先将来时
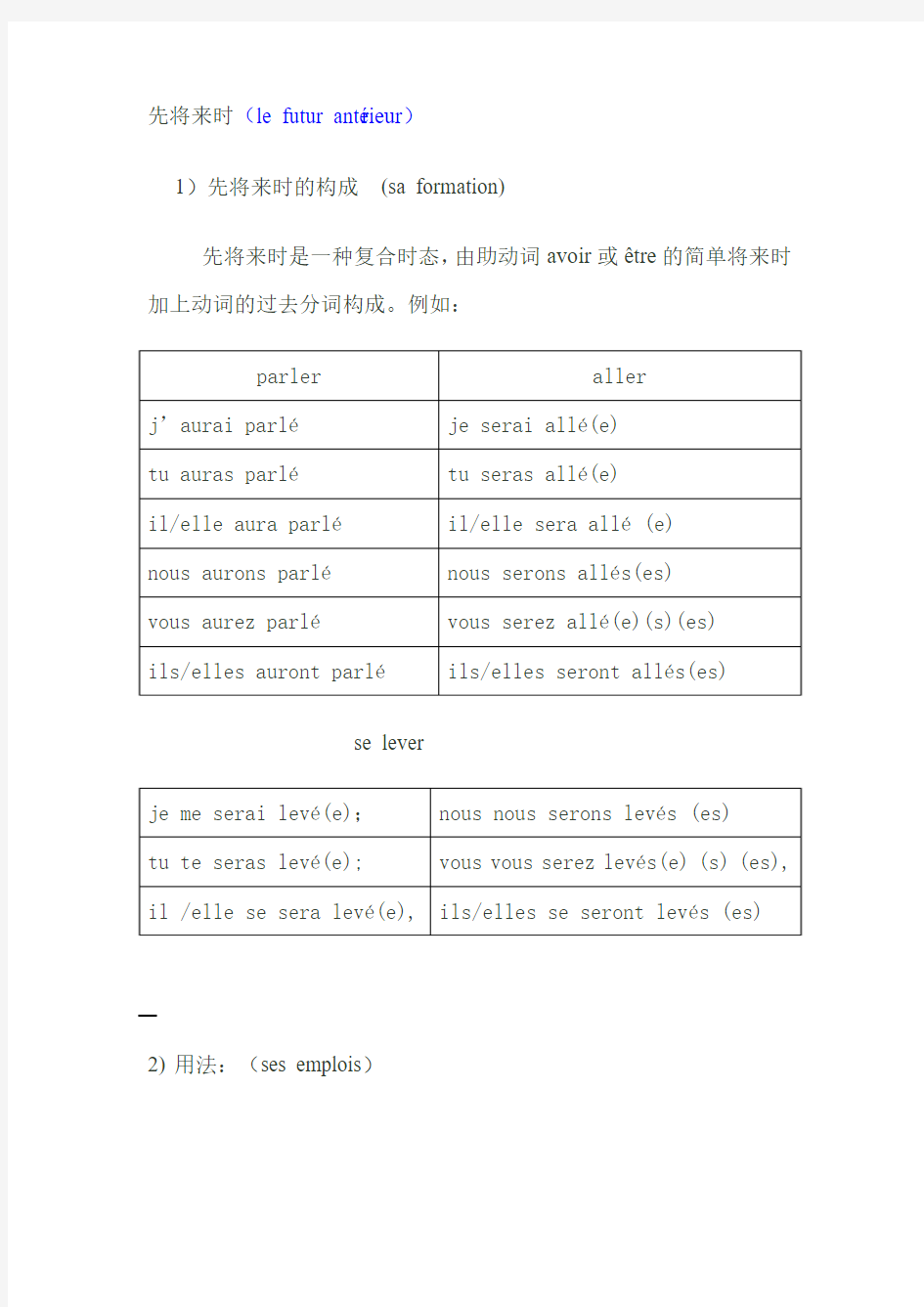

先将来时(le futur antérieur)
1)先将来时的构成(sa formation)
先将来时是一种复合时态,由助动词avoir或être的简单将来时加上动词的过去分词构成。例如:
se lever
2)用法:(ses emplois)
先将来时主要用来表示在另一个将来动作以前完成的将来动作。先将来时通常出现在以连词quand; lorsque; dès que;等引导的时间状语从句中。例句:
Quand j’aurai gagné assez d’argent, je partirai pour l’Espagne.
等我赚够了钱就去西班牙。
Dès que nous y serons arrivés, nous vous écrirons.
我们一到那里就给你们写信。
注意:
1、同时使用先将来时和简单将来时,目的在于强调两个动作之间的关系,既在一个将来的动作发生之前,另一个动作已经完成。如果不强调这种关系,两个动作都可以用简单将来时来表示。试比较:
Ce soir, quand j’aurai lu les journaux, je regarderai la télévision.
今天晚上,我看完报纸就看电视。
Ce soir, je lirai les journaux, je regarderai la télévision.
今天晚上,我要看报纸和电视。
2、先将来时有时也可以在独立句中使用,表示在将来某一确定时间之前,先完成的将来动作。如:
J’aurai fini mes devoirs dans deux heures.我将在两小时以后做完作业。Demain, à cette heure-ci, il sera parti. 明天这个时候,他已经出发了。
法语时态变位
Le temps et La conjugaison 法语的语式(le mode du fran?ais): 直陈式:客观地说明一件事实; 命令式;条件式:在一定条件下才有可能发生的动作; 虚拟式:从主观的角度来谈一件事情; 不定式:无人称变化,不能作谓语; 分词式:现在分词和过去分词,无人称变化,不能作谓语 1. 直陈式现在时(le présent de l’indicatif): 表现在存在的状态,经常发生的动作;表一个人的性格、特征;表客观事实或 普遍真理;表说话时正在发生的事情 第一组动词(les verbes du 1er groupe)由原形词根+e,es,e,ons,ez,ent 第二组动词(les verbes du 2e groupe)由原形词根+is,is,it,issons,issez,issent 2. 命令式(l’impératif):表示命令或请求 将直陈现在时主语去掉即。只有第二人称单复数(第一组动词第二人称单数词尾无s),第一人称复数; être:sois,soyons,soyez ;avoir:aie,ayons,ayez 3.最近将来时(le futur proche):表示即将发生的动作 aller 直陈现在时+不定式 4.最近过去时(le passé proche):表示刚刚发生或完成的动作 venir 直陈现在时+ de + 不定式 5. 代词式动词(le verbe pronominal – v.pr.): 表示自反意义(sens réfléchi)、相互意义(sens réciproque) 被动意义(sens passif)、绝对意义(sens absolu) 复合时态中,表被动或绝对意义,过去分词要与主语性数一致; 表自反或相互意义,如果自反代词是直接宾语,过去分词与自反代词性数配合(相当于直宾置前);是间宾不配合 6. 无人称动词(le verbe impersonnel):主语用il;il y a..., il est...表示时间, il fait...表示天气,带实质主语的无人称句: se produire, se présenter, s’écouler, se passer // venir, arriver, tomber, descendre // être dit, être fait, être défendu// Il est venu trois soldats / Il ne se passe rien / il suffit de f. qch. / Il est évident que / il arrive que chacun fasse erreur 7. 过去分词(le participe passé) 第一组动词:词根+é;第二组动词:词根+i 过去分词独立使用,在句中作表语、定语或同位语时,要与有关的名词或代词性数一致;及物动词过去分词独立使用表被动意义; 以être 作助动词构成复合时态的不及物动词,其过去分词独立使用表示主动意义
常见过去将来时最全总结
常见过去将来时最全总结 一、初中英语过去将来时 1.He after supper a couple of years ago. A. smoked B. would smoke C. smokes D. will smoke 【答案】B 【解析】【分析】句意:几年前他吃完饭就吸烟。a couple of years ago是过去时的时间状语,吸烟是吃完饭之后发生的事情,would+过去原形,表示过去习惯性的动作。故选B。【点评】考查would+动词原形表习惯性动作。 2.Mr. Wu said he ______ us to the zoo the next week. A. would take B. will take C. take D. takes 【答案】 A 【解析】【分析】句意:吴老师说他下周会带我们去动物园。在这个句子中,said 后面跟的是一个宾语从句,从句中的时态是由主句决定的。主句中said 用的是过去时,故宾语从句中也需用过去时态。the next week 下周,是一个将来的时间。故应该用过去将来时。故选A。 【点评】考查动词时态。 3.Mr. Wu said he ______ us to the zoo the next week. A. would take B. will take C. take D. takes 【答案】 A 【解析】【分析】通过分析本句可知,本句是一个宾语从句。根据next week可知,从句应该将来时,故排除CD;在宾语从句中,主句用过去时,则从句也应该用过去时的某种形式,故用would take。所以本题选A。 【点评】对于宾语从句应该注意四点:1、语序:用陈述句语序;2、引导词:A.that B.特殊疑问词C.if/whether 3、时态:?当主句是一般现在时,从句的时态根据从句的时间变化?当主句的时态是过去时时,从句应该用过去的某种时态?当从句表示客观事实或客观真理等时,从句要用一般现在时。4、人称:根据实际情况变换人称。而本题只考查了时态。 4.I didn't know when he _____ back. He said he would call me when he _____ home. A. would come, got B. came, got C. will come, gets D. came, would get 【答案】 B 【解析】【分析】句意为:我不知道他什么时候回来。他说他一回来就给我打电话。前句是when引导的宾语从句,根据语境应用一般过去时。后句是when引导的时间状语从句,主句用过去将来时,从句用一般过去时。故选B。 【点评】考查从句的时态。
将来时的动词结构
英语中表示将来时的动词结构有好几种,它们是:一“will(shall) + 动词原形”,用来表示说话时认为或预测会在将来发生的动作或状态。[例1] Do you think the car’ll start? 你认为车能发动起来吗?(预测) 二“be going to + 动词原形”,用来表示说话之前已有打算或计划的要做的事,或在说话时已有迹象预示会在未来发生的事。[例2]There is going to be a parent-teacher meeting tomorrow. 准备在明天开家长会。(事先已决定)[例3]Look—it’s going to rain. 瞧,要下雨了。(看见迹象)三按计划或安排即将要发生的动作也可以用“现在进行时”表示;按计划或安排将要发生的动作还可用“一般现在时”表示,但必须是指已经列入日程安排的或按时间表规定的会发生的动作。这些动作往往都与“移动、方向、启动(如:come、go、arrive、leave、move、return、start、begin)”等有关。[例4] He is coming.他就来。(即将发生)[例5] School begins on September 1.学校将于九月一日开学。(日程安排)四在时间或条件状语从句中,表示将来的动作常用“一般现在时”。[例6]I’ll be glad if it rains soon.要是一会儿能下雨,我就高兴了。五“be about to+动词原形”意为“正要做某事”、“正准备做某事”,通常不接时间状语。“be to+动词原形”表示按计划或安排即将发生的动作,或可能、一定会发生某种情况。[例7]]Don’t go out—we’re about to have lunch. 不要出去了,马上就要吃午饭了。[例8]They are to come to China in November.他们打算十一月份来中国。六其它结构。还有一些动词结构也能和表示将来的时间状语连用。[例9]Don’t be late for school tomorrow. 明天上学不要迟到。(祈使句)[例10]Can you help me with my English this Sunday? 本周日你能帮我复习英语吗?(情态动词)近几年全国各地中考对将来时考查的重点、难点和热点如出一辙,现将部分省市试卷中的典型试题进行归类分析,以便同学们复习时参考:一考查重点:“will(shall)+动词原形”和“be going to”结构1.“will(shall)+动词原形”是一般将来时中最基本最常用的结构。第一人称作主语时用助动词shall或will(口语中常用will,表示提供帮助、提出建议、要求给以指示和征求意见时多用shall I或shall we),第二、三人称常用will。shall 和will可缩写为’ll,shall not可缩写为shan’t,will not可缩写为won’t。典型的时间状语有:how soon,tomorrow,next week,in a year,in 2005,soon(不久),before long(不久),later on(以后)等。[例1]We will visit (visit) the Great Wall in two days. (2001南京)[例2]Shall we go out for a walk? It won’t rain (not rain) any more. (2000昆明)2.需要用“be going to+动词原形”结构的,就不能用“will(shall)+动词原形”。[例3]There___ a football game this afternoon.(will have be,is going to have,will have,is going to be)(2001辽宁)[例4] You are going to help (help) him with his English next week,aren’t you?(’99南通)二考查热点:时间或条件状语从句用一般现在时表示将来意义1 提供主句,完成从句。含有时间或条件状语从句的复合句,如果主句是将来时,从句须用一般现在时。属于这一类型的从属连词有:when,after,before,as soon as,until,if,unless等。[例5]We won’t leave until we ___ our homework.(finished/finish/will finish/are finished)(2000扬州)[例6]I’ll give him your message when he reaches (reach) home. (’96徐州)2 提供从句,完成主句。通常用“wi ll(shall)+动词原形”结构来完成主句,也有用祈使句、情态动词等其它动词结构的,但很少用“be going to”结构。[例7]“Have you seen the film?”“Not yet. I will see (see) it if I’m free.”(2000南通)[例8]You ___ eat anything until you see the doctor. (need/mustn’t/won’t be/maybe)(2001泰州)三考查难点:动词在when或if引导的宾语从句或状语从句中表示将来意义时的结构形式在时间或条件状语从句中,when(“当…的时候”)或if(“如果”)后面不用一般将来时,而用一般现在时代替。在宾语从句中,when(“什么时候”)或if(“是否”)可根据需要使用一般将来时。区别的方法是:when或if及其引导的从句能够提到主句之前的便是状语从句,否则是宾语从句。[例9]I’m not sure when he ___ tonight. But when he ___,I’ll let you know.(comes,will come/will come,comes/comes,comes/will come,will come)(’97扬州)[例10]“Mike wants to know if ___ a picnic tomorrow.”“Yes.But if it ___,we’ll visit the museum instead.”(you have,will rain/you will have,will rain/you will have,rains/will you have,rains)(2001
【英语】一般将来时详解+例句
【英语】一般将来时详解+例句 一、单项选择一般将来时 1.— Did you tell Mother you have passed the exam? — Oh, I forgot. I _______ her now. A.will call B.will be calling C.am calling D.am to call 【答案】A 【解析】 试题分析:考查情态动词。句意是:你告诉Rose关于考试的事了吗?--哦,我忘了,我现在就打电话给她。这里用will表示临时决定,故选A项。 考点 : 考查情态动词 2.“When he _____ is not known yet.” “But when he ____, he will be warmly welcomed.”A.comes, comes B.will come, will come C.comes, will come D.will come, comes 【答案】D 【解析】 试题分析:考查时态:第一个when引导的主语从句,用将来时,第二个when引导的时间状语从句,用一般现在时代替一般将来时,句意:他什么时候来还不知道。但当他回来时,他会收到热烈的欢迎。选D。 考点:考查时态语态 点评:时间条件状语从句的时态不能用一般将来时,而用一般现在时代替,考查时态还要注意语态。 3.It every day so far this month. I can't tell you if it tomorrow. A.rained; rains B.is raining; shall rain C.has been raining; rains D.has rained; will rain 【答案】D 【解析】 试题分析:本题第一空应该使用现在完成式,关键词是后面的时间状语so far(到目前为止),so far通常都是和现在完成时连用。第二空是一个if引导的宾语从句,并非if引导的条件句,在这个宾语从句中,时间状语是tomorrow,这是一个将来时的时间状语,故该宾语从句使用将来时。句义:这个月到现在为止天天都在下雨,所以我无法告诉你明天是否还要要下雨。故D正确。 考点:考察时态 4.--Jack! I have left my key to the office at home. -- Don’t worry. I _________ it for you. Wait a minute. A.get B.am going to get C.will get D.am getting
最新过去将来时一般过去时知识点梳理及经典练习(超详细)
最新过去将来时一般过去时知识点梳理及经典练习(超详细) 一、过去将来时 1.She said that she ______to the Zoo the next Sunday. A. will go B. is going C. would go D. has gone 【答案】 C 【解析】【分析】句意:她说她下周星期天去动物园。A.一般将来时;B.一般将来时;C.过去将来时;D.现在完成时。去动物园还没发生,用将来时,根据时间状语the next Sunday 可知,用过去将来时,would go,故选C。 【点评】考查动词的时态。注意过去将来时的用法。 2.—What did your son say in the letter? —He told me that he __________ the Great Wall the next day. A. will visit B. has visited C. is going to visit D. would visit 【答案】 D 【解析】【分析】句意:你的儿子在信中说什么?他告诉我他第二天要去参观长城.结合语境可知从句描述的是站在过去角度看将来发生的动作,故用过去将来时态,故选D. 【点评】英语中的时态主要是借助于时间状语与上下文语境来进行判断。解答此类题型,首先要注意句子中的时间状语,如果没有则要通过分析上下文,结合语境来判断句子的时态。英语疑问句中一般具有时态上的对应关系,注意结合这一特点进行区分。 3.Mr. Wu said he ______ us to the zoo the next week. A. would take B. will take C. take D. takes 【答案】 A 【解析】【分析】通过分析本句可知,本句是一个宾语从句。根据next week可知,从句应该将来时,故排除CD;在宾语从句中,主句用过去时,则从句也应该用过去时的某种形式,故用would take。所以本题选A。 【点评】对于宾语从句应该注意四点:1、语序:用陈述句语序;2、引导词:A.that B.特殊疑问词 C.if/whether 3、时态:?当主句是一般现在时,从句的时态根据从句的时间变化 当主句的时态是过去时时,从句应该用过去的某种时态?当从句表示客观事实或客观真理等时,从句要用一般现在时。4、人称:根据实际情况变换人称。而本题只考查了时态。 4.Tim told us that his company ______ robots to do some of the work. A. uses B. will use C. has used D. would use 【答案】 D 【解析】【分析】句意:蒂姆告诉过我,他的公司会使用机器人做工作的一部分。宾语从句
直陈式简单将来时
直陈式愈过去时 Ⅰ、构成:助动词(avoir 、être)的未完成过去时+动词过去分词。 表示的是过去时间里的先时性。 Ⅱ、用法: 1、多用在主从复合句中,表示在另一个过去的动作之前就已经完成了的动 作。 *J’ai acheté le roman dont vous m’aviez parlé. *Depuis, qu’il avait re?u cette lettre, il était mal dans sa peau. *Après qu ’il avait examinél’enfant, il a décidé de commencer le traitement. 2、用在间接引语中,与主句的过去时态配合。 *Julie m ’a dit qu’elle avait bien dormi la veille. *Je me demandais comment ils étaient venus jusqu’ici. 3、在独立句中。 A 表示另一个过去事件之前的动作或状态 *La pluie avait cessé, Le soleil a reparu. B 表示一种失望或后悔的情绪 *Ce n ’est pas ce que j’avait imaginé. C 与si 连用,表示愿望、遗憾、害怕、劝说、建议等 *Si tu avais pu me l ’expliquer. *Si tu avais suivi son conseil ! D si + 直陈式愈过去时,主句+条件式过去时表示一个过去可能实现而实际上并未实现的动作。 *S’il n’avait pas plu hier, nous serions allés en ville. *Si tu aviez suivi mon conseil,vous auriez réussi. E comme si +直陈式愈过去时“如同”(对先前发生的事作假设) *Il m’a regardé comme si j’avais dit une bêtise . *Elle a l’air fatigué, comme si elle n’avait pas dormi de la nuit. 简单将来时 R加词尾构成,
宾语从句.过去将来时
宾语从句(The Object Clause) 学习宾语从句要抓住三要素:连接词、语序和时态。 一.宾语从句的定义 宾语从句在复合句中起宾语的作用,可以作动词的宾语,也可以做介词的宾语 作动词的宾语: I heard that he would come here later on. 主语谓语动词一个句子作宾语 作介词的宾语: He said nothing about who broke the window last night. 主语谓语动词代词作动词的宾语介词一个句子作介词的宾语 二.宾语从句中引导词(连接词)的用法 在复合句中作主句的宾语,引导词有: 连词:that (that 常可省略),whether, if 代词:who, whose, what ,which 副词:when ,where, how, why 等。 ①连词: He told me (that he would) go to the college the next year 他告诉我他明年上大学. I don’t know if there will be a bus any more. 我不知道是否还会有公交车. Nobody knew whether he could pass the exam. 没有人知道他是否会通过考试. that引导的宾语从句(在非正式场合that可以省略) 可跟that从句做宾语的动词有: say, think, insist, wish, hope, demand, imagine, wonder, know, suppose, see, believe, agree, admit, deny, expect, explain, order, command, feel, dream, suggest, hear, mean, notice, prefer, request, require, propose, declare, report等。 The boy believes that he will travel through space to other planets. Attention:宾语从句的否定转移 当主句谓语动词是think, believe, suppose, expect 等词,而宾语从句的意思是否定时,常把否定转移至主句表示。I don’t think it is right for him to treat you like that. 主句的谓语动词是think,believe,imagine,suppose,consider,expect,fancy,guess等,并且主句的主语是第一人称而且为一般现在时,从句的否定词一般要转移到主句上来,其反义疑问句一般与宾语从句一致. I don’t believe that man is killed by Jim,is he? 我认为那个人不是Jim所杀的,是不是? I expect our English teacher will be back this weekend, won't she/he? We suppose you have finished the project, haven't you? 如果宾语从句中有某个含有否定意义的形容词或副词(不包含带有否定前缀的词,如:unhappy,unfair,dislike等),其反义疑问句要用肯定形式.
过去将来时一般过去时知识点总结(word)1
过去将来时一般过去时知识点总结(word)1 一、过去将来时 1.—Uncle Sam said he ________ my birthday party, but he never showed up. —That's Uncle Sam. He forgets everything! A. will attend B. would attend C. has attended D. had attended 【答案】 B 【解析】【分析】句意:——Sam叔叔说他将参加我的生日聚会,但是他从没有出现。——那是Sam叔叔,他忘记所有事情了。A.一般将来时;B.过去将来时;C.现在完成时;D.过去完成时。根据showed可知与过去有关,Sam叔叔说将参加聚会,但是没来,所以用过去将来时,故选B。 【点评】考查过去将来时,注意平时识记,理解句意。 2.—What did your son say in the letter? —He told me that he __________ the Great Wall the next day. A. will visit B. has visited C. is going to visit D. would visit 【答案】 D 【解析】【分析】句意:你的儿子在信中说什么?他告诉我他第二天要去参观长城.结合语境可知从句描述的是站在过去角度看将来发生的动作,故用过去将来时态,故选D. 【点评】英语中的时态主要是借助于时间状语与上下文语境来进行判断。解答此类题型,首先要注意句子中的时间状语,如果没有则要通过分析上下文,结合语境来判断句子的时态。英语疑问句中一般具有时态上的对应关系,注意结合这一特点进行区分。 3.Mr. Wu said he ______ us to the zoo the next week. A. would take B. will take C. take D. takes 【答案】 A 【解析】【分析】句意:吴老师说他下周会带我们去动物园。在这个句子中,said 后面跟的是一个宾语从句,从句中的时态是由主句决定的。主句中said 用的是过去时,故宾语从句中也需用过去时态。the next week 下周,是一个将来的时间。故应该用过去将来时。故选A。 【点评】考查动词时态。 4.—What did Alice say? —She said she me at eight o'clock tomorrow morning.
将来时的几种表达方式
一般将来时的几种表达方式 一般将来时表示将来某个时间要发生的动作或存在的状态,也表示将来经常或反复发生的动作,常与表示将来的时间状语连用。例如:tomorrow , tomorrow morning / afternoon …, the day after tomorrow , next year , next month …, from now on (从现在开始),in an hour (一小时后),in two days / weeks …等。一般将来时的表示方法有以下多种形式: 1. will / shall (1) will/shall do 表示将来时间时,一般要与表示将来的时间状语连用,或通过一定的上下文来体现将来时间状语。s hall只用于第一人称,will可以通用于各种人称。在问句中shall常用于第一人称表示建议或征求对方意见。例如: A. I shall write you a letter next month . 我下个月给你写信。 B. He will come. 他会来。 C. Shall we go to the park ? 我们去公园好吗? 注意:在You and I…或Both of us之后通常用will而不用shall,例: Both of us will be at the meeting tomorrow.明天我们俩都会出席会议。(2) will/shall be doing 因为在will/shall do中的will/shall也可理解为情态动词,所以有时会难区分它们是将来意义还是情态意义。在英语口语中我们常用will/shall be doing来表示“单纯的”将来时间。比较下列句子: I will come tomorrow.Will you come?我明天来!你来吗?(will表示意图和请求) I will be coming tomorrow.Will you be coming?我明天来,你来吗?(will 在句中单纯表示将来) 这一结构还表示不久或势必要发生的动作,例: The train will be arriving soon.火车很快就到站了。 I’ll be meeting you next year.我明年与你再见面。或表示将来某一时刻或某一段时间正在进行的动作,例: He’ll be working at the office at nine tomorrow morning.他明天上午九点在办公室工作。 I’ll be spending my holiday in China this summer.今年夏天我在中国度假。 (3) will/shall have done 此结构表示在将来另一个动作之前发生的动作,或者在将来某一特定时刻之前已经完成的动作,例: Tomorrow at ten o’clock,he will have received your letter.明天十点钟他将已经收到你的信了。 I’ll have finished my work by five this afternoon.今天下午五点钟我将完成工作。 (4) will/shall have been doing
一般将来时的句子
一般将来时的句子 一、主语+ be going to + 动词原形 肯定句:I am going to get up. He is going to get up. They are going to get up. 否定句:I am not going to get up. He is not going to get up. They are not going to get up. 一般疑问句:Are you going to get up? 肯定回答:Yes, I am. 否定回答:No, I’m not. 一般疑问句:Is he going to get up? 肯定回答:Yes, he is. 否定回答:No, he isn’t. 一般疑问句:Are they going to get up? 肯定回答:Yes, they are. 否定回答:No, they aren’t. 二、主语+ will + 动词原形 肯定句:I will get up. He will get up. They will get up. 否定句:I will not get up.
He will not get up. They will not get up. 一般疑问句:Will you get up? 肯定回答:Yes, I will. 否定回答:No, I won’t. 一般疑问句:Will he get up. 肯定回答:Yes, he will. 否定回答:No, he won’t. 一般疑问句:Are they going to get up? 肯定回答:Yes, they are. 否定回答:No, they aren’t.
一般过去将来时基本用法
英语语法必读法宝:动词(十一)一般过去将来时基本用法 今日语法:一般过去将来时基本用法 一般过去将来的构成如下: 肯定式否定式 I shall work I should not work He (she,it) would work He(she,it)would not work We should work We should not work You would work You would not work They would work They would not work 一般过去将来时基本用法 1 一般过去将来时表示在过去将来的某一时间发生的动作或存在的状态。一般过去将来时常用在间接引语中,主句谓语动词为过去时态。 如:You know I would come 你知道我会来的 We never imagined that John would become a doctor 我们从来没有想过约翰会成为一个医生。 2一般过去将来时有时候可带时间状语 如:Late at night on November 28, 1938.Dr Bethune got word that a battle would soon begin 1938年11月28日深夜,白求恩大夫接到通知说,一场战斗不久将打响。 如 the next day确是说话人时刻的第二天也可以用tomorrow He said he would come back tomorrow 他说他明天回来。 3 一般过去将来时可用来表示非真实的动作或是状态 如:If i had a chance to study abroad , i would study at Cambridge University. 如果我有机会出国学习的话,我就去剑桥大学 4 一般过去将来其他表达法。 was/were going to +动词原形 如:He said that he was going to live in the country when he retired 他说他退休后要住在农村 was/were +动词-ing 形式 如:Nobady know whether the guests were coming 没有人知道客人是否会赖。
一般将来时的定义、结构、例句、用法
一般将来时 一、定义: 一般将来时表示将来某一时刻的动作或状态,或将来某一段时间内经常的动作或状态。常常和表示将来的时间状语连用。 如:tomorrow(明天),next week(下周);in the future(将来)等。一般将来时由助动词shall(第一人称),will(第二、三人称)动词原形构成。美国英语则不管什么人称,一律用will。 二、结构 (一)常见结构 1、will / shall + 动词原形(否定句在will/shall后加not)这种方法一般单纯地表示将来某个时间将要发生的动作或存在的状态。will用于各种人称;shall只用于第一人称。例例如: I will / shall go to visit him next week. 下周我将去拜访他。 What time shall we go there tomorrow? 明天我们几点去那儿?
2、be going to+动词原形 be going to 相当于一个助动词(其中be有人称和数的变化),与它后面的动词原形一起构成谓语。用来表示将要发生的动作以及计划、安排和打算要做的事。 例如: There is going to be a football match this afternoon.今天下午将有一场足球赛。 I‘m going to go to the park. 我将要去公园。 (二)常用结构 1、用于"I expect, I'm sure, I think, I wonder等的宾语从句"中。 Don't worry about the exam. I'm sure you'll pass. 不要担心这次考试,我确信你会通过的。 2、用于祈使句和陈述句中。 Work hard and you will succeed. 如果你努力,就会成功的。 3、与表示时间或条件的状语从句连用。 I'll let you know as soon as he arrives. 他一到我就通知你。
英语时态 ----一般过去将来时
英语时态之一般过去将来时 一般过去将来时 一般过去将来时表示从过去的某一时间来看将来要发生的动作或存在的状态。过去将来时常用于宾语从句和间接引语中。一般过去将来时的出发点是过去,即从过去某一时刻看以后要发生的动作或状态。 基本信息 过去将来时的构成(句型如下:) 肯定句:主语+be(was,were)going to+动词原形+其它 否定句:主语+be(was,were)not going to+动词原形+其它 疑问句:Be(Was,Were)+主语+going to+动词原形+其它 肯定句:主语+would(should would)+动词原形+其它 否定句:主语+would(should would)not+动词原形+其它 疑问句:Would(Should would)+主语+动词原形+其它 过去将来时的结构 1同一般将来时,把系动词be变为过去式,把will,shall变为过去式。 例句:I didn't know if he would come. =I didn't know if he was going to come. 我不知道他是否会来。 She was sixty-six. In three years,she would be sixty-nine. 她66岁了。三年后,她是69岁。
She told us that she would not go with us,if it rained. 她告诉我们,如果下雨,她就不和我们一起去了。 I didn't know how to do it. What would be their ideas? 我不知如何去做,他们会有什么想法呢? 2.过去将来时常可用来表示过去习惯性的动作。此时,不管什么人称,一律用would。 过去将来时有时可带时间状语 注意 1"was/were going to + 动词原形"或"was/were +动词不定式完成式"可表示未 能实现的过去将来时间的动作。 2was/were about to do "was/were about to do"表示说话的瞬间就会发生的动作。 3was/were on the point of doing 提示"be about to do" 和"be on the point of doing"结构一般不与表示将来的时间状语连用,但后面可以接when引导的分句。 标志词 一、"would+动词原形"表示过去将来时 "would+动词原形"构成过去将来时,常表示根据计划或安排即将发生的事。 例1:He said he would come to see me.他说他要来看我。 例2:He told me he would go to Beijing.他告诉我他将去北京。 二、"was /were+going to+动词原形"表示过去将来时 "was /were+going to+动词原形"也可表示根据计划或安排即将发生的事。 例1:She said she was going to start at once.她说她将立即出发。
一般将来时的句子
一般将来时的句子 导读:本文是关于一般将来时的句子,如果觉得很不错,欢迎点评和分享! 1、她打算这天下午去看望王先生。She is going to see Mr。Wang this afternoon。 2、这封信明天将寄出去。The letter will be sent tomorrow。 3、这天下午我们打算开班会。We are going to have a class meeting this afternoon。 4、如果我们违反规定,我们将受到惩罚。We shall be punished if we break the rule。 5、下周会发生什么?What will happen in the following week? 6、九月份我将会返校。I will e back to school in September。 7、明天早上我要去买些东西。I am going to buy something tomorrow morning。 8、我明天要去上学。I will go yo school tomorrow。 9、他不会那样做的。He won't do that。 10、我将去买一本书。I'm going to buy a book。 11、Tom明晚点到我家来了。Tom will e to my home at PM。 12、王教授稍后将会给我们展示。Professor Wang will give us a presentation later。
13、你会明白这个问题的。You will understand the question。 14、明天谁将要来那里?Who will e here tomorrow? 15、你明天要干什么?What will you do tomorrow? 16、看那些乌云,快要下雨了。Look at the black clouds。It's going to rain。 17、明天我要去北京。I will go to BeiJing tomorrow。 18、下次你将在哪里打篮球?Where will you play basketball next time? 19、我将过去帮你。I'm going to help you。 20、我将回答那个问题。The question will be answered by me。 21、下个月我会看你的。I will visit you next month。
一般将来时
【教学目标】一般将来时态和其他时态一样,也是英语学习中一个不可缺少的尤其重要的时态之一。因此,此课的目标是让同学们掌握一般将来时态的基本概念及其用法,可以正确运用一般将来时态。 【知识要点】一般将来时的用法 【教学内容】 一般将来时(The Simple Future tense) 一般将来时表示将来某个时间要发生的动作或存在的状态,也表示将来经常或反复发生的动作,常与表示将来的时间状语连用。例如:tomorrow, tomorrow morning / afternoon …,the day after tomorrow , next year , next month … , from now on (从现在开始),in an hour (一小时后),in two days / weeks …等。一般将来时的表示方法有多种形式。 构成:(1)be going to + do (2)will/shall + do (3)be + doing (现在进行时表将来) (4)be (about )to + do 1. be going to+do的用法 (1)这种结构表示主体现在的意图,即打算在最近或将来要做某事,主语通常指人。在被动结构中,主语也可指物,但动作的执行者仍然是人。例如: A. What are you going to do next Sunday? 下星期天你打算干什么? B. She’s going to be a teacher. 她打算当一名教师。 C. The wall is going to be brushed white. 这面墙将刷成白色。 (2)表示说话人根据已有的迹象认为很可能即将发生某事。这时主语既可指人也可指物,此结构往往表示客观事态的发展,而不是表示主观的意图。例如: A. Look at these black clouds. —It’s going to rain. 看这些乌云。天快要下雨了。 B. I’m afraid I’m going to have a bad cold.恐怕我要得重感冒。 2. will / shall+do的用法 这种结构是表示将来的动作或状态。常伴有表示将来的时间状语。shall用于第一人称,will用于第二、三人称,但在现代英语中will可以通用于各种人称。在问句中shall常用于第一人称表示建议或征求对方意见。例如: A. I shall write you a letter next month. 我下个月给你写信。 B. I will go to my home town next week. 我下周去老家。 C. Shall we go to the park? 我们去公园好吗? 注:be going to与will用法上的异同及比较说明: (1)be going to与will都可用来表示即将发生的事情。前者多用于口语,后者常用于书面语和正式文告中。例如: A. There’ll (=is going to) be a football match in our school next week. 下周我校将举行(有)一场足球赛。
