外文翻译(英文1)

Lifeboat Safety Survey
Introduction
In 1994, OCIMF in conjunction with ICS, produced a report entitled “Results of a Survey into Lifeboat Safety”. This report highlighted some major concerns over equipment and the availability on board of appropriate technical information and documentation; similar concerns evidently remain. During recent years there has been continued concern among the Membership of our organisations over the number of incidents that involve lifeboats. One possible benefit from the earlier survey may well have been to make seafarers more aware of the inherent dangers of lifeboat launching and recovery procedures.
To ascertain current understanding of lifeboat issues, a questionnaire was developed and issued to all Members of INTERTANKO, OCIMF and SIGTTO. This questionnaire was not targeted at any specific type(s) of lifeboat, but it was anticipated that the majority of incidents involved totally enclosed boats and their associated hook release systems due to the comparative complexity of the design. In addition, the views of serving seafarers were sought on the practicality and suitability of designated. The 89 completed questionnaires returned varied in standard of detail, so some minor inconsistencies exist with incident numbers. However, the relative proportions of data shown in the charts are unaffected.
Findings
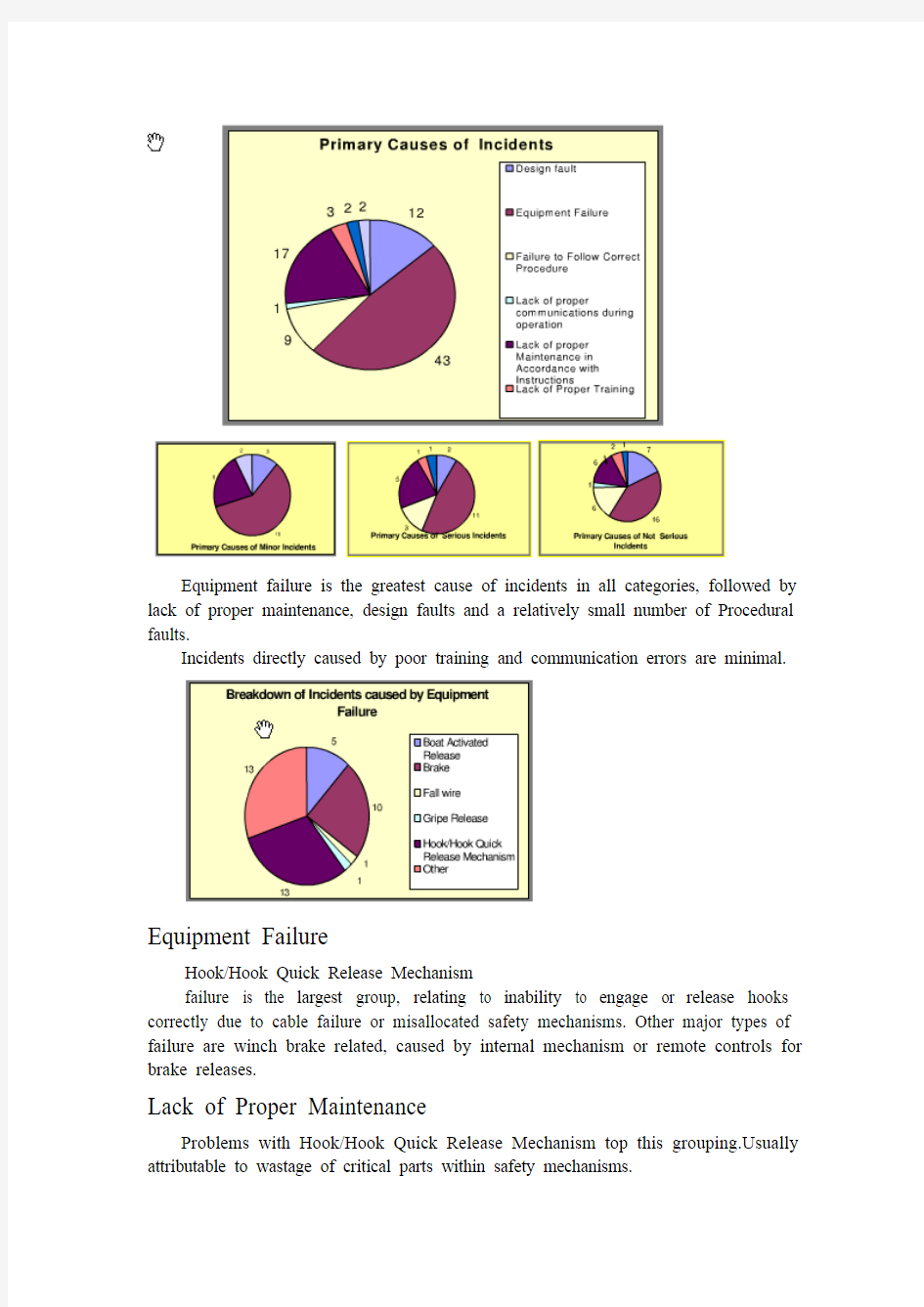
The charts below show the proportions of different lifeboat types involved in the reported incidents.
All reported incidents
were associated with either
testing or maintaining the
boats, training exercises/drills
or Surveys.
Primary Causes of
Incidents
In the charts below, an
attempt has been made to
classify the incidents into
three categories: Serious,
Non-Serious and
Minor.
Equipment failure is the greatest cause of incidents in all categories, followed by lack of proper maintenance, design faults and a relatively small number of Procedural faults.
Incidents directly caused by poor training and communication errors are minimal.
Equipment Failure
Hook/Hook Quick Release Mechanism
failure is the largest group, relating to inability to engage or release hooks correctly due to cable failure or misallocated safety mechanisms. Other major types of failure are winch brake related, caused by internal mechanism or remote controls for brake releases.
Lack of Proper Maintenance
Problems with Hook/Hook Quick Release Mechanism top this https://www.360docs.net/doc/c13929915.html,ually attributable to wastage of critical parts within safety mechanisms.
Design Faults
Again, the majority of incidents have occurred with Hook/Hook Quick Release Mechanisms followed closely by Boat Activated Release. The Lifesaving Role of the lifeboat may be compromised by an inability to launch it safely and efficiently. The design faults reported may not have become apparent without regular training exercises.
Failure to Follow the Correct Procedure
A number of incidents from failure to follow the correct procedure resulted in injury to personnel. Others resulted mainly in damage to boat or launching apparatus. Again, the Hook/Hook Release Mechanism is a substantial contributor to this type of incident.
Lack of Proper Training
Few incidents can be attributed to lack of proper training and no valid conclusion can be drawn.
Primary Causes of Injuries
Fortunately there were no fatalities reported in this survey. However, that potential existed where boats were seriously damaged or lost. The number of injuries in comparison with the number of incidents is low. It can be assumed that a deep mistrust of lifeboats has developed on board vessels, resulting in operation of the boats in a manner that limits as much as possible any exposure to potential injury.
20 injuries were reported, 6 being serious, requiring at least several days off work and 14 were minor, requiring first aid or medical treatment before continuing work. These 20 injuries occurred in 13 separate incidents, 4 of which accounted for the serious injuries.
Serious Injuries
? A major incident was a lifeboat releasing itself and falling to the water from the embarkation deck level. The height above the water was relatively small at 12 metres and three members of the lifeboat crew incurred leg and/or back injuries. Had the freeboard been , greater fatalities would have been likely.
?The other incidents were all caused by human error - failure to follow correct procedure or lack of proper training. These included a thumb crushed by a closing lifeboat door and wrist fracture whilst starting a lifeboat engine.
injury
?During a boat launch, the forward quick release hook released itself with the boat five metres above the waterline. This resulted in minor injuries to 4 seamen. The nature was not reported but the potential for more serious injury existed.
? A lifeboat was lowered to sea level but the launch aborted when one hook did not release. The other released but was reconnected and the boat recovered above
embarkation deck with the crew onboard. When the boat reached the davit head the hook that failed released itself, resulting in the boat swinging from one fall. The three crew received cuts and bruises. Great potential existed for serious or fatal injuries. The one davit proved sufficiently strong to hold the total weight of the boat on this occasion.
?Some incidents include injuries incurred whilst attempting to “hook on” to the falls for boat recovery. In one incident a seaman was struck by the swivel block and in the other a seaman incurred pinch cuts to his hands whilst holding the hook in place as the release system was engaged. The connection of waterborne lifeboats to falls has always proven a hazardous operation, but is exacerbated by release mechanisms which are difficult to engage correctly. A similar minor injury was incurred when trying to reconnect a quick release hook after maintenance. This resulted in cuts to fingers.
?Other incidents include gripe releases under tension where a seaman was struck heavily by the freed end of the gripe and one where a seaman caught his finger in the gripe release mechanism.
?More minor incidents include a seaman attaching his safety harness to the davit and being pulled off balance when the davit was lowered and a seaman losing balance whilst attempting to start a lifeboat engine. The seaman struck his head, rather than fracturing a wrist as noted in Serious Injury section.
Lessons Learned
It appears that little has changed in the incident types reported between this survey and that conducted in 1994 by OCIMF and ICS. The main difference is that in this report no fatalities are noted. This may be due to the fact that seafarers are now more aware of the risks inherent with lifeboat operations and in drills or exercises personnel are often excluded from risk where possible. Unfortunately this may reduce the effectiveness of some training exercises such as simulating a real emergency situation and therefore fully familiarizing crew in the designed use and limitations of the equipment.
Another example of the poor design of equipment (i.e. the assumption that recovery is of limited importance) is the report of a Freefall lifeboat that took a full day to recover. The equipment was unable to recover the boat in a single pull, necessitating the crew evacuating the boat from a hazardous position to reduce the winch load.
Operational human error does not appear to be a direct cause of many incidents. Human error in design and not adequately specifying launch and recovery equipment standards for practical eventualities is apparent.
One positive note is that a lack of supervision or training during drills does not appear to be a major factor.
Recommendations
The reported incidents and findings show that the marine community needs to further improve standards for the design, manufacture and maintenance of lifeboats in
a bid to ensure that not only can they be used in an emergency but can also be operated regularly at drills in a safe manner.
Some of the recommendations that follow reiterate recommendations made in the 1994 report. Their validity can only be strengthened by the apparent need for repetition.
It is recommended that Ship Operators and Owners should:
?In the case of totally enclosed lifeboats with a hook release mechanism, review the correct operation of the hook release and draw up instructions and drawings detailing the correct components, their location and method of operation. These instructions to be specific to the equipment fitted on board the vessel and to be provided to all seamen who are likely to be involved in the maintenance and operation of such equipment.
?Incorporate procedures requiring the boat recovery process to be suspended once the boat is clear of the water and ensure that the hook release mechanism is correctly secured prior to recovery of boat to embarkation deck.
?Review maintenance procedures in light of these reported incidents. Particular component failures to consider are: -
① Hook/ Hook release mechanisms to be inspected to ensure that all components are within tolerance, there is no build of scale, and that there is no wastage that could either weaken the equipment or cause it to operate incorrectly. This includes the release cable, which has been subject to a number of incident reports.
②Winch brake linings to be regularly inspected for contamination and lining thickness. The associated remote lowering wires are checked to be in good condition and to operate correctly, both on the stowage drum and within the boat.
③ Lifeboat falls should be lubricated and inspected regularly. At appropriate intervals they are to be renewed or end for ended.
④ Cut outs for recovery winches should be regularly checked for correct operation to prevent over stressing falls and davits.
?Consider installation of a secondary manual override lock to the hook release mechanism that can be released from a central point in the boat but ensures that there can be no inadvertent release of the hooks, either through human error or a hardware fault, during maintenance or drills.
?Further ensure that training includes personal safety specifically with regard to lifeboats, ensuring that seafarers are made aware of hazards such as releasing gripe wires under tension.
Lifeboat and associated equipment Designers / Builders / Installers should: -
①Simplify the design of operating equipment with a view to increasing reliability, easing maintenance ensuring simplicity of operation with regard both to launching and recovery. Components requiring fine tolerances should be avoided or constructed of material not prone to wastage.
②Provide hatchways in enclosed boats of sufficient size to enable easy access for connection of hooks. This should take into account that the reconnection may be required in a seaway, not in still water.
③Ensure that hatchways are suitable for evacuating injured and/or stretchered personnel either to another boat or by helicopter.
④ Provide a means of positive indication that hook release systems are fully engaged and locked for recovery, preferably from the coxswains conning position. This should be mechanical, directly connected to the hooks and not involve secondary indication such as lights, the position of the release handle, etc.
⑤ Simplifying the brake system for the davits/falls to improve ease of maintenance and increased reliability. Increasing brake capacity to well above the weight of a fully laden lifeboat would help ensure that braking ability is maintained even if the system weakened.
⑥ Provide a method of indicating brake lining wear or contamination external to the winch to alert ship staff of a problem.
⑦ Ensure that remote brake release systems from within the lifeboat are reliable and not inherently liable to snag within the boat.
⑧ Ensure that the recovery systems, especially the winches, are sufficiently strong to enable a lifeboat to be recovered easily and quickly with a normal drill complement onboard.
⑨ Ensure that boarding at the stowed position can be undertaken easily and safely for maintenance, whilst also ensuring safe and quick access can be achieved at embarkation level (if different) in an emergency.
⑩Ensure that there is a suitable method such as a hose connection for testing/flushing water-cooled lifeboat engines and spray systems with freshwater when boats are in the davits.
Flag States, IMO and Classification Societies
1.Review and qualify the existing requirements under SOLAS Ch3 Regs 51 and 52 – The SOLAS Training Manual and Maintenance Information/Records. In many cases the current details of lifeboats and their equipment provided are inadequate or generic. Flag States should compel owners/operators to ensure that such information is specific to each individual vessel and sufficiently detailed for vessel crews to operate easily and identify, assess and repair any individual component with ease.
2. Review other existing regulations to consider if changes may be necessary to ensure the safe and efficient launching and recovery of lifeboats during drills/training exercises (and for rescue if the lifeboat is a designated rescue boat) bearing in mind the points raised in this report.
3. In the case of Free-fall lifeboats, review the existing test launch and recovery requirements with particular regard to permitting simulated launches such as unmanned release onto a stop-chock after a few centimetres of travel and ensuring the recovery mechanism has sufficient excess power to lift cradle and laden boat easily and rapidly.
4. Review maintenance and survey requirements to confirm that lifeboats and their
associated systems fully meet the level of assurance required in (2) and (3) above with regard to launching and recovery in regular drills and exercises.
Brief Description of the Incident Established Cause Type of boat Serious Incidents
The lifeboat was in the process of being lowered to embarkation deck for survey. A rope became entangled in the after davit release mechanism causing it to release. The boat became suspended from forward hook distorting the davit arm, which required landing for repair. The boat was seriously damaged. Design Fault Totally
Enclosed with
Onboard
release
When lowering the boat the forward davit arm became momentarily delayed in release due to the forward retaining clamp being partly still in place. When freed the forward arm lined up with aft arm the shock to the system caused the forward hook to release. The boat was seriously damaged. Design Fault Totally
Enclosed with
Onboard
release
Whilst lowering boat to embarkation deck the brake failed to hold and the lifeboat proceeded to sea level in an uncontrolled manner. The vessel had to stop engines and take all way off. The winch brake was overhauled prior to recovery of the boat. The lifeboat suffered minor damage. Equipment/material
Failure
Totally
Enclosed with
Onboard
release
During launching of port side lifeboat, the forward quick release hook opened whilst boat was about 5m above water line. This caused substantial damage to the lifeboat and minor damage to the aft davit. Equipment/material
Failure
Totally
Enclosed with
Onboard
release
Both boats were being lowered to the embarkation deck as part of a drill. Both lowered with minimal braking as the remote wires from the boats were incorrectly adjusted. A turn was taken off the remote wire for starboard boat, which had the effect of stopping it. The port boat continued to sea level and, as the vessel underway at full sea speed at the time the lifeboat was a total loss. Davits on the port side also suffered considerable damage. Equipment/material
Failure
Totally
Enclosed with
Onboard
release
During an in water test of the starboard lifeboat engine in the water, the lifeboat's motor stopped after approximately 10 minutes of running due to overheating and impossible to restart. The port lifeboat was lowered to the water to rescue the starboard lifeboat, but its engine also seized for the same reason. Both boats recovered by vessel heaving anchor and manoeuvring into position. Equipment/material
Failure
Totally
Enclosed with
Onboard
release
The starboard lifeboat was being lowered on brake. When lifeboat reached embarkation deck it would not stop lowering. When boat hit water, the weight came off of falls & the brake then moved to stop position. The surging of boat in seaway first released forward fall & then the after fall. The lifeboat was a total loss. Equipment/material
Failure
Totally
Enclosed with
Onboard
release
During the hoisting of the lifeboat, just prior to reaching stowed position, the aft hook released causing the boat to fall on the structure below. One sheave mounting and both hooks were damaged. The boat was badly damaged. Equipment/material
Failure
Totally
Enclosed with
Onboard
release
During recovery of the lifeboat the winch motor was stopped but the lifeboat had inertia and touched to the davit. The forward fall parted. The boat was kept on the aft fall. The outside of the fall appeared good but the inside was found to be badly corroded. The boat suffered minor damage. Equipment/material
Failure
Totally
Enclosed with
Onboard
release
Whilst lowering boat the brake was unable to stop the boat at deck level. It continued lowering to sea level. The vessel was underway at the time and had to be stopped and all way taken off. The boat was found to be badly damaged after it had been recovered by ships crane. The davits also sustained damage. Equipment/material
Failure
Totally
Enclosed with
Onboard
release
The starboard lifeboat lowered to deck level. When tried to lift it, was not possible to do it either by winch electric motor or by hand. Equipment/material
Failure
Totally
Enclosed with
Onboard
Found winch 2nd step shaft broken.
Provisional repairs done to be able to recover
the boat.
release
During port life boat brake loading capacity test, the brake failed and the boat lowered uncontrollably to the water. The boat suffered minor damage. Equipment/material
Failure
Totally
Enclosed with
Onboard
release
During routine maintenance the forward remote release cables on both boats failed due to internal corrosion of the wires. Equipment/material
Failure
Totally
Enclosed with
Onboard
release
The crewmember responsible for taking safety pin out on aft davit arm did not do so. When the brake was released only the forward davit arm went down. The brake was applied as soon as crew attending the lowering observed the fault. However the forward part of the boat swung against the deck below sustaining minor damage. Failure to follow
correct procedure
Totally
Enclosed with
Onboard
release
During a drill the lifeboat was hoisted up to its final position when it was observed that the bow was in place but the stern still a few centimetres away from its final position. Air motor restarted and the aft fall parted causing the after end of the boat to fall damaging both the boat and davits. The boat was a total loss. Failure to follow
correct procedure
Totally
Enclosed with
Onboard
release
英文文献翻译
中等分辨率制备分离的 快速色谱技术 W. Clark Still,* Michael K a h n , and Abhijit Mitra Departm(7nt o/ Chemistry, Columbia Uniuersity,1Veu York, Neu; York 10027 ReceiLied January 26, 1978 我们希望找到一种简单的吸附色谱技术用于有机化合物的常规净化。这种技术是适于传统的有机物大规模制备分离,该技术需使用长柱色谱法。尽管这种技术得到的效果非常好,但是其需要消耗大量的时间,并且由于频带拖尾经常出现低复原率。当分离的样本剂量大于1或者2g时,这些问题显得更加突出。近年来,几种制备系统已经进行了改进,能将分离时间减少到1-3h,并允许各成分的分辨率ΔR f≥(使用薄层色谱分析进行分析)。在这些方法中,在我们的实验室中,媒介压力色谱法1和短柱色谱法2是最成功的。最近,我们发现一种可以将分离速度大幅度提升的技术,可用于反应产物的常规提纯,我们将这种技术称为急骤色谱法。虽然这种技术的分辨率只是中等(ΔR f≥),而且构建这个系统花费非常低,并且能在10-15min内分离重量在的样本。4 急骤色谱法是以空气压力驱动的混合介质压力以及短柱色谱法为基础,专门针对快速分离,介质压力以及短柱色谱已经进行了优化。优化实验是在一组标准条件5下进行的,优化实验使用苯甲醇作为样本,放在一个20mm*5in.的硅胶柱60内,使用Tracor 970紫外检测器监测圆柱的输出。分辨率通过持续时间(r)和峰宽(w,w/2)的比率进行测定的(Figure 1),结果如图2-4所示,图2-4分别放映分辨率随着硅胶颗粒大小、洗脱液流速和样本大小的变化。
外文翻译 - 英文
The smart grid Smart grid is the grid intelligent (electric power), also known as the "grid" 2.0, it is based on the integration, high-speed bidirectional communication network, on the basis of through the use of advanced sensor and measuring technology, advanced equipme nt technology, the advanced control method, and the application of advanced technology of decision support system, realize the power grid reliability, security, economic, efficient, environmental friendly and use the security target, its main features include self-healing, incentives and include user, against attacks, provide meet user requirements of power quality in the 21st century, allow all sorts of different power generation in the form of access, start the electric power market and asset optimizatio n run efficiently. The U.S. department of energy (doe) "the Grid of 2030" : a fully automated power transmission network, able to monitor and control each user and power Grid nodes, guarantee from power plants to end users among all the nodes in the whole process of transmission and distribution of information and energy bi-directional flow. China iot alliance between colleges: smart grid is made up of many parts, can be divided into:intelligent substation, intelligent power distribution network, intelli gent watt-hourmeter,intelligent interactive terminals, intelligent scheduling, smart appliances, intelligent building electricity, smart city power grid, smart power generation system, the new type of energy storage system.Now a part of it to do a simple i ntroduction. European technology BBS: an integration of all users connected to the power grid all the behavior of the power transmission network, to provide sustained and effective economic and security of power. Chinese academy of sciences, institute of electrical: smart grid is including all kinds of power generation equipment, power transmission and distribution network, power equipment and storage equipment, on the basis of the physical power grid will be modern advanced sensor measurement technology, network technology, communication
机械设计设计外文文献翻译、中英文翻译、外文翻译
机械设计 摘要:机器是由机械装置和其它组件组成的。它是一种用来转换或传递能量的装置,例如:发动机、涡轮机、车辆、起重机、印刷机、洗衣机、照相机和摄影机等。许多原则和设计方法不但适用于机器的设计,也适用于非机器的设计。术语中的“机械装置设计”的含义要比“机械设计”的含义更为广泛一些,机械装置设计包括机械设计。在分析运动及设计结构时,要把产品外型以及以后的保养也要考虑在机械设计中。在机械工程领域中,以及其它工程领域中,所有这些都需要机械设备,比如:开关、凸轮、阀门、船舶以及搅拌机等。 关键词:设计流程设计规则机械设计 设计流程 设计开始之前就要想到机器的实际性,现存的机器需要在耐用性、效率、重量、速度,或者成本上得到改善。新的机器必需具有以前机器所能执行的功能。 在设计的初始阶段,应该允许设计人员充分发挥创造性,不要受到任何约束。即使产生了许多不切实际的想法,也会在设计的早期,即在绘制图纸之前被改正掉。只有这样,才不致于阻断创新的思路。通常,还要提出几套设计方案,然后加以比较。很有可能在这个计划最后决定中,使用了某些不在计划之内的一些设想。 一般的当外型特点和组件部分的尺寸特点分析得透彻时,就可以全面的设计和分析。接着还要客观的分析机器性能的优越性,以及它的安全、重量、耐用性,并且竞争力的成本也要考虑在分析结果之内。每一个至关重要的部分要优化它的比例和尺寸,同时也要保持与其它组成部分相协调。 也要选择原材料和处理原材料的方法。通过力学原理来分析和实现这些重要的特性,如那些静态反应的能量和摩擦力的最佳利用,像动力惯性、加速动力和能量;包括弹性材料的强度、应力和刚度等材料的物理特性,以及流体润滑和驱动器的流体力学。设计的过程是重复和合作的过程,无论是正式或非正式的进行,对设计者来说每个阶段都很重要。 最后,以图样为设计的标准,并建立将来的模型。如果它的测试是符合事先要
计算机网络-外文文献-外文翻译-英文文献-新技术的计算机网络
New technique of the computer network Abstract The 21 century is an ages of the information economy, being the computer network technique of representative techniques this ages, will be at very fast speed develop soon in continuously creatively, and will go deep into the people's work, life and study. Therefore, control this technique and then seem to be more to deliver the importance. Now I mainly introduce the new technique of a few networks in actuality live of application. keywords Internet Network System Digital Certificates Grid Storage 1. Foreword Internet turns 36, still a work in progress Thirty-six years after computer scientists at UCLA linked two bulky computers using a 15-foot gray cable, testing a new way for exchanging data over networks, what would ultimately become the Internet remains a work in progress. University researchers are experimenting with ways to increase its capacity and speed. Programmers are trying to imbue Web pages with intelligence. And work is underway to re-engineer the network to reduce Spam (junk mail) and security troubles. All the while threats loom: Critics warn that commercial, legal and political pressures could hinder the types of innovations that made the Internet what it is today. Stephen Crocker and Vinton Cerf were among the graduate students who joined UCLA professor Len Klein rock in an engineering lab on Sept. 2, 1969, as bits of meaningless test data flowed silently between the two computers. By January, three other "nodes" joined the fledgling network.
外文翻译computerprogram英文.doc
Computer Program 1 Introduction Computer Program, set of instructions that directs a computer to perform someprocessing function or combination of functions. For the instructions to be carried out, a computer must execute a program, that is, the computer reads the program, and then follow the steps encoded in the program in a precise order until completion. A program can be executed many different times, with each execution yielding a potentially different result depending upon the options and data that the user gives the computer. Programs fall into two major classes: application programs and operating systems. An application program is one that carries out somefunction directly for a user, such as word processing or game-playing. An operating system is a program that manages the computer and the various resources and devices connected to it, such as RAM,hard drives, monitors, keyboards, printers, and modems,so that they maybe used by other programs. Examples of operating systems are DOS, Windows 95, OS\2, and UNIX. 2 Program Development Software designers create new programs by using special applications programs, often called utility programs or development programs. A programmer uses another type of program called a text editor to write the new program in a special notation called a programming language. With the text editor, the programmer creates a text file, which is an ordered list of instructions, also called the program source file. The individual instructions that make up the program source file are called source code. At this point, a special applications program translates the source code into machine language, or object code— a format that the operating system
外文翻译中文
运作整合 供应链协作的首要问题是提高运作整合的程度。供应链协作课达到的好处,直接关系到捕捉效率之间的职能的企业,以及全国的企业,构成了国内或国际供应链。本章重点阐述的挑战,一体化管理,由研究为什么一体化创造价值,并通过详列的挑战,双方的企业集成和供应链整合。必不可少的供应链流程是确定的。注意的是,然后向信息技术提供,以方便集成化供应链规划。本章最后审查了定价。在最后的分析,定价的做法和政府是至关重要的供应链的连续性。 为什么整合创造价值 基本的优点与挑战的综合管理介绍了在第1章。进一步解释整合管理的重要性,有用的指出客户都至少有三个角度的价值。 传统的角度来看,价值是经济价值。第二个价值的角度来看,是市场价值。 实现双方经济和市场价值是很重要的客户。然而,越来越多的企业认识到商业上的成功也取决于第三个角度来看,价值,被称为关联性。 物流一体化目标 为实现物流一体化的供应链背景下,6个业务目标必须同时取得:( 1 )响应,( 2 )差额减少,( 3 )库存减少,( 4 )托运巩固,( 5 )质量,( 6 )生命周期支持。的相对重要性,每个直接关系到公司的物流战略。 响应 一公司的工作能力,以满足客户的要求,及时被称为反应。作为一再指出,信息技术是促进反应为基础的战略,允许业务的承诺被推迟到最后可能时间,其次是加速投放。实施对应策略服务,以减少库存承诺或部署在预期客户的需求。响应服务转向业务重点从预测未来的需求,以容纳顾客对快速订单到出货的基础上。理想的情况是,在一个负责任的系统中,库存是没有部署,直到客户承诺。支持这样的承诺,公司必须有物流的属性,库存的可用性和及时交付,一旦客户订单收到。 差异减少 所有经营领域的物流系统很容易受到差额。方差结果从未能履行任何预期的层面后勤业务不如预期。举例来说,毫不拖延地在客户订单处理,意想不到的干扰,以便选择,抵港货物损坏,在客户的位置,和/或未能提供在适当的位置上的时间,所有创造无计划的差异,在订单到交货周期。一个共同的解决办法,以保障对不利的差异是使用库存安全库存,以缓冲行动。这亦是共同使用的首选运输,以克服意想不到的差异延误交货计划。这种做法,鉴于其相关的成本高,可以尽量减少使用资讯科技,以维持积极的物流控制。向程度的差异是最小化,物流的生产力将提高。因此,差异减少,消除系统中断,是一个基本的目标,综合物流管理。 库存减少 要达到的目标,库存减少,一个综合物流系统必须控制资产的承诺,并把速度。资产的承诺,是财政的价值部署清单。把速度,反映了利率,这是充实库存随着时间的推移。高转率,再加上预期的库存供货,平均资产用于库存正在迅速而有效利用,这就是整体资产承诺支持一个综合运作减至最低。 库存能够而且确实方便可取的好处这是很重要的要请记住。库存是至关重要的实现规模经济,在制造业和采购。目的是要减少和管理存货,以尽可能最低的水平,同时实现整体供应链绩效的目标。
机械设计外文翻译(中英文)
机械设计理论 机械设计是一门通过设计新产品或者改进老产品来满足人类需求的应用技术科学。它涉及工程技术的各个领域,主要研究产品的尺寸、形状和详细结构的基本构思,还要研究产品在制造、销售和使用等方面的问题。 进行各种机械设计工作的人员通常被称为设计人员或者机械设计工程师。机械设计是一项创造性的工作。设计工程师不仅在工作上要有创造性,还必须在机械制图、运动学、工程材料、材料力学和机械制造工艺学等方面具有深厚的基础知识。如前所诉,机械设计的目的是生产能够满足人类需求的产品。发明、发现和科技知识本身并不一定能给人类带来好处,只有当它们被应用在产品上才能产生效益。因而,应该认识到在一个特定的产品进行设计之前,必须先确定人们是否需要这种产品。 应当把机械设计看成是机械设计人员运用创造性的才能进行产品设计、系统分析和制定产品的制造工艺学的一个良机。掌握工程基础知识要比熟记一些数据和公式更为重要。仅仅使用数据和公式是不足以在一个好的设计中做出所需的全部决定的。另一方面,应该认真精确的进行所有运算。例如,即使将一个小数点的位置放错,也会使正确的设计变成错误的。 一个好的设计人员应该勇于提出新的想法,而且愿意承担一定的风险,当新的方法不适用时,就使用原来的方法。因此,设计人员必须要有耐心,因为所花费的时间和努力并不能保证带来成功。一个全新的设计,要求屏弃许多陈旧的,为人们所熟知的方法。由于许多人墨守成规,这样做并不是一件容易的事。一位机械设计师应该不断地探索改进现有的产品的方法,在此过程中应该认真选择原有的、经过验证的设计原理,将其与未经过验证的新观念结合起来。 新设计本身会有许多缺陷和未能预料的问题发生,只有当这些缺陷和问题被解决之后,才能体现出新产品的优越性。因此,一个性能优越的产品诞生的同时,也伴随着较高的风险。应该强调的是,如果设计本身不要求采用全新的方法,就没有必要仅仅为了变革的目的而采用新方法。 在设计的初始阶段,应该允许设计人员充分发挥创造性,不受各种约束。即使产生了许多不切实际的想法,也会在设计的早期,即绘制图纸之前被改正掉。只有这样,才不致于堵塞创新的思路。通常,要提出几套设计方案,然后加以比较。很有可能在最后选定的方案中,采用了某些未被接受的方案中的一些想法。
变电站_外文翻译_外文文献_英文文献_变电站的综合概述
英文翻译 A comprehensive overview of substations Along with the economic development and the modern industry developments of quick rising, the design of the power supply system become more and more completely and system. Because the quickly increase electricity of factories, it also increases seriously to the dependable index of the economic condition, power supply in quantity. Therefore they need the higher and more perfect request to the power supply. Whether Design reasonable, not only affect directly the base investment and circulate the expenses with have the metal depletion in colour metal, but also will reflect the dependable in power supply and the safe in many facts. In a word, it is close with the economic performance and the safety of the people. The substation is an importance part of the electric power system, it is consisted of the electric appliances equipments and the Transmission and the Distribution. It obtains the electric power from the electric power system, through its function of transformation and assign, transport and safety. Then transport the power to every place with safe, dependable, and economical. As an important part of power’s transport and control, the transformer substation must change the mode of the traditional design and control, then can adapt to the modern electric power system, the development of modern industry and the of trend of the society life. Electric power industry is one of the foundations of national industry and national economic development to industry, it is a coal, oil, natural gas, hydropower, nuclear power, wind power and other energy conversion into electrical energy of the secondary energy industry, it for the other departments of the national economy fast and stable development of the provision of adequate power, and its level of development is a reflection of the country's economic development an important indicator of the level. As the power in the industry and the importance of the national economy, electricity transmission and distribution of electric energy used in these areas is an indispensable component.。Therefore, power transmission and distribution is critical. Substation is to enable superior power plant power plants or power after adjustments to the lower load of books is an important part of power transmission. Operation of its functions, the capacity of a direct impact on the size of the lower load power, thereby affecting the industrial production and power consumption.Substation system if a link failure, the system will protect the part of action. May result in power outages and so on, to the production and living a great disadvantage. Therefore, the substation in the electric power system for the protection of electricity reliability,
机械专业外文翻译(中英文翻译)
外文翻译 英文原文 Belt Conveying Systems Development of driving system Among the methods of material conveying employed,belt conveyors play a very important part in the reliable carrying of material over long distances at competitive cost.Conveyor systems have become larger and more complex and drive systems have also been going through a process of evolution and will continue to do so.Nowadays,bigger belts require more power and have brought the need for larger individual drives as well as multiple drives such as 3 drives of 750 kW for one belt(this is the case for the conveyor drives in Chengzhuang Mine).The ability to control drive acceleration torque is critical to belt conveyors’performance.An efficient drive system should be able to provide smooth,soft starts while maintaining belt tensions within the specified safe limits.For load sharing on multiple drives.torque and speed control are also important considerations in the drive system’s design. Due to the advances in conveyor drive control technology,at present many more reliable.Cost-effective and performance-driven conveyor drive systems covering a wide range of power are available for customers’ choices[1]. 1 Analysis on conveyor drive technologies 1.1 Direct drives Full-voltage starters.With a full-voltage starter design,the conveyor head shaft is direct-coupled to the motor through the gear drive.Direct full-voltage starters are adequate for relatively low-power, simple-profile conveyors.With direct fu11-voltage starters.no control is provided for various conveyor loads and.depending on the ratio between fu11-and no-1oad power requirements,empty starting times can be three or four times faster than full load.The maintenance-free starting system is simple,low-cost and very reliable.However, they cannot control starting torque and maximum stall torque;therefore.they are
博物馆 外文翻译 外文文献 英文文献
第一篇: 航空博物馆与航空展示公园 巴特罗米耶杰·基谢列夫斯基 飞翔的概念、场所的精神、老机场的建筑---克拉科夫新航空博物馆理性地吸取了这些元素,并将它们整合到一座建筑当中。Rakowice-Czyzyny机场之前的旧飞机修理库为新建筑的平面和高度设定了模数比例。在此基本形态上进一步发展,如同裁切和折叠一架纸飞机,生成了一座巨大的建筑。其三角形机翼是由混凝土制成,却如同风动螺旋桨一样轻盈。这个机翼宽大通透,向各个方向开敞。它们的形态与组织都是依据内部功能来设计的。机翼部分为3个不平衡的平面,使内外景观在不断变化中形成空间的延续性,并且联系了建筑内的视觉焦点和室外的展览区。 新航空展示公园的设计连接了博物馆的8栋建筑和户外展览区,并与历史体验建立联系。从前的视觉轴线与通道得到尊重,旧的道路得到了完善,朝向飞机场和跑道的空间被限定出来。每栋建筑展示了一个主题或是一段飞行史。建筑周围伸展出巨大的平台,为特殊主题的室外展览提供了空间。博物馆容纳了超过150架飞机、引擎、飞行复制品、成套的技术档案和历史图片。这里的特色收藏是飞机起源开始的各种飞行器,如Jatho1903、Grade1909、莱特兄弟1909年的飞机模型和1911年的鸽式单翼机。 The first passage: Museum for aviation and aviation exhibition park Bartiomiej Kislelewski The idea of flying, the spirit of place, the structure of the historic airfield – the new Museum of Aviation in Krakow takes up these references intellectually and synthesizes them into a building. The old hangars of the former airport Rakowice Czyzyny set the modular scale for the footprint and the height of the new building. Developed from this basic shape, as if cut out and folded like a paper airplane, a large structure has been generated, with triangular wings made of concrete and yet as light as a wind-vane propeller. The wings are generously glazed and open in all directions. Their form and arrangement depend on the interior uses. In the floor plans of the wings, the three offset
机械设计外文翻译(中英文)
盛年不重来,一日难再晨。及时宜自勉,岁月不待人。 机械设计理论 机械设计是一门通过设计新产品或者改进老产品来满足人类需求的应用技术科学。它涉及工程技术的各个领域,主要研究产品的尺寸、形状和详细结构的基本构思,还要研究产品在制造、销售和使用等方面的问题。 进行各种机械设计工作的人员通常被称为设计人员或者机械设计工程师。机械设计是一项创造性的工作。设计工程师不仅在工作上要有创造性,还必须在机械制图、运动学、工程材料、材料力学和机械制造工艺学等方面具有深厚的基础知识。如前所诉,机械设计的目的是生产能够满足人类需求的产品。发明、发现和科技知识本身并不一定能给人类带来好处,只有当它们被应用在产品上才能产生效益。因而,应该认识到在一个特定的产品进行设计之前,必须先确定人们是否需要这种产品。 应当把机械设计看成是机械设计人员运用创造性的才能进行产品设计、系统分析和制定产品的制造工艺学的一个良机。掌握工程基础知识要比熟记一些数据和公式更为重要。仅仅使用数据和公式是不足以在一个好的设计中做出所需的全部决定的。另一方面,应该认真精确的进行所有运算。例如,即使将一个小数点的位置放错,也会使正确的设计变成错误的。 一个好的设计人员应该勇于提出新的想法,而且愿意承担一定的风险,当新的方法不适用时,就使用原来的方法。因此,设计人员必须要有耐心,因为所花费的时间和努力并不能保证带来成功。一个全新的设计,要求屏弃许多陈旧的,为人们所熟知的方法。由于许多人墨守成规,这样做并不是一件容易的事。一位机械设计师应该不断地探索改进现有的产品的方法,在此过程中应该认真选择原有的、经过验证的设计原理,将其与未经过验证的新观念结合起来。 新设计本身会有许多缺陷和未能预料的问题发生,只有当这些缺陷和问题被解决之后,才能体现出新产品的优越性。因此,一个性能优越的产品诞生的同时,也伴随着较高的风险。应该强调的是,如果设计本身不要求采用全新的方法,就没有必要仅仅为了变革的目的而采用新方法。 在设计的初始阶段,应该允许设计人员充分发挥创造性,不受各种约束。即使产生了许多不切实际的想法,也会在设计的早期,即绘制图纸之前被改正掉。只有这样,才不致于堵塞创新的思路。通常,要提出几套设计方案,然后加以比较。很有可能在最后选定的方案中,采用了某些未被接受的方案中的一些想法。
外文翻译中文版(完整版)
毕业论文外文文献翻译 毕业设计(论文)题目关于企业内部环境绩效审计的研究翻译题目最高审计机关的环境审计活动 学院会计学院 专业会计学 姓名张军芳 班级09020615 学号09027927 指导教师何瑞雄
最高审计机关的环境审计活动 1最高审计机关越来越多的活跃在环境审计领域。特别是1993-1996年期间,工作组已检测到环境审计活动坚定的数量增长。首先,越来越多的最高审计机关已经活跃在这个领域。其次是积极的最高审计机关,甚至变得更加活跃:他们分配较大部分的审计资源给这类工作,同时出版更多环保审计报告。表1显示了平均数字。然而,这里是机构间差异较大。例如,环境报告的数量变化,每个审计机关从1到36份报告不等。 1996-1999年期间,结果是不那么容易诠释。第一,活跃在环境审计领域的最高审计机关数量并没有太大变化。“活性基团”的组成没有保持相同的:一些最高审计机关进入,而其他最高审计机关离开了团队。环境审计花费的时间量略有增加。二,但是,审计报告数量略有下降,1996年和1999年之间。这些数字可能反映了从量到质的转变。这个信号解释了在过去三年从规律性审计到绩效审计的转变(1994-1996年,20%的规律性审计和44%绩效审计;1997-1999:16%规律性审计和绩效审计54%)。在一般情况下,绩效审计需要更多的资源。我们必须认识到审计的范围可能急剧变化。在将来,再将来开发一些其他方式去测算人们工作量而不是计算通过花费的时间和发表的报告会是很有趣的。 在2000年,有62个响应了最高审计机关并向工作组提供了更详细的关于他们自1997年以来公布的工作信息。在1997-1999年,这62个最高审计机关公布的560个环境审计报告。当然,这些报告反映了一个庞大的身躯,可用于其他机构的经验。环境审计报告的参考书目可在网站上的最高审计机关国际组织的工作组看到。这里这个信息是用来给最高审计机关的审计工作的内容更多一些洞察。 自1997年以来,少数环境审计是规律性审计(560篇报告中有87篇,占16%)。大多数审计绩效审计(560篇报告中有304篇,占54%),或组合的规律性和绩效审计(560篇报告中有169篇,占30%)。如前文所述,绩效审计是一个广泛的概念。在实践中,绩效审计往往集中于环保计划的实施(560篇报告中有264篇,占47%),符合国家环保法律,法规的,由政府部门,部委和/或其他机构的任务给访问(560篇报告中有212篇,占38%)。此外,审计经常被列入政府的环境管理系统(560篇报告中有156篇,占28%)。下面的元素得到了关注审计报告:影响或影响现有的国家环境计划非环保项目对环境的影响;环境政策;由政府遵守国际义务和承诺的10%至20%。许多绩效审计包括以上提到的要素之一。 1本文译自:S. Van Leeuwen.(2004).’’Developments in Environmental Auditing by Supreme Audit Institutions’’ Environmental Management Vol. 33, No. 2, pp. 163–1721
机器人外文翻译(文献翻译-中英文翻译)
外文翻译 外文资料: Robots First, I explain the background robots, robot technology development. It should be said it is a common scientific and technological development of a comprehensive results, for the socio-economic development of a significant impact on a science and technology. It attributed the development of all countries in the Second World War to strengthen the economic input on strengthening the country's economic development. But they also demand the development of the productive forces the inevitable result of human development itself is the inevitable result then with the development of humanity, people constantly discuss the natural process, in understanding and reconstructing the natural process, people need to be able to liberate a slave. So this is the slave people to be able to replace the complex and engaged in heavy manual labor, People do not realize right up to the world's understanding and transformation of this technology as well as people in the development process of an objective need. Robots are three stages of development, in other words, we are accustomed to regarding robots are divided into three categories. is a first-generation robots, also known as teach-type robot, it is through a computer, to control over one of a mechanical degrees of freedom Through teaching and information stored procedures, working hours to read out information, and then issued a directive so the robot can repeat according to the people at that time said the results show this kind of movement again, For example, the car spot welding robots, only to put this spot welding process, after teaching, and it is always a repeat of a work It has the external environment is no perception that the force manipulation of the size of the work piece there does not exist, welding 0S It does not know, then this fact from the first generation robot, it will exist this shortcoming, it in the 20th century, the late 1970s, people started to study the second-generation robot, called Robot with the feeling that This feeling with the robot is similar in function of a certain feeling, for
