情态动词和虚拟语气用法简表及总结

情态动词和虚拟语气用法简表及总结
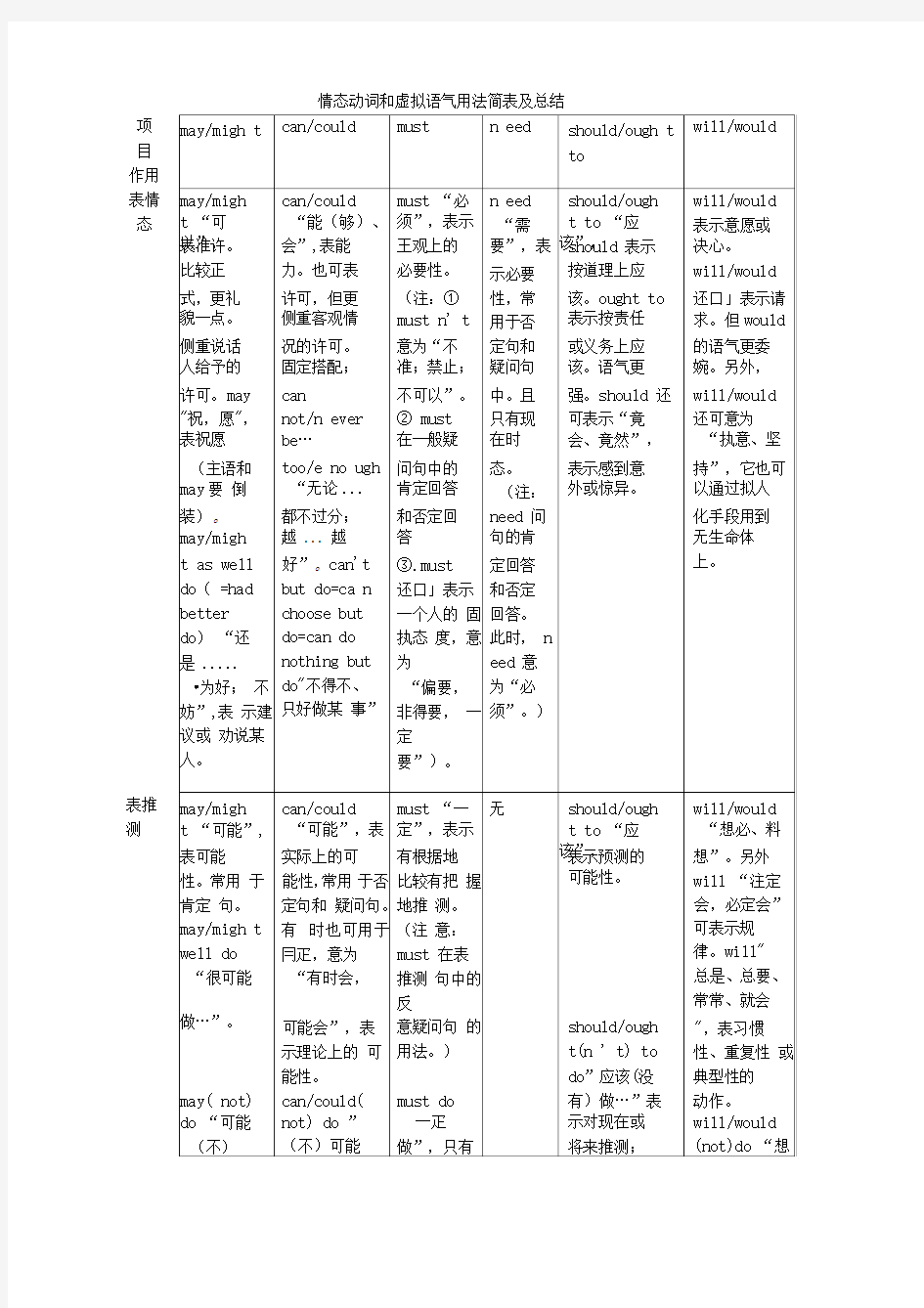
表推 测 项 目 作用
表情 态
做…”,指 实际上的 做…”表 对现在或将 肯定形 式。
表示
should/ough 必、料想(没
有)做…”, 可能性,
来推测
对现在或
t(n ' t) to 表示对现在 表示对现
将来推
have don e
“应 或将来的推 在或将来 can/could( 测。
该(
没有)做 测;
推测
not) have must
过…”,表示 will/would may/migh done “可能 have
对过去的推 (not) have t
(没有)做
done “一
测。
done “想必、 (no t)hav 过…”,表 定做
料想
(没有) e don e
“可 对过去的推
过…”,只
做过…”,表 能(没有) 测。(注:can 有肯定形
示对过去的 做过…”, have done 式,表示
推测。
表示对过 常用于否定 对过去的
去的推 句或疑冋
推测。
测。
句。)
might(n could(n ' t 无
need( n should(n ' t would( n't) 't) do 表
)do 表示对
't) )do 表示对现 do 表示对现
对现在或 现在或将来
have 在或将来的 在或将来的 将来虚 虚拟。
done
虚拟。
虚拟。
拟。
could(n ' t
“过去 should(n ' t would( n't) might(n )have done
本(不) )/ought(n ' have done
't) have “过去本
需要 t) to have “过去本将 done “过
(不)能够做
做…
done “过去本
(不)会做 去本(不) 过…(而实
(而实 (不)应该做 过…(而实
可能做 际上相
际上相 过…(而实际 际上相反)” 过…(而 反)”,表示
反)。表 上相反)”表 表示对过去 实际上相
对过去的虚
示对过
示对过去的 的虚拟。
反)”,表 拟。
去的虚
虚拟。
示对过去
拟
的虚拟。
表虚 拟 补充:
1.根据情态动词表推测的确信程度大小可作如下排序:
must>will>would>ought to>should>ca n> could>may>might
的用法:
(1) shall
(2) shall
胁、越壬 eg: ① Shall I open the win dow?
② You shall get a new bike you want very much if you get the
first p rize in the coming exam.
注:shall,will 表示命令时的区别。
⑴shall 指法律、规章、制度上的“必须”。常用于正式文件中。 ⑵will 指责任、义务上的“必须”。常用于日常交际中。
警告、
用于一、三人称疑问句中,表示征求对方的同意或向对方请示。 用于二、三人称的陈述句中,表示说话人的允诺、保证、命令、威 决心或者法律规
章上的指示和规定等。
eg: ① Each competitor shall wear a number.
② No
one will leave the examination room before ten o'clock. 3.should ⑴表意外, ⑵表推测, ⑶表可能, eg: ① I am surprised that you should speak like that. ② They should be ready by 12:00.
③ If he should come,please let me know. 与 used to 的区别 (1)
(2) (3) often 5.含
有情
态动词的一般疑问句的肯定回答和否定回答。 eg: ① May I sit down?
----- Yes,please./Yes,you may.
② --- Might/Could I use your car tomorrow? --- Yes,you may/can. 或 No,you mustn ' t/can ',I 'm afraid not.
( 注:向对方提出请求或建议时, could/might 表示语气的委婉,但是在回答 时,用 can 或 may 。 ) ③ - Must we arrive on time? --- Yes,you must./No you needn ' t. ④ -------- Need ( 必须) I give up smoking? --- Yes,you must./No,you needn ' t.
(注:含有情态动词 need 的一般疑问句作肯定回答,需用 must 。) 6.will do 既可以
表示将来时,也可以表示一般现在时,表达习惯性、重复性 的动作。区别在于:一般现在时强调“描述性”,而will do 强调“预断性”(即: 动作如此经常发生, 如此具有习惯性或重复性, 以致我们可以预断它肯定会继续 发生)。
7.can 与 be able to 的区别: ( 1)can 表示潜在的能力。只有一般现在时和一般过去时
两种时态。
( 2)be able to 表示经过努力而成功地做某事, 可用于多种时态。 其中 was/were able
to 表示过去有能力并且成功做了某事的能力。 与 have to 的区别
( 1)表示主观上“必须” 。只有一种形式。 mustn 't 意为“不准;禁止;不可 以”。 ( 2)表示客观上“不得不” 。有时态、人称等方面的变化。 don ' t have to 意
为“不必”。
表示推测时的反意疑问句中的用法。 ① He must be busy now,
② Hemust have been tired yesterday after a whole day's work,
的用法: 指说话人对某事不能理解,感到意外或惊异,意为“竟然,竟会” 指确定的或可能有的未来或希望,意为“应该” 。
常用在 if 条件句中,强调某事的可能性,意为“要是,万一” 。 二者都可表示过去重复的习惯动作。 表示过去的状态,只能用 used to, 不能用 would. used to 强调过去与现在的对比,而 would 只表示过去习惯的动作,常与 、every day 等状语连用。
③ He must have been tired , ?
的用法情态动词dare 主要用于否定句、疑问句和条件句,没有人称和数的变化,但是有时态的变化,过去式为dared 。
eg:How dare you say so?
dare 可用于习惯用语中。I dare say" 我敢说;我认为", 表示说话人有把握做出某种判断。
可以用于祈使句中,表达祝愿(其中may和主语常倒装)。
eg: ① May you be happy forever.
②May we never forget each 与can表示许可的区另
虚拟语气的用法
含义:表示与事实相反或者实现的可能性微乎其微、几乎为零或者表示一种坚持、命令、要求和建议或者在固定句型中等。
分类:一般虚拟语气和特殊虚拟语气。
用法:
1?一般虚拟语气的用法
㈠遵循的原则:
对一般现在时虚拟用一般过去时
对一般过去时虚拟用过去完成时
对过去完成时虚拟用过去完成时
对一般将来时虚拟用过去将来时
㈡表现形式:
⑴条件句中的虚拟语气。
eg:If he were indoors,he wouldn ' t feel cold.
⑵wish后所跟宾语从句中的虚拟语气。
eg:①I wish I were a bird. ② I wish she had taken my advice.
(3) would rather后所跟宾语从句中的虚拟语气。
eg: ① I ' d rather you paid the money yourself.
② I ' d rather she hadn' t done that.
⑷If only (要是……就好了;但愿)+句子中的虚拟语气。
eg:If only I were a flying bird.
If only I had seen the film.
If only Mr. Wang were here now,you would not be punished.
⑸as if/though , even if/though 从句中的虚拟语气。(注:在as if 引导
的从句中,如果从句所说的内容是真实的或可能是真实的,应用真实语气;如果从句所说的内容与事实相反或非真实情况,应用虚拟语气。)
eg:①He talks as if he knew all about it.
②Even if he were here,he couldn ' t solve the problem.
③ He talks as if he were drunk.
⑹含蓄虚拟条件句:介词短语without、but for、otherwise等可替代虚拟条件句,表
达虚拟语气。
注:在对be(am/is/are) 动词虚拟时,一律用were 来表示。
eg:①But for your help,we couldn ' t have succeeded.
②She wasn' t feeling well,otherwise she wouldn ' t have left the
meeting so early.
2?特殊虚拟语气的用法
㈠遵循的原则:从句一般用(should ) +V原形来表示。
㈡表现形式:
⑴一坚定二命令三要求四建议,后跟特殊虚拟语气作宾语。(注:insist
如果坚持的是一种事实时,应用真实语气;如果坚持的是一种主张时,应用虚拟语气。
suggest 如果意为“暗示,表明”时,从句应用真实语气。 ) 注:这些动词所对应的名词形式也需用特殊虚拟语气。另外,对应的名词形名词idea 等所构成的从句中也应该用虚拟语气。
eg:①He insisted that we (should) take our teacher ' s advice.
②The man ager dema nded that Tom (should) fin ish it in a week.
③I suggest that you (should) have eno ugh slee p.
④My idea is that we (should) have a meeting to discuss it together.
⑤Our decisi on is that the meeti ng (should) be put off.
⑵在句型
It 's important/necessary/essential/vital/proper/right/impossible/str
ange/natural/a pity/a shame/a surprise/an honor+that 从句。”中,
that 从句要用特殊虚拟语气。
eg:It ' s very important that we (should) think before we decide.
但在句型“ It ' s strange(surprising/unthinkable,etc) +that 从句”
中,should 常译为“竟然”,表示一种不可思议的状况。
eg:It ' s surprising that you (should) waste so much time.
3?虚拟语气的特殊用法
⑴在“ It ' s (high)time +that 从句”中,that 从句可用一般虚拟语气或特殊虚拟
语气( should 不可省),但二者同时出现时,一般虚拟语气优先使用。
eg: It ' s (high)time that he got rid of his bad habit.
⑵if在虚拟条件句中的倒装。
eg:If he came tomorrow,I would tell you as soon as possible.
=If he should cometomorrow,I would tell you as soon as possible. =Should he come tomorrow,I would tell you as soon as possible.
=If he were to cometomorrow,I would tell you as soon as possible.
=Were he to come tomorrow,I would tell you as soon as possible.
⑶在in case that ( 以免,免得),lest( 唯恐,免得),for fear that ,in order that,so that 等引导的目的状语从句
中,that 从句要用情态动词(could/might/would/should)+V 原形, 表示虚拟。
⑷混合虚拟条件句:
当条件从句与主句所表示的时间并不一致,变为虚拟语气时,可根据它们各自的时态进
行变化。
eg: ① If I had married her,I would be happy now.
②If you had taken my advice then,you wouldn' t be in trouble now.
③ Bring some more money in case you (should) use it later.
(5) had hoped/planned/wanted/expected to do “本希望/ 计划/ 想要/ 期望……”,可表示过去未曾实现的愿望或打算。
eg:①I had hoped to take his I didn ' t.
② The boy had meant to come in, but the teacher refused him.
⑹在句式“主句主语+vt+that+ 从句主语+(should) do. ”其中主句谓语动词主语urge(极力主张),prefer(宁
愿),desire(请求),ma in tai n(主张),direct(指导)及以上这些动词所对应的其他形式要用虚拟语气。
eg:She preferred that nobody should come to see her.
初中英语情态动词详细用法归纳(含练习及答案)
初中英语情态动词详细用法归纳(含练习及答案) 1. can 的用法: (1).表示能力、许可、可能性。表示能力时一般译为“能、会”,即有种能力,尤其是生来具备的能力.如:She can swim fast, but I can’t . 她能游得很快,但我不能。 I can see with my eyes. 我用眼睛看。could是can的过去式。表示过去的能力。 be able to do sth. 常常指经过努力,花费了时间和劳力之后才能做到某事。is/am/are able to do sth was/were able to do sth. (2).表示许可,常在口语中。如:You can use my dictionary. 你可以用我的字典。 (3).表示推测,可能性,意为“可能”,常用于否定句和疑问句中,此时can’t 译为“ 不可能”。如:Can the news be true? 这个消息会是真的吗?—Can it be our teacher?那个人有可能是我们老师吗?—No, it can’t be our teacher. He is on a visit to the Great Wall.不可能。咱们老师正在游览长城呢。 【例题】—I think Miss Gao must be in the library. She said she would go there. —No. She __be there, I have just been there. A.can’t B.mustn’t C.needn’t D.wouldn’t 【解析】根据下文“我刚去过那儿”可知,应为“ 不可能”,can’t 表示推测[答案] A could的用法: (1).can的过去式,意为“ 能、会”,表示过去的能力。如:He could write poems when he was 10. 他十岁时就会写诗。 (2). could在疑问句中,表示委婉的语气,此时could 没有过去式的意思。如:Could you give me a hand? 你能帮我个忙吗?—Could I use your pen? 我能用一下你的钢笔吗? —Yes, you can.可以。(用could问,不能用could答。) 2. may的用法: (1).表示请求、许可,比can 正式,如:May I borrow your bike? 我可以借你的自行车吗?You may go home now. 现在你可以回家了。 【例题】—_______ I borrow your MP3? —Sure . Here you are. A. May B.Should C.Must D. Would 【解析】在此处表示请求,意为“ 做……可以吗”。答案:A (2) .表示推测,谈论可能性,意为“ 可能,或许”,一般用于肯定句中。如:It may rain tomorrow . 明天可能会下雨。She may be at home. 她可能在家呢. may not 翻译为“可能不” (3) .may的过去式为might ,表示推测时。可能性低于may。如:He is away from school. He might be sick. 他离开学校了,可能是他生病了。 (4) . 表示希望、祈求、祝愿,常可译为“祝愿”。通常是用may +主+V 例如:May you have a good time. 祝你过得愉快。May you be happy! 祝你幸福!May you succeed!祝你成功! 3. must的用法: (1).must 表示主观看法,意为“必须、一定”。如:You must stay here until I come back.在我回来之前你必须呆在这儿。Must I finish my homework right now? 我必须现在交作业吗?(must引导的疑问句) 肯定回答:yes ,you must. 否定回答:No, you needn’t/ don’t have to (2) 其否定形式mustn’t表示“ 一定不要” “千万别” “禁止, 不许”. 如:You mustn’t play with fire. 你不许玩火。You mustn’t be late. 你一定不要迟到。 (3)must表示有把握的推测,用于肯定句,指百分百肯定。如: The light is on, so he must be at home now.灯亮着,他现在肯定在家。 (4)①must 和have to 都有”必须”的含义,但侧重点不同: must强调说话者主观(自己)的看法。 have to强调客观(外力作用)的需要,也可以翻译为“不得不”。
英语情态动词用法总结(完整)
英语情态动词用法总结(完整) 一、单项选择情态动词 1.--- Difficulties always go with me! --- Cheer up! If God closes door in front of you, there be a window opened for you. A.must B.would C.could D.can 【答案】A 【解析】 【详解】 考查情态动词辨析。句意:——困难总是伴随着我!——高兴点! 如果上帝在你面前关上了门,一定有一扇窗户为你打开。A. must必须;B. would将要;C. could能,会;D. can能,会。must表示对现在的状态推测时,意为“一定”,表示可能性很大的推测。符合语境。故选A。 【点睛】 1) must用在肯定句中表示较有把握的推测,意为"一定"。 2) must表对现在的状态或现在正发生的事情的推测时, must 后面通常接系动词be 的原形或行为动词的进行式。 3) must 表示对已发生的事情的推测时,must 要接完成式。 4) must表示对过去某时正发生的事情的推测,must 后面要接完成进行式。 5) 否定推测用can't。 本句中的。must表示对现在的状态推测时,意为一定,表示可能性很大的推测。符合第2点用法。 2.Paul did a great job in the speech contest. He many times last week. A.need have practised B.might practise C.must have practised D.could practise 【答案】C 【解析】 【详解】 考查情态动词。句意:保罗在演讲比赛中表现得很好。他上星期一定练习了很多次。must have done是对过去发生的动作最有把握的猜测,意思是“一定”。故C选项正确。 3.He is a bad-tempered fellow, but he ________ be quite charming when he wishes. A.shall B.should C.can D.must 【答案】C 【解析】 【详解】 考查情态动词辨析。句意:他是个脾气不好的家伙,但当他希望自己有魅力的时候,他可
英语虚拟语气语法归纳总结
虚拟语气: 表示说的话不是事实,不可能发生或者说可能性很小的情况,表达一种愿望、建议、假设。 if were/did, would do if had done, would have done if were to do/should do, would do 举例: If I were you, I would do nothing about it. If you had taken your teacher’s advice, you wouldn’t have made such a mistake. If it were to/ should rain tomorrow(表示降水率很低),they wouldn’t go shopping. 附注: 虚拟语气,条件状从倒装 状语从句中,去掉if,提前were/ had/ should 如:If I were you, I would give up. →Were I you, I would give up If you had taken the advice, you would have…. →Had you taken the advice, you would have… If the world shou ld come to an end,…… →Should the world come to an end…… 另外,without, but for, otherwise构成的条件状语从句中,也有含蓄的虚拟语气But for the popularization of electricity, we would lead a whole different life today. (popularization 普及,publicity 宣传) Without your help, I would have failed. We’ll go earlier, otherwise we wouldn’t get a seat.(表示可能性小)
可用虚拟语气的用法总结
虚拟语气的用法总结 语气:语气是动词的一中形式,它表示说话人对某一行为或事情的看法和态度。 虚拟语气表示动作或状态不是客观存在的事实,而是说话人的主观愿望,假设或推测等。如If I were you, I should study English. 一.虚拟语气在条件从句的用法 条件句有两类,一类是真实条件句;一类是非真实条件句,也就是虚拟条件句。 如果假设的情况是有可能发生的,就是真实条件句,谓语要用陈述语气。如If it doesn’t rain tomorrow, we will go to the park. 如果假设的情况是过去或现在都不存在的,或将来不大可能发生的,则是虚拟条件句。如If he had seen you yesterday, he would have asked you about it. 在含有虚拟条件句的复合句中,主句 If her mother had taken the doctor’s advice, she would/might have got well earlier. If it were to rain tomorrow, the match would be canceled. 有时候省略if,采用局部倒装语序。把had /should/were 等动词(不包括行为动词)移到从句的句首。例如: Were it to rain tomorrow, our picnic would be canceled. Had it not been for the storm, we would have arrived in time. Should the earth stop running, what would happen? 二. 错综时间条件句 有时条件从句的动作和主句动作发生的时间不一致,这时需要根据意思采用表示不同时间的动词形式来进行调整。 If she had taken the doctor’s advice, she might still be alive. If I were you, I would have accepted their terms. 三.含蓄条件句
初中英语情态动词详细用法归纳(含练习及答案)(直接打印版)
初中英语情态动词详细用法归纳(含练习及答案)(直接打印版) 情态动词有具体的词义,但也同助动词一样,需要与其他词语一起构成句子的谓语,另外情态动词没有人称和数的变化,情态动词后必须跟动词原形。 1. can 的用法: (1).表示能力、许可、可能性。表示能力时一般译为―能、会‖,即有种能力,尤其是生来具备的能力,此时may 和must 均不可代替它。如:She can swim fast, but I can’t . 她能游得很快,但我不能。I can see with my eyes. 我用眼睛看。 (2).表示许可,常在口语中。如:You can use my dictionary. 你可以用我的字典。 (3).表示推测,意为―可能‖,常用于否定句和疑问句中,此时can’t 译为― 不可能‖。如:Can the news be true? 这个消息会是真的吗?—Can it be our teacher?那个人有可能是我们老师吗?—No, it can’t be our teacher. He is on a visit to the Great Wall.不可能。咱们老师正在游览长城呢。 【例题】—I think Miss Gao must be in the library. She said she would go there. —No. She __be there, I have just been there. A.can’t B.mustn’t C.needn’t D.wouldn’t 【解析】根据下文―我刚去过那儿‖可知,应为― 不可能‖,can’t 表示推测[答案] A 2. could的用法: (1).can的过去式,意为― 能、会‖,表示过去的能力。如:He could write poems when he was 10. 他十岁时就会写诗。 (2). could在疑问句中,表示委婉的语气,此时could 没有过去式的意思。如:Could you do me a favour? 你能帮我个忙吗?—Could I use your pen? 我能用一下你的钢笔吗? —Yes, you can.可以。(注意回答) 3. may的用法: (1).表示请求、许可,比can 正式,如:May I borrow your bike? 我可以借你的自行车吗?You may go home now. 现在你可以回家了。 【例题】—_______ I borrow your MP3? —Sure . Here you are. A. May B.Should C.Must D. Would 【解析】在此处表示请求,意为― 做……可以吗‖。答案:A (2) .表示推测,谈论可能性,意为― 可能,或许‖,一般用于肯定句中。如:It may rain tomorrow . 明天可能会下雨。She may be at home. 她可能在家呢. (3) .may的过去式为might ,表示推测时。可能性低于may。如:He is away from school. He might be sick. 他离开学校了,可能是他生病了。 (4) . 表示希望、祈求、祝愿,常可译为“祝愿”。通常是用may +主+V 例如:May you have a good time. 祝你过得愉快。May you be happy! 祝你幸福!May you succeed!祝你成功! 4. must的用法: (1).must 表示主观看法,意为―必须、一定‖。如:You must stay here until I come back.在我回来之前你必须呆在这儿。Must I hand in my homework right now? 我必须现在交作业吗? (2) 其否定形式mustn’t表示― 一定不要‖ ―千万别‖ ―禁止, 不许‖. 如:You mustn’t play with fire. 你不许玩火。You mustn’t be late. 你一定不要迟到。 (3)对must引导的疑问句,肯定回答为must,否定回答为needn’t 或don’t have to .如:—Must I finish my homework?我现在必须完成作业吗?—No, you needn’t.不,你不必。 (4)must表示有把握的推测,用于肯定句。如: The light is on, so he must be at home now.灯亮着,他现在肯定在家。 注意其反意问句的构成形式: 当must表示肯定的判断、推测时,其反意疑问句要用实际问句的助动词来构成。如:She must have seen the film before,hasn’t she?(注意反意疑问句的后半部分)You must have met uncle Wang in the shop yesterday,didn’t you? (注意反意疑问句的后半部分)
英语虚拟语气类型用法
二、虚拟语气的判断: 1. if 条件状语从句中虚拟语气的判断。if 条件状语从句有真实条件句和非真实条件句。假设条件可以实现的句子为真实条件句,反之为非真实条件句,要用虚拟语气。其形式分为以下三种: (1) 与过去事实相反的假设。结构为:从句的谓语动词用“had + 过去分词”,主句用“should (would, could, might) + have + 过去分词”。例如: If it had not rained so hard yesterday, we could have played tennis. 如果昨天没有下大雨,我们就能玩网球了。 (2) 与现在事实相反的假设。结构为:从句的谓语动词用过去式,系动词用were,主句的谓语用“should (would, could, might) + 动词原形”。例如: If I were in your position, I would marry her. 如果我是你,我就娶她为妻。 (3) 与将来事实相反的假设。结构为:从句的谓语动词用“should (were to) + 动词原形”,主句用“should (would, could, might) + 动词原形”。例如: If you should miss the chance, you would feel sorry for it. 如果你错过了这次机会,你会难过的。 2. 宾语从句中的虚拟语气。 (1) wish后接宾语从句中的虚拟语气:根据从句的意义来判断。 A: 表示与现在和将来事实相反的愿望,从句谓语动词用过去时态。例如: I wish they were not so late. 要是他们来得不是这么晚就好了。 B: 表示与过去事实相反的愿望,从句谓语动词用过去完成时态。例如: I wished he hadn't done that. 我真希望那件事不是他做的。 (2) 表示“要求、建议、命令”等动词后面的宾语从句中的虚拟语气。用于此结构的动词有:advise, direct, agree, ask, demand, decide, desire, insist, order, prefer, propose, request, suggest 等。从句的谓语动词用“should + 动词原形”,其中should 可以省去。例如: I insisted that he (should) go with us. 我坚持让他和我们一起去。 注意:当insist 表示“坚持认为”、suggest表示“表明,显示”时,不用虚拟语气。例如:
高中英语提高之虚拟语气用法
虚拟语气用法 虚拟语气用法
概念
虚拟语气用来表示说话人的主观愿望或假想, 而不表示客观存在的事实, 所说的是一个条件, 不一定是事实,或与事实相反。虚拟语气通过谓语动词的特殊形式来表示。英语中的语气分 为陈述语气、祈使语气、虚拟语气三类。
应用条件
在表示虚假的、与事实相反的或难以实现的情况时用虚拟语气,表示主观愿望或 某种强烈情感时,也用虚拟语气。即当一个人说话时欲强调其所说的话是基于自己的 主观想法,而不是根据客观实际,就用虚拟语气。
在非真实条件状语从句中的用法
真实条件状语从句与非真实条件状语从句
条件句可分为两类,一类为真实条件句,一类为非真实条件句。非真实条件句表 示的是假设或实际可能性不大的情况,故采用虚拟语气。 例: If he doesn’t hurry up, he will miss the bus. 如果他不快点,他 将错过巴士。( 真实) If he is free, he will ask me to tell stories. 如果 他是空闲的,他会要求我讲故事。 (真实) If I were you, I would go at once. 如果我是你, 我马上就会去。(非真实, 虚拟语气) If there were no air, people would die. 如果没有空气,人就会死亡。 (非真实,虚拟语气)
用法及动词形式
从句
If+主语 +did If+ 主语+did 主语 were) ( be 动词 were )
主句
与现在事实相反
主语+should/would/ 主语 +should/would/ could/might+do
初中情态动词用法总结
专项:情态动词 一考点:情态动词的用法和辨析,情态动词表示推测和可能,由情态动词引导的一般疑问句的回答。 二类型:1 只是情态动词:can, could, may, might, must 2 可做情态动词,可做实义动词:need, dare 3 可做情态动词,可做助动词:will, would, shall, should 4 特殊:have to, ought to, used to 三特征:1 有一定的词义,但不能单独作谓语,必须与行为动词和系动词连用构成谓语。 2 无人称和数的变化。(have to 除外) Eg: He has to stay here. 3 后接动词原形。 4 具有助动词作用,可构成否定,疑问或简短回答。 四用法: 1. can ①表示能力,“能,会”。Eg : Can you play basketball? ②表示怀疑,猜测,常用于否定句或疑问句。 Eg :Li hua can’t be in the classroom. ③表示请求,允许,多用于口语,译“可以”= may. Eg: you can go now. ④can 开头的疑问句,肯定句,否定句用can或can’t. 2.could①can 的过去式,表示过去的能力。 Eg :I could swim when I was seven years old. ②could 开头的疑问句,肯定和否定回答用could, couldn’t如果could 表示现在的委婉,用can 回答。 Eg: Could I have a drink? Yes, you can. 3.may①表示推测,“可能,也许”,用于肯定句。 Eg: He may come tomorrow. ②表示请求,“许可,可以”。Eg: May I borrow your book? 注:表示请求,许可时,主语为第一人称的一般疑问句,否定回
高中英语虚拟语气的用法
高中英语虚拟语气的用法 一、考查虚拟语气在条件从句中的用法 时间从句谓语形式(be用were不可改变)主句谓语形式 将来一般过去时(be用were) would/should/might/could+动词原形 现在一般过去时(be用were) would/should/might/could+动词原形 过去现在完成时would/should/might/could+had done (1)If he my advice, he wouldn' t have lost his job. A. followed B. should follow C. had followed D. would follow (2)If we the other road, we might have arrived here in time for the meeting. A. taken B. had taken C. took D. have taken (3) -John went to the hospital alone. -If he me about it, I would have gone with him. A. should tell B. tells C. told D. had told 二、考查特殊句型中的虚拟语气 英语中需要使用虚拟语气的特殊句型不多,主理有以下类: 1.“倒装”类虚拟语气 当虚拟条件句中含有were, should, had时,有时可将引导虚拟条件句的连词if省略,而将从句中的were,should, had提到句首,构成倒装形式的虚拟语气。如: If he were here, she would agree too.→Were she here, she would agree too.如果她在这里,她也同意的。. If it should rain tomorrow, we should have to put off the match. →Should it rain tomorrow, we should have to put off the match.假若明天下雨,我们只好推迟这场比赛。 If we had found him earlier we could have saved his life.→Had we found him earlier we could have saved his life. 要是我们当时早点找到他的话,我们就可以救活他。 注意,如果条件从句的谓语为否定式,其中的否定词not应置于主语之后,而不能与were,should, had等缩略成Weren' t, Shouldn' t, Hadn'场置于句首。如:我如不是警告了你,你就可能丧命了。 正: If I hadn' t warned you, you could have been killed. 正: Had I not warned you, you could have been killed. 误: Hadn' t I warned you, you could have been killed. 另外,有时省略if后提前到句首的had可能不是助动词,而是实义动词。 如: Had I time, I would go with you.假如我有时间,我就同你们一起去。句中的had不是构成过去完成时的助动词,而是表示“有”,如果不省略if ,完整形式为:If I had time, I would go with you. (1) Had I known about this computer program, a huge amount of time and energy____. (2010浙江卷) A.would have been saved B. had been saved C. will be saved D. was saved (2) fired, your health care and other benefits will not be immediately cut off. (2006湖北) A. Would you be B. Should you be C. Could you be D. Might you be 2.“宁愿”类虚拟语气 这里说的“宁愿”主要是指would rather。当它后接句子的时候,句子的谓语通常要用虚
虚拟语气用法总结讲课稿
虚拟语气用法总结
虚拟语气用法总结 朱世梅 新时代大学英语中针对虚拟语气的练习题较多,而学生们往往把握不好虚拟语气的正确使用,现将其用法总结如下: 一.虚拟语气在英语里主要用来表达: a. 非真实的情景,不可能发生的事,即某种与事实相反或难以实现的情况,或说话人主观愿望。 b. 与客观事实相反地情景,即强制性虚拟语气,表示建议、命令、劝告这一类的意思上,表示强烈的要求做到、必须做到这样的含义。 c. 虚拟语气的表达形式是通过动词的变化形式表达的,其特点是主从句时态的不一致,而且一般有明显得标志。 二.虚拟语气的考点为: 1.If 句型 (共有三种句型) 非真实条件句: a.与现在的事实相反:从句用一般过去时,主句的谓语用would (could, might) +动词原形 If I were Bill Gates, I would not work so hard every day. b.与过去的事实相反:从句用过去完成时,主句的谓语用would (could, might) +现在完成时 If I had gone to America when I graduated from middle school, I would have got my PhD degree. c.与将来的事实相反:从句用should (were to,did) + 动词原形,主句的谓语用would (could, might) +动词原形 If it should/were to snow tomorrow, I would go skiing.
注意:虚拟条件句的倒装虚拟条件句的从句部分如果含有were, should, 或had, 可将if省略,再把were, should或had 移到从句句首,实行倒装。 Eg: Should it rain, the crops would be saved. =Were it to rain, the crops would be saved. Eg:_____ to do the work, I should do it some other day. A. If were I B. I were C. Were I D. Was I 答案C. 在虚拟条件状语中如果有were, should, had这三个词,通常将if省略,主语提前, 变成 were, should, had +主语的形式。但在虚拟条件状语从句中,省略连词的倒装形式的句首不能用动词的缩略形式。如我们可说 Were I not to do., 而不能说 Weren't I to do. d.混合条件句主句与从句的动作发生在不同的时间,这时主,从句谓语动词的虚拟语气形式因时间不同而不同,这叫做混合条件句。例如:条件句动作发生在过去,主句的动作发生在现在)谓语动词要根据表示的时间进行调整。 Eg: If it had rained last night (过去), it would be very cold today (现在). 2.Wish 句型表达“但愿…,要是…多好”的语气表示与事实相反的情况,或表示将来不太可能实现的愿望。其宾语从句的动词形式为: He wished he hadn't said that. 他希望他没讲那样的话。 I wish it would rain tomorrow. 我希望明天下雨就好了。 Wish to do表达法: Wish sb / sth to do I wish to see the manager. = I want to see the manager. I wish the manager to be informed at once. (= I want the manager to be informed at once.) 3.在强制性语气的宾语从句中的运用即表示建议、命令、劝告、决心等主观色彩的动词 + that + (should) + 动词原形,其中should 经常被省略。这类动词包括: suggest, propose, recommend, demand, order, command, desire, require, insist,
初中英语情态动词用法归纳
初中英语情态动词用法归纳 话题:动词情态教育学习 情态动词有具体的词义,但也同助动词一样,需要与其他词语一起构成句子的谓语,另外情态动词没有人称和数的变化,情态动词后必须跟动词原形。考点一:can,may,must 等情态动词在陈述句中的用法:1. can的用法:(1).表示能力、许可、可能性。表示能力时一般译为“能、会”,即有种能力,尤其是生来具备的能力,此时may和must均不可代替它。如:She can swim fast, but I can’t .她能游得很快,但我不能。I can see with my eyes.我用眼睛看。(2).表示许可,常在口语中。如:You can use my dictionary.你可以用我的字典。(3).表示推测,意为“可能”,常用于否定句和疑问句中,此时can’t译为“不可能”。如:Can the news be true?这个消息会是真的吗?—Can it be our teacher?那个人有可能是我们老师吗?—No, it can’t be our teacher. He is on a visit to the Great Wall.不可能。咱们老师正在游览长城呢。【例题】—I think Miss Gao must be in the library. She said she would go there.—No. She __be there, I have just been there. A.can’t
B.mustn’t C.needn’t D.wouldn’t【解析】根据下文“我刚去过那儿”可知,应为“不可能”,can’t表示推测[答案] A2. could 的用法:(1).can的过去式,意为“能、会”,表示过去的能力。如:He could write poems when he was 10.他十岁时就会写诗。(2). could在疑问句中,表示委婉的语气,此时could 没有过去式的意思。如:Could you do me a favour?你能帮我个忙吗?—Could I use your pen?我能用一下你的钢笔吗?—Yes, you can.可以。(注意回答)3. may的用法:(1).表示请求、许可,比can正式,如:May I borrow your bike?我可以借你的自行车吗?You may go home now.现在你可以回家了。【例题】—_______ I borrow your MP3?—Sure . Here you are.A. May B.Should C.Must D. Would【解析】在此处表示请求,意为“做……可以吗”。答案:A(2) .表示推测,谈论可能性,意为“可能,或许”,一般用于肯定句中。如:It may rain tomorrow .明天可能会下雨。She may be at home.她可能在家呢.(3) .may的过去式为might,表示推测时。可能性低于may。如:He is away from school. He might be sick.他离开学校了,可能是他生病了。(4) .表示希望、祈求、祝愿,常可译为“祝愿”。通常是用may +主+V例如:May you have a good time.祝你过得愉快。May you be happy!祝你幸福!May you succeed!祝你成功!4. must的用法:(1).must表示主观看法,意为“必须、一定”。如:You must stay here until I come back.
谈英语中虚拟语气的用法
连云港育青外国语学校李老师谈英语中虚拟语气的用法 虚拟,在汉语中表示一种假设的,不存在的情况,同样,英语中虚拟语气是用来表示说话人 的主观愿望或假想,而不表示客观存在的事实,所说的是一个条件,不一定是事实,或与事 实相反。虚拟语气通过谓语动词的特殊形式来表示。在初中阶段,虚拟语气一般用于下列情况: 一、条件状语从句 1、与现在事实相反 若与现在事实相反,虚拟语气的条件从句的谓语用过去式(be通常用were),主句谓语用“should (would, could, might)+动词原形”。如: If I were you, I would take an umbrella. 如果我是你,我会带把伞。(事实上我不可能是你) If I knew her number I could ring her up. 要是我知道她的电话号码,我就可以给她打电话了。 (事实上我不知道) 2、与过去事实相反 若与过去事实相反,从句:主语+had done ,主句:主语+should/would/could/might+have done,例如: If I'd left sooner,I'd have been on time. 要是我早点动身,我就准时到了。(但我动身太迟了) If I had got there earlier, I should/could have met her. 如果我早到那儿,我就会见到她。(事实:去晚了) 3、与将来事实相反 从句:①if+主语+were to do 主句:①主语+should/would/could/might+do ②if+主语+did/were ②主语+should/would/could/might+do ③if+主语+should+do ③主语+should/would/could/might+do 例如:If he went,would you go too? 如果他去,你也去吗?(大概他不会去) If he should come here tomorrow, I would talk to him. 如果他明天来这儿的话,我就跟他 谈谈。(事实:来的可能性很小) 注意与说明:对于与将来事实相反的情形,请注意以下几点: 一是这里说的与将来事实相反,实为对将来情况的推测; 二是此用法中的条件从句谓语除用过去式外,有时也用“should+动词原形”( 表示可能性极小, 表示与将来事实相反的假设); 常译为“万一”) 或“were to+动词原形”( 三是当条件从句使用“should+动词原形”这样的谓语时,主句谓语除可用“should (would, could, might)+动词原形”这样的虚拟语气外,也可用陈述语气或祈使语气。如: I should see him, I'll tell him. 万一我见到他,我就告诉他。 万一明天下雨,就别等我了。 If it should rain tomorrow, don’t expect me. 二、wish 后宾语从句 1、表示与现在事实相反的愿望,谓语动词用过去式。例如: I wish I had your brains. 我希望我有你那样的头脑。(事实:我根本比不上你) 2、表示与过去事实相反的愿望,谓语动词:had+done 例如: I wish I had knownthe truth of the matter. 我希望我那时就知道这件事情的真相。(事实:那时还不知道) 3、表示将来难以实现的愿望,谓语动词:should/would(情态动词)+ 动词原形 I wish I should havea chance again. 我希望我还能有一次这样的机会。(事实:很难再有 这样的机会了) 常见考法
(完整)虚拟语气用法归纳,推荐文档
虚拟语气用法归纳 虚拟语气主要指的的是带有非真实条件状语从句的复合句,表达的是说话人的遗憾后悔的语气,愿望以及建议,命令,要求等等的情感,往往说的是与事实相反或者没办法实现改变的东西。虚拟语气主要表现为在对过去现在或者将来的情况做出假设后,有可能出现的情况。 虚拟语气的内容主要有三大模块,第一模块就是涉及到条件从句部分的内容。这一部分的虚拟语气主要体现在三个方面:基本用法,各自为政,以及含蓄之美。 下表就是条件从句虚拟语气的基本用法: 通常,在上面表格里反映的是非真实条件句的虚拟语气模式,从句和主句的谓语动词时间是一致的,如果两者时间不一致,此时就是混合型虚拟语气。混合型虚拟语气的使用要求“各自为政”,即从句和主句根据各自假设的时间不同,采用上面表格中对应的的谓语动词形式。 如何“各自为政”呢?这就像是数学里的排列组合,一边有三种情况,交叉一搭配就出现了好多种情况。不管怎样,我们要遵循一个原则,就是“各自为政”。例如,从句是对过去情况的假设,而主句则是对现在情况的假设,那我们在使用时,从句就用过去完成式,而主句要用would/could do的形式。当然,也不是所有的AB配就是合理的,有时候在具体语境下,会出现矛盾的情况,这时我们就要结合要表达的意思来判断他们是对什么情况的假设,选择合适的形式。一般而言,主句的假设时间会发生在从句的假设时间之后。因为是有这么一个条件才会出现主句的现状。因此在此类的完成句子练习中,我们要特别提醒注意时间状语的暗示 1. If I had seen you, I would not be so worried now. (从句是对过去的假设,主句是对现在的假设) 2. If you had not watched television so late last night, you would not be so sleepy now.( 从句是对过去的假设,主句是对现在的假设) 3. If I were you, I would seize the chance to go abroad. (从句和主句都是现在的假设) 4. Had you followed the doctor’s suggestion, you would be fine now.( 从句是对过去的假设,主句是对现在的假设) 5. If I had made some money last summer, I would go on holiday next month.( 从句是对过去的假设,主句是对将来的假设) 6. You didn’t let me drive. If we had driven in turns, you wouldn’t be so tired now. (从句是对过去的假设,主句是对现在的假设) 7. If Jack hadn’t met Rose on his voyage, he would be alive now. (从句是对过去的假设,主句是对现在的假设) 8. If Lily didn’t attend today’s party, she could not have the chance to work in the company next week. (从句是对现在的假设,主句是对将来的假设) 9. Had Father followed my travel plan , our family would not stay at home now. (从句是对
初中英语情态动词用法归纳
初中英语情态动词用法归纳 情态动词有具体的词义,但也同助动词一样,需要与其他词语一起构成句子的谓语,另外情态动词没有人称和数的变化,情态动词后必须跟动词原形。 考点一:can,may,must 等情态动词在陈述句中的用法: 1. can 的用法: (1).表示能力、许可、可能性。表示能力时一般译为“能、会”,即有种能力,尤其是生来具备的能力,此时may和must均不可代替它。如:She can swim fast, but lean 她能游.得很快,但我不能。I can see with my eyes我用眼睛看。 (2).表示许可,常在口语中。如:You can use my dictionary. 你可以用我的字典。 (3).表示推测,意为可能”常用于否定句和疑问句中,此时can'译为不可能”女口:Can the news be true?这个消息会是真的吗?一Can it be our teacher那个人有可能是我们老师吗?一No, it can' t be our teacher. He is on a visit to the GreatlW不可能。咱们老师正在游览长城呢。 【例题】一I think Miss Gao must be in the library. She said she would go ther—No. She __be there, I have just been there. A.can ' t B.mustn ' t C.needn ' t D.wouldn 't 【解析】根据下文我刚去过那儿”可知,应为不可能” can'表示推测[答案]A 2. could 的用法: (1).can的过去式,意为能、会”表示过去的能力。女口:He could write poems when he was 10. 他十岁时就会写诗。 (2). could在疑问句中,表示委婉的语气,此时could没有过去式的意思。如:Could you do me a favour?你能帮我个忙吗?一Could I use your pen?我能用一下你的钢笔吗?一Yes, you can可以。(注意回答) 3. may 的用法: (1) .表示请求、许可,比can正式,如:May I borrow your bike?我可以借你的自行车吗?You may go home now现在你可以回家了。 【例题】一______ I borrow your MP3?- Sure . Here you are. A. May B.Should C.Must D. Would 【解析】在此处表示请求,意为做……可以吗”答案:A (2) .表示推测,谈论可能性,意为“可能,或许”,一般用于肯定句中。如:It may rain tomorrow .
