刘润清版新编语言学教程1-3章复习

1.1.1 填空判断:
①linguistics can be defined as the scientific or systematic study of language. It is a science studies the rules systems and principles of language. 3 cannons(标准):exhaustiveness全面性consistency 一致性economy.
②linguistics study the origin, growth, organization. Nature and development of language and discovers the general rules and principles governing language. 2 purposes: study the nature, establish a theory and describe language by that theory; examines all language and seeks understanding ways to fulfill the needs human need.
1.1.2 填空判断选择:
Linguistics differ from traditional grammar:
①linguistics describes languages and does not lay down rules of correctness. ②linguists regard spoken as primary not written. Speech came earlier than writing system. ③traditional grammar based on Latin while linguistics describes each language on its own merits.
1.1.4 名词解释
Microlinguistics: Phonetics(语音学), phonology(语音学), morphology(形态学),syntax(句法学), semantics(语义学),pragmatics(语用学).
Macrolinguistics: sociolinguistics(社会语言学),psycholinguistics(心理语言学),stylistics(文体学),discourse analysis(话语分析), computational linguistics(计算语言学),cognitive linguistics(认知语言学)
1.2.1 全especially判断
Language is a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used for human communication.
Language is a system, arbitrary, vocal. Language is used for human communication.
1.2.3
Arbitrariness(任意性): refers to the fact that there is no logical or intrinsic connection between a particular sound and the meaning it is associated with.
Duality(二元性):organization of language into two levels - a level of sounds which combine into a second level of larger units is called duality. language works on two levels: 1 have no meaning but combine to form unites at another level have meaning.
Productivity(创造性): linguistic ability enables to produce and understand sentences. Interchageability(可交换性):man can both produce and receive messages easily. Displacement(移位性):enable people to talk a thing in other space and time. Specialization:man does not have a total physical involvement in the act of communication. Cultural transmission(文化传递):language is culturally transmitted. Cannot be transmitted through heredity.
1.2.4
Phatic function交际功能, directive function 指示功能, informative function信息功能, interrogative function询问功能, expressive function表情功能, evocative function召唤功能, performative function施为功能, recreational function娱乐功能, metalingual function元语言功能(language can talk itself)
1.3.1 descriptive and prescriptive grammar 描写式&规定式
Descriptive describes what actually say, descriptive grammars attempt to tell what is in the language while prescriptive grammars tell people what should be in the language.
1.3.2 synchronic and diachronic linguistics 共时性和历时性
1.3.3 langue and parole 语言和言语
Langue Parole
Abstract knowledge concrete manifestation
Social conventional individualized
Code message
Stable and systematic subject to personal and situational
1.3.4 competence and performance 语言能力和应用
Competence refers to the knowledge that native speaker have of their language as a system of abstract relations, while performance refers to their actual linguistic behavior, that is, the actual use of this knowledge.
1.3.5 syntagmatic and paradigmatic relations
1.3.6functionalism and formalism功能主义和形式主义
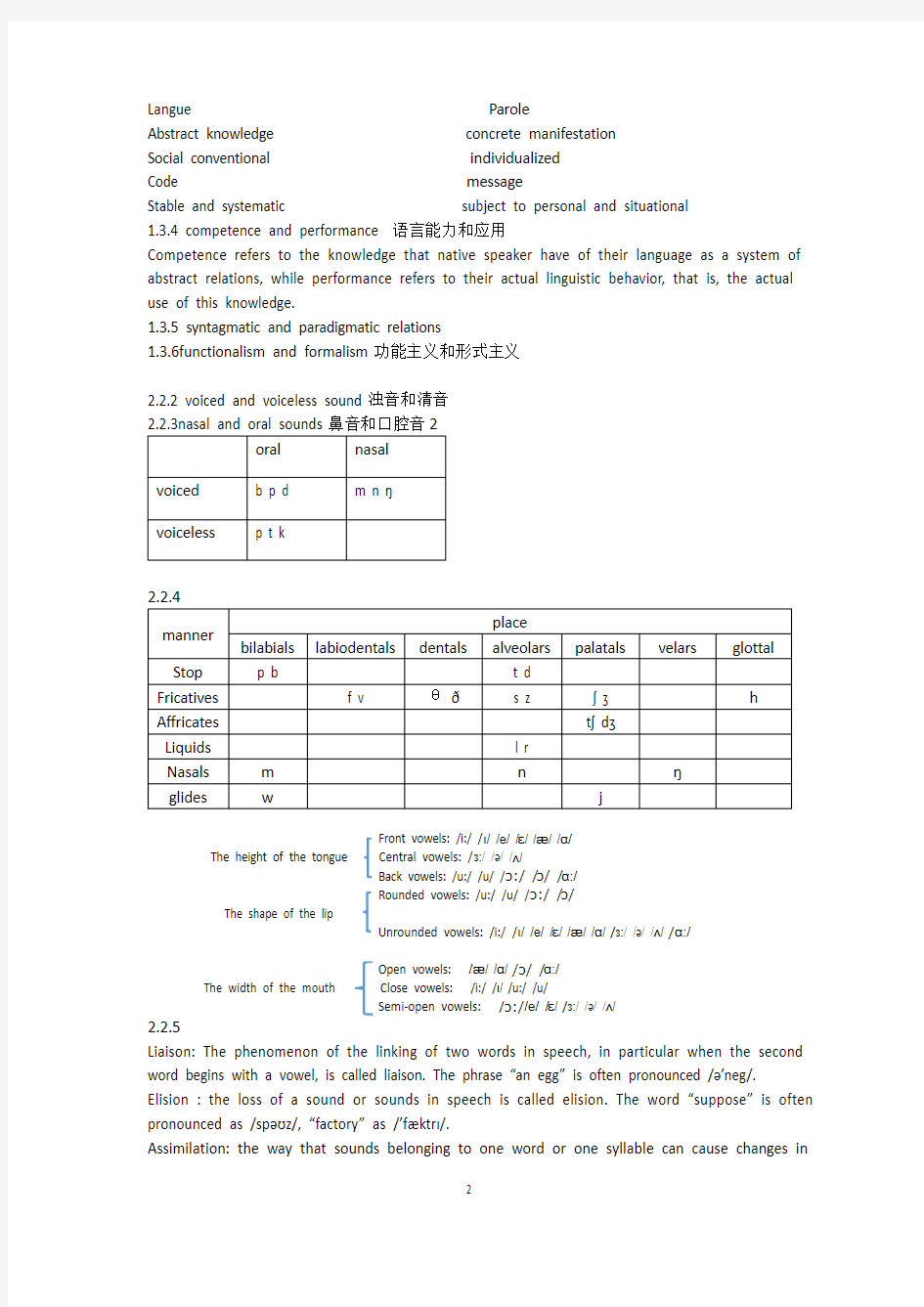
2.2.2 voiced and voiceless sound浊音和清音
Front vowels: /i:/ /?/ /e/ /?/ /?/ /ɑ/
The height of the tongue Central vowels: /з:/ /?/ /?/
Back vowels: /u:/ /u/ /?:/ /?/ /ɑ:/
Rounded vowels: /u:/ /u/ /?:/ /?/
The shape of the lip
Unrounded vowels: /i:/ /?/ /e/ /?/ /?/ /ɑ/ /з:/ /?/ /?/ /ɑ:/
Open vowels: /?/ /ɑ/ /?/ /ɑ:/
The width of the mouth Close vowels: /i:/ /?/ /u:/ /u/
Semi-open vowels: /?://e/ /?/ /з:/ /?/ /?/
2.2.5
Liaison: The phenomenon of the linking of two words in speech, in particular when the second word begins with a vowel, is called liaison. The phrase “an egg” is often pronounced /?’neg/. Elision : the loss of a sound or sounds in speech is called elision. The word “suppose” is often pronounced as /sp??z/, “factory” as /’f?ktr?/.
Assimilation: the way that sounds belonging to one word or one syllable can cause changes in
sounds belonging to neighboring words or syllables is called assimilation. In English the negative prefix occurs as “im-” before words such as “possible”---”impossible”.
2.3 Phonology : is the description of the systems and patterns of speech sounds in a language. 2.
3.1 Phoneme is the phonological units of language, and it is an abstract collection of phonetic features which and distinguish meaning.
For example, sip and zip is signaled by the fact that the initial sound of the first word is s/s/ and the initial sound of the second word is z/z/./s/and /z/can therefore distinguish or contrast words. Such distinctive sounds are called phonemes.
2.3.2minimal pairs and sets最小对立体
Minimal pairs are two words which are identical in every way except for one sound segment that occurs in the same place in the string
Minimal pairs are pairs of words which differ from each other only by one sound.
When a group of words can be differentiated each one from the others, by changing one phoneme (always in the same position), then we have a minimal set.
2.3.3 free variation
when two or more sounds occur in the same positon without any apparent change of meaning, they are said to be in free variation.
For example, there are two pronunciation of the word either,we can say /i:δ?r/ and /’a?δ?r/.
2.3.4distinctive features
When a feature distinguishes one phoneme from another it is a distinctive feature (or a phonemic feature).For example, seal and zeal distinguishes by /s/ ad /z/,/s/ is voiceless and /z/ is voiced,so /s/ and /z/ is a voicing difference.
2.3.5 syllables and consonant cluster音节和辅音丛
Syllable structure
syllable
onset rime(rhyme)
nucleus(peak) coda
consonant(s) vowel consonant(s)
consonant cluster:
In English some words may contain a sequence of two or more consonants in one syllable, for example, /spl/ in /’splendid/. Sequences of consonants like this are called consonant clusters.
Initial cluster: /spl/ in /’spl??/ splash Final cluster: /st/ in /test/ test Medial cluster: /str/ in /’pe?str?/ pastry A word which begins with three-consonant clusters always observes three strict rules:
The first consonant must be /s/
The second phoneme must be /p /or /t/ or /k/
The third consonant must be /l / or /r / or /w / or /j /
3.2 a morpheme is a minimal unit of meaning or grammatical function
3.2.1Free morphemes
a word must contain an element that can stand by itself, that is, a morpheme.
The free morphemes can be generally considered as the set of separate English word-forms. Free morphemes can be divided into two categories:1 lexical morphemes, the set of ordinary nouns, verbs and adjectives which carry the content of message we convey. 2 functional morphemes, consists of the functional words in the language such as conjunctions, articles, prepositions and pronouns.
3.2.2Bound morphemes
Some morphemes cannot normally stand alone, but function only as part of words are called bound morphemes. Bound morphemes are actually affixes.
Prefixes: affixes at the beginning of the root or stem
Suffixes: affixed at the end of the root or stem
2 categories:①derivational morphemes: used to make new word in the language and are often used to make words of a different grammatical category from the stem. ②inflectional morphemes: are not used to produce new words, but rather to show aspects of the grammatical function of a word
free morphemes free root
morphemes bound root
bound morphemes inflectional affixes prefixes
derivational affixes
suffixes
3.3 morphs and allomorphs
Morphs are the smallest meaningful phonetic segments of an utterance in the level of parole. Allomorph is a member of a set of morphs which represent the same morpheme.
3.4 types of word formation
Compound合成构词法:收尾词什么词性复合词就是什么词性
Derivation派生构词法:adding affixed to other words or morphemes
Conversion转类构词法:noun become verb or verb become noun
Backformation逆向构词法
Clipping截断构词法
Blending混成构词法e.g. gasohol=gasoline+alchol motel=motor+hotel
Acronym首字母拼音词pronounce as single words
Initialism首字母拼写词pronounce by saying each letter
语言学教程第一章ppt
语言学教程胡壮麟主编
Contents ?Chapter 1 Invitations to Linguistics Chapter 2 Speech Sounds(Phonetics) Chapter 3 From Morpheme to Phrase (Morphology) Chapter 4 From Word to Text(Syntax) Chapter 5 Meaning(Semantics) Chapter 6 Language and Cognition ?Chapter 8 Language in Use(Pragmatics)
Chapter 1 Invitations to Linguistics ?1.1 Why study linguistics? ?1.2 What is language? ?1.3 Features of language ?1.4. Origin of language ?1.5. Functions of language ?1.6. What is linguistics ?1.7 Main branches of linguistics ?1.8. Macrolinguistics ?1.9 Important distinctions in linguistics
Lead-in ?Qestion1: Other animals can beat us in many different ways, but what makes us superior to all of them? ?Qestion2: Why are children easy to undrstand their mother's tongue??Qestion3: Why do people in different social classes speak in different ways??Qestion4: Why is it "I love you" in English, but "私はあなたを愛して" in Japanese?
语言学教程第四版第二章 胡壮麟 主编
Chapter 2 Speech sounds Contents ?How sounds are made? ?Consonants and vowels ?Phonological processes, phonological rules and distinctive features ?Suprasegmentals 超音段 ?Two major areas for studying speech sounds: phonetics and phonology ?Phonetics: it studies how speech sounds are made, transmitted and perceived. ?Three branches of phonetics: ?Articulatory phonetics发声语音学 is the study of the production of speech sounds. ?Acoustic phonetics声学语音学 is the study of the physical properties of the sounds produced in speech. Auditory phonetics听觉语音学 is concerned with the perception of speech sounds ?Phonology:it deals with the sound system of a language by treating phoneme 音素 as the point of departure. ?It studies the sound patterns and sound systems of languages. ?Ultimately it aims to discover the rules that underlie the sound patterns of all languages. How speech sounds are made? ? speech organs 言语器官 ?Speech organs are also known as vocal organs(发音器官). ?Parts of human body involved in the production of speech sounds: lungs, trachea (windpipe) 气管, throat, nose, mouth ? organs of speech (Figure 2.2, p.26 on our books)
《语言学教程》中文笔记(完整)
语言学教程笔记 第一章语言学导论 语言的定义特征:从本质上将人类语言与动物语言区分开的人类语言的区别性特点。 1. 任意性:任意性是指语言符号的形式与所表示的意义没有天然的联系,任意性是语言的核 心特征。例如,我们无法解释为什么一本书读作 a /buk/,一支钢笔读作a /pe n/。 任意性具有不同层次:(1)语素音义关系的任意性。(2)句法层面上的任意性。 (3) 任意性和规约性。 2. 二层性:二层性是指拥有两层结构的这种特性,上层结构的单位由底层结构的元素构成, 每层都有自身的组合规则。话语的组成元素是本身不传达意义的语音,语音的唯一作用就是 相互组合构成有意义的单位,比如词。因为底层单位是无意的,而上层单位有明确的意义,所以我们把语音叫做底层单位,与词等上层单位相对。二层性使语言拥有了一种强大的能产 性。 3. 创造性:创造性指语言的能产性,指语言有制造无穷长句的潜力,这来源于语言的二层性 和递归性。利用二重性说话者可以通过组合基本语言单位,无止境地生成句子,大多数都是以前没有过的或没有听过的。 4. 移位性:是指人类语言可以让使用者在交际时用语言符号代表时间上和空间上并不可及的 物体、时间或观点。因此我们可以提及孔子或北极,虽然前者已经去世两千五百五十多年而 后者位置距我们非常之远。语言使我们能够谈及已不存在或还未出现的事物。移位性赋予人 们的概括与抽象能力使人类受益无穷。词在指称具体物体时,并不总是出现在即时、形象化 的语境中。他们通常为了体现指称含义而被使用。 5. 文化传递性:语言不是靠遗传,而是通过文化传递的。 6. 互换性:指人可以是信息的发出者,也可以是信息的接受者,即人作为说话者和听话者的 角色是可以随意更换的。 元语言功能:我们的语言可以用来讨论语言本身。比如说,我可以用“书”指代一本书,也可以用“书这个词”来指代“书”这个词本身。这使语言具有无限的自我反身性:人类可以谈论“说话”,也可以思考“思考"。所以只有人类才能提问:元语言功能对交际、思考及人类的意义是什么?
(完整版)胡壮麟《语言学教程》测试题及答案
胡壮麟《语言学教程》(修订版)测试题 第一章:语言学导论 I. Choose the best answer. (20%) 1. Language is a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used for human A. contact C. relation B. communication D. community 2. Which of the following words is entirely arbitrary? A. tree C. crash B. typewriter D. bang 3. The function of the sentence “ Waterboils at 100 degrees Centigrade. i”s A. interrogative C. informative B. directive D. performative 4. In Chinese when someone breaks a bowl or a plate the host or the people present are likely to say “碎碎(岁岁)平安”asa means of controlling the forces which they believes feel might affect their lives. Which functions does it perform? A. Interpersonal C. Performative B. Emotive D. Recreational 5. Which of the following property of language enables language users to overcome the barriers caused by time and place, due to this feature of language, speakers of a language are free to talk about anything in any situation? A. Transferability C. Displacement B. Duality D. Arbitrariness 6. Study the following dialogue. What function does it play according to the functions of language? —A nice day, isn 't it? Right! I really enjoy the sunlight. A. Emotive C. Performative B. Phatic D. Interpersonal 7. __________ refers to the actual realization of the ideal language usesr knowledge of the rules of his language in utterances. A. Performance C. Langue B. Competence D. Parole 8. When a dog is barking, you assume it is barking for something or at someone that exists hear and now.
语言学第七章知识点总结
语言学第七章知识点总结 Language is an essential part of a given culture. It is an indispensable carrier of culture. It is regarded as a mirror of society. In primitive culture, the meaning of a word greatly depended on its occurrence in a given context. Firth-Context of Situation -illustrate the close relationship between language use and its co-occurrence factors. 1.The relevant features of the participants, persons, and personalities The verbal action of the participants; the non-verbal action of the participant 2.The relevant objects 3.The effects of the verbal action Speech Community It refers to a group of people share the same rules of speaking and one linguistic variety as well. Sapir-Whorf Hypothesis Our language helps mould our way of thinking. Different languages may probably express speakers' unique ways of understanding the world. https://www.360docs.net/doc/9117139219.html,nguage may determine our thinking patterns
刘润清《新编语言学教程》笔记和课后习题(认知语言学)【圣才出品】
第10章认知语言学 10.1 复习笔记 本章要点: 1. Cognitive linguistics 认知语言学 2. Categorization and categories 范畴化与范畴 3. Conceptual metaphor and metonymy 概念隐喻与转喻 4. Iconicity and grammaticalization 象似性与语法化 常考考点: 认知语言学定义;范畴化与范畴定义分类等;概念隐喻与转喻的定义,层次分类;象似性的分类以及语法化等。 本章内容索引: I. Definition of cognitive linguistics II. Categorization and categories
1. Definition of categorization 2. The classical theory 3. The prototype theory 4. Levels of categorization III. Conceptual metaphor and metonymy 1. Conceptual metaphor 2. Conceptual metonymy IV. Iconicity 1. Iconicity of order 2. Iconicity of distance 3. Iconicity of complexity V. Grammaticalization I. Definition of cognitive linguistics (认知语言学定义) 【考点:名词解释】 Cognitive linguistics is an approach to the analysis of natural language that focuses on language as an instrument for organizing, processing, and conveying information. 认知语言学是一种研究自然语言的方法,集中研究语言组织,处理与传达信息的作用。 II. Categorization and categories (范畴化与范畴) 1. Definition of categorization and categories (定义)
刘润清《新编语言学教程》章节题库-第四章至第七章【圣才出品】
第4章句法 I.Fill in the blanks. 1.IC is the short form of immediate_____used in the study of syntax.(北二外2003研) 【答案】constituent 【解析】直接成分分析法是一种句法分析方法。它指先把句子分析为直接成分——词组(或短语),再把这些直接成分依次切分,得到各自的直接成分,层层切分,直到最终 成分为止。 2.______refers to ties and connections which exist within texts.They are also called formal links between sentences and between clauses.(人大2007研) 【答案】Cohesion 【解析】衔接不是一个句法概念,它指文本中存在的一种意义上的联系或关系,也包括句子或分句之间存在的一种形式上的联系。 3.A______sentence contains two clauses joined by a linking word,such as“and”,“but”,“or”. 【答案】coordinate 【解析】并列从句是指一个句子由两个分句组成,这两个分句通常是由如but,and,or这些并列连词来连接的。
4.A clause that takes a subject and a finite verb,and at the same time stands structurally alone is known as a______clause. 【答案】finite 【解析】限定性从句通常有一个主语和一个限定性动词,且在结构上是独立的。 5.Syntactic movement is dictated by rules traditionally called_____rules,whose operation may change the syntactic representation of a sentence. 【答案】transformational 【解析】句法移位是一种转换规则,指一个句子的任意成分从原来的位置移到另一个新位置。 它可能会引起句子句法的变化。 6.The level of syntactic representation that exists before movement takes place is commonly termed______structure. 【答案】deep 【解析】深层结构是指一个结构体的句法属性的抽象表述,即不同成分之间的结构关系,深层结构一般指移位前的结构。 7.A______is a structurally independent unit that usually comprises a number of words to form a complete statement,question or command. 【答案】sentence 【解析】句子在结构上是一个独立的单位,通常包括许多词用以构成一个完整的陈述,提问或者命令。
语言学教程课后习题答案第一章资料(最新整理)
Chapter 1 Invitations to Linguistics 1. Define the following terms: design feature: the distinctive features of human language that essentially make human language distinguishable from languages of animals. function: the role language plays in communication (e.g. to express ideas, attitudes) or in particular social situations (e.g. religious, legal). synchronic: said of an approach that studies language at a theoretical ‘point’ in time. diachronic: said of the study of development of language and languages over time. prescriptive: to make authoritarian statement about the correctness of a particular use of language. descriptive: to make an objective and systematic account of the patterns and use of a language or variety. arbitrariness: the absence of any physical correspondence between linguistic signals and the entities to which they refer. duality: the structural organization of language into two abstract levels: meaningful units (e.g. words) and meaningless segments (e.g. sounds, letters). displacement: the ability of language to refer to contexts removed from the speaker’s immediate situation. phatic communion: said of talk used to establish atmosphere or maintain social contact. metalanguage: a language used for talking about language. macrolinguistics: a broad conception of linguistic enquiry, including psychological, cultural, etc. competence: unconscious knowledge of the system of grammatical rules in a language. performance: the language actually used by people in speaking or writing.
新编语言学教程第2版第4章答案
《新编简明英语语言学教程》第二版第4章练习题参考答案Chapter 4 Syntax 1. What is syntax? Syntax is a branch of linguistics that studies how words are combined to form sentences and the rules that govern the formation of sentences. 2. What is phrase structure rule? The grammatical mechanism that regulates the arrangement of elements (i.e. specifiers, heads, and complements) that make up a phrase is called a phrase structure rule. The phrase structural rule for NP, VP, AP, and PP can be written as follows: NP →(Det) N (PP) ... VP →(Qual) V (NP) ... AP →(Deg) A (PP) ... PP →(Deg) P (NP) ... We can formulate a single general phrasal structural rule in which X stands for the head N, V, A or P. 3. What is category? How to determine a word's category? Category refers to a group of linguistic items which fulfill the same or similar functions in a particular language such as a sentence, a noun phrase or a verb. To determine a word's category, three criteria are usually employed, namely meaning, inflection and distribution. 若详细回答,则要加上: Word categories often bear some relationship with its meaning. The meanings associated with nouns and verbs can be elaborated in various ways. The property or attribute of the entities denoted by nouns can be elaborated by adjectives. For example, when we say that pretty lady, we are attributing the property ‘pretty’ to the lady designated by the noun. Similarly, the properties and attributes of the actions, sensations and states designated by verbs can typically be denoted by adverbs. For example, in Jenny left quietly the adverb quietly indicates the manner of Jenny's leaving. The second criterion to determine a word's category is inflection. Words of different categories take different inflections. Such nouns as boy and desk take the plural affix -s. Verbs such as work and help take past tense affix -ed and progressive affix -ing. And adjectives like quiet and clever take comparative affix -er and superlative affix -est. Although inflection is very helpful in determining a word's category, it does not always suffice. Some words do not take inflections. For example, nouns like moisture, fog, do not usually take plural suffix -s and adjectives like frequent, intelligent do not take comparative and superlative affixes -er and -est.
胡壮麟《语言学教程》笔记1_3章
胡壮麟语言学重难点 Chapter 1 Invitations to Linguistics 常考考点:1. 语言: 语言的定义;语言的基本特征;语言的功能;语言的起源 2. 语言学:语言学的定义;现代语言学与传统语法学研究的三个显著区别;语言学研究的四个原则及简要说明;语言学中的几组重要区别;每组两个概念的含义、区分及其意义;普通语言学的主要分支学科及各自的研究范畴;宏观语言学及应用语言学的主要分支及各自的研究范畴。 1. 语言的定义特征 1.1. 任意性 1.2. 二重性 1.3. 创造性 1.4. 移位性 1.5. 文化传递性 1.6. 互换性 2. 语言的功能 1.1. 信息功能 1.2. 人际功能 1.3. 施为功能 1.4. 感情功能 1.5. 寒暄功能 1.6. 娱乐功能 1.7. 元语言功能
3. 微观语言学 3.1. 语音学 3.2. 音系学 3.3. 形态学 3.4. 句法学 3.5. 语义学 3.6. 语用学 4. 宏观语言学 4.1. 心理语言学 4.2. 社会语言学 4.3. 应用语言学 4.4. 计算语言学 4.5. 神经语言学 5. 重要概念及其区分 5.1. 描写式&规定式 5.2. 共时&历时 5.3. 语言&言语 5.4. 语言能力&语言应用 5.5. 唯素的&唯位的 5.6. 传统语法&现代语法 5.7. 语言潜势&实际语言行为 Chapter 2 Speech Sounds
常考考点:1. 语音学语音学的定义;发音器官的英文名称;英语辅音的定义;发音部位、发音方法和分类;英语元音的定义和分类;基本元音;发音语音学;听觉语音学;声学语音学;语音标记,国际音标;严式与宽式标音法 2. 音系学音系学的定义;音系学与语音学的联系与区别;音素、音位、音位变体、最小对立体、自由变体的定义;音位理论;自由变异;音位的对立分布于互补分布;语音的相似性;区别性特征;超语段音位学;音节;重音;音高和语调。 1. 语音学及其三大领域 1.1. 语音学定义 1.2. 语音学三大领域 ①发音语音学 ②声学语音学 ③听觉语音学 2. 辅音 2.1. 辅音定义 发音时,声道的某些部位受到压缩或阻碍后,使得气流在口腔里转向、受阻或完全被阻塞,由此产生的音叫做辅音。 2.2. 发音方式 发音方式是指发音器官之间的关系,以及气流经过声道的某些部位的方式 2.3. 发音部位 发音部位是指声道的哪些部位发生气流摩擦、狭窄化或阻碍。 3. 元音
语言学教程[第一章语言学导论]山东大学期末考试知识点复习
第一章语言学导论 复习笔记 Ⅰ.语言的定义 语言是人类以口头交流的任意的符号系统。该定义揭示了语言的五个要素:系统,任意,口头,符号,人类。 Ⅱ.语言的定义特征 语言的定义特征是人类语言区别于其他动物交流系统的特点。 1.任意性 任意性是语言的核心特征,是指符号的形式或者声音与意义之间没有逻辑或内在联系。虽然语言从本质上讲是任意的,但也不是完全任意的。一些词语,例如一些拟声词的发音与其意义还是有一定联系的。 2.二重性 二重性是指拥有两层结构的这种属性,底层结构是上层结构的组成成分,每层都有自身的组合规则。二重性只存在于这样的系统之中,既有元素又有它们组合成的单位。 3.创造性 创造性指语言的能产性,它能够使人造出和理解无穷的长句,其中很多句子是以前从未听过的。 4.移位性 移位性是指人类语言可以让使用者在交际时用语言符号代表时间上和空间上并不可及的物体、事件和观点。移位性赋予人们的概括和想象力使人类受益无穷。 5.文化传递性
语言不是靠遗传,而是通过文化传递的。 6.互换性 互换性是指人可以是信息的发出者,也可以是信息的接受者,即人作为说话者和听话者的角色是可以随意更换的。 Ⅲ.语言的起源 1.圣经的记载 语言是上帝的恩赐。 2.“汪汪”理论 语言是模仿自然的声音,例如动物的叫声,如 (鸭子)的刮刮声,嘎嘎声,布谷鸟的叫声。 3.“噗噗”理论 语言来源于人本能的情感声音,表达疼痛或喜悦。 4.“哟一嘿一吼”理论 语言起源于原始人共同劳动时发出的有节奏的哼哟声。 5.进化理论 语言起源于劳动的过程,满足了社会的需求。 Ⅳ.语言的功能 1.信息功能 语言用来陈述某件事情,提供信息或用作推理。信息功能是语言最重要的功能,一般出现在陈述句中。 2.人际功能 人际功能是语言最重要的社会功能。人们由此建立和维持他们的身份和社会
新编语言学教程刘润清版1,2章复习大纲
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Definition : linguistics can be defined as the scientific or systematic study of language. It is always guided by the three cannons of science:exhaustiveness, consistency and economy. Linguistics Linguistics versus traditional grammar: Scope Microlinguistics Phonetics Phonology Morphology Syntax Semantics Pragmatics Macrolinguistics Sociolinguistics Psycholinguistics Neurolinguistics Stylistics Discourse analysis Computational linguistics Cognitive linguistics Definition: Ding-Dong Theory: human speech developed from primitive man giving vocal expression to the objects he encountered. Sing-Song Theory: language developed from primitive ritual songs of praise. Pooh-Pooh Theory: language came from interjections, which express he speaker ’s emotions. Origins Yo-He-Ho Theory: language came from the cries uttered, during strain of work. Ta-Ta Theory : language came from the combination of certain gestures and tongues movements. Bow-Wow Theory: language came from imitation of animal cries and other sounds heard in nature. Design features Linguistics describes languages and does not lay down rules of correctness while traditional grammar emphasizes correctness. Linguists regard the spoken language as primary, not the written while traditional grammar emphasizes the priority of written language. Traditional grammar is based on Latin and it tries to impose the Latin categories and structures on other languages. Linguistics describes each language on its language is a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used for human communication. Language is a system---elements in it are not arranged and combined randomly, but according to some rules and principles. Language is arbitrary --- there is no intrinsic connection between the word . pen) and the thing. what we write with).Language is vocal---the primary medium for all languages is sound. Language is used for human communication ---it is human-specific, very different form Arbitrarines s: this refers to the fact that there is no logical or intrinsic connection between a particular sound and the meaning it is associated with. For example, English should use the sounds/d?g/ to refer to the animal dog, but Chinese should use “gou ” to refer to te same animal. A dog may be called a pig if the first man happens to name it as a “pig ”. So, the relationship between the sounds and their meaning is quite accidental. Of course, onomatopoetic words such as “quack-quack ” and “bang ” are exceptions, but words these are relatively few compared withe the total number of words in language. Duality: language operates on two levels of structure. At one level are elements which have no meaning in themselves but which combine to form units at another level which do have meaning. Productivity : productivity or creativity refers to man ’s linguistic ability which enables him to produce and understand an infinitely large number of sentences in our native language, including the sentences which were never heard before. Interchangeability : interchangeability or reciprocity refers to the fact that man can both produce and receive messages, and his roles as a speaker and a hearer can be exchanged at ease. Displacement: displacement is a property of language enabling people to talk about things remote either in space or in time. Specialization : specialization refers to the fact that man does not have a total physical involvement in the act of communication. Cultural transmission : language is culturally transmitted. It cannot be transmitted through heredity. A human being brought up in isolations simply doesn ’t acquire language, as is demonstrated by the studies of children brought up by animals without human contact. Animals transmit their cries simply from parent to child, while human baby doesn ’t speak any language at birth. What language a baby is going to speak
胡壮麟语言学教程第二章专业术语解释
2. Articulatory phonetics发音语言学: the study of production of speechsounds.研究语言的发生 phonetics声学语言学:is the study of physical properties of speech sounds.研究语音的物质特征 or Auditory phonetics感知语音学或听觉语音学:is concerned with the perception of speech sounds.研究语音的感知 音系学is the study of the sound patterns and sound systems of languages.研究各种语言的语音模式和语音系统 6. IPA国际音标表: the abbreviation of International Phonetic Alphabet 变音符:are additional symbols or marks used together with the consonant and vowel symbols to indicate nuances of change in their pronunciation.是与元音或辅音符号结合使用的一些附加符号或记号,用于表示元音或辅音在发音上的微小变化 辅音: are sound segments produced by constricting or obstructing the vocal tract at some place to divert,impede,or completely shut off the flow of air in the oral cavity.声道紧闭,或声道变窄的程度达到无法 9. Vowl元音:are sound segments produced without such obstruction,so no turbulence of a total stopping of the air can be perceived.气流可以相对不受阻碍的从口腔或鼻腔中排出 排出,一旦排出就会产生可闻的摩擦,这样发生的音叫辅音 10. Coarticulation协同发音: a kind of phonetic process in which simultaneous or overlapping articulations are
