轮机英语11规则(大管轮)

轮机英语
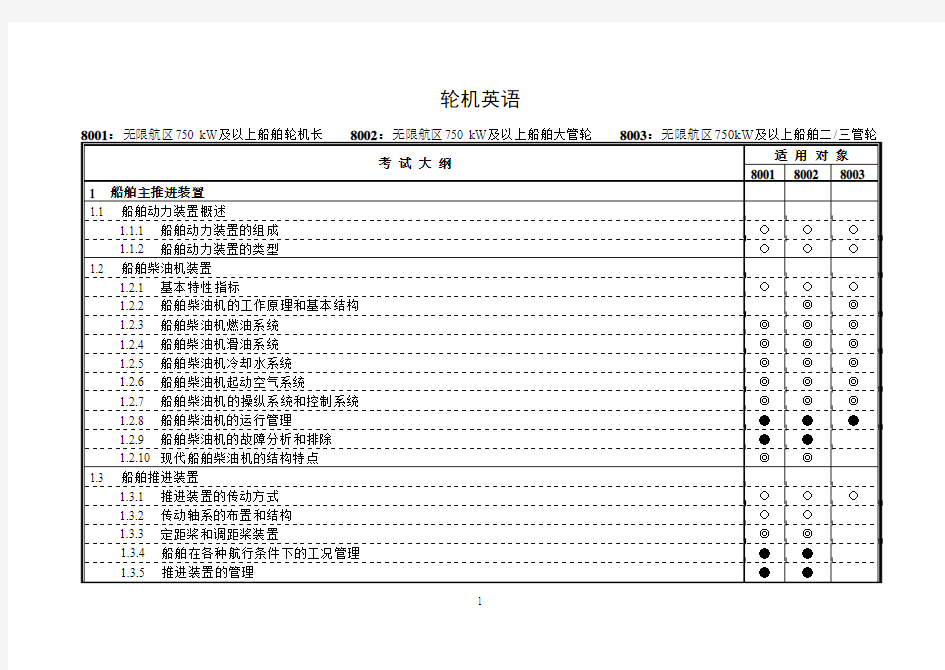
8001:无限航区750 kW及以上船舶轮机长 8002:无限航区750 kW及以上船舶大管轮 考 试 大 纲 1 船舶主推进装置 1.1 船舶动力装置概述 1.1.1 船舶动力装置的组成 1.1.2 船舶动力装置的类型 1.2 船舶柴油机装置 1.2.1 基本特性指标 1.2.2 船舶柴油机的工作原理和基本结构 1.2.3 船舶柴油机燃油系统 1.2.4 船舶柴油机滑油系统 1.2.5 船舶柴油机冷却水系统 1.2.6 船舶柴油机起动空气系统 1.2.7 船舶柴油机的操纵系统和控制系统 1.2.8 船舶柴油机的运行管理 1.2.9 船舶柴油机的故障分析和排除 1.2.10 现代船舶柴油机的结构特点 1.3 船舶推进装置 1.3.1 推进装置的传动方式 1.3.2 传动轴系的布置和结构 1.3.3 定距桨和调距桨装置 1.3.4 船舶在各种航行条件下的工况管理 1.3.5 推进装置的管理
1
8003:无限航区750kW及以上船舶二/三管轮 适 用 对 象 8001 8002 8003
○ ○ ○ ◎ ◎ ◎ ◎ ◎ ● ● ◎ ○ ○ ◎ ● ●
○ ○ ○ ◎ ◎ ◎ ◎ ◎ ◎ ● ● ◎ ○ ○ ◎ ● ●
○ ○ ○ ◎ ◎ ◎ ◎ ◎ ◎ ●
○
2 船舶辅助机械 2.1 船用锅炉 2.1.1 船用锅炉的类型 2.1.2 典型船用锅炉的结构特点 2.1.3 船用锅炉的运行管理 2.1.4 船用锅炉的故障分析和排除 2.2 船用泵 2.2.1 船用泵类型 2.2.2 常见船用泵的工作原理和结构特点 2.2.3 船舶通用泵系的布置原则和特点 2.2.4 常见船用泵的运行管理和故障排除 2.3 船舶制冷和空调装置 2.3.1 制冷原理和制冷循环 2.3.2 船舶制冷系统的组成及主要设备 2.3.3 船舶空调系统的组成及主要设备 2.3.4 船舶制冷装置的运行管理 2.3.5 船舶空调装置的运行管理 2.3.6 船舶制冷装置的故障分析和排除 2.3.7 船舶空调装置的故障分析和排除 2.4 船舶防污染设备 2.4.1 油水分离器的工作原理及运行管理 2.4.2 焚烧炉的工作原理及运行管理 2.4.3 生活污水处理装置的工作原理及运行管理 2.5 分油机、空压机和海水淡化装置 2.5.1 分油机的工作原理及运行管理 2.5.2 分油机的故障分析和排除 2.5.3 空压机的工作原理及运行管理
2
●
●
○ ○ ● ● ○ ○ ◎ ● ◎ ○
◎ ●
◎ ● ◎ ○ ●
○ ○ ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
●
2.5.4 空压机的故障分析和排除 2.5.5 海水淡化原理 2.5.6 海水淡化装置的主要设备和运行管理 2.6 船舶甲板机械 2.6.1 液压泵、控制阀件和油马达的结构特点 2.6.2 起货机的结构特点及其故障分析和排除 2.6.3 锚机的结构特点及其故障分析和排除 2.6.4 绞缆机的结构特点及其故障分析和排除 2.6.5 舵机的工作原理及结构特点 2.6.6 舵机的故障分析和排除 2.6.7 液压系统管理 3 船舶电气和自动化 3.1 船用发电机 3.1.1 船用发电机的结构特点 3.1.2 船用发电机的并车和解列 3.1.3 船用应急发电机 3.2 船用配电板 3.2.1 主配电板的组成 3.2.2 应急配电板 3.2.3 配电箱 3.3 船舶电气设备 3.3.1 船舶电气设备 3.3.2 电气控制设备 3.3.3 电气设备运行管理 3.4 船舶自动化 3.4.1 自动控制基本原理 3.4.2 自动控制仪表
3
● ● ◎ ● ● ● ◎ ● ● ◎
● ○ ● ◎ ● ● ● ◎ ●
● ●
◎ ● ● ○ ○ ○ ◎ ◎ ● ○ ○
● ○ ○
◎ ● ● ○ ○ ○ ◎ ◎ ● ○ ○
◎ ◎ ● ○ ○
3.4.3 3.4.4 3.4.5 3.4.6
典型的自动控制系统 集中监视和报警系统 无人机舱的基本涵义及功能要求 船舶计算机网络基础
◎ ◎ ◎ ◎
◎ ◎ ◎ ◎
◎ ◎
4 船舶轮机管理业务 4.1 操作规程 4.1.1 备车 4.1.2 巡回检查 4.1.3 完车 4.2 安全管理知识 4.2.1 轮机部操作安全注意事项 4.2.2 船舶防火防爆的措施及守则 4.2.3 机舱应急设备的使用及管理 4.2.4 船员个人安全知识 4.3 油料、物料和备件的管理 4.3.1 燃油的管理 4.3.2 润滑油的管理 4.3.3 物料和备件的管理 4.4 船舶修理和检验 4.4.1 修理的类别 4.4.2 轮机坞修工程 4.4.3 试验与试航 4.4.4 船舶检验的类别与作用 4.4.5 轮机设备检验证书 4.5 防污染管理及PSC检查 4.5.1 海洋环境保护知识 4.5.2 《油类记录簿》与IOPP证书的管理
4
● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ○ ○ ● ○ ○ ○ ●
● ● ● ● ● ● ●
● ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
● ● ○ ○ ● ○
● ○
○ ●
○ ●
4.5.3 PSC检查中的明显理由与更详细检查 4.5.4 PSC检查报告和缺陷的纠正 4.6 机舱资源管理的基本知识 5 国际公约、规则 5.1 STCW公约 5.1.1 轮机值班的基本原则 5.1.2 轮机员的基本职责和道德 5.1.3 驾机联系制度 5.2 MARPOL公约 5.2.1 MARPOL公约中有关污染物的排放规则 5.2.2 有关国家、港口的防污染规则 5.3 SOLAS公约 5.3.1 SOLAS公约的基本精神和基本原则 5.3.2 SOLAS公约的主要内容 5.3.3 SIM规则 5.3.4 ISPS规则简介 5.4 ILO公约及其他公约和规则 5.4.1 ILO公约 5.4.2 其他最新公约和规则 6 轮机业务书写 6.1 轮机日志与油类记录簿 6.1.1 填入轮机日志的主要内容 6.1.2 正确书写轮机日志 6.1.3 正确填写油类记录簿 6.2 修理单 6.2.1 修理单的种类 6.2.2 正确书写修理单
5
● ● ○
● ● ○
● ● ○
◎ ◎ ◎ ● ● ◎ ◎ ◎ ◎ ◎ ◎
◎ ◎ ◎ ● ● ◎ ◎ ◎ ◎ ◎ ◎
◎ ◎ ◎ ● ●
◎ ◎ ◎ ◎ ◎
○ ● ● ○ ●
○ ● ● ○ ●
○ ● ● ○ ●
6.3 备件、物料订购单 6.3.1 一般格式 6.3.2 正确书写订购单 6.4 事故报告 6.4.1 事故报告应包涵的内容 6.4.2 正确书写事故报告 6.5 工作报告、信函、传真及电子邮件 6.5.1 航次报告 6.5.2 保修和索赔报告 6.5.3 信函、传真及电子邮件 6.6 正确书写轮机关键设备的操作规程
○ ● ○ ● ● ● ● ●
○ ● ○ ●
○ ●
● ● ●
●
注:● 熟练
◎掌握
○了解
6
轮机英语
轮机英语词汇 1、pump 泵 ①Supply pump供给泵②transfer pump 输送泵 ③circulating pump 循环泵④bilge pump 舱底水泵 ⑤ballast pump 压载水泵 1、tank ①drain tank 泄放柜②service tank 日用柜 ③settling tank沉淀柜④storage tank 储存柜 ⑤circulating tank 循环柜⑥used oil tank 废油柜 ⑦buffer tank 缓冲柜⑧overflow tank 溢流柜 ⑨Collecting tank 收集柜⑩expansion water tank 膨胀水箱 2、water ①sea water (S.W.) 海水②fresh water (F.W.)淡水 ③operating water 工作水④sanitary water 卫生水 ⑤washing water冲洗水⑥refilling water 再注水 ⑦feed water给水⑧condensate water 冷凝水 ⑨bilge water 舱底水⑩sewage污水 2、oil ①fuel oil (F.O.) 燃油②lubricating oil (L.O.) 滑油 ③engine oil 机油④cylinder oil 气缸油 ⑤diesel oil (D.O.) 柴油⑥turbine oil 透平油 ⑦cool oil 冷却油⑧seal oil 密封油 3、temperature (temp) 温度 4、flow 流量 5、pressure(press)压力 6、power 功率 10、level 液位 11、vibration 振动 12、normal/abnormal 正常/异常 13、main/auxiliary (aux.) 主要/辅助的 14、inlet/exhaust 进气/排气 15、fire alarm 火警 16、fail/failure 故障 17、overload 过载 18、no-voltage 失电 19、leak/leakage 泄漏 20、wrong-way 错向 21、insulation(insul) 绝缘 22、oil mist 油雾 23、viscosity 粘度 24、density 浓度 25、salinity 盐度 26、oil content 油含量
轮机大管轮英语真题48期
中华人民共和国海事局 2009年第5期海船船员适任证书全国统考试题(总第48期) 科目:轮机英语试卷代号:803 适用对象:无限、近洋航区3000KW及以上船舶大管轮 (本试卷卷面总分100分,及格分为70分,考试时间为100分钟) 答题说明:请选择一个最合适的答案,并将该答案按答题卡要求,在其相应位置上用2B铅笔涂黑。第1题至82题,每题1分,第83题至94题,每题1.5分。 一、单项选择题: 1. The reason why more and more of the large merchant vessels are being powered by medium-speed diesel engines is . A. they operate between 150 and 450 rpm B. they are connected to the propeller by gearing C. their smaller size and weight D. they can be connected directly to the propeller without gearing 2. The closing of the exhaust valves used on a modern, large, low-speed, main propulsion diesel engine may be directly provided by . A. large conical springs B. compressed air pressure C. hydraulic pressure D. exhaust gas pressure 3. One of the factors limiting the amount of toad which can be put on a modem marine diesel engine is the . A. governor sensitivity B. exhaust temperature C. fuel injection pressure D. speed of the cam shaft 4. The desirable properties or a marine fuel oil should inc lude . A. high flash point and high viscosity B. low flash point and high viscosity C. low heating value and high sulphur content D. high heating value and low sulphur content 5. As the plunger moves upwards in the barrel, injection will commence once the plunger bas the spill ports and the pressure builds up. A. opened up B. closed off C. lined up D. taken off 6. In an auxiliary diesel engine bypass type lubricating oil system, the main lube oil pump forces . A. all of the oil used by the engine through a filter B. some of the oil used by the engine through a filter C. some of the oil used by the engine through a centrifuge D. all of the oil used by the engine through a centrifuge 7. Because the circulating water is in a closed loop, is installed to cater for expansion and contraction of the water at different conditions of operation. A. an expansion joint B. a drain tank C. a head tank D. a contraction tank 8. The high air velocity leaving the compressor of an exhaust gas turbocharger is converted to pressure in the . A. inlet nozzle ring B. turbine wheel blade C. diffuser passages D. inlet volute 9. is usually driven by the engine camshaft and supplies pilot air to the cylinder air start valve. A. An air receiver B. An operating valve C. An automatic valve D. An air distributor 10. Diesel engines driving alternators operating in parallel must maintain a set frequency regardless of load changes. The governor characteristic used to accomplish this is known as . A. actuation B. sensitivity C. compensation D. promptness 11. By comparing the exhaust gas temperature of each cylinder, the operator can determine if the load is balanced throughout the engine. The device most commonly used is a . A. tachometer B. pyrometer C. dynamometer D. calorimeter 12. When the ship is going to enter into the harbor, ____. A. change from heavy fuel oil to diesel oil for main engine B. pumping out bilge water C. change sea chest from high level one to lower level one D. test emergency generator 13. If the jacket water temperature rises rapidly above normal in a diesel engine, you should first . A. place standby cooler in operation B. reduce engine toad C. check thermostatic valve D. clean sea water strainer 14. Air cocks, usually positioned at the in a circulating system, is used to get rid of the air in the system. A. bending joint B. expansion tank C. weld D. the highest point 15. Which of the following conditions could contribute to the cracking of a diesel engine cylinder head? A. Leaking seal ring B. Insufficient heat transfer from the exhaust valves C. Blocked cooling water passages to the head D. Excessive scavenging air provided to the engine 16. of an engine crankshaft can be detected by measuring deflections of' crank webs for each unit of the engine. A. Misalignment B. Length C. Strength D. Stresses 17. can be a direct cause of faulty operation of diesel engine fuel injection nozzles. A. Excessive fuel nozzle holder cooling B. Sediment in the fuel supply C. Distortion of the fuel spray pattern D. Improper atomization of the fuel 18. When fuel is injected late into a diesel engine cylinder . A. the exhaust will be clear B. fuel consumption will be low C. all the fuel will be burned at top dead center D. fuel consumption will be high 19. A large change in ambient temperature, or using an oil of a viscosity different than the one recommended by the manufacturer in a mechanical hydraulic governor, will result m the need to adjust the . A. pilot valve opening B. compensating needle valve C. compensating spring tension D. accumulator spring tension 20. Which of the following factors tends to increase scale formation on the saltwater side of a heat exchanger used in a diesel engine cooling water system? A. Baffle plates that have been bent during prior removal. B. Leaks m the cooler tube nest. C. Operating the engine while maintaining a high sea water outlet temperature. D. A punctured sea water strainer supplying cooling water to the heat exchanger. 21. If the scavenge fire is of a more major nature, if there is a risk of the fire extending or if the scavenge trunk is adjacent to the crankcase with risk of a hot spot developing it sometimes becomes necessary to the engine. A. stop B. start C. speed up D. slow down 22. In an operating diesel engine, which of the following conditions is an indication of a leaking air starting valve?
三管轮轮机英语大证考试真题41期
中华人民共和国海事局 2006年第3期海船船员适任证书全国统考试题(总第41期) 科目:轮机英语试卷代号:805 适用对象:无限、近洋航区3000KW及以上船舶二/三管轮 (本试卷卷面总分100分,及格分为70分,考试时间为100分钟) 答题说明:请选择一个最合适的答案,并将该答案按答题卡要求,在其相应位置上用2B铅笔涂黑。第1题至74题,每题1分,第75题至78题,每题1.5分,第79题至80题, 每题10分。 一、单项选择题 1. A diesel engine is similar to a gasoline engine except that the former has no ______. A. cross-head B. spark plug C. connecting rod D. cylinder 2. A diesel engine which is rated for normal operation at a crankshaft speed of 800 RPM, is commonly classed as a ______. A. slow-speed diesel B. medium-speed diesel C. high-speed diesel D. constant-speed diesel 3.Which of the diesel engine components listed increases air density and helps to improve engine operating efficiency? A. Impeller B. Compressor C. After-cooler D. Exhaust diffuser 4.For a given size engine, the two-stroke/cycle diesel engine will deliver more power than a four- stroke/cycle diesel engine because ______. A. it has a longer power stroke B. more air gets into the cylinder each stroke C. it develops twice as many power strokes at the same speed D. higher combustion pressure is developed 5.The intake valves in a diesel engine are reseated by ______. A. cam followers B. push rods C. combustion gases D. valve springs 6.According to the way the energy of the exhaust gases is utilized, pressure-charging can be divided into two main systems, namely, the constant-pressure system and ______. A. the pulse-phase system B. the pulse Doppler system C. the pulse system D. the pulse interval system 7.An over-speed safety device is usually fitted to a generator engine for______in the event of over- speed. A. cutting power off the engine B. increasing the fuel pump setting C. braking the crankshaft D. stabilizing the ship speed 8.What preventative maintenance should be done frequently to diesel engine starting air receivers? A. Drain the accumulated moisture. B. Test the relief valves. C. Watch the temperature to prevent fluctuations in pressure. D. Clean the interior to remove oil and foreign matter. 9.Immediately after any diesel engine is started, the engineer should check the ______. A. crankcase pressure B. lube oil pressure C. seawater pressure D. exhaust temperature 10. A controllable pitch propeller on a diesel driven vessel eliminates the need for ______. A. friction clutches B. disconnect clutches C. reversing gears D. reduction gears 11.In motor ship, ______is often used to recover some of the heat carried in the exhaust gases from the main engine. A. an diesel oil heater B. a waste heat boiler C. a fresh water generator D. a donkey boiler 12.An exhaust gas bypass is installed on a waste heat boiler in order to ______. A. bypass exhaust gas at high loads to prevent excessive back pressure B. bypass a portion of the exhaust gas at peak loads for better efficiency C. recycle exhaust gas to the turbocharger D. minimize moisture condensation in the boiler gas passages at low loads 13.Prior to lighting off a cold automatically fired auxiliary boiler, you should ______. A. check and regulate the water level B. close the air cock once fires are lit C. blow down the gage glass D. assure protective steam flow 14.Flame failure in an automatically fired auxiliary boiler can mostly result from a/an ______. A. incorrect electrode setting B. incorrect nozzle position C. clogged fuel nozzle D. broken high tension lead 15.Waterside scale in a fire-tube boiler may cause ______. A. increased heat transfer B. fireside erosion C. high steam demand D. overheated tubes 16.Which of the following will be the advantage of a centrifugal pump as compared with a reciprocating pump? I. Its discharge is continuous; II. It has no internal valves; III. Upon accidental closing of discharge valve, excessive pressure will not build up A. I, II B. II, III C. I, II, III D. II only 17.Why are removable sleeves installed on centrifugal pump shafts? A. They make it easier to replace the pump shaft packing. B. They can be economically replaced as they wear out. C. They can be removed when it is necessary to lighten the weight of the pump. D. They increase the strength of the shaft. 18.If one of the bilge system manifold valves does not properly seat, the ______. A. bilge well connected to that valve, plus the second bilge well being pumped will be completely emptied B. bilge system will lose vacuum and prevent the other bilges from being pumped out C. bilge well aft connected to that valve will siphon(虹吸) its contents to the forward bilge wells D. discharge pressure will be too high. 19.Which of the listed statements is correct concerning the starting of centrifugal pumps? A. They should always be started with the discharge valve closed. B. They should always be started with the discharge valve opened. C. A priming pump is always required to flood the impeller suction. D. They should always be started with the sealing line valves closed. 20.The simplest method to use for determining if a centrifugal pump is operating as designed, is to ______. A. closely observe the pump discharge temperature B. close off the discharge valve, and watch for a rise in pressure C. momentarily close off the suction valve, and watch for a rise in pressure D. use a clamp on ammeter and compare the readings to past records
船舶、轮机英语词汇大全
船舶英语 目录 一.职位及工种 (Titles and type of work) (1) 二、柴油机类 (Words about diesel engine) (3) 三、船舶机械类 (Words about marine machinery) ·· 11 四、阀门(Words about valve) (14) 五、泵类(Words about pump) (16) 六、甲板机械类(Deck machinery) (18) 七、工具类(Word about tools) (20) 八、常用物料(Material in common use) 26 九、常用紧固件 (Part of fixation in common use) (28) 十、常用油类(Oil in common use) (28) 十一、常用量词 (Quantifier in common use) (29) 十二、国家名称(Name of country) 。 30 十三、常用缩语 (abbreviation in common use) (31) 十四、船用动态常用单词(marine tends word) 32 十五、船舶机电设备操作词汇 (manipulate of marine equipment) ·33 十六、故障常用单词 (words about malfunction) (35) 十七、保养检修常用词汇 (Words about maintain and examination) 38 十八、常用数字(Numeral in common use) 40 十九、时间、季节与方向 (Time、Season and Direction) (42) 二十常用词组(Phrases in common use)·45 二十一、常用动词和例句 (Verb in common use and example) (48) 二十二、问候和常用表达语 (Greeting and common expression) (67) 二十三、主机提交过程用语 (Delivery expressions for main engine) 68 二十四、空压机和空气系统用语 (Air compressor and Air system) (75) 二十五、锅炉提交用语 (Delivery expressions for boiler) (77) 二十六、锚绞车提交过程用语(Delivery expressions for anchor windlass) 79 二十七、舵机提交过程用语 (Steering gear delivering) (87) 二十八、付机提交过程用语 (Delivery expression for A/E) (91) 二十九、救生艇提交过程用语 (Delivery expressions for lifeboat) ··92 三十、其他提交项目 (Delivery expressions for other items) (95) 三十一、甲板机械系泊试验 (Mooring test for deck machinery) (96) 三十二、机舱设备系泊试验 (Mooring test for the equipment in E/R) (98) 三十三、谈论故障常用语 (Expressions for trouble) (100) 三十四、谈论检修常用语 (Expressions for overhaul) (101) 三十五、谈论试验和检验 (Talking about test & check) (103) 三十六、谈论技术要求 (Talking about technology required) (105) 一.职位及工种(Titles and type of work) 1.船长 Captain 2.大副 Chief officer 3.二副 Second officer 4.三副 Third officer 5.四副 Fourth officer 6.水手长 Boatswain 7.水手 Sailor & Seaman 8.木匠 Carpenter 9.轮机长 Chief engineer 10.大管轮 Second engineer 11.二管轮 Third engineer 12.三管轮 Fourth engineer 13.机匠长 Chief motorman 15.机匠 Fitter 16.加油工 Oil man 17.大电 Chief electrician 18.电工 Electrician 19.车间主任 Workshop director 20.工长 Section chief 21.班长 Fore man 22.钳工 Fitter 23.主管工程师 Engineer in charge 24.机务&船东 Superintendent &Super &Owner 25.助理工程师 Assistant engineer 26.验船师(机)Register 27.验船师(船)Surveyor 28.油漆工 Painter 29.焊工 Welder 30.大橱 Chief cook 31.物料员 Store keeper 32.加油工 Oiler 33.机工 Mechanic 34.甲板员 Deck man 35.电线工 Wireman 36.外包工 Laborer 37.铸工 Molder 38.管子工 Pipe fitter 39.起重工 Crane operator 二、柴油机类(Words about diesel engine) 1.主机 Main engine 2.二冲程柴油机 Two-stroke diesel engine 3.四冲程柴油机 Fore-stroke diesel engine 4.高速柴油机 High speed diesel engine 5.中速柴油机 Middle speed diesel engine 6.低速柴油机 Low speed diesel engine 7.气缸盖(缸头) Cylinder head 8.安全阀 Safety valve 9.释放阀 Relief valve 10.示功阀 Indicator valve 11.示功考克 Indicator cock 12.空气起动阀 Air starting valve 13.起动空气分配器 Air starting distributor 14.油头(燃油喷射器) Fuel injector 15.排气阀 Exhaust valve 16.气缸套 Cylinder liner 17.冷却水套 Cooling water jacket 18.气缸注油器 Cylinder lubricator 19.活塞 Piston 20.活塞头 Piston crown 21.活塞裙 Piston skirt 22.活塞销 Piston gudgeon pin 24.活塞杆 Piston rod 25.活塞环 Piston ring 26.活塞环槽 Piston ring groove 27.压缩环 (气环) Compression ring 28.刮油环 (油环) Oil scraper ring 29.减磨令 Wear ring (copper ring) 30.伸缩管(水拉管) Telescopic pipe 31.活塞冷却空间 Piston cooling space 32.填料箱(函) Stuffing box 33.填料箱密封环Sealing ring for Stuffing box 34.填料箱压缩环 Pressure ring for Stuffing box 35.填料箱刮油环Scraper ring for Stuffing box 36.扫气箱 Scavenging receiver 37.扫气口 Scavenging port 38.排气口 Exhaust port 39.十字头 Cross head 40.十字头销 Crosshead pin 41.十字头轴承 Crosshead bearing 42.十字头滑块 Crosshead slipper 43.滑块 Guide shoe 44.十字头导板 Crosshead guide plate 45.连杆 Connecting rod 46.连杆大端轴承 Bid end bearing 47.连杆小端轴承 Small end bearing 48.曲柄轴承 Crank bearing 49.曲柄销 Crank pin 50.曲轴 Crank shaft 51.曲轴颈 Crank journal 52.曲柄臂 Crank web 53.拐档差 Crank deflection 54.主轴承 Main bearing 55.主轴颈 Main journal 56.轴承瓦 Bearing bush 57.上轴瓦 Upper bearing bush 58.上轴瓦 Upper half 59.下轴瓦 Lower bearing bush 60.下轴瓦 Lower half 61.推力轴承 Thrust bearing 62.推力块 Thrust pad 63.推力盘 Thrust disc 64.推力轴 Thrust shaft 65.底座 Bed plate 66.机架 Frame 67.曲柄箱 Crank case 68.曲柄箱导门 Crank case door 69.曲柄箱防爆门 Explosion-proof Crank case. 70.定时齿轮 Timing gear 71.飞轮 Flying wheel 72.凸轮 Cam 73.凸轮轴 Cam shaft 74.喷油凸轮 Fuel injection cam 75.链条 Chain 76.链条轮 Chain wheel 77.链条箱 Chain box 78.推杆 Push rod 79.摇臂 Rocker arm 80.排气阀 Exhaust valve 81.吸气阀 Suction valve 82.排气总管 Exhaust manifold 83.进气总管 Air inlet manifold 84.高压燃油管 High pressure fuel pipe 85.活塞冷却水管 Piston cooling water pipe 86.法兰 Flange 87.贯穿螺栓 Tie bolt (tie rod) 89.滑油泵 Lubricating oil pump 90.燃油泵 Fuel oil pump 91.滑油泵齿轮 Gear for lubricating oil pump 92.燃油泵齿轮 Gear for fuel oil pump 93.叶轮 Impeller 94.柱塞 Plunger 95.导杆 Guide rod 96.导套 Sleeve 97.滚动轴承 Ball bearing 98.滑动轴承 Sliding bearing 99.推力滚动轴承Thrust ball bearing 100.推力面 Thrust surface (thrust side) 101.盘车机 Turning gear 102.增压器 Turbocharger 103.涡轮机(透平) Turbine 104.涡轮 Turbine wheel 105.涡轮叶片 Turbine blade 106.喷嘴 Nozzle 107.废气叶轮 Exhaust impeller 108.废气叶轮片 Exhaust blade 109.废气端 Exhaust side 110.透平端 Turbine side 111.转子轴 Rotor shaft 112.油泵 L.O.pump 113.换向装置 Reversing device 114.换向伺服期 Reversing servomotor 115.压气机(鼓风机) Blower 116.膨胀接 Expansion joint 117.调速器 governor 118.飞重 Flying weight 119.补偿阀 Compensate valve 120.针阀 Needle valve 121.开口销 Cotter pin 122.轴封 Shaft seal 123.机械密封 Machinery seal 4
轮机英语专业词汇
专业词汇Special Terms 第一部分柴油机 Diesel Engine 二冲程船用柴油机two stroke marine diesel engine 四冲程船用柴油机four stroke marine diesel engine 高(中,低)速柴油机high(medium,lower)speed engine 气缸cylinder 气缸盖cylinder cover(cylinder head) 苏尔寿发动机Sulzer engine B&W型发动机Burmeister and Wain engine 哥塔维根型发动机Gotaverken engine 曼恩型发动机 V型发动机V-type engine 直流扫气式发动机uniflow scavenging type engine 回流扫气式发动机loop flow scavenging type engine 横流扫气式发动机crow-flow scavenging type engine 十字头式发动机crosshead engine 筒形活塞式发动机trunk-ppiston engine 涡轮增压式发动机turbocharge engine 固定部件fixed parts 耐磨部件wear parts 运动部件moving parts 互换部件interchangeable parts 气缸套cylinder liner 示功阀indicator cock(indicator valve) 安全阀safety valve 气缸启动阀cylinder air starting valve 缸套顶圈head ring for cylinder liner 排气阀exhaust valve 进气阀air inlet valve(suction valve) 气阀传动机构valve driving mechanism 顶杆tapper rod 推杆push rod 摇臂rocker rod (rocking lever) 活塞pistion 十字头式活塞crosshead type pistion 筒形活塞trunk pistion 活塞头pistion crown(head) 活塞裙pistion skirt 活塞体pistion body 活塞销pistion pin(gudgeon pin) 活塞环pistion ring 气环(压缩环)compression ring 刮油环oil scraper ring(oil ring,scraper ring)
船舶轮机英语单词总结
船舶轮机英语单词总结 A layer of lubricant 润滑层 abrasive 有磨蚀的 accommodation 住舱 accommodation ladder 舷梯 accommodation 居住舱室 Accomplish 完成,达到,实现 activate 使活动,起动 Adjustment 调整 Administrative offices 管理办公室 adopt 采用 advantage 优势,优点,效益应用 affect 影响 Aforesaid 上述的,前述的(常用于法律文件) aft ballast tank 艉压载舱 Aggregate 合计,总计 air cushion craft 气垫船 air draught 水面上高度 air pipes,sounding pipes and overflow pipes 空气管、测量管和溢流管路alarm 警报器 alkalinity 碱度,碱性 all duties pump 总用泵 alloy 合金 alternative 替换物,选择对象 alternator 交流发电机 aluminum 铝 Aluminum 铝 among 在……之中 Analyze 分析 anchor 锚 anchor arrangement 锚泊设备 anchor bell 锚钟 anchor hoisting winch 起锚绞车 anchor light 锚灯 Anchorage 锚地 Anchor-heaving trial 抛锚试验 anti-corrosive oil 防腐油 Aperture 孔,穴 Applicant 申请者 Applicant 申请者 application 应用 application 应用,运用 Approach 方法,步骤,途径
