正常血流动力学参数表电子教案

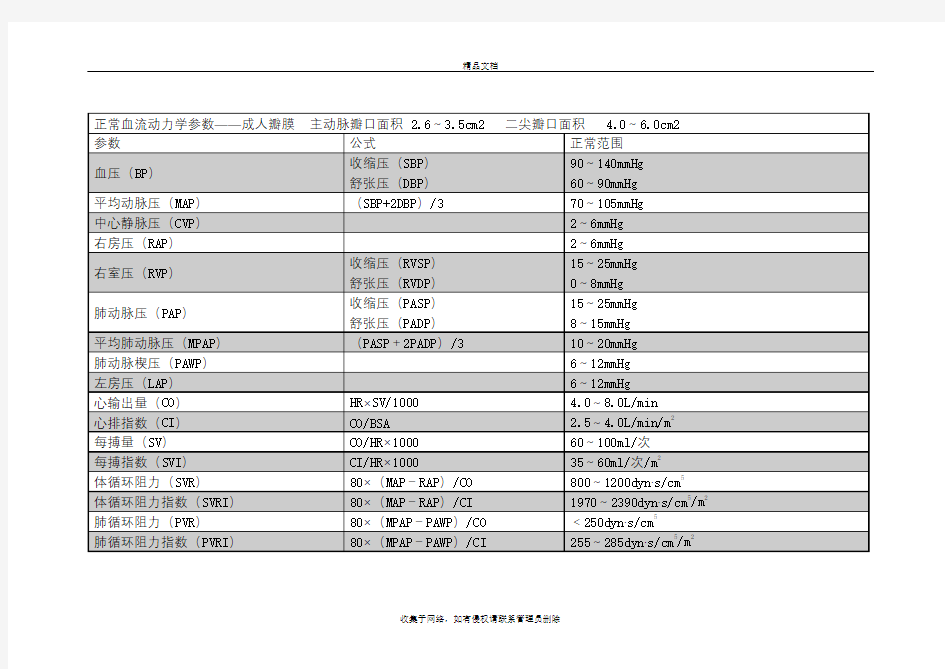
正常血流动力学参数
表
精品文档
收集于网络,如有侵权请联系管理员删除
简明常用血流动力学参数意义对照表
简明常用血流动力学参数意义对照表 1. LSI 左心搏指数 2. RSI 右心搏指数 3. LCI 左心排指数 4. RCI 右心排指数 以上四个指数代表心脏的功能指数,其中左心排指数最重要,等同于心脏指数(CI),一般来说,CI<1.5=预后极差;1.5—2.0= 心源性休克;2.0—2.2=前向性心功能不全。 5. CWT 心脏总功率:反映心脏的负荷,一般运动时,功率会增大,如果正常情况总功率偏大,则代表心脏负荷偏大;偏小则视情况而定,有身体强健者,心脏功率不必很大,但器质性偏小,则有可能造成供血不足,头晕眼花等等。 6. LWE 左心室有效功率 7. LTPF 左心室总泵力 8. LWT 左心室功率 9. LEWK 左心室机械效率 10. JP 左心室喷血压力:该指数与血压有关,如果该指数偏大,则需要小心高血压了。 11. VP 左心室有效泵力 12. EF 喷血分数:非常重要的指标,EF值长期偏小,则有很大可能性是心衰。 13. AWK 动脉机械效率 14. EPE 射流压力 15. LCRI 左室等容指数 16. RCRI 右室等容指数 15/16两个参数代表心脏的容血量,其意义不如有效循环容量重要。 17. LVDV 左室舒张末血量 18. LVDP 左室舒末期压力 19. CR 左室喷血阻抗 20. PDM 平均舒张压:高血压的判断指标之一 21. PSM 平均收缩压:高血压的判断指标之一 22. PPM 平均脉压:高血压的判断指标之一 23. MAP 平均动脉压:高血压的判断指标之一 24. HR 心率 25. CVPS 中心静脉收缩压 26. CVPM 中心静脉平均压:非常重要的指标 严重升高:1.静脉充盈过量(循环超负荷) 2.静脉充血(心脏压塞、PEEP
血流动力监测各指标及临床意义
血流动力监测各指标及临床意义 血流动力学监测的每个参数都有他的临床意义,怎样结合其它参数或临床等等都是我们应该掌握和经常思考的,而且只有在临床中不断运用、思考才能真正理解这些参数。本文介绍了直接测量所得指标:上肢动脉血压、心率、中心静脉压、右心房压、右心室压、肺动脉压、肺毛细血管嵌顿压、心输出量。由直接测量指标所派生的指标:心脏排血指数、心脏搏出量、肺血管阻力、心室做功指数和PICCO参数:血管外肺水、胸血容量。介绍了临床应用于判断左心功能、疾病的鉴别、心功能状态的治疗原则、指导疾病的治疗等。供大家参考。 1、主要监测指标 1.1直接测量所得指标 1.1.1上肢动脉血压(AP) 正常值:收缩压1 2.0~18.7kPa(90~140mmHg),舒压8.0~12.0kPa(60~90mmHg)。心排量、全身血管阻力、大动脉壁弹性、循环容量及血液粘度等均可影响动脉血压。一般用袖带血压计测量。在休克或体循环直视心脏手术时,应以桡动脉穿刺直接测量为准[1]。血压是反应心排量水平和保证器官有效灌注的基础,过高时增大左室后负荷和心肌耗氧,过低不能保证重要器官有效灌注。当MAP低于75mmHg 时,心肌供血曲线变陡下降,因此,MAP75~80mmHg,是保证心肌供血大致正常的最低限度[2]。对原有高血压病人,合理的MAP应略高于此。 1.1.2心率(HR)正常值:60~100次/min。反映心泵对代改变、应激反应、容量改变、心功能改变的代偿能力。心率适当加快有助于心输出量的增加,<50次/min或>160次/min,心输出量会明显下降[3]。 1.1.3中心静脉压(CVP)正常值:0.49~1.18kPa(5~12cmH20)。体循环血容量改变、右心室射血功能异常或静脉回流障碍均可使CVP发生变化,胸腔、腹腔压变化亦可影响
(2009)血流动力学参数集合
Sang-Wook Lee Biomedical Simulation Laboratory, University of Toronto, 5King’s College Road Toronto, Toronto,ON M5S3G8Canada; School of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering, University of Ulsan, Ulsan680-749,South Korea Luca Antiga Department of Bioengineering, Mario Negri Institute for Pharmacological Research, 24020Ranica(BG),Italy David A.Steinman1 Biomedical Simulation Laboratory, University of Toronto, 5King’s College Road Toronto, Toronto,ON M5S3G8Canada e-mail:steinman@mie.utoronto.ca Correlations Among Indicators of Disturbed Flow at the Normal Carotid Bifurcation A variety of hemodynamic wall parameters(HWP)has been proposed over the years to quantify hemodynamic disturbances as potential predictors or indicators of vascular wall dysfunction.The aim of this study was to determine whether some of these might,for practical purposes,be considered redundant.Image-based computational?uid dynamics simulations were carried out for N?50normal carotid bifurcations reconstructed from magnetic resonance imaging.Pairwise Spearman correlation analysis was performed for HWP quantifying wall shear stress magnitudes,spatial and temporal gradients,and harmonic contents.These were based on the spatial distributions of each HWP and, harmonic(DH)parameter were found to depend on how the wall shear stress magnitude was de?ned in the presence of?ow reversals.Many of the proposed HWP were found to provide essentially the same information about disturbed?ow at the normal carotid bifurcation.RRT is recommended as a robust single metric of low and oscillating shear. On the other hand,gradient-based HWP may be of limited utility in light of possible redundancies with other HWP,and practical challenges in their measurement.Further investigations are encouraged before these?ndings should be extrapolated to other vas-cular territories. ?DOI:10.1115/1.3127252? Keywords:wall shear stress,atherosclerosis,hemodynamic wall parameter,carotid bifurcation 1Introduction There is much evidence suggesting that initiation and progres-sion of atherosclerotic disease is in?uenced by“disturbed?ow”?1?.Notwithstanding the imprecise nature of this term?2?,various metrics have been proposed over the years to quantify?ow dis-turbances.Originally focused on the magnitudes of wall shear stress?WSS??3,4?these hemodynamic wall parameters?HWP?have since incorporated spatial and temporal gradients of WSS ?5–8?and,more recently,the harmonic content of time-varying WSS waveforms?2,9?. In a recent computational?uid dynamics?CFD?study of the relationship between geometry and disturbed?ow at the carotid bifurcations of young adults?10?,we noted that our?ndings were relatively insensitive to the choice of either time-averaged wall shear stress magnitude?TAWSS?or oscillatory shear index?OSI?as metrics of disturbed?ow.This was found to be explained by a strong and signi?cant inverse correlation between these two quan-tities.Such correlations among HWP are not unexpected,as rec-ognized early by Friedman and Deters?11?;however,they have been little-investigated in light of the growth in the number and complexity of candidate HWP. With this in mind,the objective of the present study was to use a representative sample of normal carotid bifurcation geometries to comprehensively test for correlations among established and recently-proposed HWP.Especially in the context of large-scale studies of so-called geometric and hemodynamic risk factors in atherosclerosis,we aimed to determine whether a subset of HWP, or even a single HWP,might serve as a suf?ciently robust marker of disturbed?ow. 2Materials and Methods 2.1Computational Fluid Dynamics.N=50anatomically re-alistic carotid bifurcation geometries were digitally reconstructed from black blood magnetic resonance imaging?MRI?of25osten- sibly healthy young adults,as described previously?12?.CFD simulations were carried out using a well-validated in-house ?nite-element-based CFD solver?13–15?.Quadratic tetrahedral- element meshes were generated by a commercial mesh generator ?ICEM-CFD;ANSYS,Berkeley,CA?using a nominally uniform node spacing of0.2mm,previously shown to be suf?cient for resolving wall shear stresses to within10%accuracy?16?.Rigid walls and Newtonian rheology were assumed.Pulsatile?ow boundary conditions were prescribed based on representative waveform shapes and allometrically-scaled inlet and outlet?ow rates.Further details of the CFD simulations are provided else- where?10?. For each tetrahedral element the vector WSS,?w,was calcu-lated as the projection of the stress tensor onto the element’s sur-face at each node,using the element’s quadratic shape functions. As nodes are connected to multiple elements,contributions to each nodal?w were averaged together.From these time-varying nodal WSS vectors,a variety of HWP were computed,as summa-rized in Table1,and detailed below. 1Corresponding author. Contributed by the Bioengineering Division of ASME for publication in the J OUR-NAL OF B IOMECHANICAL E NGINEERING.Manuscript received August12,2008;?nal manuscript received January1,2009;published online May11,2009.Review con-ducted by Fumihiko Kajiya.Paper presented at the2008Summer Bioengineering Conference?SBC2008?,Marco Island,FL,June25–29,2008.
血流动力学参数
血流动力学参数 关键词:血流动力学监测,参数,运用,意义 摘要:血流动力学监测已经广泛应用于危重症,但其数据多,每个参数因为它来源的监测手段和影响因素等等的不同,其临床意义不同。血流动力学监测的每个参数都有他的“背景”、有它的长处和短处。哪个参数有什么意义,怎样结合其它参数或临床等等都是我们应该掌握和经常思考的,而且只有在临床中不断运用、思考才能真正理解这些参数。本文介绍了直接测量所得指标:上肢动脉血压、心率、中心静脉压、右心房压、右心室压、肺动脉压、肺毛细血管嵌顿压、心输出量。由直接测量指标所派生的指标:心脏排血指数、心脏搏出量、肺血管阻力、心室做功指数和PICCO参数:血管外肺水、胸内血容量。介绍了临床应用于判断左心功能、疾病的鉴别、心功能状态的治疗原则、指导疾病的治疗等。 1、主要监测指标 1.1直接测量所得指标 1.1.1上肢动脉血压(AP) 正常值:收缩压1 2.0~18.7kPa(90~140mmHg),舒张压8.0~12.0kPa(60~90mmHg)。心排量、全身血管阻力、大动脉壁弹性、循环容量及血液粘度等均可影响动脉血压。一般用袖带血压计测量。在休克或体循环直视心脏手术时,应以桡动脉穿刺直接测量为准[1]。血压是反应心排量水平和保证器官有效灌注的基础,过高时增大左室后负荷和心肌耗氧,过低不能保证重要器官有效灌注。当MAP低于75mmHg 时,心肌供血曲线变陡下降,因此,MAP75~80mmHg,是保证心肌供血大致正常的最低限度[2]。对原有高血压病人,合理的MAP应略高于此。 1.1.2心率(HR)正常值:60~100次/min。反映心泵对代谢改变、应激反应、容量改
无创心脏血流动力学监测仪的
无创心脏血流动力学监测仪的 工作原理、参数意义和临床价值 1 心脏血流动力学的监测方法 心脏血流动力学的监测方法可分为两大类。 1.1 有创法 是经典法。优点:准确;缺点:存在一定的潜在不安全性,操作技术水平要求高,不适于长时间、多次反复使用,监测参数少,适用范围受限(不适用于危重患者、轻症患者和健康人),监测费用高。 1.2 无创法 有多种方法,目前认为心阻抗法最好。优点:安全,操作简易,可长时间、多次反复使用,可迅速连续逐搏监测多个参数,适用范围广,监测费用低廉。心阻抗法过去由于受科学技术水平的限制,一些关键技术问题没有得到解决,如阻抗的信号噪声比小,信号基线受呼吸影响大,参数计算方法不当等,所以测出的参数值的准确性和重复性差,适用范围也受一定限制。现在一些关键技术问题已得到解决,心阻抗法与有创法的相关系数达0.9左右,一致性好。 2 心阻抗法的工作原理 2.1 心阻抗法的工作原理 左心室开始收缩后,……这就是心阻抗法的工作原理。 2.2 心阻抗法的工作波形图 阻抗图……代表阻抗减小,即血管容积增大;阻抗微分图……有4个主要的波,波的峰点、谷点和B点是……特征点……反映左心室射血随时间的变化规律,即血流动力学状态;心电图(ECG):将Q起点作为一个心动周期的始点;心音图(PCG):除必要时用于自动找点或人工调点外,也可单独用于对心音图的分析。 3 心阻抗法的临床价值 心脏血流动力学参数的监测,可以提供很多极有价值的生理信息,对医疗和科研都具有重要的临床价值。心阻抗法是一种安全、可靠、简易、准确、价廉、不影响心脏泵工作的监测心脏血流动力学参数的无创法。无创心脏血流动力学监测仪能够实时连续逐搏检测血流动力学参数。而且,由于它的准确性和重复性好,能提供长时间连续监测所需要的参数值变化趋势图,这在许多临床应用中,比单次检测参数值更有使用价值,因为医生们更关心通过观察血流动力学参数的变化,了解治疗效果,以改善治疗方案或及时进行抢救。 心阻抗法在有创法不能使用场合(危重患者、轻患者、导管禁忌患者和健康人),是心脏病患者和健康人的无创心功能检测的理想方法。 心阻抗法在多个医学领域正在推广应用,现作简要介绍。 3.1 干部保健科及健康体检中心:
