四川方言音系与英语音系的初步比较研究

语言学知识_音系学
音系学 一.音系学(Phonology)的定义: 音系学主要有以下两个任务:其一,发现某一特定语言中出现的所有能够区别意义的语音;其二,找出语音是如何组织起来表达意义的。 二.音素(Phone)、音位(Phoneme)和音位变体(Allophone): 音素(Phone):一个语音单元或音段。 音位(Phoneme):一个具有区别性价值的单位,是一组语音特征的抽象集合体。 音位变体(Allophone):同一个音位在不同语音环境下的实现的方式。 三.音位的分布(Distribution of Phonemes): 音位对立(phonemic contrast)以及互补分布(complementary Distribution):相似的音素之间相联系的方式主要有两种:如果它们是同一个音位的音位变体,不区别意义,就处于互补分布状态;如果它们不是同一个音位的音位变体,且能够区分意义,就构成了音位对立。 自由变异(free variation): 如果两个音素出现在一个相同的语音环境中,并不区别意义,换而言之,用一个音素替换另一个音素而不产生一个新词,仅仅产生同一个词的不同读音,那么这两个音素就处于自由变异。 最小对立体(minimal pairs): 如果两个单词,除了出现在同一个位置上的一个音以外,其余的都相同,则这两个词就构成了一个最小对立体。若最小对立体按照相同的条件进一步的扩展,扩展到多对,就构成了一个最小对立集(minimal set)。例如:hook和book,book和look,look和cook就构成了三对对立体,而这六个词则构成了一个最小对立集。 四.音系学的一些规则(Some Rules of Phonology): 在音系学中,孤立的音素是没有意义的。因此为了表达意义,音素必须组合在一起,但是也需要符合一定的组合原则。 1)序列原则(Sequential rules):即语音组成词在排列顺序上要受到一定的制约。音位系统规定了哪些音位可以放在词首,哪些可以放在哪些可以相互搭配。 2)同化原则(assimilation rule):一个音通过吸收其相邻音的特点,变得与其相似,这种音系规则叫做同化原则(assimilation rule)。如果后面的音同化了前面的邻音,这种同化叫做逆同化(regressive assimilation);反之,则叫做顺同化(progressive assimilation)。常见的同化有鼻音化(nasalization),齿音化(dentalization)和软腭 化(velarization)。 3)省略原则(deletion rule):有关于在什么条件下某个音被省略掉,即只有拼写形式存在而不发音的音系规则。 五.超音段特征(Suprasegmental Features): 超音段特征主要有音调(tone)、重音(stress)和语调(intonation)。 重音(stress):在产生一个音节过程中所用力的程度。重音分为两种:单词重音和句子
六年级英语辨音题
( )1. A. name B. cake C. grape D. map ( )2. A. after B. happy C. class D. f a t h e r ( )3. A. lesson B. she C. these D. we ( )4. A. kite B. fish C. like D. tiger ( )5. A. open B. go C. does D. sofa ( )6. A. bed B. red C. let’s D. e v e n i n g ( )7. A. good B. look C. room D. c l a s s r o o m ( )8. A. cut B. music C. puppet D. p u z z l e ( )9. A. show B. how C. follow D. p i l l o w ( )10. A. school B. kitchen C. teacher D.C h i n a 辨音练习(2) ( )1. A. usually B. music C. plus D. s t u d e n t ( )2. A. bread B. please C. seat D. s p e a k ( )3. A. apple B. family C. bad D. b a n a n a ( )4. A. exercise B. bend C. neck D. t h e s e ( )5. A. fight B. dinner C. primary D. w h i t e ( )6. A. copy B. other C. pot D. shop ( )7. A. year B. here C. there D. ear ( )8. A. eat B. head C. bread D. s w e a t e r ( )9. A. sister B. sit C. like D. big ( )10. A. cat B. away C. bag D. jacket 辨音练习(3) ( )1. A. what B. who C. where D. when ( )2. A. holiday B. lot C. come D. on ( )3. A. there B. three C. these D. t h e m
英语重读规则
英语重读规则 英语是重音因素最为明显的一种语言。对于以英语为母语的人士来说,重音位置和轻重音之间的对照是他们通过听觉识辨识单词的主导因素,一旦说话人对重音把握出现错误,就会造成交流障碍。反过来,如果学习英语单词时重音没有读准,在听英语时也很难准确辨识。在不借助词典的情况下,即使碰到不认识的词,也能准确发音的能力,是英语素养的重要部分。因为元音字母如何发音,基本取决于是否重读和音节性质(开音节、闭音节)两大因素。由于英语非重读音节中的元音发音规则相对简单,一旦重读音节中的元音发准了,英语单词的基本语音轮廓就勾勒出来了。由此可见,判断重音位置是英语学习中一个无法绕过的拦路虎。本文将从词汇学的角度,对英语重音的大致规律作一个介绍。 影响英语重音基本上有五个因素:归化程度、音节数、词性、词缀以及倒数第二音节辅音特征,其中后缀和倒数第二音节辅音特征才是决定英语重音的最关键因素,而这一点长期以 来一直被研究者所忽视。 1、归化程度 归化程度是指由其他语言引入英语的单词在多大程度上融入了“本土”词汇大家庭。英语虽然属于印欧语系中的日耳曼语族,但从词汇角度看,只有少数词汇是从日耳曼语言继承的,80%的词汇反而源于拉丁语,与拉丁语的密切关系甚至超过了法语(最初是拉丁语的方言)与拉丁语的血缘关系。如今,绝大部分拉丁词语已经本土化,但仍有少量词语和短语被视为外来语。另外,英语中还吸纳了大量其他语言的词汇,其中相当一部分已经本土化,遵从英语的一般重音模式,但部分词汇的重音仍然模仿源语言中的重音。下面是一些例子: 1)法语词汇:–aire(如millionaire、questionnaire,与英语后缀-ary等价)、–ee(由法语过去分词变来,如referee、absentee、trustee)、–ette(表示“小”,如novelette)等后缀均遵循法语重音模式,最后一个音节重读。renaissance一词从语音上说还未完全归化,既可按照英语模式在第二个音节上重读,也可按照法语模式在最后一个音节上重读。 2)西班牙语词汇:-ado是典型的西班牙语后缀,重音在字母a上,如Colorado, aficionado (……迷),等等。 3)拉丁词汇:比如ad infinitum(直至无限)中infinitum就按照拉丁语模式,在倒数第二个音节重读。拉丁语对英语重音最大的影响,在于倒数第二音节的辅音特征对重音位置有决定作用(详见第4部分)。 2、音节数、词性和前缀 音节数对英语重音位置也有明显的影响。下面我们分成三种情况考虑。第一种是单音节词。所有的单音节词都是重读的。第二种是双音节词,双音节词的重音主要受词性影响,其次是前缀。如果该词是动词、形容词、介词,重音往往在第二个音节上,如果是名词,重音往往在第一个音节上。前一类如defend,irate,above,后一类如window,cable等等。下面几个具有双重词性的单词最具启发性:作为动词,project(投射)、object(反对)、refuse (拒绝)、produce(生产)重音均在第二个音节上;作为名词,它们的重音都在第一个音节上(意思分别是项目、客体、垃圾、农产品)。前缀对双音节词影响较大,特别是a-、be-和en-(有em-、in-、im-等多个变体),以它们开头的词重音普遍在第二个音节。differ 的重音很特殊,它是动词,相同后缀的双音节动词(infer,confer,refer)重音都在后面,differ的重音却在前面,估计是为了与defer(遵从)相区分。第三种是三音节和更多音节的词。这一类词的重音位置主要取决于后缀。因此我们在下一部分单独分析。 3、后缀与多音节单词重音 为了论述的简洁,我们引入三个术语:ultimate——末音节,penult——次末音节,antepenult ——倒数第三音节。许多后缀对多音节英语单词重音位置的影响是首位的、决定性的,也即是说无论原来的单词重音在什么位置,都必须按照后缀给定的规则加以更改。我们可以根据
生成语言学与认知语言学的比较
生成语言学与认知语言学的比较 The Comparison between the Generative Linguistics and Cognitive Linguistics 姓名黄秋娟 班级英语09-4 Abstract In the present fields of linguistics studies, the generative linguistics and the cognitive linguistics have occupied prominent positions. They form the different view points on language. Then they put forward the different research goals and research methods. However, the generative linguistics and the cognitive linguistics are not different completely. They also have something in common from the above perspectives. According to this clue, the article makes the comparison between them. Key words: cognitive linguistics ; generative linguistics ; task of linguist; research method Introduction In 1957, a book of Chomsky, the Syntax Structure, was published, which announced the coming of At the same time, cognitive linguistics put forward new, challenging point of views when compared with the generative linguistics. No matter how complex they are, there are two aspects which should not be neglected. One is the task of the linguists, the other is the research methods. Chapter1 T ask of Linguists 1.1The Task of Generative Linguistics Linguists Generative linguistics distinguishes competence and performance, and focuses on the former one. They hold the opinion that the task of linguistics is studying the competence of speaker. The representative, Chomsky, hold the opinion that linguists ‘s object of study is the idealized speaker s’language, that is the language which fully meets the grammar rules. Because language is an independent sign system, linguists should ignore complex context factor, focus on the study of language itself, especially syntactic. This decides that an important task of linguists is to find common phenomenon of all languages through researching one grammar and to establish common rules shared by all human languages ----universal grammar. Therefore, linguists don't have to master a
《语音学和音系学引论》 第二版
《语音学和音系学引论》(第二版) 分章导读 第一章导言 本章是全书的开篇,分为四个小题目:语音学和音系学,理论和分析,与其他领域的关系,全书的框架。 第一小节介绍本学科的研究范围。作者提出语音学和音系学从两个层面研究人类语音的发生和感知:第一个层面是语音的解剖和生理层面,涉及发音器官及功能、语音、传递语音的声波、听者对语音声波的分析和处理。在这一层面上的研究称为“语音学”,可以细分为语音的解剖学和生理学、发音语音学、声学语音学和听觉(或感知)语音学。在第二个层面上,语音被看作是一种有目的的人类活动,具有传达意义的目的,在这一层面上的语音研究称为“音系学”,因此音系学常被看作是与特定语言内部的语音构造有关的。 第二小节论述理论和实践的关系,指出本书旨在介绍一种科学的理论方法,是与会不会发音或会不会模仿截然不同的。普通人通过说话表达意义,从不有意识地考虑自己的哪些器官在做什么样的动作,但语言学家所感兴趣的恰恰是说话者的这些细微的过程和活动,并对此进行分析,对器官的动作和活动如何表达意义作出解释。 第三小节首先讲解语音学和音系学对口语的记录和描述以及对英语拼写的指导作用,然后讨论其在外语教学中的应用和有关英语标准发音(RP)的争论,最后说明语音研究与科学技术的相互联系。从事录音、语言描述和语言教学工作的人对语音知识会有一定的兴趣,而从事听力学、语言矫治和言语病理学的人员需要具备坚实的语音学和音系学基础。二十世纪的科技进步为语音研究提供了新的手段,使语音研究的成果与生理学、物理学和电子学有了更密切的关系。近年来语音研究与科学技术结合在语音合成和语音-文本转换方面也有了可喜的进展,具有很高的商业价值和对理论探索的兴趣,使语音学家和音系学家得以更加紧密地与计算机和人工智能方面的专家进行合作。 第四小节叙述本书的框架,指出各章的目的和方法。本书在结构上比较特别,语音学和音系学的内容交叉进行。第二、三、六、七、八章明显属于语音学的内容,其余各章属于音系学内容。这样做的目的是模糊语音学和音系学的界限,使这两个在很长一段时间独立进行研究的学科更加一致起来。 思考题: 1.语音学和音系学在对语音的研究上有哪些异同点? 2.语音学和音系学与我们平时发音的关系是什么? 3.语音学和音系学知识可以应用于哪些其他领域? 4.语音学和音系学与语言学的其他分支学科有什么关系?
六年级英语辨音练习
六年级辩音练习(推荐生考试)一、下列各组词中,有一个词划线部分的读音与其他三个词划线部分的读音不同,请 选出。 ( )1. A. clothes B. home C. hello D. sorry ( )2. A. duty B. student C. bus D. excuse ( )3. A. clock B. those C. go D. coat ( )4. A. bus B. put C. cup D. up ( )5. A. down B. brown C. yellow D. how ( )6. A. desk B. next C. dress D. we ( )7. A. cake B. hat C. baby D. same ( )8. A. look B. room C. school D. broom ( )9. A. think B. thank C. they D. three ( )10. A. school B. Chinese C. chair D.teacher 二、下列各组词中,有一个词划线部分的读音与其他三个词划线部分的读音不同,请 选出。 1.A.with B .then C. clothes D. month 2.A.mean B. meant C. bread D .heavy 3.A.popular B .half C. aunt D.last 4.A.food B. noodle C. foot D. broom 5.A.don’t B. hope C. ago D. body 6.A.down B. crow C. how D. town 三、下列各组词中,有一个词划线部分的读音与其他三个词划线部分的读音不同,请 选出。 1、A、bag B、map C、thank D、class 2、A、no B、row C、one D、old 3、A、five B、bike C、fine D、English 4、A、desk B、yes C、eleven D、pencil 5、A、good B、book C、afternoon D、goodbye 6、A.go B.some C.son D.mother 7、A.window B.how C.now D.down 8、A.us B.mum C.duty D.but 9、A.China B.school C.chair D.teacher
语音学和音位学 练习题
第2章语音学和音位学 Phonetics&Phonology 1.phonetics is the study of_______. A.all the sounds that occur in the world’s languages B.sppech sounds used by human languages to represent C.the differernces between sounds used in human languages and sounds in nature D.how phonological differences can lead to misunderstanding 2./m, n/ are ____. A.fricatives B.dentals C.glides D.nasals 3./w, j/ belong to ____. A.fricatives B. dentals C. glides D. nasals 4.Which of the following vowel is the rounded vowel? A.[i:] B.[u:] C.[i] D.[a:] 5.In the field of phonology, which of the following does NOT belong to the suprasegmental features? A.stress B.tone C.intonation D.syllable 6.Classification of vowels are made up of the followings EXCEPT____. A.the position of the tongue B.the openness of the mouth C.The shape of the lip D.The width of the vowels 7.A sound which is capable of distinguishing one word or one shape of a word from another in a given language is a______. A.phoneme B.allophone C.phone D.allomorph 8./p, t, k / are______. A.fricatives B. affricates C. glides D.stops 9./kuku:/ is a bird’s call. The name of such a bird is CUCKOO which is an example of ______. https://www.360docs.net/doc/f116247045.html,nguage universals B.onomatopoeia C.teaching grammars D.morphs 10.The vowel [u:] in [fu:d] (food) is a____ vowel.
实验音系学
第五章实验音系学 Experimental Phonology 张杰 Jie Zhang 美国堪萨斯大学 University of Kansas, USA [内容提要] 语言学课本中的“音系”指的是可从语言中直接观察的语音的组织规律,但在生成语法中,“音系”特指为说话人对语音组织规律的潜在知识。这决定了以实验方法直接从说话人那里采集数据实际上是生成音系研究不可或缺的一部分。本章对实验音系学近年的发展作一个简单的概述,着重讨论实验对音系结构的认识所起的作用及其对现有音系理论的挑战,也指出汉语研究与实验音系学之间相互促进、相辅相成的关系。 Abstract The textbook definition of “phonology” refers to sound patterns directly observable from language. But in generative grammar, “phonology” refers to the speakers’ tacit knowledge of sound patterns. This determines that using experimental methods to collect data directly from the speakers is an indispensable part of research in generative phonology. This chapter summarizes the recent advances in experimental phonology, focusing on the roles that experiments play in our understanding of phonological patterns and the challenges experiments pose for current theories of phonology. It also discusses the roles of Chinese dialects in experimental phonology as well as the importance of experiments in Chinese phonological research. [关键词] 生成音系学(generative phonology),实验音系学(experimental phonology),优选论(Optimality Theory),随机优选论(stochastic Optimality Theory),最大熵值语法(Maximum Entropy Grammar)
六年级英语辨音练习
六年级辩音练习 一、下列各组词中,有一个词划线部分的读音与其他三个词划线部分的读音不同,请选出。 ( )1. A. clothes B. home C. hello D. sorry ( )2. A. duty B. student C. bus D. excuse ( )3. A. clock B. those C. go D. coat ( )4. A. bus B. put C. cup D. up ( )5. A. down B. brown C. yellow D. how ( )6. A. desk B. next C. dress D. we ( )7. A. cake B. hat C. baby D. same ( )8. A. look B. room C. school D. broom ( )9. A. think B. thank C. they D. three ( )10. A. school B. Chinese C. chair D.teacher 二、下列各组词中,有一个词划线部分的读音与其他三个词划线部分的读音不同,请选出。 1.A.with B .then C. clothes D. month 2.A.mean B. meant C. bread D .heavy 3.A.popular B .half C. aunt D.last 4.A.food B. noodle C. foot D. broom 5.A.don’t B. hope C. ago D. body 6.A.down B. crow C. how D. town 三、下列各组词中,有一个词划线部分的读音与其他三个词划线部分的读音不同,请选出。 1、A、bag B、map C、thank D、class 2、A、no B、row C、one D、old 3、A、five B、bike C、fine D、English 4、A、desk B、yes C、eleven D、pencil 5、A、good B、book C、afternoon D、goodbye 6、A.go B.some C.son D.mother 7、A.window B.how C.now D.down 8、A.us B.mum C.duty D.but 9、A.China B.school C.chair D.teacher 10、A.come B.nice C.coat D.clock 四、下列各组词中,有一个词划线部分的读音与其他三个词划线部分的读音不同,请选出。 1. A.think B.thank C.English D.student 2. A. bus B. put C. cup D. up 3. A.mother B.thirty C.father D.brother 4. A.my B.family C.duty D.sorry 5. A.please B.meet C.friend D.jeep 6. A.nice B.license C.come D.pencil 7. A.sister B.sit C.son D.his 8. A.daughter B.morning C.or D.wrong 9. A.father B.dad C.bag D.family 10.A.team B.jeep C.yellow D.me
英语音标发音规则70030
1 元音: 1) [i:] 字母组合:ee ea e ie three tree green sheep meet beef see seek eat tea meat leave lead teacher team mean speak clean please he she me piece receive ceiling 2) [i] 发音字母i y e sit picture it is list six mix fix fit pig big build miss myth many twenty happy dictionary defect decide delicious 3) [] 发音字母a bag hand and ant happy hat map mad bad black back glad flag shall man 4) [e] 字母组合ea e a head bread pleasure elephant electric remember sell shell lesson better bed desk hotel yes many any 5) [ε:] 字母组合ir ur ear ur or girl shirt skirt thirty thirteen third bird turn burn murder nurse turtle Thursday burger learn earn earth heard term her nerd serve
work worm work world 6) [ε] 字母组合er or ou ar o a e u teacher leader remember player speaker farmer powder doctor actor mayor author tractor delicious gracious pleasure familiar collar dollar together tomorrow today shallop lesson Washington control polite around account ago elephant manta banana Canada Japan china men listen famulus Saturday 7) [a:] 字母组合ar a car farm card arm garden fast class last glass plant aunt calm 8) [] 发音字母u o ou oo up supper lunch fun gun hunt cup bus come mother dose brother love above trouble rough flourish blood flood 9) []字母组合al or au our ar small wall talk tall hall ball call walk short more lord horse for forty sport door floor store author caught autumn
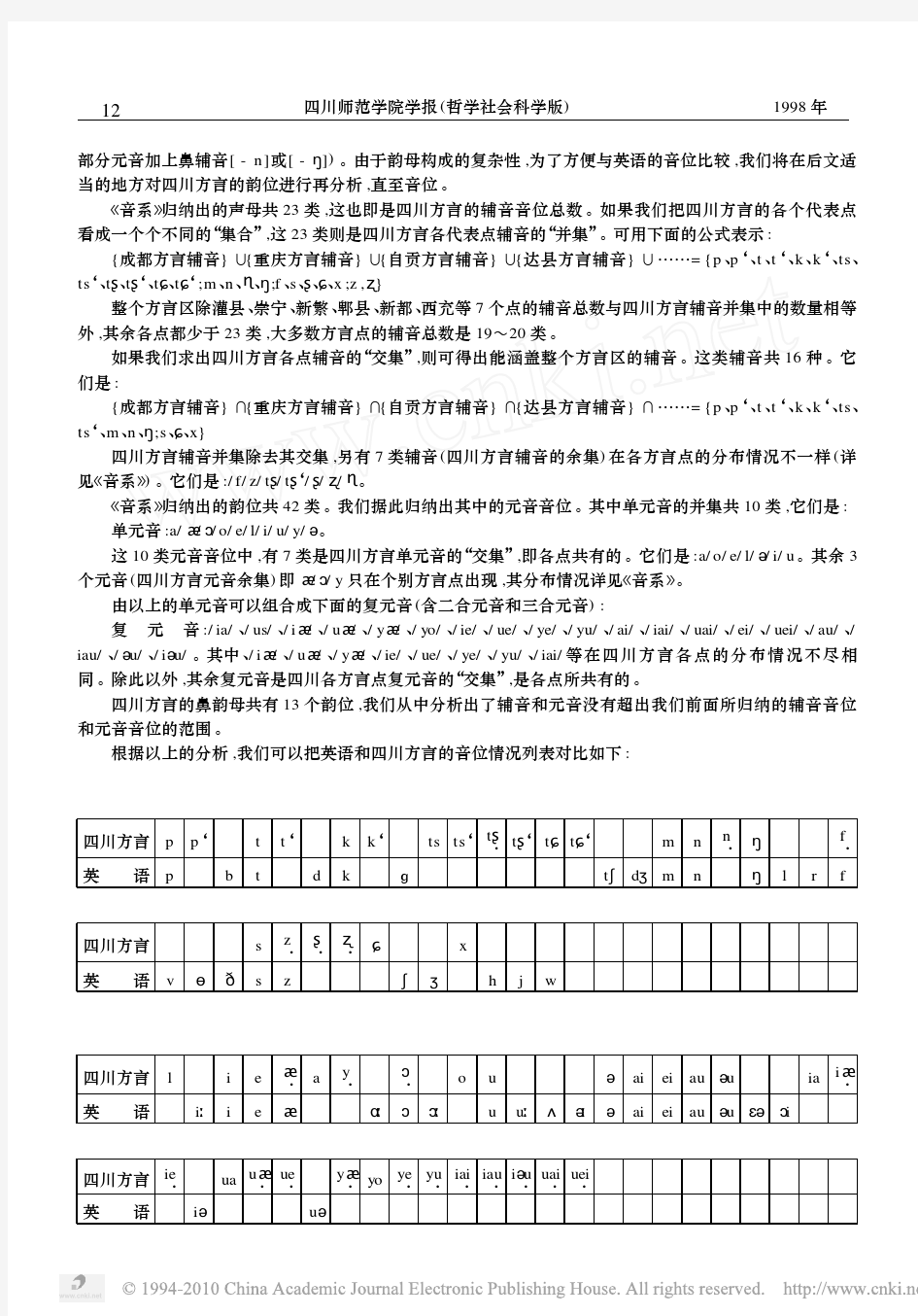
语言学复习资料 音系学(英语)
Chapter 2:Phonology I. Decide whether each of the following statements is True or False: 1. Voicing is a phonological feature that distinguishes meaning in both Chinese and English. 2 If two phonetically similar sounds occur in the same environments and they distinguish meaning, they are said to be in complementary distribution. 3. A phone is a phonetic unit that distinguishes meaning. 4. English is a tone language while Chinese is not. 5. In linguistic evolution, speech is prior to writing. 6. In everyday communication, speech plays a greater role than writing in terms of the amount of information conveyed. 7. Articulatory phonetics tries to describe the physical properties of the stream of sounds which a speaker issues with the help of a machine called spectrograph. 8. The articulatory apparatus of a human being are contained in three important areas: the throat, the mouth and the chest. 9. Vibration of the vocal cords results in a quality of speech sounds called voicing. 10. English consonants can be classified in terms of place of articulation and the part of the tongue that is raised the highest. 11. According to the manner of articulation, some of the types into which the consonants can be classified are stops, fricatives, bilabial and alveolar. 12. Vowel sounds can be differentiated by a number of factors: the position of tongue in the mouth, the openness of the mouth, the shape of the lips, and the length of the vowels. 13. According to the shape of the lips, vowels can be classified into close vowels, semi-close vowels, semi-open vowels and open vowels. 14. Any sound produced by a human being is a phoneme. 15. Phones are the sounds that can distinguish meaning. 16. Phonology is concerned with how the sounds can be classified into different categories. 17. A basic way to determine the phonemes of a language is to see if substituting one sound for another results in a change of meaning. 18. When two different forms are identical in every way except for one sound segment which occurs in the same place in the strings, the two words are said to form a phonemic contrast. 19. The rules governing the phonological patterning are language specific. 20. Distinctive features of sound segments can be found running over a sequence of two or more phonemic segments. II. Fill in each of the following blanks with one word which begins with the letter given: 21. A ____ refers to a strong puff of air stream in the production of speech sounds. 22. A___________ phonetics describes the way our speech organs work to produce the speech sounds and how they differ. 23. The four sounds /p/,/b/,/m/ and /w/ have one feature in common, i.e,
英语中的一些发音规则
英语语音知识 学习英语语音的几个概念 1、字母:英文有26个字母,分成5个元音字母a,e,i,o,u 和一个半元音字母y ,21个辅音字母b,c,d.f,g,h,j,k,l,m,n,p,q,r,s,t,v,w,x,y,z。 2、音素:音素是英语读音的最小单位。英语有20个元音音素和28个辅音音素。表示音素的符号叫音标.一个音标代表一个音素. 音标:标记单词读音.音标共有48个,其中元音20个辅音28.元音又分为单元音(12)和双元音(8)单元音又分为长元音(5)与短元音(7).辅音分为清辅音(11)与浊辅音(17). 3、音节:音节是读音的基本单位。元音是音节的主体,元音和它前面的辅音构成不间断音,在朗读时不能间断。任何单词的读音,都是分解为一个个音节朗读。音节分成重读音节、非重读音节。 1)、重读音节:英语的双音节或多音节的词中,有一个读得特别响亮的音节,叫重读音节。重读音节按重读音节的读音规则读音。 2)、非重读音节:按重读音节的读音规则读音,但不重读的音节。 在重读音节中,根据元音字母a,e,i,o,u 的读音,划分以下5种音节类型: (1)、开音节:有两种开音节,一种在元音字母后没有辅音字母,如:we 我们,no 没有,die 死。另一种在元音字母后有一个辅音字母(r除外),还有一个不发音的元音字母e,如:name 名字,like 象。 (2)、闭音节:元音字母后有辅音字母(r除外)时,这个元音字母构成的音节叫闭音节。如:map 地图,bag 书包。 ( 3)、-r音节:元音字母与辅音字母-r结合构成的音节。如:car 汽车,park 公园。 ( 4)、-re 音节:元音字母与-re 结合构成的音节。如:care 照料,here 这里。 ( 5)、元音字母组合音节:由元音字母和元音字母组合。如:wait 等候,tea 茶。 其中有些英语书中,把四、五类不算作一类,大家作一些了解即可。 发音规律:单词的拼写与单词的发音之音存在一定的联系和规律,我们把这种规律称之为发音规律 单词分类:(1)开音节单词(2)闭音节单词(3)R音节单词 开音节:以元音字结尾单词的音节,我们称之为开音节单词No he try photo time 闭音节:以辅音字结尾单词的音节,我们称之为闭音节单词. Bad bed not this bus much lesson R音节:以元音字母+R的音节我们称为R音节Ar or er ir ur Car for serve bird nurse 元音字母在开音节中发字母本身的音,在闭音节中发短音。 怎样注单词的音标 一般说来有四个步骤 (1)看单词音节类型(2)找出单词中哪些是字母组合 (3)找出单词中元音字母发音(4)标出单词的重读 重读 (1)在单词中的重读 (2)在句子中的重读 单词的重音:说话时发得比较重的音,使得某些音节突显,有时在多音节单词中还有第二个重音,它是比第一个重音念的轻些,但重于其它非重读音节,这叫次重读。主重读一般标在单词的左上角,次重读一般标在单词左下角。Examination
新版六年级英语下册课课练题库
LESSON 1 请你试着做以下练习: 单词辨音:从下列每组词中找出划线部分读音与众不同的一个: ()1、A. idea B. spring C. exciting D. sing ()2、A. school B. good C. foot D. football ()3、A. many B. class C. father D. last ()4、A. holiday B. Tuesday C. Wednesday D. Sunday 按要求写出下列各词: 1、eat(过去式) 2、is(过去式) 3、are(过去式) 4、go(过去式) 5、eat(三单) 6、go(三单) 7、do(过去式) 8、begin(三单) 9、city(复数) 10、see(过去式) 用动词的适当形式填空: 1、How (be) your holiday? 2、I (go) to Beijing yesterday? 3、you (have) a good time last week? 4、We (like) it very much. 5、Do you want (go) there? 选择填空: ( ) 1. The programmes very exciting last night. A. was B. were C. is D. are ( )2. She the Spring Festival. A.likes B. like C. to like D. liking ( )3.Where were you during the holiday? I at home. A. was B. were C. is D. are ( )4.I spent the holiday Tianjing. A.in B. on C. of D. to ( )5.I went to Beijing my parents. A.in B. with C. of D. in 句型转换: 1、My holiday was very wonderful.(根据划线部分提问) 2、I was at home during my holiday? 3、Did they have a good time?(同意句) 4、I like jiaozi.(否定句) 5、She is a student now.(用last year改写句子) Lesson2 请你试着做以下练习: 单词辨音:从下列每组词中找出划线部分读音与众不同的一个: ()1、A. English B. spring C. exciting D. sing ()2、A. watch B. that C. map D. thank ()3、A. think B. soon C. turn D. again ()4、A. England B. sing C. dancing D. evening 按要求写出下列各词: 1、were (原型动词) 2、was (原型动词) 3、turn(过去式) 4、listen(过去式) 5、have(三单) 6、sit (现在分词) 用动词的适当形式填空: 1、She is good at (sing and dance). 2、The book is very (excite). 3、I have three (toy car). 4、We like (play) football. 5、I’d like (go fishing) there? 选择填空: ( ) 1. Can you say it English? A. in B. of C. with D. for ( )2. The picture –book is very . A.interest B. interesting C. interested D. to interest ( )3.Where was she during the holiday? She at home. A. was B. were C. is D. are ( )4.Is Bill ? B.in B. on C. of D. to ( )5. Where were they during the holiday? They were Kunming. B.in B. with C. of D. in 句型转换: 1、She is counting the numbers.(根据划线部分提问)
