must be done 8.People who drink wine ____________ to drive after May Day. A. don't allow B. isn't allowed C. mustn't allow D. mustn't be allowed 9.It's difficult for the village children to cross the river to get to school. We think a bridge________ over the river A. was built B. should be built C. has been built D. is being built 10.Things should ________ here before you enter the library. A. keeps B. are kept C. be kept D. keep 11.The robot needs _______ once a month. And we will check it for you for free. A. to check B. checked C. checking D. to checking 12.The young mothers are told little kids can't ___________ alone at home. A. leave B. to leave C. left D. be left 13.The television ________. It doesn't work now. A. must be repaired B. was repairing C. must repair D. has repaired 14.Don't put off today's work till tomorrow. I mean, today's work today. A. must be done B. must do C. may be done 15.—Can I my hair colored, Mom? —No. As a student, you ________ do that. A. let; are allowed to B. got; should be allowed to C. get;may not D. get; shouldn't be allowed to
情态动词,被动语态小测
情态动词练习(小测) 1.Buses and cars ______ stop when the traffic lights are right. A. can B. must C. may D. need 2. –Excuse me, Can you tell me the way to the railway station? Oh, sorry, but I don’t know.You ____ go and ask that policeman. A.may B. must C.would D. should 3. –Children all like this book. -I think it ______ very interesting. A. need be B. must be C. may be D. can be 4. To make our hometown (家乡) more beautiful , you _____ throw rubbish into the river. A. needn’t B.mustn’t C. must D. may 5. She ______ know the answer .I’m am not sure. A. maybe B.may be C.may D. must 6. –Must I go with tomorrow? –No. you ______ . A. must B. shouldn’t C.needn’t D.can’t 7.-_______ I have your name ,please? –Yes,Michael. M-I-C-H-A-E-L. A.Must B. Will C.May D. Need 8. Since(因为) the road is wet this morning,_______ last night. A. it must rain B. it must have rained C.it must be rained D.it must have been rained 9.Work _______ come first.. A. can B.may C.should D. must 10. He _____ come here tomorrow. A. don’t need B.doesn’t need to C.needn’t to D.needs not 11.In our school ,classrooms ______ cleaned every Sunday. A. will do B. shall do C.must be D.can be 12.-Please don’t use my computer.-Sorry, I _______ do it again. A. can’t B. must not C. won’t D. should 13. –Sir, you _____ sit here. It’s for women or children only. A. don’t B. can’t C. won’t D. needn’t 14.My boy, you _____ talk to your father like that. A.won’t B. don’t C. shouldn’t D.has to 15. -_______Iwatch TV now, Mum? -No, you _______ finish your homework first. A. Must, needn’t B. Can ,may C. May, must D. May,mustn’t 16. –You must be here at 5:30 tomorrow. –Sorry ,I _____be here so early. A.won’t B. don’t C. shouldn’t D.has to 17. Last Summer ,it was very dry. I ________ it every day. A. must water B. have to water C. had to water D. didn’t have to 句型转换 1.He must be a policeman.(否定句) He _______ be a policeman. 2. I’m sure he is sleeping. (同义句) He _______ be sleeping. 3.You don’t have to get up early.(同义句) You __________ get up early. 形容词的比较级和最高级 用所给词的适当形式填空 1.Summer is the ________(hot) of the four seasons. 2.Tommy’s homework is much _______(good) than it was last
情态动词的被动语态
情态动词的被动语态 教学设计 一、教学目标 1. 了解情态动词的被动语态结构 2. 掌握情态动词的被动语态的变换方法 二、教学准备 多媒体,微课软件,纸和笔 三、教学步骤 1.通过例句学习变换方法 Ann can take good care of the cats . The cats can be taken good care of by Ann. 2. 总结结构: S+ can/must/should等情态动词+ be+过去分词 3.练习题 ① You must clean your bedroom every day. ② Parents should encourage teenagers to do social work. ③ Can Lucy do her homework tomorrow instead? 4.更多练习
I. 用括号内所给单词的适当形式填空。 1.How many magazines ____(can borrow) in your library every week? 2.In many countries, teenagers under 18 ____(should not allow) to go into Internet bars. 3.Some people think trees ____(should plant) on Tree planting Day only. 4.The flowers ____(must water) every day. 5.A dictionary ____(can use) in the exam. II.同义句转换,每空一词。 1.Students should clean their classroom every day. Their classroom ____ _____ ____ every day. 2.Can you mend this radio? ____ this radio ____ ____? 3.We should not allow fifteen-year-olds to work at night. Fifteen-year-olds ____ ____ ____ to work at night.
含有情态动词的被动语态
一、基本含义 含有情态动词的被动语态用来说明某人或某物被动性动作所反映出的感情和态度。 二、基本结构 含有情态动词的被动语态的基本结构为:情态动词 + be + 及物动词的过去分词。例如: The computer must be repaired now. 这台电脑必须立刻修理。Many trees should be planted on the mountains. 应该在山上种植许多树。 三、转变方法 1. 将主动句的宾语变成被动句的主语; 2. 把“情态动词 + 动词原形”变成“情态动词 + be + 及物动词的过去分词”。例如: You should finish your homework at once. →Your homework should be finished (by you) at once. You can take this book home. →This book can be taken home (by you). 四、句式变换 含有情态动词的被动语态的疑问句、否定句的变化均需借助于情态动词来完成。 1. 一般疑问句。直接将被动语态的陈述句中的情态动词提到句首。例如: This work must be done right now. →Must this work be done right now? His homework should be finished before six. →Should his homework be finished before six? 2. 特殊疑问句。由疑问词加上含有情态动词的被动语态的一般疑问句构成。例如: Where can the book be found? 这本书在什么地方能被找到呢?
(完整版)含情态动词的被动语态
含情态动词的被动语态 【考点链接】 1. —Some of the plastic bags can’t after June 1. —Yes, people will use environmental bags instead. A. use B. be use C. be used D. are used 2. —There is a lot of wind in North China. —Well, more trees every year to stop the wind. A. must be planted B. can planted C. should planted 【结构】情态动词(should/can/must/may/could等) + be + 及物动词的过去分词 【句式】 1. 否定句式:主语+情态动词+not be +及物动词的过去分词。如: The word couldn’t be used this way. 2. 一般疑问句式:情态动词+主语+be+及物动词的过去分词。如: —Should the letter be finished today? —Yes, it should. /No, it shouldn’t. 【跟踪练习】根据要求完成句子。 1. Teenagers should be allowed to play with friends at night. (改为否定句) Teenagers to play with friends at night. 2. The flowers must be watered once a day. (改为一般疑问句) the flowers once a day? 3. Should the classroom be cleaned on time? (作肯定回答) , . 4. Parents should allow children to choose their clothes. (改为被动语态) Children to choose their clothes. 5. The young tree can be planted now. (改为主动语态) We the young tree now.
情态动词+被动语态
高中英语情态动词的用法一.can和could 情态动词用法例句 can/could 表示能力 1.“I don’t think Mike can type.” “Yes, he can.” 2.I can speak fluent English now , but I couldn’t last year. 在肯定句中,表示客观可能 性,并不涉及具体某事会发 生,常用来说明人或事物的 特征(译为“有时会”)。要表 达具体某事实际发生的可能 性时,不用can,需用could, may,might。 1.As a human being, anyone can make a mistake. 2.I’m confident that a solution can be found. 3.He can be very forgetful sometimes. 4.I may stay at home this weekend.(实际可能性) 5.Peter might come to join us.(实际可能性) 6.It will be sunny in the daytime ,but it could rain tonight.(实际可能性) 表示请求和允许。表示请求, 口语中常用could代替can, 使语气更委婉。 1.Can we turn the air conditioner on? 2.Any police officer can insist on seeing a driver’s license. 3.In soccer, you can’t touch the ball with your hands. 4.Could you have her call me back when she gets home, please? 5.I wonder if I could just ask you to sign this. 表示对现在的动作或状态进 行主观的猜测,主要用在否 定句和疑问句中。 1.It can’t be easy caring for a man and a child who are not your own. 2.Can the man over there be our head master?
含情态动词的被动语态教案资料
精品文档 精品文档含情态动词的被动语态 【考点链接】 1. —Some of the plastic bags can’t after June 1. —Yes, people will use environmental bags instead. A. use B. be use C. be used D. are used 2. —There is a lot of wind in North China. —Well, more trees every year to stop the wind. A. must be planted B. can planted C. should planted 【结构】情态动词(should/can/must/may/could等) + be + 及物动词的过去分词 【句式】 1. 否定句式:主语+情态动词+not be +及物动词的过去分词。如: The word couldn’t be used this way. 2. 一般疑问句式:情态动词+主语+be+及物动词的过去分词。如: —Should the letter be finished today? —Yes, it should. /No, it shouldn’t. 【跟踪练习】根据要求完成句子。 1. Teenagers should be allowed to play with friends at night. (改为否定句) Teenagers to play with friends at night. 2. The flowers must be watered once a day. (改为一般疑问句) the flowers once a day? 3. Should the classroom be cleaned on time? (作肯定回答) , . 4. Parents should allow children to choose their clothes. (改为被动语态) Children to choose their clothes. 5. The young tree can be planted now. (改为主动语态) We the young tree now.
情态动词被动语态
Teenagers should be allowed to choose their own clothes 含情态动词的被动语态 含情态动词的被动语态是情态动词和被动语态中的重要内容,也是中考的重要考点,学习时应注意以下三点: 一、理解含情态动词的被动语态的概念 含情态动词的被动语态说明某个被动性动作所反映出的感情和态度。初中阶段可用于被动语态的情态动词有can,may,must,need,should等,分别表示“能够被……”,“可以被……”,“必须被……”,“需要被……”,“应该被……”等。 二、掌握含情态动词的被动语态的不同句式的变换方法 含情态动词的被动语态的疑问句、否定句的变化均借助于情态动词完成。 (一)一般疑问句 直接将陈述句被动语态中的情态动词提前。如: Must this work be done at once? 这项工作必须立即完成吗? Should your homework be finished before six? 你的家庭作业应在六点前完成吗? (二)特殊疑问句 由疑问词加上一般疑问句被动语态构成。如: When must this work be done? 这工作必须在什么时候完成? Where can the lost book be found? 这本失踪的书能在什么地方被找到? (三)反意疑问句 借助情态动词构成附加疑问部分。如: This bridge can be built next year, can’t it? 这座桥明年能建成,是吗? This book shouldn’t be taken out of the library, should it? 这本书不应被带出图书馆,是吗?(四)否定句 在情态动词后面加上not或never即可,但must表“必要”时否定式为needn’t。如: This work needn’t be done at once. 这项工作没必要立即做。 This dustbin shouldn’t be put here. 这个垃圾箱不应放在这儿。 三、含情态动词的被动语态的一般疑问句的回答 含情态动词的被动语态的一般疑问句的回答应保留原情态动词,但must表“必须”时,其否定回答应用needn’t,need表“必要”时,其肯定回答应用must。如:
情态动词的被动语态
情态动词的被动语态 1.Do let your mother know the truth. She appears________ everything. A.to tell B.to be told C.to be telling D.to have been told 2.Visitors_ _______not to touch the exhibits(展品). A.will request B.request C.are requesting D.are requested 3.Mr. Lopes was much disappointed(失望)to find the bike he had had_ _______went wrong again. A.it repaired B.repaired C.repaired it D.to be repaired 4.—Why did you come by taxi? —My bike broke down last night and I ________it repaired. A.didn't have B.don't have C.won't have
D.haven't had 5.Your clothes need________ .________she wash them for you? A.to be washed; shall B.To wash; shall C.washing; Will D.being washed; Will 6.This kind of cloth ________well. A.wash B.is washed C.washes D.washing 7.—What do you think of the speech? —The speaker said almost nothing worth________. A.listening B.being listened to C.listening to D.being listening 8.Bob, quickly get this film ________.I want to know if this camera works well. A.washed B.developed C.printed D.shown 9.He firmly asked_ _______a chance to try his luck, which at once encouraged(鼓励)_______. A.to give ;the others four B.to be given; the other four C.be given; four the other D.giving; the four others 10.—I'd like a pen which ________well.
含有情态动词的被动语态
含有情态动词的被动语态 ◆温故◆ 在英语中,动词有两种语态,即主动语态和被动语态。主动语态表示主语是动作的执行者,被动语态表示主语是动作的承受者。在八年级同学们已初步学习了被动语态,它的结构为:助动词be +及物动词的过去分词。 ◆知新◆ 本单元我们主要了解含有情态动词的被动语态。它的结构是什么呢?观察下面例句中含情态动词被动语态的各种形式,然后补全结论中所缺的内容。 【例句】 1. Many trees should be planted in the mountains. 应该在山上种许多树。 2. You can take this book home. (改为被动语态) →This book can be taken home (by you). 3. This problem can’t be worked out very easily. 这道题轻易算不出来。 4. Must the work be done at once? 这项工作必须立即完成吗? 【结论】 A. 含有情态动词的被动语态的结构为:情态动词+_____+及物动词的______。 B. 含有情态动词的主动语态变为被动语态时,要把主动语态的_____变成被动语态的主语。 C. 变为否定句时只需要在情态动词后加________。
D. 变为一般疑问句时只需把________提到句首。 Key: A. be, 过去分词 B. 宾语C. not D. 情态动词 【运用】 Ⅰ. 选择最佳答案。 ( )Young trees should ________ every year. A. be planted B. planted C. plant Ⅱ. 按要求完成下列各句,每空一词(含缩写)。 1. We must do the work right now. (改为被动语态) _______ _______ _______ _______ _______ right now. 2. Teenagers should be allowed to go out with their friends on school nights. (改为否定句) Teenagers _______ _______ _______ to go out with their friends on school nights. 3. A book should be read each month. (改为一般疑问句) _______ _______ _______ _______ _______ each month? Grammar Focus Ⅰ. A Ⅱ. 1. The work must be done 2. shouldn’t be allowed 3. Should a book be read
(易错题精选)初中英语语法知识—情态动词的分类汇编(1)
一、选择题 1.-Could you help me with my English homework, Nancy? -Of course I____________. Glad to help. A.could B.can C.must D.do 2.You run with the train when it is coming. It’s dangerous. A.may not B.mustn’t C.needn’t 3.(2018·山东临沂) Could you please speak a little louder? I ______ hear you very well. A.can’t B.mustn’t C.shouldn’t D.needn’t 4.—Is that Kate’s green bike? —It ____________be hers. She likes pink. A.can’t B.could C.mustn’t D.might 5.—________your house be cleaned right now? —No,it needn't.It may be cleaned this afternoon.() A.Must B.May C.Can 6.—Is that cap Bob’s? —No, it ________ be his. His is blue. A.can’t B.mustn’t C.needn’t D.may not 7.—Can we walk across the road now? —No, we . We have to wait until the light turns green. A.couldn’t B.needn’t C.shouldn’t D.mustn’t 8.—Can I take some milk and biscuits to the reading room? —No, our school has a rule that students _______ eat or drink there. A.can’t B.mustn’t C.needn’t D.may not 9.— Mom, I got a big box from express(快递). What is it? —I’m not sure. It ________be a present from your grandmother. A.should B.might C.must D.will 10.—I’d like ________ Guo Jingming’s Tiny Times. —You had better________ his books. The stories he tells are far from real life. A.buying, don’t read B.to buy, not read C.buying, not read D.to buy, not to read 11.— I would like________ to see a movie. —It’s too late. You’d better ________alone. A.to go, go B.go, not go C.to go, not go D.going, go 12.I’m sorry, children over 1.4 meters________pay the full pr ice for the show. A.may B.must C.can D.ought to 13.We _______ keep the new traffic law and learn how to protect ourselves. A.may B.should C.can D.need
被动语态以及情态动词构成及用法详解
被动语态用法详解 TENSE 主动语态被动语态 一般现在时be+V.\V.s am\is\are+V (p.p) 一般将来时will\be going to\be (about)to+V. will be +V(p.p) 现在进行时am\is\are+V.ing am\is\are+b eing+V(p.p) 一般过去时①was\were②V.ed was\were+V( p.p) 现在完成时have\has+V.p.p have\has+be en+V(p.p) 过去完成时had+V.p.p had+been+V( p.p) 过去进行时was\were+V.ing was\were+be
ing+V(p.p) 情态动词情态动词+V. 情态动词+be+V(p.p) 被动语态牢记一点, be加动词过去分词。分析句中主和谓,承受者作主语即被动。 短语动词不可忘介、副词。另有不及物动词,只有主动无被动。还要注意其时态, 与主动语态全相同。 不用被动语态的情况 1)不及物动词或动词短语无被动语态(即多数的瞬间动词):appear, die(死亡),disappear(消失), end (vi. 结束), fail, happen, last, lie, remain, sit, spread, stand break out, come true, fall asleep, keep silence, lose heart, take place. After the fire, very little remained of my house. 比较: rise, fall, happen 是不及物动词;raise, seat是及物动词。 (错)The accident was happened last week. (对)The accident happened last week. 要想正确地使用被动语态,就须注意哪些动词是及物的,哪些是不及物的。特别是一词多义的动词往往有两种用法。解决这一问题唯有在学习过程中多留意积累。 2)不能用于被动语态的及物动词或动词短语:fit, have, hold, marry, own, wish, cost, notice, watch agree with, arrive at / in, shake hands with, succeed in, suffer from, happen to, take part in, walk into, belong to This key just fits the lock. 3)系动词无被动语态(“keep”除外):appear, be become, fall, feel, get, grow, look, remain, seem, smell, sound, stay, taste, turn It sounds good. 4)带同源宾语的及物动词,反身代词,相互代词,不能用于被动语态: die, death, dream, live, life She dreamed a bad dream last night. 5)当宾语是不定式时,很少用于被动语态。 (对)She likes to swim. (错)To swim is liked by her. 有些动词可以带双宾语在用于被动结构时,有些动词可以带双宾语。在这种情况下,主动结构中的间接宾语变为主语时,直接宾语仍然保留在谓语后面;直接宾语变为主语时,间接宾语前通常加上介词for/to, etc.。即:S+V+IO+DO→IO+ be done +DO→DO+ be done + prep. +IO We often hear him play guitar. He is often heard to[1]play guitar. →It is often heard from him to play guitar. 新被动语态 Get+过去分词也可以构成被动语态,用这种结构的句子侧重于动作的结果而不是动作本
含情态动词的被动语态讲解及练习
第七单元语法知识 含有情态动词的被动语态,情态动词有should, may, might, can, could, must,will,would等。 一、基本句型结构: 1、肯定句:主语+情态动词+be+过去分词 ....(+by...) eg: Teenagers should be allowed to go shopping. Tables can be made of stones. The work must be finished today. The flowers may be planted in February. 2、否定句:主语+情态动词+not +be+ 过去分词 ....(+by...) eg: Teenagers shouldn’t be allowed to go shopping. Tables can’t be made of stones. The work mustn’t be finished today. (mustn’t [?m?snt]:不能) The flowers mayn’t [me?nt] be planted in February. 3、一般疑问句:情态动词+主语+be+过去分词 ....(+by...)? eg: Should teenagers be allowed to go shopping? Yes, they should. No, they shouldn’t. Can tables be made of stones? Yes, they can. No, they can’t. Must the work be finished today? Yes, it must. No, it needn’t./ No, it don’t have to. May the flowers be planted in February? Yes, they may. No, they mayn’t. 4、特殊疑问句:特殊疑问词+情态动词+主语+be+ 过去分词 ....(+by...)? eg: What should teenagers be allowed? What can tables be made of? When must be work be finished? When may the flowers be planted?
情态动词详解与被动语态句式结构
情态动词详解 [第一关]概念关 英语动词有两种语态,即主动语态和被动语态。主动语态表示主语是动作的执行者,被动语态表示主语是动作的承受者。如: We should plant many trees on the mountains. 我们应该在山上种许多树。 Many trees should be planted on the mountains. 应该在山上种许多树。 [第二关]构成关 被动语态由“助动词be+及物动词的过去分词”构成。人称、数和时态的变化通过助动词be的变化来体现(我们将在第9单元作详细介绍)。本单元学到的是含有情态动词的被动语态,其结构为“情态动词+助动词be+及物动词的过去分词”。如: Teenagers should be allowed to go out with their friends.来源:https://www.360docs.net/doc/9f5477416.html, 应该允许青少年和朋友外出。 [第三关]用法关 1. 不知道或没有必要说出动作的执行者是谁或者大家都清楚动作的执行者是谁时,常用被动语态。如: The children should be allowed to go to the movies with friends on Friday nights. 孩子们应当被允许星期五晚上和朋友们一起去看电影。 2. 强调动作的承受者,而不是动作的执行者时,常用被动语态。如: Tables can be made of stone. 桌子可由石头做成。 [第四关]句式关 含有情态动词的被动语态变为否定句时,应在情态动词后面加not;变为一般疑问句时,应将情态动词移到句首。如:
情态动词及其被动语态
中考复习八 情态动词及其被动语态 (一)情态动词概说 1.情态动词也是“辅助性”动词,用来表示说话人的语气或情态。情态动词所表示的情态有:请求、命令、允诺、可能、需要、敢于、愿望、义务、能力等。 2.情态动词本身有词义,但词义不完全,不能单独用作谓语,没有人称和数的变化,且后面只跟动词原形。如: 她会唱英文歌曲。 She cans sing an English song.(F) She can sings an English song.(F) She can sing an English song.(T) 3.有些情态动词的过去时与其原形相同,有些与原形不同。 (1) 与原形相同的有: must --- must ought to --- ought to (2) 与原形不同的有: can --- could will --- would may --- might shall --- should need --- needed dare --- dared have to --- had to 4.大多数的情态动词后面可以用动词不定式(多不带to)的进行时、完成时或被动形式,如:may, can, must等。 (二)情态动词的种类:(见下表) 原 形过去式词 义 can could能 may might可以(或许) must must(had 必须(不得不) to) will would愿意 shall should应该 need needed需要 dare dared敢于 (三)情态动词的否定形式: cannot --- can’t could not --- couldn’t may not---mayn’t might not--- mightn’t must not --- mustn’t will not --- won’t would not --- wouldn’t need not --- needn’t shall not --- shan’t
