日本公定书《食品添加剂使用标准》
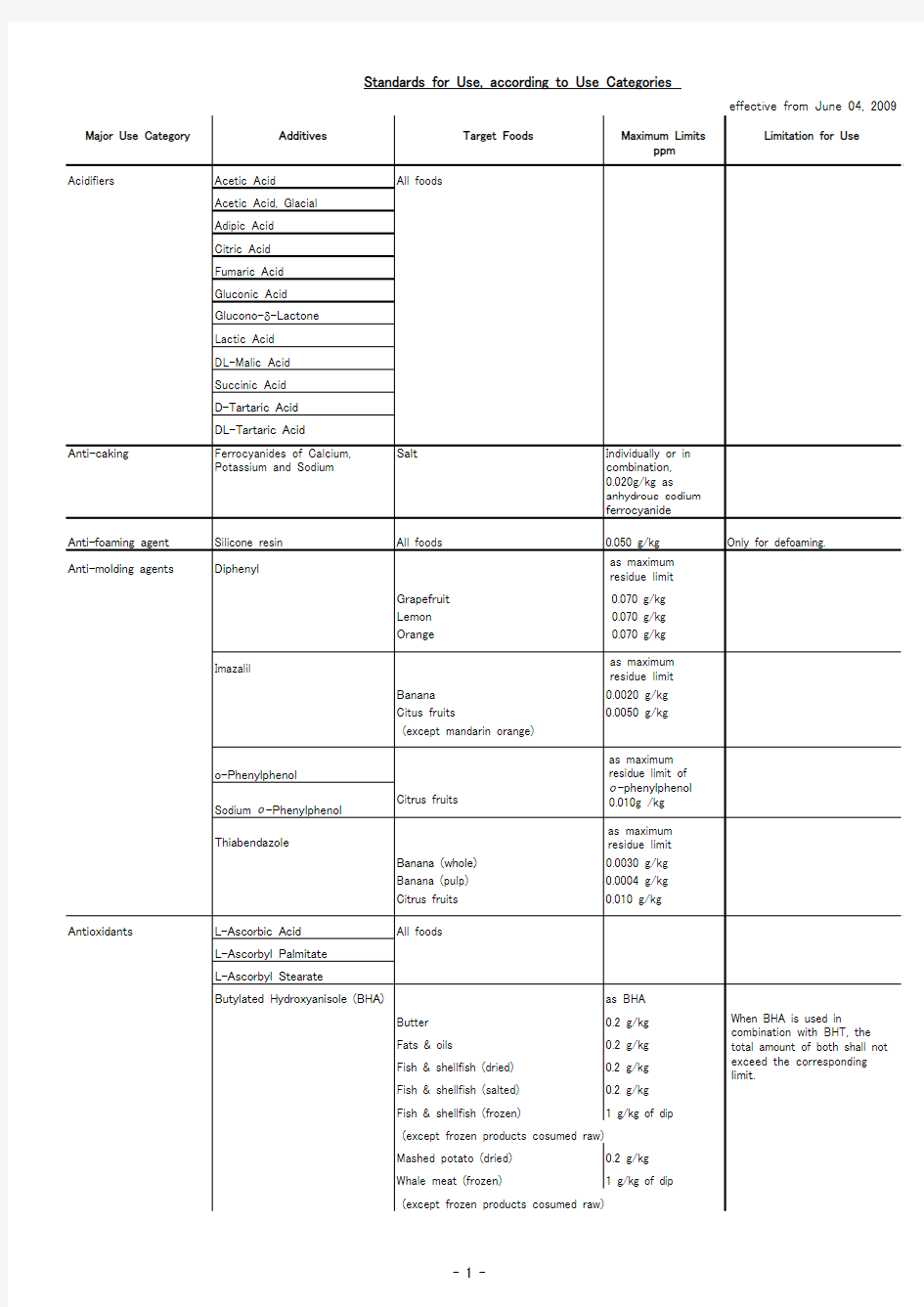

Major Use Category
Additives
Target Foods
Maximum Limits
Limitation for Use
ppm
Acidifiers Acetic Acid All foods
Acetic Acid, Glacial Adipic Acid Citric Acid Fumaric Acid Gluconic Acid Glucono-δ-Lactone Lactic Acid DL-Malic Acid Succinic Acid D-Tartaric Acid DL-Tartaric Acid
Anti-caking
Ferrocyanides of Calcium,Potassium and Sodium
Salt
Individually or in combination,0.020g/kg as
anhydrous sodium ferrocyanide Anti-foaming agent Silicone resin All foods
0.050 g/kg Only for defoaming.
Anti-molding agents
Diphenyl
Grapefruit 0.070 g/kg Lemon 0.070 g/kg Orange
0.070 g/kg Imazalil
Banana 0.0020 g/kg Citus fruits
0.0050 g/kg
(except mandarin orange)
o-Phenylphenol Sodium o -Phenylphenol Citrus fruits
Thiabendazole
Banana (whole)0.0030 g/kg Banana (pulp)0.0004 g/kg Citrus fruits
0.010 g/kg
Antioxidants
L-Ascorbic Acid All foods L-Ascorbyl Palmitate L-Ascorbyl Stearate
Butylated Hydroxyanisole (BHA)
as BHA Butter 0.2 g/kg Fats & oils
0.2 g/kg Fish & shellfish (dried)0.2 g/kg Fish & shellfish (salted)0.2 g/kg Fish & shellfish (frozen)
1 g/kg of dip
(except frozen products cosumed raw)Mashed potato (dried)0.2 g/kg Whale meat (frozen)
1 g/kg of dip
(except frozen products cosumed raw) Standards for Use, according to Use Categories
effective from June 04, 2009
When BHA is used in
combination with BHT, the total amount of both shall not exceed the corresponding limit.
as maximum residue limit
as maximum residue limit as maximum residue limit of o -phenylphenol 0.010g /kg as maximum residue limit
Antioxidants Butylated Hydroxytoluene as BHA (continued) (BHT)
Butter
0.2 g/kg Chewing gum 0.75 g/kg Fats & oils
0.2 g/kg Fish & shellfish (dried)0.2 g/kg Fish & shellfish (salted)0.2 g/kg Fish & shellfish (frozen) 1 g/kg of dip
(except frozen products cosumed raw)
Mashed potato (dried)0.2 g/kg Whale meat (frozen)
1 g/kg of dip
Calcium Disodium as EDTA-CaNa 2 Ethylenediamine-0.035 g/kg tetraacetate
0.25 g/kg
Bread Fruit juice
as EDTA-CaNa 2
0.035 g/kg Other canned and bottled foods 0.25 g/kg
Erythrobic Acid
All foods
Isopropyl Citrate
Butter
0.10 g/kg Fats and oils
0.10 g/kg Guaiac Resin
Butter
1.0 g/kg Fats and oils 1.0 g/kg Propyl Gallate
Butter 0.10 g/kg Fats and oils
0.20 g/kg
Sodium L-Ascorbate All foods Sodium Erythorbate
All foods
dl -α-Tocopherol All foods
Antisticking D-Mannitol Candies
40 %Chewing gum
20 %FURIKAKE (sprinkleover only products containing granues)RAKUGAN (dried rice-flour cakes)30 %25 %
All foods as CHOMIRYO (seasoning)*
When BHA is used in
combination with BHT, the total amount of both shall not exceed the corresponding limit.
(except frozen products cosumed raw)
Canned and bottle non- alcoholic beverages
Disodium Ethylene- diaminetetraacetate
Canned and bottle non- alcoholic beverages
Other canned and bottle foods Shall be chelated with calcium ino before the preparation of the finished food.
Not permitted for nutritive purposes in fish paste
products (excluding SURIMI)or bread.
Only for antioxidizing purposes in other foods.
as monoisopropyl citrate Not permitted for nutritive purposes in fish paste
products (excluding SURIMI)or bread.
Only for antioxidizing purposes in other foods.
Only for antioxidizing, except when included in preparation of β-Carotene, Vitamin A,Vitamin A Esters of Fatty Acids, or Liquid Paraffin.
L-Cysteine Monohydro- chloride
TSUKUDANI (food boiled down in soy sauce, only products made of KONBU (kelp))
50 % of granules (as maximum residue limit)
* When used in formula with Potassium Chloride and
Glutamate for seasoning foods or enhancing their original flavor, no limits are specified. (only cases where D-Mannitol does not exceed 80% of the sum of Potassium Chloride, Glutamates and D-Mannitol)
Color fixatives Ferrous Sulfate All foods
Potassium Nitrate
less than:
Meat products 0.070 g/kg Whale meat bacon
0.070 g/kg (as residue limit of NO 2
Sodium Nitrate as maximum Sodium Nitrite
residue limit of nitrite Fish ham 0.050 g/kg Fish sausage
0.050 g/kg IKURA (salted/processed 0.0050 g/kg salmon roes)Meat products
0.070 g/kg SUJIKO (salted salmon roes)0.0050 g/kg TARAKO
0.0050 g/kg Whale meat bacon 0.070 g/kg Color adjuvant Ferrous Gluconate
Table olive
0.15 g/kg
Dietary Supplements
L-Ascorbic acid 2-glucoside All foods
Biotin Foods with health claims Bisbentiamine All foods
Calcium Carbonate*as Ca Calcium Chloride All foods
1.0 %Calcium Citrate Chewing gum*
10 % *
Calcium Dihydrogen Pyrophosphate Calcium Dihydrogen Phosphate
Cacium Gluconate
Calcium Glycerophosphate Calcium Hydroxide
Calcium Lactate
Dietary Supplements Calcium Monohydrogen All foods
(continued)
Phosphate
Calcium Pantothenate Calcium Sulfate
Cholecalciferol
All foods
Same as for Potassium Nitrate
The above limits do not apply to foods approved to be labeled as "special. dietary use."
Only when indispensable for manufacturing or processing the food, or when used for nutritive purposes.
* Only applied to Calcium Carbonate
May also be used as dietary supplement.
See the section, "Dietary supplements"
Only for nutritive purposes.Only when indispensable for manufacturing or processing the food, or when used for nutritive purposes.
Only when indispensable for manufacturing or processing the food, or when used for nutritive purposes.
Only when indispensable for manufacturing or processing the food, or when used for nutritive purposes.
May be used as fermentation regulator. See the section,"Miscellenous."
Dietary Supplements Copper Gluconate
as copper
(continued)
Substitutes for human milk
0.60 mg/L
Foods with health claims
5 mg/recommended daily portion of each food
Cupric Sulfate
as copper Substitutes for human milk
0.60 mg/L
Dibenzoyl Thiamine All foods
Dibenzoyl Thiamine Hydrochloride Dry Formed Vitamin A Ergocalciferol
Ferric Ammonium Citrate Ferric Chloride Ferric Citrate Ferric Pyrophosphate Ferrous Gluconate
Dried milk for pregnant and lactating women.
Substitutes for human milk.Weaning foods
Folic Acid
All foods
L-Histidine Monohydro- chloride Iron Lactate L-Isoleucine L-Lysine L-Aspartate L-Lysine L-Glutamate
L-Lysin Monohydrochloride DL-Methionine L-Methionine Methyl Hesperidin Nicotinamide Nicotinic Acid L-Phenylalanine All foods
Pyridoxine Hydrochloride Riboflavin
Riboflavin 5'-Phosphate Sodium
Riboflavin Tetrabutyrate Sodium Ferrous Citrate Sodium Pantothenate Thiamine Dicetylsulfate Thiamine Dilaurylsulfate Thiamine Hydrochloride Thiamine Mononitrate
when formulated into a standard concentration.The limit does not apply to cases where these additives are used in formulated dried milk under approval by the Minister of Health, Labor and Welfare.
Not permitted in fresh
fish/shellfish (including fresh whale meat) or meat.
May also be used as color adjuvant.
See the section, "Color adjuvant."
when formulated into a standard concentration.
The limit does not apply to cases where these additives are used in formulated dried milk under approval by the Minister of Health, Labor and Welfare.
ppm
Dietary Supplements Thiamine Naphthalene-All foods
(continued) 1, 5-disulfonate
Thiamine Thiocyanate
DL-Threonine
L-Threonine
all-rac-α-Tocopheryl Acetate Foods with health claims as α-Tocopherol
R,R,R-α-Tocopheryl Acetate150
mg/recommended
daily portion of each
food
Tricalcium Phosphate All foods as Ca
1.0 %
DL-Tryptophan All foods
L-Tryptophan
L-Valine
Vitamin A
Vitamin A Esters of
Fatty Acids
Vitamin A in Oil
Zinc Gluconate Only substitutes for human milk as zinc
Foods with health claims15 mg/ recommended
daily portion of each
food
Zinc Sulfate Only substitutes for human milk as zinc
Emulsifiers Calcium Strearoyl Lactylate
Bread. 4.0 g/kg
Butter cakes. 5.5 g/kg
Confections(baked or fried wheat
flour products only).
4.0 g/kg
Moist cakes (rice flour products only). 6.0 g/kg
Macaroni and other such products.* 4.0 g/kg**as dry noodles.
Mixed powder:
for manufacturing bread. 5.5 g/kg
for manufacturing confections (fried
wheat flour products only).
5.5 g/kg
for manufacturing confections
(baked wheat flour products only).
5.0 g/kg
for manufacturing moist cakes (rice
flour products only).
10 g/kg
for manufacturing sponge cakes,
butter cakes and steamed breads.
8.0 g/kg
for manufacturing steamed
MANJYU (bun made by steaming
wheat flour dough).
2.5
Noodles(excluding instant noodles and dry noodles)4.5 g/kg**** as boiled noodles.
6.0 mg/L
When formulated
into a standard
concentration.
Not applied to cases where the
Only when indispensable for
manufacturing or processing
the food, or when used for
nutritive purposes.
The above limit do
not apply to foods
approved to be
labeled as "special.
dietary use."
6.0 mg/L
When formulated
into a standard
concentration.
additives is used in for-
mulated dried milk under
approval by the Minister of
Health, Labor and Welfare.
Not applied to cases where the
additives is used in for-
mulated dried milk under
approval by the Minister of
Health, Labor and Welfare.
ppm Emulsifiers Calcium Strearoyl Lactylate Sponge cakes.
5.5 g/kg (continued)
(continued)
Steamed bread (bread made by steaming wheat flour dough). 5.5 g/kg Steamed MANJYU
2.0 g/kg
Glycerol Esters of Fatty All foods
Acids Lecithin
Polysorbate 20as polysorbate 80
Polysorbate 60 Capsule- and tablet-form foods excluding confections 25 g/kg Polysorbate 65 Chewing gum
5.0 g/kg Polysorbate 80
Cocoa and chocolate products 5.0 g/kg Milk-fat substitutes 5.0 g/kg Sauces
5.0 g/kg Seasonings for instant noodles 5.0 g/kg Shortening
5.0 g/kg Bakery confections
3.0 g/kg Decorations for confections 3.0 g/kg (Sugar coatings and icings) Dressing 3.0 g/kg Ice creams 3.0 g/kg Mayonnaise
3.0 g/kg Mix powder for bakery confections and moist sweet cake
3.0 g/kg Moist sweet cake, unbaked cake 3.0 g/kg
(Including fruit tart, cream cake, rare cheese cake, custard pudding, and like products)
Sweetened yoghurt 3.0 g/kg Candies
1.0 g/kg Edible ices including sherbet 1.0 g/kg Flour paste* 1.0 g/kg Soup
1.0 g/kg Pickled sea weed 0.50 g/kg Pickled vegetables 0.50 g/kg Chocolate drinks 0.50 g/kg Unripened cheese
0.080 g/kg Canned and bottled sea weed 0.030 g/kg Canned and bottled vegetables 0.030 g/kg Other foods 0.020 g/kg
Propylene Glycol Esters All foods
of Fatty Acids Sorbitan Esters of Fatty Acids
Sucrose Esters of Fatty Acids
Film-forming agents
Morpholine Salts of Fatty Acids Rind of fruits Polyvinyl Acetate*Rind of vegetables
Sodium Oleate
Flavoring agents Acetaldehyde
All foods
Only for flavoring.
Acetophenone
Aliphatic Higher Alcohols (excluding substances generally recognized as highly toxic)
Aliphatic Higher Aldehydes (excluding substances generally recognized as highly toxic)
If it is used together with one of polysorbate 60, 65, and 80,the sum of each amount used shall be not more than the corresponding maximum levels as polysorbate 80. The above standards are not applied for products that are approved or recognized as foods for special dietary use.
Flour paste*: In this list, flour paste is confined to paste products of cocoa and
chocolate that are prepared with sugar, fat/oil, powder milk,egg, or wheat flour as secondary ingridients, and pasteurized.They are used as
fillings or coatings of bread or bakery confections.
* Polyvinyl Acetate may also be used as chewing gum base.
See the section, "Chewing gum base."Only as film-forming agent.
ppm
Flavoring agents Alphatic Higher Hydro-All foods Only for flavoring. (continued) carbons (excluding sub-
stances generally recog-
nized as highly toxic)
Ally Cyclohexylpropionate
Ally Hexanoate
Ally Isothiocyanate
Amylalcohol
α-Amylcinnamicaldehyde
Anisaldehyde
Aromatic Alcohols
Aromatic Aldehydes
(excluding substances
generally recognized as
highly toxic)
Benzaldehyde
Benzyl Acetate.
Benzyl Alcohol
Benzyl Propionate
d-Borneol
Butanol
Butyl Acetate
Butyl Butyrate
Butyraldehyde
Butyric Acid
Cinnamic Acid
Cinnamaldehyde
Cinnamyl Acetate
Cinnamyl Alcohol
Citral
Citronellal
Citronellol
Citronellyl Acetate
Citronellyl Formate
Cyclohexyl Acetate
Cyclohexyl Butyrate
Decanal
Decanol
2,3-Dimethylpyrazine
2,5-Dimethylpyrazine
2,6-Dimethylpyrazine
Esters
Ethers
ppm
Flavoring agents Ethyl Acetate
All foods
(continued)
Ethanol
Yeast extract Vinyl acetate resin
Ethyl Acetoacetate All foods Only for flavoring.
Ethyl Butyrate Ethyl Cinnamate Ethyl Decanoate Mixture of
2-Ethyl-3,5-dimethylpyrazine and 2-Ethyl-3,6-dimethylpyrazine Ethyl Heptanoate Ethyl Hexanoate Ethyl Isovalerate 2-Ethyl-3-methylpyrazine Ethyl Octanoate Ethyl Phenylacetate Ethyl Propionate Ethylvanillin 1,8-Cineole Eugenol Fatty Acids
Furfural and its derivatives (excluding substances generally recognized as highly toxic)Geraniol Geranyl Acetate Geranyl Formate Hexanoic Acid Hydroxycitronellal Hydroxycitronellal Di- methylacetal
Indole and its derivatives Ionone Isoamyl Acetate
Only for flavoring, execpt when:1. Used for denaturing ethanol which is used for the removal astringency of persimons, the manufacture of crystalline fructose, the preparation of granules or tablets of spices, or the manufacture of KONNYAKU-KO (Konjac powder), or which is used as a solvent for Butylated Hydroxytoluene of Butylated
Hydroxyanisole or as an ingredient for the manufacture of vinegar;2. Used for accelerating- yeast-autolysis in the extract (water-soluble fraction obtained by autolysis of yeast;)
3. Used as a solvent for vinyl acetate resin.
Ethyl Aceteta used in manu-facturing yeast extract shall be removed before the preparation of the finished food.
ppm
Flavoring agents Isoamylalcohol All foods Only for flavoring. (continued)Isoamyl Butyrate
Isoamyl Formate
Isoamyl Isovalerate
Isoamyl Phenylacetate
Isoamyl Propionate
Isobutanol
Isobutyraldehyde
Isobutyl Phenylacetate
Isoeugenol
Isopropanol
Isothiocyanates
(excluding substances generally
recognized as highly toxic)
Isovaleraldehyde
Ketones
Lactones
(excluding substances
generally recognized as
highly toxic)
Linalool
Linalyl Acetate
Maltol
dl-Menthol
l-Menthol
l-Menthyl Acetate
Methyl Athranilate
2-Methylbutanol
Methyl Cinnamate
Methyl N-Methylanthra-
nilate
Methyl β-Naphthyl Ketone
5-Methylquinoxaline
Methyl Salicylate
p-Methylacetophenone
γ-Nonalactone
Octanal
l-Perillaldehyde
Phenethyl Acetate
Phenols
(excluding substances
generally recognized as
highly toxic)
Phenol Ethers
(excluding substances
generally recognized as highly toxic)
Piperonal
Propanol
Propionic Acid* Terpene Hydrocarbons Terpineol
Terpinyl Acetate * Propionic Acid may also be used as preservative. See the section, "Preser-
vatives."
ppm
Flavoring agents 2,3,5,6-Tetramethylpyrazine All foods Only for flavoring.
(continued)
Thioethers
(excluding substances generally recognized as highly toxic)
Thiols
(excluding substances generally recognized as highly toxic)2,3,5-Trimethylpyrazine γ-Undecalactone Valeraldehyde Vanillin
Flour treatment agents Ammonium Persulfate Wheat flour 0.30 g/kg
Benzoyl Peroxide
Wheat flour
Chloride Dioxide Wheat flour
Diluted Benzoyl Peroxide Wheat flour
0.30 g/kg
Potassium Bromate
Bread (only products made of wheat 0.030 g/kg of wheat flour)
flour
Food Colors Annato, water-soluble
β-Carotene
Copper Chlorophyll
as copper 0.0004 g/kg
Chewing gum 0.050 g/kg Chocolate
0.0010 g/kg Fish-paste products 0.030 g/kg (excluding SURIMI)
Fruits and vegetables for preserva-0.10 g/kg
tion.*KONBU (kelp)
0.15 g/kg of dry kelp Copper Chlorophyll Moist cakes (excluding bread with 0.0064 g/kg
(continued)
sweet fillings or toppings)
Can be used only as diluted Benzoyl Peroxide by mixing with one or more of Alum, calcium salts of Phosphoric Acid, Calcium Sulfate, Calcium
Carbonate, Magnesium Carbonate, and Starch.
Not permitted in fresh fish/shellfish including (fresh whale meat), KONBU (kelp)/WAKAME (sea weed) (both Laminariales ), legumes/
pulses, meat NORI (laver), tea,or vegetables.
Agar jelly in MITSUMAME (prepared by mixing agar jelly,cut fruits, gree beans, etc. with sugar syrup) packed into cans or plastic containers.
* Foods which are processed for preserving, including dried foods, salted foods, pickled foods in vinegar, and preserved foods in syrup.
Shall be decomposed or removed before the
preparation of the finished food.
Not permitted in fresh fish/shellfish (including whale meat), KONBU
(kelp)/WAKAME (sea weed)(both Laminariales ),
legumes/pulses, meat, NORI (laver) (except when gold is used on NORI), tea leaves,or vegetables.
ppm
Food Colors Food Blue No. 1 (Brilliant (continued)
Blue FCF) and its Alumi- num Lake
Food Blue No. 2 (Indigo Carmine) and its Alumi- num Lake
Food Green No. 3 (Fast Green FCF) and its Alu- minum Lake
Food Red No. 2 (Amaranth) and its Aluminum Lake Food Red No. 3 (Erythro- sin) and its Aluminum Lake Food Red No. 40 (Allura Red) and its Aluminum Lake
Food Red No. 102 (New Coccine)Food Red No. 104 (Phloxine)
Food Red No. 105 (Rose Bengale)Food Red No. 106 (Acid Red)
Food Yellow No. 4 (Tartra- zine) and its Aluminum Lake
Food Yellow No. 5 (Sunset Yellow) and its Aluminum Lake
Food colors other than chemically synthesized food additives
Iron Sesquioxide Banana (stem only)KONNYAKU (konjac)
Preparations of tar colors Same as for Food Blue No. 1.
Sodium Copper Chlorophyllin as copper
0.0004 g/kg
Candies
0.020 g/kg Chewing gum 0.050 g/kg Chocolate
0.0064 g/kg Fish-paste products (except SURIMI)0.040 g/kg Fruits and vegetables for preserva-0.10 g/kg
tion.*
KONBU (kelp)
0.15 g/kg of dry kelp Sodium Copper Chlorophyllin Moist cakes (excluding bread with 0.0064 g/kg (continued)
sweet fillings or toppings)Syrup
0.064 g/kg
Not permitted in fish pickles,fresh fish/shellfish (including whale meat) KASUTERA (a type of pound cake), KINAKO (roasted soybean flour),
KONBU (kelp)/WAKAME (sea weed) (both Laminariales ),legumes/pulses, marmalade,meat, meat pickles, MISO (fermented soybean paste),noodles (including Wantan),NORI(laver), soy sauce,sponge cakes, tea leaves,vegetables, or whale meat pickles.
Not permitted in fresh fish/shellfish (including whale meat), KONBU
(kelp)/WAKAME (sea weed)(both Laminariales ),
legumes/pulses, meat, NORI (laver) (except when gold is used on NORI), tea leaves, or vegetables.
Agar jelly in MITSUMAME (pre-pared by mixing agar jelly, cut fruits, gree beans, etc. with sugar syrup) packed into cans or plastic containers.* Foods which are
processed for preserving,including dried foods, salted foods, pickled foods in vinegar, and preserved foods in syrup.
ppm
Food Colors Sodium Iron Chlorophyllin
(continued)
Titanium Dioxide
Humectant Sodium Chondroitin Sulfate Fish sausage 3.0 g/kg
Mayonnaise20 g/kg
Dressing20 g/kg
Insecticide Piperonyl Butoxide Cereal grains0.024 g/kg
Non-nutritive Sweeteners Acesulfame Potassium An (sweetened bean paste) 2.5 g/kg
Confectionary 2.5 g/kg
Chewing gum 5.0 g/kg
Edible ices (including sherbets, 1.0 g/kg
flavored ices, and other similar
foods)
Fermented milk*0.50 g/kg
Flour paste 1.0 g/kg.
Ice creams 1.0 g/kg
Jam 1.0 g/kg
Foods with health claims 6.0 g/kg
(only tablets)
Lactic acid bacterial bevarages* 0.50 g/kg
Milk drinks*0.50 g/kg
Miscellaneous alcoholic beverages*0.50 g/kg
Moist cakes 2.5 g/kg
Nonalcoholic beverages0.50 g/kg
Pickles 1.0 g/kg
Sugar substitutes**15 g/kg
Tare (a dip or sauce mainly for 1.0 g/kg
Japanese or Chinese foods)
Wine*0.50 g/kg
Other foods 0.35 g/kg
Aspartame
Disodium Glycyrrhizinate MISO (fermented soybean paste)
Soy sauce
Saccharin Chewing gum0.050 g/kg
Sodium Saccharin as residue limit
of sodium saccharine
less than:
KOZI-ZUKE (preserved in KOJI, 2.0 g/kg
fermented rice
SU-ZUKE (vinegar-pickled foods)
TAKUAN-ZUKE (rice bran-pickled
radishes)Only for coloring.
Not permitted in fish pickles, fresh fish/shellfish (including whale meat) KASUTERA (a type of pound cake), KINAKO (roasted soybean flour), KONBU (kelp)/WAKAME (sea weed) (both Laminariales), legumes/pulses, marmalade, meat, meat pickles, MISO (fermented soybean paste), noodles (including Wantan), NORI(laver), soy sauce, sponge cakes, tea leaves, vegetables, or whale meat pickles.
** Products used by
directly adding to drinks, such as coffee and tea.
* Applied to dilutions, in the case of concentrated
products.
These maximum limits do
not apply to foods
approved to be labeled
as special dietary use. Same as for Annato, water-soluble
ppm Non-nutritive sweeteners Sodium Saccharin Nonalcoholic beverages (powdered) 1.5 g/kg (continued)(continued)KASU-ZUKE (lee-pickled foods) 1.2 g/kg
MISO-ZUKE (MISO-pickled foods)
SHOYU-ZUKE (soy sauce-pickled
foods)
Fish/shellfish (processed, excluding
fish paste, TSUKUDANI (foods
boiled down with soy sauce),
pickles, and canned or bottled
foods)
Processed sea weeds0.50 g/kg
Simmered beans
Soy sauce
TSUKUDANI (foods boiled down with
soy sauce)
Edible ices0.30 g/kg
Fish paste
Lactic acid bacterial drinks
Milk drinks
Nonalcoholic beverages
Sauces
Syrup
Vinegar
An (sweetened bean paste)0.20 g/kg
Fermented milk
Flour paste
Ice cream products
Jams
MISO (fermented soybean paste)
Pickles (preserved or pickled foods,
excluding those listed in this
column)
Confectionary0.10 g/kg
Canned or bottled foods, excluding 0.20 g/kg
those listed above.
D-Sorbitol All foods
Sucralose Chewing gum 2.6 g/kg
Confectionary 1.8 g/kg
Jam 1.0 g/kg
Lactic acid becterial beverages*0.40 g/kg
Milk drinks*0.40 g/kg
Miscellaneous alcoholic bverages*0.40 g/kg
Moist cakes 1.8 g/kg
Nonalcoholic beverages*0.40 g/kg
Sake*0.40 g/kg
Sake (compounded)*0.40 g/kg Sugar substitutes**12 g/kg Wine (any kind of fruit wine)*0.40 g/kg Other foods0.58 g/kg
** Products used by directly adding to drinks, such as coffee and tea.
* Applied to dilutions, in the case of concentrated
products.
These maximum limits do not apply to foods approved to be labeled as special dietary use. These maximum limits do
not apply to foods
approved to be labeled
as special dietary use.
(less than 1.5 g/kg in case of materials for nonalcoholic beverage or lactic acid bacteria drinks or fermented milk product to be diluted not less than 5-fold before use, less than 0.90 g/kg in case of vinegar to be deluted not less than 3-fold before use)
ppm
Non-nutritive sweeteners Xylitol All foods
(continued)D-Xylose
Preservatives Benzoic Acid Caviar 2.5 g/kg
Margarine 1.0 g/kg
Nonalcoholic beverages0.60 g/kg
Soy sauce0.60 g/kg
Syrup0.60 g/kg
Butyl p-Hydroxybenzoate as p-hydroxybenzoic
acid
Fruit sauce0.20 g/kg
nonalcoholic beverages0.10 g/kg
Rind of fruits and fruit vegetables 0.012 g/kg
Soy sauce0.25 g/L
Syrup0.10 g/kg
Vinegar0.10 g/L
Calcium Propionate as propionic acid
Bread and cakes 2.5 g/kg
Cheese 3.0 g/kg
Ethyl p-Hydroxybenzoate
Isobutyl p-Hydroxybenzoate
Isopropyl p-Hydroxybenzoate
Nisin
As polypeptide
containing Nisin A Cheese (except processed cheese)0.0125g/kg
Meat products
Whipped creams
Dressing0.010g/kg
Mayonnaise
Sauces*
Fine bakery products0.00625g/kg
Processed cheese
MISO (fermented soybean paste)0.0050g/kg
Processed eggs products
Moist, unbaked, sweet cakes made
maainly of cereal grains or starch**
0.0030g/kg
Potassium Sorbate as sorbic acid
0.30 g/kg When the additive is used in margarine with Sorbic Acid or Potassium Sorbate, or a preparation containing either of these two additives, the total amount of them as benzoic acid and as sorbic acid shall not be more than 1.0 g/kg.
When the additive is used in cheese with Sorbic Acid or Potassium Sorbate, or a preparation containing either of these two additives, the total amount of them as propionic acid and as sorbic acid shall not be more than 3.0 g/kg.
Same as for Butyl p-Hydroxybenzoate.
AMAZAKE (beverages made from fermneted rice using KOJI (Asp. oryzae), and confined to
products to be coonsumed in 3- fold or more dilution.)
Cheese: When used in combination with propionic acid, calcium propionate, or sodium propionate, total level of the additives as sorbic acid and as propionic acid shall not be more than 3.0 g/kg.
The maximum use levels are not apply to products permmited or recognized by the Minister of Health, Labour and Welfare as foods for special dietary uses. The foods include five types of products: foods for the ill, milk powder for pregnant and lactating women, formulated milk powder for infants, foods for the aged, foods for specified health uses.
* Sauces refer to all kinds of sauces including Oriental thick Worcester sauce, cheese souce, and ketchup, but excluding fruit sauce and its analogues used for cakes.
** They refer to rice pudding and tapioca puding, and their analogues, but excluding Oriental sweet dumplings.
ppm
Preservative Potassium Sorbate AN (sweetened bean paste) 1.0 g/kg
(continued)(continued)Candied cherries 1.0 g/kg
Cheese 3.0 g/kg
Dried fish/shellfish (excluding 1.0 g/kg
smoking cuttlefish & octopus)
Dried prune0.50 g/kg
Fermented milk (as raw materials for0.30 g/kg
lactic acid bacterial drinks)
Fish-paste products (excluding 2.0 g/kg
SURIMI)
Flour paste products for bread and 1.0 g/kg
confectionary
Fruit juice (including concentrated 1.0 g/kg
fruit juice) for confectionary
Fruit paste for confectionary 1.0 g/kg
Gnocchis 1.0 g/kg
Jams 1.0 g/kg
KASU-ZUKE (lees-pickled foods) 1.0 g/kg
Ketchup0.50 g/kg
KOJI-ZUKE (KOJI (Asp. oryzae)- 1.0 g/kg
pickled foods)
Lactic acid bacterial beverages (ex-0.050 g/kg cluding sterilized bevarages)
Lactic acid bacterial beverages (as 0.30 g/kg ingredients of lactic acid bacterial
beverages, excluding sterilized
beverages)
Margarine 1.0 g/kg Meat products 2.0 g/kg Miscellaneous alcoholic beverages 0.20 g/kg MISO (fermented soy bean paste) 1.0 g/kg MISO-ZUKE (MISO-pickled foods) 1.0 g/kg Salted vegetables 1.0 g/kg Sea urchin products 2.0 g/kg SHOYU-ZUKE (soy sauce-pickled 1.0 g/kg foods)
Simmered beans 1.0 g/kg Smoked cuttlefish & octopus 1.5 g/kg Soup (excluding potage-type soup)0.50 g/kg SU-ZUKE (vinegar-pickled foods)0.50 g/kg Syrup 1.0 g/kg TAKUAN-ZUKE (rice bran-pickled 1.0 g/kg radish)
TARE (a dip or sauce mainly for 0.50 g/kg Japanese or Chinese foods)
TSUKUDANI (foods boiled down in 1.0 g/kg soy sauce)
TSUYU (a sauce mainly for Japanese0.50 g/kg noodles)
Whale meat products 2.0 g/kg Wine (any kind of fruit wine)0.20 g/kg When the additive is used in margarine with Benzoic Acid or Sodium Benzoate, the total amount of them as benzoic acid and as sorbic acid shall not be more than 1.0 g/kg.
When the additive is used in MISO-ZUKE, the total amount of Sorbic Acid used in the product, and Sorbic Acid and its salts cntaining in MISO as ingredient shall not be more than 1.0 g/kg.
3.0 g/kg.
Preservative Propionic Acid (continued)
Propyl p -Hydroxybenzoate Sodium Benzoate
as benzoic acid Caviar
2.5 g/kg 1.0 g/kg
Margarine
1.0 g/kg Nonalcoholic beverages 0.60 g/kg Soy sauce 0.60 g/kg Syrup
0.60 g/kg
Sodium Dehydroacetate
Butter 0.50 g/kg Cheese 0.50 g/kg
Margarine
0.50 g/kg
Sodium Propionate Sorbic Acid
as sorbic acid 0.30 g/kg
AN (sweetened bean paste) 1.0 g/kg Candied cherries 1.0 g/kg Cheese
3.0 g/kg Dried fish/shellfish (excluding 1.0 g/kg
smoking cuttlefish & octopus)Dried prune
0.50 g/kg Fermented milk (as raw materials for 0.30 g/kg
lactic acid bacterial drinks)Fish-paste products (excluding 2.0 g/kg
SURIMI)
Flour paste products for bread and 1.0 g/kg
confectionary Gnocchis 1.0 g/kg Jam
1.0 g/kg KASU-ZUKE (lees-pickled foods) 1.0 g/kg Ketchup
0.50 g/kg KOJI-ZUKE (KOJI (Asp. oryzae )- 1.0 g/kg
pickled foods)
Lactic acid bacterial beverages (ex-0.050 g/kg
cluding sterilized bevarages)Lactic acid bacterial beverages (as 0.30 g/kg
ingredients of lactic acid bacterial beverages, excluding sterilized beverages) Margarine
1.0 g/kg
Same as for Calcium Propionate
Same as for Butyl p-Hydroxybenzoate
Fruit paste and fruit juice (including
concentrated juice) used for manufacturing confectionary.When the additive is used in margarine with Sorbic Acid or Potassium Sorbate, the total amount of them as benzoic acid and as sorbic acid shall not be more than 1.0 g/kg.
as dehydroacetic Same as for Calcium Propionate
AMAZAKE (beverages made from fermneted rice using KOJI (Asp . oryzae ), and confined to products to be coonsumed in 3-fold or more dilution.)
When the additive is used in margarine with Benzoic Acid or Sodium Benzoate,the total amount of them as benzoic acid and as sorbic acid shall not be more than 1.0 g/kg.
When the additive is used in MISO-ZUKE, the total amount This additive may also be used as flavoring agent.See the section, "Flavoring agents."
Preservative Sorbic Acid Meat products 2.0 g/kg (continued)(continued)Miscellaneous alcoholic beverages 0.20 g/kg
MISO (fermented soy bean paste) 1.0 g/kg
MISO-ZUKE (MISO-pickled foods) 1.0 g/kg
Salted vegetables 1.0 g/kg
Sea urchin products 2.0 g/kg
SHOYU-ZUKE (soy sauce-pickled 1.0 g/kg
foods)
Simmered beans 1.0 g/kg
Smoked cuttlefish & octopus 1.5 g/kg
Soup (excluding potage-type soup)0.50 g/kg
SU-ZUKE (vinegar-pickled foods)0.50 g/kg
Syrup 1.0 g/kg
TAKUAN-ZUKE (rice bran-pickled 1.0 g/kg
radish)
TARE (a dip or sauce mainly for 0.50 g/kg
Japanese or Chinese foods)
TSUKUDANI (foods boiled down in 1.0 g/kg
soy sauce)
TSUYU (a sauce mainly for Japanese0.50 g/kg
noodles)
Whale meat products 2.0 g/kg
Wine (any kind of fruit wine)0.20 g/kg Quality sustainer Propylene Glycol Crust of Chinese pastry (shao mai, 1.2 %
spring roll, wonton, zaio-z)
Smoked cuttlefish 2.0 %
Raw noodles 2.0 %
Other foods0.60 %
Raising agents Aluminum Ammonium
Sulfate
Aluminum Potassium
Sulfate
Ammonium Bicarbonate All foods
Ammonium Carbonate
Ammonium Chloride
Baking Powder
? Single Baking Powder
? Duplex Baking Powder
? Ammonia Type Baking
Powder
Potassium L-Bitartrate
Potassium DL-Bitartrate
Potassium Carbonate
Sodium Bicarbonate
Seasonings DL-Alanine All foods
L-Arginine L-Glutamate
Calcium 5'-Ribonucleotide
Disodium 5'-Cytidylate
Disodium 5'-Guanylate
Disodium 5'-Inosinate MISO-ZUKE, the total amount of Sorbic Acid used in the product, and Sorbic Acid and its salts cntaining in MISO as ingredient shall not be more than 1.0 g/kg.
Not permitted in MISO (fermented soy bean paste).
ppm
Seasonings Disodium 5'-Ribonucleotide (continued)
Disodium Succinate Disodium DL-Tartrate Disodium L-Tartrate Disodium 5'-Uridylate L-Glutamic Acid Glycine
Monocalcium Di-L-All foods
as calcium Glutamate
1.0 %
Monomagnesium Di-L-All foods
Glutamate
Monopotassium Citrate Monopotassium L- Glutamate
Monosodium L-Aspartate Monosodium Fumarate Monosodium L-Glutamate Monosodium Succinate Potassium Chloride All foods
Potassium Gluconate Sodium Gluconate Sodium Lactate Sodium DL-Malate L-Theanine Tripotassium Citrate Trisodium Citrate
Acetone
Fats and oils Guarana nuts
Glycerol All foods
Hexane
Sterilizer High-Test Hypochlorite All foods
Hypochlorous Acid Water
Sodium Hypochlorite
Not permitted in sesame.
Solvents or extracting agents
Not applied to foods approved to be labeled as "special dietary use."
Only for extracting
components from such nuts in the process of the manufac-ture of guarana beverages or for fractionating components of fats or oils.
Shall be removed before the preparation of the finished food.
Only for extracting fats or oils in manufacturing edible fats or oils.
Shall be removed before the preparation of the finished food.
Shall be decomposed or removed before the
preparation of the finished food.
ppm Thickening agents or Ammonium Alginate All foods
stabilizers
Casein
All foods
Calcium Alginate
All foods
Calcium Carboxymethyl- 2.0 %
cellulose
Methyl cellulose All foods 2.0%
Potassium Alginate
Propylene Glycol Alginate All foods 1.0 % Sodium Alginate
Sodium Carboxymethylcellulose All foods 2.0 % Sodium Carboxymethylstarch All foods 2.0 % Sodium Caseinate
All foods
Sodium Polyacrylate All foods0.20 %When used with one or more of the following additives, the total amount shall not be more than 2.0 % :
Methyl Cellulose, Sodium Carboxymethylcellulose, and Sodium Carboxymethyl-strach.
When used with one or more of the following additives, the total amount shall not be more than 2.0 %:
Calcium Carboxymethyl-cellulose, Methyl Cellulose, and Sodium Carboxymethyl-strach.
When used with one or more of the following additives, the total amount shall not be more than 2.0 %:
Calcium Carboxymethyl-cellulose, Methyl Cellulose, and Sodium Carboxymethyl-strach.
When used with one or more of the following additives, the total amount shall not be more than 2.0 %:
Calcium Carboxymethyl-cellulose, Methyl Cellulose, and Sodium Carboxymethyl-cellulose.
新版标准日本语中级(下)30课语法 电子版 有例句
1、~に先立って “Aに先立ってB”意思是在A之前先进行B动作,用于B是为A做准备或者练习的场合,是很正式的表达方式。使用形式为“名词+に先立って”意思相同的表达方式还有“~に先立ち”,如果修饰名词,则使用“~に先立つ”。 まず、海外企画部ではこのプロジェクトに先立って、中国市場に対する綿密な調査を実施しました。 トレーニングの開始にに先立ち、細かいスケジュールを立てた。(训练开始之前,首先制定了详细的日程表。) 会社の事業内容拡大に先立つ準備で忙しい。(忙着为扩大营业范围做准备。) 2、被动句的用法 一般来说,当没有必要出现动作主体时,便使用被动句,省略动作主体。 中国国内のテレビ普及率は95%以上、インターネット利用者数は世界第2位という結果が報告されました。 来週、水産業に関する展示会が開催されるそうです。(听说下周要举行一个水产也方面的展览会。) 林さんは部長に呼ばれて、部長といっしょに出かけました。(小林被部长叫上一起出去了。) 3、~を通した “Aを通してB”“Aを通したB”表示在进行B时把A作为手段或者中介。A为名词。表达相同意思的还有“~を通じて”“~を通じた”。但与表示时间段的“~通して”“~通じて”用法不同,使用时要注意。 私たちはテレビCMの制作とオームページを通した宣伝が効果的だと判断しました。(我们判断,通过制作电视广告和进行网上宣传是非常有效的。) 妻とは、わたしと妻の共通の友人を通して知り合いました。(我和妻子是通过我们共同的朋友认识的。) 今後は両国が国際交流を通じた相互理解を進める必要があります。(今后两国有必要通过国际交流来增进相互理解。) その映画スターは、代理人を通じて離婚のコメントを発表した。(那个电影明星,通过代理人宣布了自己的离婚声明。) 4、~ということは?~ということです “~ということは”用于举出某种行为,然后对其本质或性质进行描述。使用“~ということは,~ということです”的形式。前接小句是,也可以表示针对某些事的发生,对其原因或逻辑结果加以阐述。 テレビの普及率高く、インターネットの利用者数が多いということは、中国の人がちがそれを見慣れているということです。(电视机普及率高、互联网使用人数多,表明中国人对这些已经习以为常了。) 彼が怒ったということは、相当ひどいことを言われたということでしょう。(连他都火儿了,一定是别人说了太难听的话吧。) 5、効果が上がる “効果が上がる(有效果)”并不是“效果提高”的意思,而是“効果が現れる(效果
新版中日交流标准日本语初级上二十
第4单元小李的公司生活一② 172 ?乙? *道查 s ^-r <行。T , *橋 查 0 ±V?*3 L 包 U ?李右九《毎朝 7時1 二 人 ? iotzUt 来年 2. g [相继发生①] 表述两个以上的动作依照时间顺序相继发生时,可以使用“动词T 形+动词”的形式来 表示。 ? 9^0亍V 《一卜久^o T , 餐i L S L f c 。(昨天去商场买东西r 。) 1?龙 坊足 ?家久帰o T ,宿題查(回家.〈然后〉做作业。) t i' a 九 O' u 犬 jj >龙 ?図書館八行o T 本$借U T ,家久帰0圭言。(去图书馆借书,〈然后〉回家J 3. _T #e > _ [相继发生②] 表述两个以上的动作依照时间顺序相继发生时,也可以使用“动词T 形+ #?> +动词”的 表达形式。其语义和"动词丁形+动词”基本相同,但不能在一个句子中反复使用两 次以上。 ? 才查?圭才。(小李毎晚听了收音机后睡觉。) X>i U 九 ft T ?昼二'飯查食人T #e >出寸S T 。(吃了午饭后出门。) 。?龙 负龙 a iz ?A . r* 彳九i 丄i ?象、帰—度日本語勉強查I ■圭守。 (回家后,再学一遍日语。) 4.
新版中日交流标准日本语初级上下册
新版中日交流标准日本语初级上下册单词测试
初级上册 第1课 〔名〕中国人〔名〕日本人〔名〕韩国人〔名〕美国人〔名〕法国人〔名〕(大)学生 〔名〕老师〔名〕留学生〔名〕教授〔名〕职员〔名〕公司职员 〔名〕店员〔名〕进修生〔名〕企业〔名〕大学(我)父亲〔名〕科长〔名〕总经理,社长 〔名〕迎接〔名〕那个人〔代〕我〔代〕你〔副〕非常,很 〔叹〕哎,是(应答);是的〔叹〕不,不是 〔叹〕哎,哎 呀 〔专〕李 〔专〕王 〔专〕张 〔专〕森 〔专〕林 〔专〕小野 〔专〕吉田 〔专〕田中 〔专〕中村 〔专〕太郎 〔专〕金 〔专〕迪蓬 〔专〕史密斯 〔专〕约翰逊 〔专〕中国 〔专〕东京大 学 〔专〕北京大 学 〔专〕日中商 社 --------------- ------ 你好 对不起,请问 请 请多关照 初次见面 我才要(请您 ~) 是(这样) 不是 不知道 实在对不起 ~さん∕~ち ゅん∕~君く ん 第2课 〔名〕书 〔名〕包,公 文包 〔名〕笔记本, 本子 〔名〕铅笔 〔名〕伞 〔名〕鞋 〔名〕报纸 〔名〕杂志 〔名〕词典 〔名〕照相机 〔名〕电视机 〔名〕个人电 脑 〔名〕收音机 〔名〕电话 〔名〕桌子, 书桌 〔名〕椅子 〔名〕钥匙, 锁 新版中日交流标准日本语初级上、下册单词汇总
〔名〕钟,表〔名〕记事本〔名〕照片〔名〕车〔名〕自行车〔名〕礼物〔名〕特产,名产 〔名〕丝绸〔名〕手绢〔名〕公司〔名〕(敬称)位,人 〔名〕人〔名〕家人,家属 〔名〕(我)母亲 〔名〕母亲〔名〕日语〔名〕汉语,中文 〔代〕这,这个 〔代〕那,那个 〔代〕那,那个 〔疑〕哪个〔疑〕什么〔疑〕谁〔疑〕哪位〔连体〕这,这个〔连体〕那, 那个 〔连体〕那, 那个 〔连体〕哪个 〔叹〕啊 〔叹〕哇 〔叹〕(应答) 嗯,是 〔专〕长岛 〔专〕日本 〔专〕汕头 〔专〕伦敦 --------------- ------ 谢谢 多大 何なん~∕~ 歳さい 第3课 〔名〕百货商 店 〔名〕食堂 〔名〕邮局 〔名〕银行 〔名〕图书馆 〔名〕(高级) 公寓 〔名〕宾馆 〔名〕便利店 〔名〕咖啡馆 〔名〕医院 〔名〕书店 〔名〕餐馆, 西餐馆 〔名〕大楼, 大厦 〔名〕大楼, 建筑物 〔名〕柜台, 出售处 〔名〕厕所, 盥洗室 〔名〕入口 〔名〕事务所, 办事处 〔名〕接待处 〔名〕降价处 理大卖场 〔名〕自动扶 梯 〔名〕衣服 〔名〕风衣, 大衣 〔名〕数码相 机 〔名〕国,国 家 〔名〕地图 〔名〕旁边 〔名〕附近,
新版标准日本语初级语法上册(21-24)课
新版标准日本语初级语法上册21~24课 第21课 **************************** 1、动词的“た形” “た形”的变换方式是把“て形”的“て”换成“た”,把“で”换成“だ”。※ 2、动(た形)ことがあります ▲わたしはすき焼きを食べたことがあります。(我吃过日式牛肉火锅) ▲北京へ行ったことがありますか。(你去过北京吗) --いいえ,一度も行ったことがありません。(没有,一次也没有去过。) --いいえ,ありません。(不,没有。) 表示过去的经历。大致相当于汉语的“(曾经)~过”。通常用于至少半年前发生的事情,而在叙述“昨天”等离现在很近的以前的经历时,不能使用本句型。本句型既可用于叙述经历的时间、次数,也可只用于谈及某种经历。其否定形式时“动词た形+ことがありません”。强调完全没有某种经历时,有时候可以加“一度も”。疑问的表达形式是“动词た形+ことがありますか”。疑问句一般只问有无某种经历。回答时,可以重复问句中的部分词语,也可以只说“はい,あります”“いいえ,ありません”。而不能说“はい,ことがあります”“いいえ,ことがありません”。 3、动(た形)後あとで,~ ▲会社が終わった後で,飲みに行きます。(公司下班后去喝酒) ▲映画を見た後で,食事をしました。(看完电影后吃了饭) 表示一个动作在另一个动作之后发生时,使用这个句型。 ▲仕事の後で,映画を見ます。(工作之后看电影) 这个句型也可以以“名词+の+後で”的形式使用。“~前まえ”的后面必须是“に”,而“~後あと”的后面必须是“で”。“~前に”前面的动词形式必须是“基本形”,而“~後あとで”前面的动词形式必须是“た形”。 4、动(た形)ほうがいいです ▲もっと野菜を食べたほがいいですよ。(还是多吃点蔬菜好啊) ▲そんなに慌てないほうがいいですよ。(别那么慌张啊) ▲ホテルを予約したほうがいいですか。(饭店还是先预约为好啊) 本句型用于在两种事物中进行选择时。否定表达形式为“ない+ほうがいいです”。当建议对方做思想的动作、行为时,句尾多加“よ”。5、动ましょうか[提议] ▲何か食べましょうか。(吃点什么吗) 用于提议对方和自己一起做某事或向对方提议自己为对方做某事。“~ませんか” “~ましょう”只表示提议对方和自己一起做某事,而“~ましょうか”则另外还有向对方确认自己的提议是否可行的意思。翻译时一般在其后加“好吗?”之类使语气轻柔的词语。 ▲荷物を持ちましょうか。(我来帮你拿行李吧?) --はい,お願いします。(好的,拜托你了。) ▲窓を閉めましょか。(关上窗子好吗?) --いいえ,閉めないでください。(不,请别关。)
新版标准日本语初级语法总结
新版标准日本语初级语法总结 第1课 **************************** 1、名总名疋歹 ▲李中国人(小李是中国人。) ▲^^L^日本人^To (我是日本人。) ▲^^L^王IT 。(我姓王。) 相当于汉语的“?是?” ° “?总”是主语部分,“?IT ”是谓语部分。助词“味’用于提 示主题,读做“初” ° (森先生不是学生。 ) (我不是日本人。 ) (我不是田中。 ) 笳◎去乜人”的“m”在口语中有时会发成 Pp 3、 名总名IT 力、 ▲笳肚尢总小野^e^T 力、。 (您是小野女士吗?) --小野^To (是的,我是小野。) ▲丰厶中国人^T^o (金女士是中国人吗?) -J7、元,中国人 m 笳◎去乜人。 (不,不是中国人。) 相当于汉语的“?是?吗?”。助词“力、”接在句尾表示疑问。日语的问句在句尾不使 用“?”。 回答时可以只用“m‘或“元” ,也可以在之后加上“乞^^T” ,在5"、 元”之后加“弐力"、去T”或“乞笳◎去乜人”。不知道的时候用“分力、(不 知道)” ° 4、 名①名[从属机构、国家][属性] ▲李JC 企画①社員^To (小李是JC 策划公司的职员) ▲北京旅行社总中国①企業^To (北京旅行社是中国的企业) ▲〒二朮大学①先生^To (迪蓬先生是大学老师) 一般情况下相当于汉语“的”的意思。助词“①”连接名词和名词,表示前面的名词是后面 名词从属 的机构、国家或属性。※ **************************** 第2课 **************************** 1、 名IT “乙柑 遜n” “笳n”是指示事物的词。相当于汉语的“这、这个” “那、那 个”。 汉语里 有“这” “那”两种说法,而日语里“ in” “乞n” “笳n ”三种说法。其用法如下: ▲ ^n^本IT 。(这是书) 2、名总名m 笳◎去乜人 ▲森学生 m 笳◎去乜人。 ▲^^L^日本人m 笳◎去乜人。 ▲^^L^田中笳◎去 乜人。 相当于汉语“?不是?”
标准日本语中级笔记
第一課 こんにちは 一.形式体言:うち 1.うちは 接続:用言の連体形「動詞ている+うちは」/ 名詞+の+うちは 意味:表示在这一段时间内持续的状态。 訳詞:~~的时候。 例:朝のうちは涼しいです。 風が吹いているうちは外に出ることができない。 彼は若いうちは元気いっぱいです。 2.うちに 意味:① <その状態が変わる前に何かをする。>/在状态改变之前做某事。瞬间完成。(一切主观意志都属于瞬间性的动作) 訳詞:趁着…… 例:日本にいるうちに,一度京都を訪ねたいと思っている。 子供が寝ているうちに、掃除をしてしまいましょう。 若いうちに、いろいろ経験したほうがいい。 扩展:ないうちに 接続:動詞の未然形+ないうちに 意味:表示一种形为,动作没有进行就发生后面的动作。 訳詞:趁着还没~~ 例:空が暗くないうちに家へ帰りましょう。 冷めないうちに,どうぞ召し上がってください。(さめる) 意味:②~~の間に/~~期間 <その間に,はじめはなかったことが起きる。>/在这期间发生了开始没发生的事。表示在某种动作、行为进行过程中,不知不觉出 现了事先未料到的其他情况。 訳詞:在……过程中…… 例:母の手紙を読んでいるうちに涙がこぼれた。 寒かったが,走っているうちに体が暖かくなった。 本を読んでいるうちに眠くなった。 意味:③表示在某时间,距离,场所的范围之内。 訳詞:……内…… 例:二キロも行かないうちに車が故障してしまった 二、三日のうちにお尋ねします。 辨:ⅰ、うちに 一般不宜用于未来。 ○来週(×来週のうちに)行きます。 ⅱ、うちに与間に均可表示某个期间之内。但在表示会议,节日等,已经被规定,认可的期间时一般不宜使用うちに。 ○会議の間に(×うちに),居眠りをしてしまった。 扩展:~か~ないかのうちに 接続:「動詞-終止形/た形」+か+「動詞-未然形」+ないかのうちに 意味:~とほぼ同時に/几乎同时 <一つのことが終わったかどうかはっきりしないうちに,続いてすぐ次のことが起きる>/表示前一动作和行为的完成与后一动作、
新版标准日本语初级上21课
第21课 わたしはすき焼きを食べたことがあります ことば(言葉)〔名〕 ①语言,言词★言葉数の少ない人(沉默寡言的人) ②说法,措词★言葉で言い表せない(用语言表达不出来) メールアドレス〔名〕邮件地址 ★ミールアドレスを教えてください。(请告诉我你的邮件地址) れんきゅう(連休)〔名〕连休 ★連休を利用して海外旅行に行きたい。(想利用连休去海外旅行。) ゴールデンウィーク〔名〕黄金周 ★ゴールデンウィークの期間に切符を買いにくい。(黄金周期间票不好买。) おわり(終わり)〔名〕结束 ★初めから終わりまで(从头到尾,自始至终) きゅうけいじかん(休憩時間)〔名〕休息时间 ★休憩時間はいつも何をしますか。(休息时间总是干什么呢?) きょうげき(京劇)〔名〕京剧 ★京劇は中国の伝統的な文芸だ。(京剧是中国的传统文艺。) きっぷ(切符)〔名〕票(券) ★東京までの切符を1枚ください。(请给我一张到东京去的票。) からだ(体)〔名〕 ①身体,身子★体の調子が悪い(身体不舒服) ②身材★体のほっそりした女(身材苗条的女人) ③体质★肉食は私の体に合わない(肉食不适合我的体质) ④健康,体力★体が続(つづ)かない(体力支持不住) じしん(地震)〔名〕地震 ★今朝かなりの地震があった。(今天早上发生了相当了厉害的地震。) どろぼう(泥棒)〔名〕小偷,盗贼 ★夕べ隣の家に泥棒が入った。(昨夜邻家进了小偷。) ちゅうしゃじょう(駐車場)〔名〕停车场 ★この辺りには駐車場がない。(这一带没有停车场。) わたします(渡します)〔他动1〕 ①渡,送过河★船で人を渡す(用船渡人) ②架,搭★川に橋を渡す(在河上架桥) ③交,交给,付★この手紙を彼に渡してください。(请把这封信交给他。) おくれます(遅れます)〔自动2〕 ①晚,耽误★約束の時間に1時間遅れた。(比约定的时间晚了一个小时。) ②没赶上,迟到★学校に遅れた(上课迟到了) ④(表)慢★僕の時計は5分遅れている。(我的表慢了五分钟。) かんがえます(考えます)〔他动2〕
新版标准日本语初级单词(全) (1)
第1课 ちゅうごくじん(中国人)〔名〕中国人 にほんじん(日本人)〔名〕日本人 かんこくじん(韓国人)〔名〕韩国人 アメリカじん(~人)〔名〕美国人 フランスじん(~人)〔名〕法国人 がくせい(学生)〔名〕(大)学生 せんせい(先生)〔名〕老师 りゅうがくせい(留学生)〔名〕留学生 きょうじゅ(教授)〔名〕教授 しゃいん(社員)〔名〕职员 かいしゃいん(会社員)〔名〕公司职员 てんいん(店員)〔名〕店员 けんしゅうせい(研修生)〔名〕进修生 きぎょう(企業)〔名〕企业企業 だいがく(大学)〔名〕大学大学 ちち(父)〔名〕(我)父亲 かちょう(課長)〔名〕科长 しゃちょう(社長)〔名〕总经理,社长 でむかえ(出迎え)〔名〕迎接出迎え あのひと(あの人)〔名〕那个人 わたし〔代〕我私 あなた〔代〕你貴方 どうも〔副〕非常,很 はい〔叹〕哎,是(应答);是的 いいえ〔叹〕不,不是 あっ〔叹〕哎,哎呀 り(李)〔专〕李 おう(王)〔专〕王 ちょう(張)〔专〕张 もり(森)〔专〕森 はやし(林)〔专〕林 おの(小野)〔专〕小野 よしだ(吉田)〔专〕吉田 たなか(田中)〔专〕田中 なかむら(中村)〔专〕中村 たろう(太郎)〔专〕太郎 キム(金)〔专〕金 デュポン〔专〕迪蓬 スミス〔专〕史密斯 ジョンソン〔专〕约翰逊 ちゅうごく(中国)〔专〕中国中国 とうきょうだいがく(東京大学)〔专〕东京大学ペキンだいがく(北京大学)〔专〕北京大学
ジェーシーきかく(JC企画)〔专〕JC策划公司 ペキンりょこうしゃ(北京旅行社) 〔专〕北京旅行社旅行者 にっちゅうしょうじ(日中商事)〔专〕日中商社 -------------------------------------------- こんにちは你好 すみません对不起,请问 どうぞ请 よろしくおねがいします(~お願いします)宜しく御願いします 请多关照 はじめまして初次见面 こちらこそ我才要(请您~) そうてす是(这样) ちがいます不是 わかりません(分かりません)不知道 どうもすみません实在对不起 ~さん∕~ちゅん∕~君くん 第2课 ほん(本)〔名〕书本 かばん〔名〕包,公文包かばん ノート〔名〕笔记本,本子ノート えんぴつ(鉛筆)〔名〕铅笔鉛筆 かさ(傘)〔名〕伞傘 くつ(靴)〔名〕鞋靴靴靴 しんぶん(新聞)〔名〕报纸新聞 ざっし(雑誌)〔名〕杂志雑誌 じしょ(辞書)〔名〕词典辞書 カメラ〔名〕照相机カメラ テレビ〔名〕电视机テレビ パソコン〔名〕个人电脑パソコン ラジオ〔名〕收音机ラジオ でんわ(電話)〔名〕电话電話番号 つくえ(机)〔名〕桌子,书桌机 いす〔名〕椅子いす かぎ〔名〕钥匙,锁 とけい(時計)〔名〕钟,表時計 てちょう(手帳)〔名〕记事本 しゃしん(写真)〔名〕照片 くるま(車)〔名〕车車車 じてんしゃ(自転車)〔名〕自行车自転車自転車 おみやげ(お土産)〔名〕礼物お土産お土産 めいさんひん(名産品)〔名〕特产 シルク〔名〕丝绸
标准日本语中级 上
中日交流标准日本语中级上册课文 - 1 - 一、会話出会い JC 策划公司上海分公司主任李秀丽从日本出差回来,到达 上海浦东机场。 (一位日本男子掉了记事本,李秀丽捡起来追了上去……) 李:あのう、すみません。 男性:えっ? 李:これ、落ちましたよ。 男性:あっ!すみません。ありがとうございます。 (在从浦东机场开往市区的磁悬浮列车上.李秀丽又发现了 刚才那位男士,便跟他打招呼) 李:あのう、失礼ですが、先ほどの方じゃありませんか。 男性:ああ。さっきは、どうもありがとうございました。助かりました。李:いいえ、どういたしまして。 男性:中国の方ですか、日本語がお上手ですね。 李:いいえ、まだまだです。勉強すればするほど、難しくなる感じ がします。上海へは、お仕事でいらっしゃったんですか。 男性:ええ、こちらに転勤になったんです。空港はすっかり変わり ましたね。驚きました。 李:街もずいぶん変わっていますよ。変化が早くて、わたしたちも ついていけないくらいです。 男性:そうでしょうね。 李:ほら、高層ビルが見えてきたでしょう?あの辺は上海の新し い中心地なんです。 男性:すごい。まるでニューヨークみたいですね。 (不久磁悬浮列车到达终点。在车站站台) 李:じゃあ、ここで。 男性:ええ、どうもありがとうございました。さようなら。 二、課文日本の鉄道 日本には、JR、私鉄、公営の3 種類の鉄道会社があります。JR とは、Japan Railways の略です。以前は国営の鉄道でしたが、 1987 年に民営化されました。世界的に有名な新幹線もJR の路線 の1つで、日本の主要な都市と都市を結んでいます。最高時速は 300 キロを超えます。最初に完成したのは東海道新幹線ですか、 山陽新幹線、東北新幹線、九州新幹線など、路線がどんどん延 びています。 私鉄とは、JR 以外の民間企業が経営する鉄道会社で、大都市 には大きな私鉄がたくさんあります。また,公営の鉄道は,地方自 治体などが経営するものです。
新版中日交流标准日本语 初级上册 课文 译文 单词
新版中日交流标准日本语初级课文译文单词 基本课文 1.李さんは中国人です。 2.森さんは学生ではありません。 3.林さんは日本人ですか。 4.李さんはJC企画の社員です。 A甲:わたしは李です。小野さんですか。 乙:はい,そうです。小野です。 B甲:森さんは学生ですか。 乙:いいえ,学生ではありません。会社員です。C甲:吉田さんですか。 乙:いいえ,ちがいます。森です。 D甲:李さんはJC企画の社員です。 乙:はい,そうです。 应用课文:出迎え 飞机准点到达成田机场。小野绿和同事森健太郎在候机大厅等着小李。小李办完入境手续,到大厅后,看到写着“李秀麗樣”字样的牌子。 (小李朝牌子的方向走去) 李:JC企画の小野さんですか。 小野:はい,小野です。李秀麗さんですか。 李:はい,李秀麗です。はじめまして,どうぞよろしくお願いします。 小野:はじめまして。小野緑です。 (森在一旁插话) 森:李さん,こんにちは。 李:吉田さんですか。 森:いいえ,わたしは吉田じゃありません。森です。 李:あっ。森さんですか。どうもすみません。 森:いいえ,どうぞよろしくお願いします。 李:李秀麗です。こちらこそ,よろしくお願いします。<基本课文译文> 1.小李是中国人。 2.森先生不是学生。 3.林先生是日本人吗? 4.小李是JC策划公司的职员。 A甲:我姓李。(您)是小野女士吗? 乙:是的,(我)是小野。 B甲:森先生是学生吗? 乙:不,不是学生。是公司职员。 C甲:您是吉田先生吗? 乙:不,不是。我是森。 D甲:小李是JC策划公司的职员吗? 乙:是的。 <应用课文译文>机场迎接 飞机准点到达成田机场。小野绿和同事森健太郎在候机大厅等着小李。小李办完入境手续.到大厅后,看到写着“李秀麗樣”字样的牌子。 (小李朝牌子的方向走去) 李:(您)是JC策划公司的小野女士吗? 小野:是的,我是小野。是李秀丽女士吗? 李:是的,我是李秀丽。初次见面,请多关照。小野:初次见面。我叫小野绿。 (森在一旁插话) 森:李女士,你好! 李:(您)是吉田先生吗? 森:不,我不是吉田。(我)是森。 李:啊,是森先生呀。对不起。 森:没关系。请多关照。 李:我是李秀丽。以后请您多多关照。 第1課李さんは中国人です
新版中日交流标准日本语初级下同步测试卷(第35-39课)37
一、将下列汉字用平假名填入_____中。(0.5X20) 1.携帯 2.用事 3.長城 4.観光 5.海外 6.新鮮 7.釈放 8.直通 9.鉄道10.遺産 11.全長12.単位13.実際14.規模15.財布 16.塩17.合格18.成功19.練習20.飛行機 二、将下划线部分的假名用汉字填入_____内。(0.5X20) 1.わたる 2.はつげんする 3.ひよう 4.かんこう 5.やさい 6.えきまえ 7.れっしゃ 8.こうそく 9.ちょうじょう10.きらい11.きゅうりょう12.けいたい13.ゆうしょう14.こまる15.ふくしゅう16.すずしい17.すし18.わるい19.はつげん20.きびしい 三、从下列①②③④中选择正确答案并将其填入_____处。(1 X 10) 1.映画_____見に行きませんか。 ①では②でも③にも④へも 2.魚を_____駅前のスーパーがいいですよ。 ①買うと②買ったら③買えば④買うなら 3.高速道路を利用すれば_____2時間ぐらいです。 ①ほとんど②たぶん③だいたい④だいぶ 4. _____見ると、本当に規模が大きいですね。 ①実際で②実際を③実際に④実際と 5.東大合格ですか。_____加藤さんの息子ですね。 ①本当に②本当③さすがに④さすが 6.天気もいいし、_____、海に行きましょう。 ①日曜日ですから②日曜日なので③日曜日だし④日曜日ですし 7.この仕事は、女性に_____と思います。
①向けている②向ける③向いている④向く 8.わたしたちの若い_____は、それが普通でした。 ①時②ころ③間④うち 9._____仕事をしていても、給料が違うこともあります。 ①同じの②同じな③同じ④同じくらい 10.将来、もっと増えて_____でしょう。 ①来る②来た③行く④行った 四、从下文①②③④中选择恰当的答案填人()中。(1X10) 1.お酒は好きじゃないので()飲みません。 ①よく②あまり③とても④少し 2.むこう()田中さんが歩いて来ました。 ①に②へ③から④まで 3.あの人は来ないと思っていましたが()来ませんでした。 ①やっぱり②もちろん③ならほど④なかなか 4.もう8時です。()帰りましょう。 ①いよいよ②やらと③そろそろ④だんだん 5. ()帰るんですか。もっとゆっくりしていってください。 ①やっと②まだ③もう④すでに 6.レストランで夕食を食べてから、映画を()いきましょう。 ①みる②みて③みた④みに 7.ラジオがうるさいので()。 ①けしました②きえました③しめました④しまりました
新标准日本语初级课文翻译上册(2020年整理).pdf
1.小李比森先生年轻。 2.和日本相比,中国更辽阔。 3.神户没有大阪那么繁华。 4.在各种体育活动中,足球最有意思。 A甲:北京比东京冷吗? 乙:是的。冬天的北京比东京冷多了。 B甲:日语和英语,哪个难学? 乙:日语难学。 C甲:森先生很会打网球啊! 乙:(嗯……)不。不如长岛先生打得好。D甲:(四个)季节当中,(你)最喜欢哪个? 乙:我最喜欢春天。 <应用课文译文>酒与茶 李:长岛,你经常喝酒吗? 长岛:是的。我非常喜欢喝酒,每天晚上都喝。 李:啤酒和日本酒,你喜欢哪一种? 长岛:哪种都喜欢。不过,我最喜欢的还是烧酒。 小野:烧酒近来很受欢迎。 李:小野也喜欢喝烧酒吗? 小野:不。比起烧酒来,我更喜欢喝葡萄酒。不过,我也经常喝啤酒。 长岛:中国有很多种茶啊。 李:是啊。乌龙茶啦、茉莉花茶啦、绿茶啦,很多很多。 小野:哪种茶最受欢迎呢? 李:还是乌龙茶。 小野:小李,(你)也经常喝茶吗? 李:是的。我每天都喝乌龙茶或者茉莉花茶。 长岛:哪种好喝? 李:哪种都好喝。不过我更喜欢喝茉莉花茶……
1.桌子上有3本书。 2.小李每天工作7小时。 3.小李一周去两次游泳池(游泳)。 4.下午去邮局托运包裹。 A甲:对不起,请给我5张明信片。乙:好的。5张250日元。B甲:(你)经常看电影吗? 乙:是。1个月看两次左右。 C甲:从你家到公司需要多少时间? 乙:乘电车需要1小时左右。D甲:(你)昨天干什么了? 乙:去新宿看了电影。 <应用课文译文>酒馆 小野:现在我要和森一起去附近一家酒馆喝酒。你也一起去怎么样? 李:我?方便吗?好吧。 李:森先生,你们常来这个酒馆吗? 森:是的。我每周大约来两次。 小野:我也经常来。 森:(对不起,)先来3杯生啤。 李:1扎生啤300日元? 森:这里的酒和饭菜都很便宜。5根烤鸡肉串才400日元。 小野:炸鸡、土豆炖肉一盘350日元。 李:别的店卖多少钱呢? 森:生啤大概是1扎400或450日元。 小野:烤肉串1根150日元左右。 李:那,这儿真便宜啊。 14 1.昨天去商场买东西了。
新版标准日本语初级上册语法总结
新版标准日语初级上册语法总结 ㈠日语常用的词汇分类及用法: 1 名词:在句子中作主语,谓语,宾语,定语(名词+の名词)。 2 形容词:定语,谓语。 3 形容动词:定语,谓语。 4 动词:定语,谓语。 5 副词:可做状语,修饰动词,形容词,形容动词。 6 助词:相当中文里的助词,用于说明一个句子或一个词,与其它句子或词的关系。 ㈡动词的分类及「て形」、「ない形」、「た形」的变形规则。 动词的分类: 「て形」: 「ない形」: 「た形」: ㈢名词,形容词,形容动词,动词的简体及敬体变形 ㈣上册所学语法中与「て」「ない」「た」相关的语法。 ㈤常见助词用法的归纳总结。 ㈥连词:连接句子于句子的词。 ㈦疑问词: ㈧副詞及接续词: 动词的分类: 1动词「ます形」的最后一个假名以「い」段假名结尾时,则为一类动词 例えば:買います立ちます走ります 読みます遊びます死にます 書きます泳ぎます行きます 話します 2动词「ます形」的最后一个假名以「え」段假名结尾时,则为二类动词。其中有一部分特殊的二类动词(它们看起来类似一类)信じる起きる浴びる着るできる 見るいる降りる借りる足りる 例えば:食べます出かけます鍛えます 起きます浴びます着ます
できます見ますいます 降ります足ります借ります(部分特殊的二类动词) 3通常情况下是两个汉字加上します,也有两个汉字加上一个假名再加上します,或者全部是片假名情况,除此之外还有一个「来ます」这种类型的动词则为三类动词。 例えば:運動します復習します練習します 買い物しますクリックしますチェックします 动词「て形」的变形规则: 1、一类动词: ①动词「ます形」的最后一个假名以「い、ち、り」结尾时,将它们改为「って」 買います買って 立ちます立って 走ります走って ②动词「ます形」的最后一个假名以「み、び、に」结尾时,将它们改为「んで」 読みます読んで 遊びます遊んで 死にます死んで ③动词「ます形」的最后一个假名以「き」结尾时,将它改为「いて」 書きます書いて ④动词「ます形」的最后一个假名以「ぎ」结尾时,将它改为「いで」 泳ぎます泳いで ⑤行きます行って ⑥話します話して 2、二类动词:直接去掉「ます」加「て」 食べます食べて出かけます出かけて 鍛えます鍛えて起きます起きて 3、三类动词:直接去掉「します」加「して」。「来ますー来(き)て」。 運動します運動して復習します復習して 買い物します買い物してチェックしますチェックして 动词「ない形」的变形规则:
新版标准日本语中级学习笔记完全版1
Radium的 学习笔记
前言 1、作者的话 本笔记是由笔者2008年7月~8月间在北京某日语班学习新版标日中级课程时所记纸质笔记整理而成的。由于新版标日上市时间还很短,市面上尚缺少新版标日中级对应的教辅书籍,很多日语自学者都因为缺乏资料而苦恼,因此笔者将自己的笔记整理发布出来,希望能对广大日语学习者有所帮助。 本笔记最早在笔者的blog (https://www.360docs.net/doc/b63839890.html,/radiumking) 和咖啡日语论坛的“综合日语学习”版面上同步连载,得到了广大网友的支持和鼓励,在此谨表谢意。现在,我将网上发表的笔记进一步整理成word格式,方便大家查阅及打印。 但是,虽然说本笔记能对学习新版标日中级有所帮助,但是,基于以下几点理由,它并不能代替由专家和资深教师编写的教辅书籍: 首先,笔者记笔记时不可能将所有有用的内容都记下来,必然是选择对笔者本人最有用的内容进行记录; 其次,由于笔者和大家一样,也是日语学习者,记笔记的时候记错了、整理的时候发现不了的地方肯定是存在的,这样的话有可能会对学习造成误导。 因此,本笔记仅可作为日语学习的参考之用,敬请注意。 最后,祝大家日语水平天天向上! Radium 2008年10月15日 2、有限授权 本笔记允许在网络上自由转载,但是在转载时必须保证文本的完整性(包括全部的正文内容和前言),并明确标示转载来源为本人blog (https://www.360docs.net/doc/b63839890.html,/radiumking)。 允许自行修改、打印和传播打印稿,但是未经本人同意不得在网络上传播修改后的笔记。需要者请联系e-mail: radiumking@https://www.360docs.net/doc/b63839890.html,,说明情况并附修改后的笔记。 该笔记的全部或任意部分不得用于商业目的,除非经过本人同意。 3、免责声明 本人不保证笔记内容的正确性。本人不对因本笔记内容的错误而造成的任何后果负责。
新版中日交流标准日本语初级下册课文译文单词
新版中日交流标准日本语初级下册课文译文单词 1 基本课文 1. これは明日会議で使う資料です 2. 私は明日乗る飛行機は中国航空です 3. 中国で買ったCD を友達に貸しました 4. 操作が簡単なパソコンが欲しいです A 甲:李さん,この人はだれですか。 乙:その人は中国でとても人気がある女優です。 B 甲:あの窓のところにいる人はだれですか。 乙:あれは受付の戴さんですよ。 C 甲:何をしているんですか。 乙:昨日李さんにもらった本を読んでいます。 D 甲:この会社で歌がいちばん上手な人は誰ですか。乙:森さんだと思います。 应用课文:北京市街ヘ 森健太郎到北京的那天,小李和北京分公司的 职员马国祥去机场迎接。寒暄后,由小马开车,三 人去了市内宾馆。 (上了车) 森:今日泊まるホテルは天安飯店でしたね。 李:ええ。1 か月ぐらいホテルに泊まってください。 ゆっくり住むを探しましょう。 (上了高速公路) 森:ずいぶんまっすぐな道路ですね。 馬:これは空港と北京市街をむすぶ高速道路で, 市街までだいたい30 分ぐらいです。 (车内响起日语歌曲) 森:あっ,これ,日本の歌ですね。 馬:はい,そうです。日本人の友達にもらったCDです。森:日本の歌ガ好きなんですか。 馬:ええ,大好きです。中国には日本の歌ガ好き な人ガたくさんいますよ。 (高速公路两侧的几座大楼映入眼帘。森指着右侧 前方的大楼问题......) 森:あそこにある大きな白い建物は何ですか。 李:あれは最近できた建物ですね。馬さん知って いますか。 馬:ああ,あれは自動車の部品工場ですよ。 (接近北京市区,进入三环后开始堵车了) 森:だいぶ車ガ多くなりましたね。 馬:ええ,今走っている道路は三環路ですガ,こ のあたりはよく渋滞します。 李:三環路は北京でいちばん交通量ガ多い道路で
标准日本语初级 第 22 课
标准日本语初级第 22 课 课程正文 第22課田中さんは毎朝新聞を読んだり、テレビを見たりします 重点 1、…たり、たりします/です(动词) 2、…かったり、…かったりします/です(形容词) 3、…だったり,…だたりします/です(形容动词、名词) (1) 田中さんは毎朝新聞を読んだり、テレビを見たりします。 田中さんは駅の売店でスポーツ新聞を買ったり、週刊誌を買ったりします。 たくさんの人が電車の中で新聞を読んだり、週刊誌を読んだりします。 (2) 日本人は毎日新聞を家で読んだり、電車の中で読んだりします。 新聞のほかにテレビを見たり、ラジオを聞いたりして、ニュースを知ります。 日本の新聞には一般紙と専門紙があります。 一般紙には朝刊と夕刊があります。 専門紙にはたくさんの種類があります。 スポーツの専門だったり、経済の専門だったりです。新聞社によって同じニュースでも見出しが大きかったり、小さかったりします。 記事の書き方も新聞社によって違います。 人々は自分の仕事や趣味によって新聞を選びます。(3) 張う:日本は新聞の種類が多いですね。 田中:ええ、おおいです。日本人は毎朝家で読んだり、電車の中で読んだりします。 張:そうですね。朝の電車の中ではほとんどの人が新聞を読んだり、週刊誌を読んだりしていますね。 田中:張さんは1日に何種類の新聞を読みますか。 張:1種類しか読みません。朝刊と夕刊でけです。 田中:わたしは3種類です。一般紙とスポーツ新聞と経済新聞を読みすま。 張:すごいですね。 田中:新聞のほかに夜家でテレビを見たり、ラジオを聞いたりします。 張:いろいろな方法でニュースを知ることができますね。 课程译文 第 22 课田中每天早上又看报纸,又看电视 (1) 田中每天早上又看报纸,又看电视。 他在车站的小卖部或买体育报或买 周刊杂志。有很多人在电车上或看报或看杂志。 (2) 日本人每天或在家里看报、或在电车上看报。除了报纸以外,还看电视、听收音机来获得消息。 日本的报纸分为一般性报纸和专业 性报纸。一般性报纸有"朝刊"和"夕刊"。专业性报纸种类很多,或是体育方面的,或是经济方面的。 同样一则新闻,由于报社不同,文章的标题也不同,有的大,有的小。报道的写法也因报社而异。 人们根据自己的工作或兴趣选择报 纸。 (3) 张:日本报纸的种类真多啊! 田中:嗯,挺多的。日本人每天或在家里或在电车上阅读报纸。 张:是啊,早上电车里大多数人都在看报,或者看周刊杂志。 田中:张先生一天看几种报纸? 张:就一种,只看"朝刊"和"夕刊"。 田中:我看3种报纸,一般性报纸和体育报、经济报。 张:那么多啊! 田中:除了看报之外,晚上还在家里看电视、听收音机。 张:(这样,)您就能用各种方法知道消息啦!
新版标准日本语初级上册1-12课教案
新版《中日交流标准日本语》教案 第一課李さんは中国人です 一、教学目的与要求: 目的:掌握新句型和新单词的用法。 要求:能够用标准的语音读出新单词,用新句型造简单的句子。 二、教学重点与难点: 重点:1.词汇:先生、社員、父、出迎え、課長 2.句型:(1)~~は~~です; (2)~~は~~ではありません; (3)~~は~~ですか。 (4)はい、そうです/いいえ、そうではありません。 3.格助词「の」的用法。 4.词语用法说明:(1)~~さん;(2)はじめまして;(3)~~人 难点:判断助动词「です」的变化。 三、教学方法和手段: 方法:日汉对比法。 手段:课堂面授。讲练结合。 四、授课内容:(四号加黑) 1.重点词汇的讲解: (1)先生:“老师、教师”的意思。日语中「教師」也是“老师、教师”的意思,郑重场合使用。此外,「先生」一词还有“大夫”的意思。 例:先生、おはようございます。(老师,早上好。) 川崎さんは病院の先生です。(川崎是医院的大夫。) (2)社員:“职员”的意思。表示具体某一个公司的人。「会社員」表示一种职业,意思是“公司职员”“在公司工作的人”。 例:この会社は社員が多い。(这个公司职员多。) 小野さんは会社員です。(小野是公司职员。) (3)父:“父亲、爸爸”的意思。在向他人提起自己父亲时称「父」;而提起他人的父亲时则称呼为「お父さん」。 例:父は今年50歳です。(我爸爸今年50岁。) お父さんはおいくつですか。(您父亲今年多大岁数了?) (4)出迎え:是由「でる」「迎える」组成的复合动词「出迎える」的连用形作名词的形式。“迎接”的意思。 例:空港へお客さんを出迎えに行きます。(去机场迎接客人。)
新标准日本语初级下语法总结
动词小句加“の”时期名词化,标示“做某动作”的意思 (这钟名词化性质做主语而谓语是表示性质、状态的一类形容词或二类形容词是,主语要用助词“は”来表示) E.g 自転車に2人で乗るのは危ないです。骑自行车带人很危险 パソコンで表を作るのは楽しいです。用电脑制表是很愉快的 动词小句加“の”的名词化形式还可以做宾语: の+を E.g手紙を出すのを忘れました。我忘了寄信 E.g森さんが発言するのを聞きました。听了森先生的发言 表示说话人对自己和听话人都不能断定的事情进行推测,常与“たぶん”呼应使用 “でしょう”的简体形是“だろう”(表示推测的表达形式) (动词小句和一类形容词用简体形后续“でしょう”) (二类形容词小句和名词小句则把简体形的“だ”换成“でしょう”) E.g 明日の朝は大雨になるでしょう。明天早晨会下大雨吧 E.g この本お値段は判りませんが,たぶん高いでしょう。 我不知道这本术的价格,大概很贵吧 表示有可能发生模式,其可能性一般为百分之五十左右(发生某事的表达形式): E.g 森さんは今日会社を休むかもしれません。森今天也许不会来公司上班了 E.g 来週は暇かもしれません。下个星期也许有空 表示时间的短语名词 小句为动词小句时分两种情况: ①表示后项动作实现时前项动作尚未完成:~する(基本形)+時 E.g 日本に行く時,たくさの土産を買いました。去日本的时候买了许多礼物(之前买的) ②表示后项动作实现时前项动作已经完成:~した(た形)+時 E.g 日本に行った時,たくさの土産を買いました。去了日本的时候买了很多礼物 小句为一类形容词小句时用其简体形直接+“時” E.g忙しい時,家族みんなで仕事をします。忙时全家人一起干活 小句为二类形容词小句和名词小句时要用“二类形容词+な+時”“名词+の+時” E.g暇な時,私は町で買い物をします。有空时我上街买东西 小句为一类、二类形容词和名词小句时,前项是后项的动作进行的时间 E.g 子供の時,大きな地震がありました。我小时候发生过大地震 表示同一主体时进行两个动作,其中后面的动作是主要动作的句型: E.g李さんはテレビを見ながら食事をしています。李边看电视边吃饭 E.gそのことを考えながら歩いていました。一边考虑着那件事一边走着
旧版小本标准日本语中级电子书(下册)
第21課火山と温泉 词汇Ⅰ 火山(かざん) (1) [名] 火山 温泉(おんせん) (0) [名] 温泉 地球上(ちきゅうじょう) (0) [名] 地球上 陸地(りくち) (0) [名] 陆地 なんと(1) [副] 多么……,竟然 存在(そんざい) (0) [名] 存在 頻繁だ(ひんぱんだ) (0) [形动] 频繁 噴火(ふんか) (0) [名] (火山)喷发 噴き上げる(ふきあげる) (4) [动2] 喷起 火山灰(かざんばい) (2) [名] 火山灰 市民(しみん) (1) [名] 市民 農作物(のうさくぶつ) (4) [名] 农作物 しばしば(1) [副] 常常,每每 溶岩(ようがん) (1) [名] 熔岩 流れ出す(ながれだす) (4) [动1] 流出 住民(じゅうみん) (0) [名] 居民 一時(いちじ) (2) [名] 短时间,短暂 避難する(ひなんする) (1) [动3] 避难 騒ぎ(さわぎ) (1) [名] 骚乱,混乱 ありがたい(4) [形] 难得,值得庆幸 恵み(めぐみ) (0) [名] 恩惠,好处 いたる所(いたるところ) (6) [词组] 到处,各处 湧き出る(わきでる) (3) [动2] 喷涌 硫黄(いおう) (0) [名] 硫磺 カルシウム(3) [名] 钙 成分(せいぶん) (1) [名] 成分 含む(ふくむ) (2) [动1] 包含,含有 働き(はたらき) (0) [名] 作用,效用 湯治(とうじ) (0) [名] 温泉疗法 景観(けいかん) (0) [名] 景色,景观 恵む(めぐむ) (0) [动1] 施恩惠 数少ない(かずすむない) (1) [形] 数目少 娯楽(ごらく) (0) [名] 娱乐 緑(みどり) (1) [名] 绿色 眺める(ながめる) (3) [动2] 眺望,远眺 あるいは(2) [接续] 或,或是 つかる(0) [动1] 浸泡 温泉につかる(おんせんにつかる) (0)+(0) [惯用] 洗温泉このうえない(5) [词组] 无上
