第1课 生活中的算法
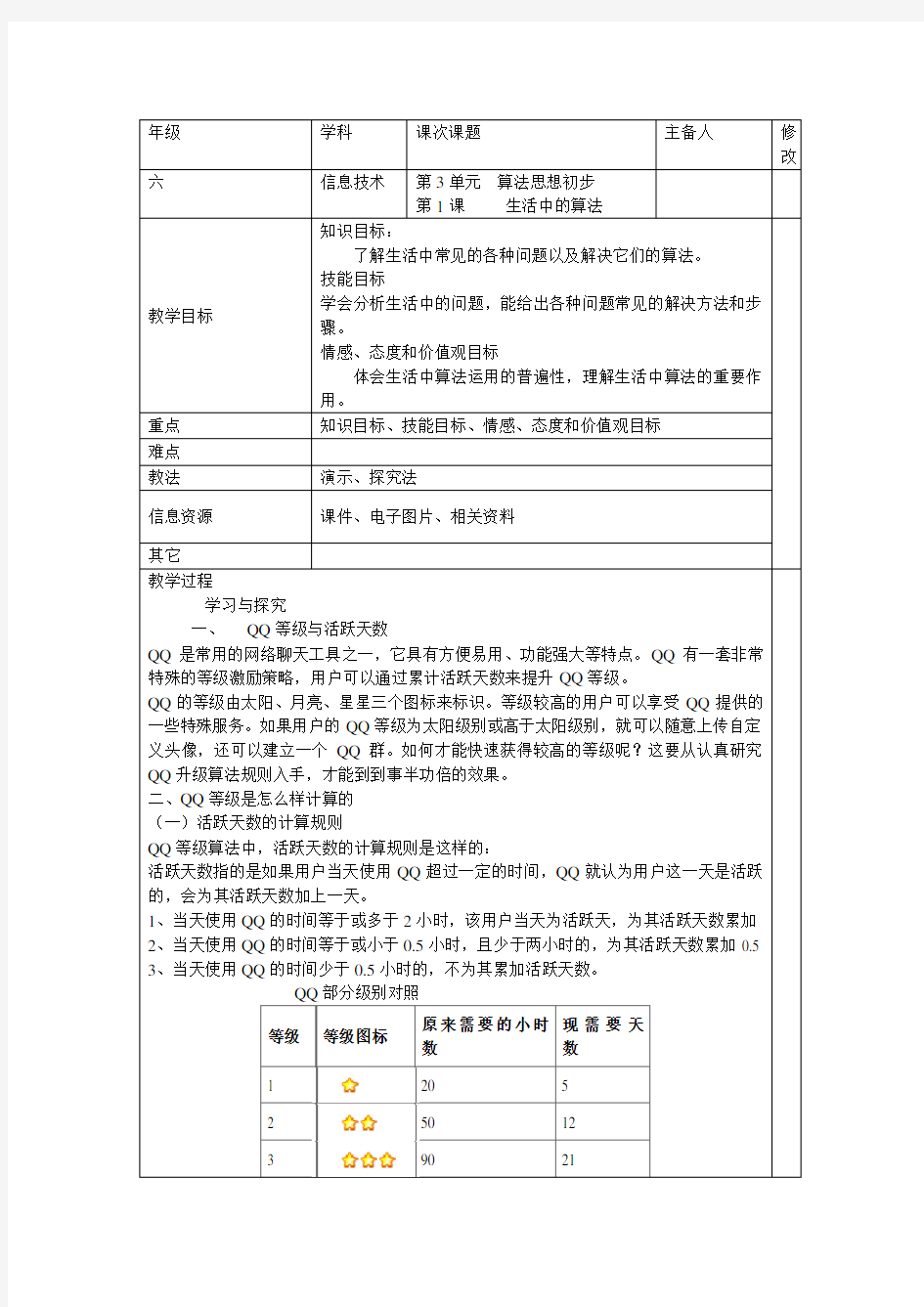
20 50 90
4 140 32
5 200 45
6 270 60
7 350 77
8 440 96
12 900 192
16 1520 320
32 5600 1152
48 12240 2496
(二)QQ等级与活跃天数的计算公式
QQ等级与活跃天数的计算公式为:
第N级所需累积的活跃天数=N×N+4×N
例如:假设有一用户其目前等级正好为13级,则其活跃天数为:活跃天数=131×3+4×13=221天。
利用QQ的等级算法,我们可以在使用中有效控制使用时间,通过不断累积QQ的活跃天数,就可以提升QQ等级。在生活中有许多类似的法则,可以快速提升自己相应的权限。
在好友资料和Tips中查看在线等级。
三、手工洗衣的算法
日常生活中,洗衣服是最常做的家务。洗衣时,我们常用的方法是用洗衣机洗衣和手工洗衣。现在虽然洗衣机已经十分普及,但在衣服比较少时,我们还要采用手工洗衣的方式来洗衣服。
手工洗衣时,掌握正确的洗衣方法很重要。我们通常采用下面的步骤:
第1步:用清水泡几分钟。
方法,这种顺序和方法我们称为炒菜的算法。
与计算机下象棋自动提款机
借助计算机,人们很多的算法思想正在变成现实。如把中国象棋的规则方法借助计算机来实现,可以实现人与计算机下棋;工业机器人可以实现生产流水线上的各种操作步骤,而且做起来更精确,提高了生产的质量,降低了成本;利用银行自动提款机的各种提示进行操作,可以实现自动提款。
实践与创新:古希腊亚历山大里亚的著名数学家刁藩都,人们只知道他是公元3世纪的人,其年龄和生平史籍上都没有明确的记载。但是,在他的墓碑上可以得知一二,而且它告诉人们,他终年是84岁。
刁藩都的墓碑是这样的:
刁藩都长眠于此,倘若你懂得碑文的奥秘,它会告诉你刁藩都的寿命。诸神赐予他的生命的6分之1是童年,再过了生命的12分之1,他长出了胡须,其后刁藩都结了婚,不过还不曾有孩子,这样又度过了一生的7分之1,再过5年,他获得了头生子,然而他的爱子竟然早逝,只活了刁藩都寿命的一半,丧子以后,他在数学研究中寻求慰藉,又度过了4年,终于也结束了自己的一生。
解:
算术解
题中只有一个四年和五年是具体数量,所以要考虑这九年占的分率,相除即可得出单位“1”即丢番图活的岁数。
(4+5)/(1-1/6-1/12-1/7-1/2)=9/(3/28)=84岁
答:丢番图活了84岁.
方程解
设丢番图活了x岁.
x=1/6x+1/12x+1/7x+5+1/2x+4
x=25/28x+9
3/28x=9
x=84 所以丢番活了84岁
我的收获:
教后记
人教版八年级道德与法治上册(部编版)课堂练习:第二课网络生活新空间第1课时 网络改变世界
第二课网络生活新空间 第1课时网络改变世界 关键词网络的积极作用 1.网络的积极作用有哪些?【是什么】 (1)网络________日常生活。 ①网络让我们日常生活中的________和________变得方便迅捷。②网络打破了传统人际交往的________________,促进了________________。③网络让我们的生活变得更加________和________。借助互联网,不用舟车劳顿,我们就可以____________、________资料、学习新知、购买物品、寻医问药、休闲娱乐,从而大大节约了成本,提高了效率。 (2)网络推动________________。 ①网络为经济发展注入________。互联网大大促进了人才、资金、技术、物资的流动,已经成为社会生产的新工具、经济贸易的__________。②网络促进____________的进步。互联网丰富了民主形式,________了民主渠道,使人们更加便利、有序地参与社会生活和政治生活,对保障公民的知情权、参与权、表达权、监督权发挥着重要作用。③网络为________传播和________创新搭建新平台。互联网促进了科技创新所需的物质与信息资源快速流动,加速了各种创新资源的汇聚、融合与共享。 关键词网络的弊端 2.网络的消极作用有哪些?【是什么】 (1)网络信息____________。 ①歪曲事实,________大众。②随意宣泄情绪,谩骂、中伤他人,侵犯他人________。 ③实施网络________,侵害他人利益。④恶意发布暴力、色情和________社会稳定的信息,造成恶劣影响。 (2)________于网络,影响学习、工作和生活。 (3)个人________容易被侵犯。在开放的网络世界里,________泄露、手机窃听、窥密偷拍等侵犯个人________的行为,让人防不胜防。各种侵犯个人隐私的行为会给被侵权人造成困扰和伤害,给社会带来恐慌和不安。 小提示:背诵见《期末冲刺随身宝》P98~99,你找到了吗? 1.通过网络,我们可以与世界各地的人及时交流。这说明了() A.网络交往很诱人,我们中学生应学会上网 B.只要打开网页,我们的愿望就可以实现 C.在网络交往的新空间里,随时可以找到学习资源和志同道合的朋友 D.网络打破了传统人际交往的时空限制,促进了人际交往 2.网络生活很丰富,打开网页,我们可以利用网络() ①学习新知②购买物品③查阅资料④寻医问药 A.②③④B.①③④C.①②③D.①②③④ 3.中学生小浩沉迷于网络游戏,无心学习。由于没钱上网,他开始敲诈勒索低年级同学,最终被公安机关逮捕。这告诉我们,沉迷于网络() ①会浪费学习的时间②会损害身心健康③一定会走向违法犯罪④会影响人际交往 A.①②③B.②③④C.①③④D.①②④ 4.结合漫画,回答问题。 (1)漫画说明了什么?
中学八年级信息技术 第一单元 第1课《算法基础知识》教案
第1课《算法基础知识》 教材分析本节课是青岛出版社初中《信息技术》八年级下册第一单元第一课内容,本节课内容包括算法的概念、算法的描述、算法的优化等方面的内容,目的是让学生学会分析问题、提取问题形成算法描述、掌握流程图的概念,让学生形成初步的算法意识,能够运用算法相关的知识解决日常生活、学习中的实际问题。 本课教学时,教师可以从“看商品猜价格”的游戏或者其他学生比较感兴趣的故事入手,提炼出算法的概念,即解决问题的方法。算法是个较为抽象的概念,教师在讲解时,不可简单地一句带过,可以多举实例或利用课件的形式帮助学生加深对算法的理解,引导他们尝试用不同的方式将解决问题的方法表达出来。其中,自然语言学生比较容易接受。但对于流程图,学生理解起来可能会有一定的难度。在讲解的过程中,教师可以借“烧水泡茶”的实例,启发、引导学生积极思考,从而理解算法优化的意义。这样,学生在对算法已有了充分的理解之后,更容易掌握算法的优化。这时,可以让学生结合实际生活举出算法优化的例子,引导他们做个细心的人,培养他们善于观察的能力以及通过算法优化解决实际问题的好习惯。最后给出两个练习让学生选择合适的方式来描述算法。 在整个教学过程中,要注重培养学生主动利用算法解决问题的意识。 教学目标 (1) 了解算法的含义,体会算法的思想。 (2) 能够用流程图描述算法。 (3) 能够对算法进行择优。 情感、态度与价值观 算法是解决问题的重要手段,通过对问题的研究和分析,设计算法对问题进行求解,提高分析问题和解决问题的能力,体会算法分析的魅力。 教学过程: 一、游戏情境导入新课 师:同学们都看过《幸运52》,其中有个游戏“看商品猜价格”找位同学来说说这个游戏规则。 生:主持人给出一款商品,由游戏者来报价,如果给出的价格高出实际的价格,主持人就说高了,游戏者继续报价,直到报出正确的价格。 师:今天我们也来玩下这个游戏,找两位同学分别来扮演主持人和选手 出示商品,价格在0~8000元之间 解决这一问题有哪些策略?哪一种较好? 解:第一步:报4000 第二步:若主持人说“高了”,就说2000,否则,就说6000
算法导论 第三版 第21章 答案 英
Chapter21 Michelle Bodnar,Andrew Lohr April12,2016 Exercise21.1-1 EdgeP rocessed initial{a}{b}{c}{d}{e}{f}{g}{h}{i}{j}{k} (d,i){a}{b}{c}{d,i}{e}{f}{g}{h}{j}{k} (f,k){a}{b}{c}{d,i}{e}{f,k}{g}{h}{j} (g,i){a}{b}{c}{d,i,g}{e}{f,k}{h}{j} (b,g){a}{b,d,i,g}{c}{e}{f,k}{h}{j} (a,h){a,h}{b,d,i,g}{c}{e}{f,k}{j} (i,j){a,h}{b,d,i,g,j}{c}{e}{f,k} (d,k){a,h}{b,d,i,g,j,f,k}{c}{e} (b,j){a,h}{b,d,i,g,j,f,k}{c}{e} (d,f){a,h}{b,d,i,g,j,f,k}{c}{e} (g,j){a,h}{b,d,i,g,j,f,k}{c}{e} (a,e){a,h,e}{b,d,i,g,j,f,k}{c} So,the connected that we are left with are{a,h,e},{b,d,i,g,j,f,k}, and{c}. Exercise21.1-2 First suppose that two vertices are in the same connected component.Then there exists a path of edges connecting them.If two vertices are connected by a single edge,then they are put into the same set when that edge is processed. At some point during the algorithm every edge of the path will be processed,so all vertices on the path will be in the same set,including the endpoints.Now suppose two vertices u and v wind up in the same set.Since every vertex starts o?in its own set,some sequence of edges in G must have resulted in eventually combining the sets containing u and v.From among these,there must be a path of edges from u to v,implying that u and v are in the same connected component. Exercise21.1-3 Find set is called twice on line4,this is run once per edge in the graph,so, we have that?nd set is run2|E|times.Since we start with|V|sets,at the end 1
大连理工大学软件学院算法导论第一次大作业源码
\documentclass{ctexart} \usepackage{amsmath} \usepackage{amssymb} \usepackage{fancyhdr} \begin{document} \pagestyle{fancy} \title{算法分析与设计第一次作业} \author{XXXX XXX\XXXXXX} \date{2013/9/11} \maketitle \noindent 3.1-2\ 证明: 证明$(n+a)^b=\Theta(n^b)$等价于证明存在$c_{1},c_{2},n_{0}>0$使得对于任意的 $n>n_{0}$,都有$0\leq c_{1}n^b \leq (n+a)^b \leq c_{2}n^b$成立。 $\because$ $n+a\leq n+|a|$,$\therefore$当$n\geq |a|$时,$n+a\leq 2n$。 又$\because$ $n+a\geq n-|a|$,$\therefore$当$|a|\leq \frac{1}{2}$时,$n+a \geq \frac{1}{2}n$。综上,当$n\geq 2|a|$时,$0\leq \frac{1}{2}n \leq (n+a) \leq 2n$。 $\therefore$ 对于$b>0$,有$0\leq (\frac{1}{2}n)^b \leq (n+a)^b \leq (2n)^b$ $\therefore$ 存在$c_{1} = (\frac{1}{2}n)^b$,$c_{2} = (2n)^b$,$n_{0}=2|a|$, 使得$0\leq c_{1}n^b \leq (n+a)^b \leq c_{2}n^b$成立。\ \ \ $\therefore$原命题得证。 \\ \noindent 3.1-3\ 解释:设运行时间为$F(n)$,则$F(n)\geq 0(n^2)$, $\therefore$ 若$F_{1}(n) = 0(n^2)$,则$F(n)\geq F_{1}(n)$, 又$\because$ $\forall$ n,$T(n)=0$时,$T(n)=0(n^2)$,且运行时间都大于0, $\therefore$对于所有的运行时间$F(n)$都有$F(n)\geq 0(n^2)$, $\therefore$这句话是没有意义的。 \\ \noindent
算法导论第二章答案
第二章算法入门 由于时间问题有些问题没有写的很仔细,而且估计这里会存在不少不恰当之处。另,思考题2-3 关于霍纳规则,有些部分没有完成,故没把解答写上去,我对其 c 问题有疑问,请有解答方法者提供个意见。 给出的代码目前也仅仅为解决问题,没有做优化,请见谅,等有时间了我再好好修改。 插入排序算法伪代码 INSERTION-SORT(A) 1 for j ← 2 to length[A] 2 do key ←A[j] 3 Insert A[j] into the sorted sequence A[1..j-1] 4 i ←j-1 5 while i > 0 and A[i] > key 6 do A[i+1]←A[i] 7 i ←i ? 1 8 A[i+1]←key C#对揑入排序算法的实现: public static void InsertionSort
算法导论 第三版 第六章 答案 英
Chapter6 Michelle Bodnar,Andrew Lohr December31,2016 Exercise6.1-1 At least2h and at most2h+1?1.Can be seen because a complete binary tree of depth h?1hasΣh?1 i=02i=2h?1elements,and the number of elements in a heap of depth h is between the number for a complete binary tree of depth h?1exclusive and the number in a complete binary tree of depth h inclusive. Exercise6.1-2 Write n=2m?1+k where m is as large as possible.Then the heap consists of a complete binary tree of height m?1,along with k additional leaves along the bottom.The height of the root is the length of the longest simple path to one of these k leaves,which must have length m.It is clear from the way we de?ned m that m= lg n . Exercise6.1-3 If there largest element in the subtee were somewhere other than the root, it has a parent that is in the subtree.So,it is larger than it’s parent,so,the heap property is violated at the parent of the maximum element in the subtree Exercise6.1-4 The smallest element must be a a leaf node.Suppose that node x contains the smallest element and x is not a leaf.Let y denote a child node of x.By the max-heap property,the value of x is greater than or equal to the value of y.Since the elements of the heap are distinct,the inequality is strict.This contradicts the assumption that x contains the smallest element in the heap. Exercise6.1-5 Yes,it is.The index of a child is always greater than the index of the parent, so the heap property is satis?ed at each vertex. 1
MIT麻省理工学院 算法导论公开课Problem Set 1
Introduction to Algorithms September7,2005 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.046J/18.410J Professors Erik D.Demaine and Charles E.Leiserson Handout5
(a) (b) (c) (d)and(note the little-) (e)and Problem1-2.Recurrences Give asymptotic upper and lower bounds for in each of the following recurrences.Assume that is constant for.Make your bounds as tight as possible,and justify your answers. (a) (b) (c) (d)
Figure1:An example of a convex polygon represented by the array.is the vertex with the minimum-coordinate,and are ordered counterclockwise. (b)Give an algorithm to?nd the vertex with the maximum coordinate in time. (c)Give an algorithm to?nd the vertex with the maximum coordinate in time.
人教版道德与法治上册教案 第一单元 第二课 网络生活新空间 第1课时 网络改变世界
第一单元走进社会生活 第二课网络生活新空间 第1课时网络改变世界 知识目标 1.知道网络对我们个人日常生活社会生活的积极作用。 2.了解网络对社会发展的作用。 能力目标 1.提高全面看待网络正面或积极作用的能力,而不是只看到其中一点或几点。 2.网络对社会进步和发展的推动作用要从经济、政治、文化三个方面来分析,提高对社会领域的认识水平和能力。 情感、态度与价值观 1.增强利用网络积极作用的观念,从而培养自己爱好网络,利用网络为我服务的意识。 2.开拓自己的眼界,与时代、与世界接轨,用互联网思维认识世界,为将来进入社会服务。 重点 1.网络对个人的积极作用。 2.网络对社会进步的推动作用。 难点 1.对网络积极作用认识、分析的方法。 2.网络促进民主政治的进步。 教师准备:有关网络利民便民的图片,提前做好幻灯片。 学生准备:预习新课,了解网络的作用。 一、情景导入,场景激趣 有人说:“互联网一半是天使,一半是魔鬼。”为什么“一半是天使,一半是魔鬼”?要想解开这个谜底,我们一起来学习第二课——网络生活新空间。 请同学们齐声把第二课下的引文读一遍。 二、问题导读,新知探讨 (一)网络丰富日常生活 1.请同学思考第10页的“运用你的经验”下的两个问题,然后请同学回答问题。 教师总结:网络的作用:让我们日常生活中的信息传递和交流方便、快捷。具体表现在:网络让我们日常生活中的信息传递和交流变得方便迅捷。随着科学技术的不断发展,互联网已经成为一座拥有海量信息、开放的移动图书馆,不仅给人们提供信息,而且提供便捷的信息检索渠道。我们可以随时随地进入网络空间,获取所需要的信息。 教师提出问题,引导学生认识这一作用。 提问:(1)在互联网出现前后,知识和信息通过什么传递?
算法导论 第三版 第七章 答案 英
Chapter7 Michelle Bodnar,Andrew Lohr April12,2016 Exercise7.1-1 13199512874212611 13199512874212611 13199512874212611 91913512874212611 95131912874212611 95131912874212611 95819121374212611 95871213194212611 95874131912212611 95874131912212611 95874219122113611 95874261221131911 95874261121131912 Exercise7.1-2 If all elements in the array have the same value,PARTITION returns r.To make PARTITION return q= (p+r)/2 when all elements have the same value,modify line4of the algorithm to say this:if A[j]≤x and j(mod2)= (p+1)(mod2).This causes the algorithm to treat half of the instances of the same value to count as less than,and the other half to count as greater than. Exercise7.1-3 The for loop makes exactly r?p iterations,each of which takes at most constant time.The part outside the for loop takes at most constant time.Since r?p is the size of the subarray,PARTITION takes at most time proportional to the size of the subarray it is called on. Exercise7.1-4 To modify QUICKSORT to run in non-increasing order we need only modify line4of PARTITION,changing≤to≥. 1
算法导论 第三版 第二章 答案 英
Chapter2 Michelle Bodnar,Andrew Lohr April12,2016 Exercise2.1-1 314159264158 314159264158 314159264158 263141594158 263141415958 263141415859 Exercise2.1-2 Algorithm1Non-increasing Insertion-Sort(A) 1:for j=2to A.length do 2:key=A[j] 3://Insert A[j]into the sorted sequence A[1..j?1]. 4:i=j?1 5:while i>0and A[i] Chapter24 Michelle Bodnar,Andrew Lohr April12,2016 Exercise24.1-1 If we change our source to z and use the same ordering of edges to decide what to relax,the d values after successive iterations of relaxation are: s t x y z ∞∞∞∞0 2∞7∞0 25790 25690 24690 Theπvalues are: s t x y z NIL NIL NIL NIL NIL z NIL z NIL NIL z x z s NIL z x y s NIL z x y s NIL Now,if we change the weight of edge(z,x)to4and rerun with s as the source,we have that the d values after successive iterations of relaxation are: s t x y z 0∞∞∞∞ 06∞7∞ 06472 02472 0247?2 Theπvalues are: s t x y z NIL NIL NIL NIL NIL NIL s NIL s NIL NIL s y s t NIL x y s t NIL x y s t 1 Note that these values are exactly the same as in the worked example.The di?erence that changing this edge will cause is that there is now a negative weight cycle,which will be detected when it considers the edge(z,x)in the for loop on line5.Since x.d=4>?2+4=z.d+w(z,x),it will return false on line7. Exercise24.1-2 Suppose there is a path from s to v.Then there must be a shortest such path of lengthδ(s,v).It must have?nite length since it contains at most|V|?1 edges and each edge has?nite length.By Lemma24.2,v.d=δ(s,v)<∞upon termination.On the other hand,suppose v.d<∞when BELLMAN-FORD ter-minates.Recall that v.d is monotonically decreasing throughout the algorithm, and RELAX will update v.d only if u.d+w(u,v) 《生活在网络中》教学设计 2月 知识目标:1、了解网络概念,体会生活中网络无处不在。 2、了解电脑网络的概念,体验电脑网络的作用。 3、了解常用的上网方式。 情感目标:激发学生对网络学习的热情。 教学重点: 了解电脑网络的概念及作用。 教学难点: 了解电脑网络的概念。 教学教程: 一、了解生活中的网络: 1、“网”的概念理解:线与线的连接与交叉构成“网”。 2、说一说生活中的一些网:(如:蜘蛛网、渔网、铁丝网等)。 3、了解生活中的常见的网络: 电话网、银行网、铁路网、邮电网、航空网、公路网、航海网、电视网…… 二、了解什么是电脑网络? 简单地说,计算机网络就是通过电缆、电话或无线通讯将两台以上的计算机互相连接起来成为一个网状的线路网,这就是电脑网络,电脑网络有如下一些特点: 1、用于计算机之间进行数据的相互传送。 2、能连接各种不同类型的计算机(电脑)。 3、:所有的网络节点都一样重要,没有国界、种族之分的。 4、了解学校的电脑网络的分布情况: 因特网→教育局交换机→学校路由器→分为教师办公室、电脑机房、普通教室三大块→每一大块通过交换机连接到各计算机上。 三、了解电脑网络的作用: 1、观看课本第3面下边的图示。 2、说一说,人们可以通过电脑网络做哪些工作? (远程教育学习、网上购物、查询资料、远程医疗、收发邮件、聊天、看电影、发布信息等) 四、了解“如何上网” 1、了解网络的连接方式。 现在电脑网络的线路的连接方法有:有线接入和无线接入两种。 目前,电脑的上网方式有:拨号上网、宽带上网、光纤上网等,其中拨号上网连接数据传输速度较慢,光纤上网数据传输的速度最快。 我们学校现在上网的方式是宽带上网。 2、数据的接收、发布 可用台式电脑与外部进行连接。 可用手提电脑与外部进行连接。 可遥手机上网,与外届发生连接。 五、作业: 通过上网,我们可以阅读新闻、_________、__________、___________、____________、____________。____________。____________。 六、课堂总结:这节课主要了学习了什么知识?(汇报一下) “同桌”互相交流。 1 算法导论第三次习题课 2008.12.17 2 19.1-1 如果x 是根节点:degree[sibling[x]] > sibling[x] 如果x 不是根节点:degree[sibling[x]] = sibling[x] –119.1-3 略 3 19.2-2 过程略( union 操作) 19.2-3 (1)decrease-key (2)extract-min 过程略 19.2-6 算法思想:找到堆中最小值min ,用min-1代替-∞. [遍历堆中树的根节点] 4 15.1-1 15.1-2 略P195 或P329 15.1-4 f i [j]值只依赖f i [j-1]的值,从而可以从2n 压缩为2个。再加上f*、l*、l i [j]。 Print-station(l, I, j ) //i 为线路,j 为station if j>1 then Print-station(l, l i [j], j-1 ) print “line”I, “station”j; 5 15.2-1 略(见课本) 15.2-2 15.2-4 略 MATRIX-CHAIN-MULTIPLY(A, s, i, j) if j>i x= MATRIX-CHAIN-MULTIPLY(A, s, s(i,j), j) y= MATRIX-CHAIN-MULTIPLY(A, s, s(i,j)+1,j) return MATRIX-MULTIPLY(x, y) else return A i 6 15.3-1 (归纳法)递归调用 枚举15.3-2 没有效果,没有重叠子问题 15.3-4 略 (3)n Ο3/2(4/) n n Θ 最大长方体问题 Problem description 一个长,宽,高分别为m,n,p 的长方体被分割成个m*n*p 个小立方体。每个小立方体内有一个整数。试设计一个算法,计算出所给长方体的最大子长方体。子长方体的大小由它所含所有整数之和确定。 Input 输入的第1 行是3 个正整数m,n,p,1≤m,n,p≤50。接下来m*n行每行p个正整数,表示小立方体中的数。 Output 程序运行结束时,输出计算出的最大子长方体的大小。 Sample Input 3 3 3 0 -1 2 1 2 2 1 1 -2 -2 -1 -1 -3 3 -2 -2 -3 1 -2 3 3 0 1 3 2 1 -3 Sample Output 14 #include "stdio.h" #include } int MaxSum2(int m,int n,int a[][50]){//用动态规划算法计算“最大子矩阵问题”,对应二维数组 int sum=0; int b[50]; memset(b,0,sizeof(b)); int i=0,j=0,k=0; for (i=1;i<=m;i++) { for(k=1;k<=n;k++) b[k]=0; for (j=i;j<=m;j++) { for(k=1;k<=n;k++) b[k]+=a[j][k]; int max=MaxSum(n,b); if(max>sum) sum=max; } } return sum; } int MaxSum3(int m,int n,int p,int a[][50][50]){//用动态规划算法计算“最大子长方体问题”,对应 int sum=0; int b[50][50]; memset(b,0,sizeof(b)); int i,j,k1,k2; for (i=1;i<=m;i++) { memset(b,0,sizeof(b)); for(j=i;j<=m;j++){ for(k1=1;k1<=n;k1++) for(k2=1;k2<=p;k2++) b[k1][k2]+=a[j][k1][k2]; int max=MaxSum2(n,p,b); if(max>sum) sum=max; } } return sum; } int main(){ Chapter2 Getting Start 2.1 Insertion sort 2.1.2 将Insertion-Sort 重写为按非递减顺序排序 2.1.3 计算两个n 位的二进制数组之和 2.2 Analyzing algorithms 当前n-1个元素排好序后,第n 个元素已经是最大的元素了. 最好时间和最坏时间均为2()n Θ 2.3 Designing algorithms 2.3.3 计算递归方程的解 22()2(/2)2,1k if n T n T n n if n for k =?=?+ = >? (1) 当1k =时,2n =,显然有()lg T n n n = (2) 假设当k i =时公式成立,即()lg 2lg 22i i i T n n n i ===?, 则当1k i =+,即12i n +=时, 2.3.4 给出insertion sort 的递归版本的递归式 2.3-6 使用二分查找来替代insertion-sort 中while 循环内的线性扫描,是否可以将算法的时间提高到(lg )n n Θ? 虽然用二分查找法可以将查找正确位置的时间复杂度降下来,但 是移位操作的复杂度并没有减少,所以最坏情况下该算法的时间复杂度依然是2()n Θ 2.3-7 给出一个算法,使得其能在(lg )n n Θ的时间内找出在一个n 元素的整数数组内,是否存在两个元素之和为x 首先利用快速排序将数组排序,时间(lg )n n Θ,然后再进行查找: Search(A,n,x) QuickSort(A,n); i←1; j←n; while A[i]+A[j]≠x and i Partial Solutions for Introduction to algorithms second edition Professor: Song You TA: Shao Wen ACKNOWLEDGEMENT CLASS ONE: JINZI CLASS TWO: LIUHAO, SONGDINMIN, SUNBOSHAN, SUNYANG CLASS FOUR:DONGYANHAO, FANSHENGBO, LULU, XIAODONG, CLASS FIVE:GAOCHEN, WANGXIAOCHUAN, LIUZHENHUA, WANGJIAN, YINGYING CLASS SIX: ZHANGZHAOYU, XUXIAOPENG, PENGYUN, HOULAN CLASS: LIKANG,JIANGZHOU, ANONYMITY The collator of this Answer Set, SHAOWen, takes absolutely no responsibility for the contents. This is merely a vague suggestion to a solution to some of the exercises posed in the book Introduction to algorithms by Cormen, Leiserson and Rivest. It is very likely that there are many errors and that the solutions are wrong. If you have found an error, have a better solution or wish to contribute in some constructive way please send an Email to shao_wen_buaa@https://www.360docs.net/doc/7d8655192.html, It is important that you try hard to solve the exercises on your own. Use this document only as a last resort or to check if your instructor got it all wrong. Have fun with your algorithms and get a satisfactory result in this course. Best regards, SHAOWen算法导论 第三版 第24章 答案 英
浙摄版小学信息技术四年级下册第1课《生活在网络中》教学设计
《算法导论2版》课后答案_加强版2
算法导论课程设计_最大长方体问题
算法导论习题答案
算法导论 课后题答案
