Suppress Winfree Turbulence by Local Forcing Excitable Systems

Suppress Winfree Turbulence by Local Forcing Excitable Systems
Hong Zhang,1Zhoujian Cao,2Ning-Jie Wu,1He-Ping Ying,1and Gang Hu3,2,*
1Zhejiang Institute of Modern Physics and Department of Physics,Zhejiang University,Hangzhou310027,China 2Department of Physics,Beijing Normal University,Beijing,100875,China 3Chinese Center for Advanced Science and Technology(World Laboratory),Beijing8730,China
(Received25November2004;published12May2005)
The occurrence of Winfree turbulence is currently regarded as one of the principal mechanisms underlying cardiac?brillation.We develop a local stimulation method that suppresses Winfree turbulence in three-dimensional excitable media.We?nd that Winfree turbulence can be effectively suppressed by locally injecting periodic signals to only a very small subset(around some surface region)of total space sites.Our method for the?rst time demonstrates the effectiveness of local low-amplitude periodic excitations in suppressing turbulence in3D excitable media and has fundamental improvements in ef?ciency,convenience,and turbulence suppression speed compared with previous strategies.
Therefore,it has great potential for developing into a practical low-amplitude de?brillation approach.
DOI:10.1103/PhysRevLett.94.188301PACS numbers:82.40.Ck,05.45.2a,82.20.2w
The problems of pattern formation and transition(in-cluding both ordered and turbulent patterns)are central to nonlinear science concerning extended systems.Different patterns represent different functions and properties in realistic systems.Some patterns are bene?cial and others harmful.Therefore,the topic of pattern and turbulence control for realizing wanted patterns and avoiding undesir-able ones is of broad interest in practical applications. Cardiac systems are typical excitable extended systems and support various patterns including rest patterns,scroll wave patterns,and turbulent patterns[1,2].Transitions from scroll wave patterns to turbulence(due to spiral wave breakup or scroll wave?lament expansion)may induce ventricular?brillation leading to serious cardiac disease,even to sudden cardiac death[3–8].Therefore, the problem of scroll wave and turbulence suppression to return the excitable media to a stable rest state is highly relevant to cardiac de?brillation[2].
The only clinical method currently accepted in perform-ing cardiac de?brillation is to apply a large shock to body surface or directly to cardiac muscle[9,10].These large-amplitude shocks may damage the cardiac tissue and cause serious pains[11].Therefore,in both nonlinear science and cardiac physiology?elds there is a growing experimental and theoretical effort to develop low-amplitude de?brilla-tion methods.However,most of the theoretical works regarding de?brillation of cardiac systems have considered only two-dimensional(2D)systems(or few coupled2D systems layered together)[12–14],while real ventricles are clearly3D objects.Global controls in3D media have been investigated[15,16].In particular,in[15]the authors have performed suppression of Winfree turbulence by applying global periodic forcing[17].The dif?culty of injecting an external signal into the whole3D space sites restricts the practical utilization of this global method.A number of previous experiments have explored the use of local-low-amplitude and high-frequency pacing as an al-ternative de?brillation technique[18].However,in these experiments,the pacing had only a local effect,resulting in only small areas of organized electrical activity.Once the pacing was suspended,the local region of capture was reinvaded by surrounding electrical activity,and the tissue remains in a state of?brillation.Calcium channel blocking with a drug has been suggested to improve the effect of local pacing[19].Nevertheless,how to use local-low-amplitude pacing for globally de?brillating cardiac tissue remains still an unsolved problem.
In the last decade,many local and global control meth-ods,including both feedback[20–23]and nonfeedback [24–26]methods,have been developed for taming chaotic extended systems.Most of the works on spatiotemporal chaos suppression have been restricted in1D or2D spatial systems.In this work we propose for the?rst time to suppress scroll waves and turbulence in3D excitable me-dia by applying local and periodic excitations and focus on optimizing turbulence suppression in terms of ef?ciency, convenience,and rapidity.
We use the general Barkley model,a simpli?ed mono-domain model,to describe the electrical activities of car-diac tissue[27].
@u
@t
1
"
u 1?u
u?
v b
a
r2u;
@v
@t
u?v;(1)
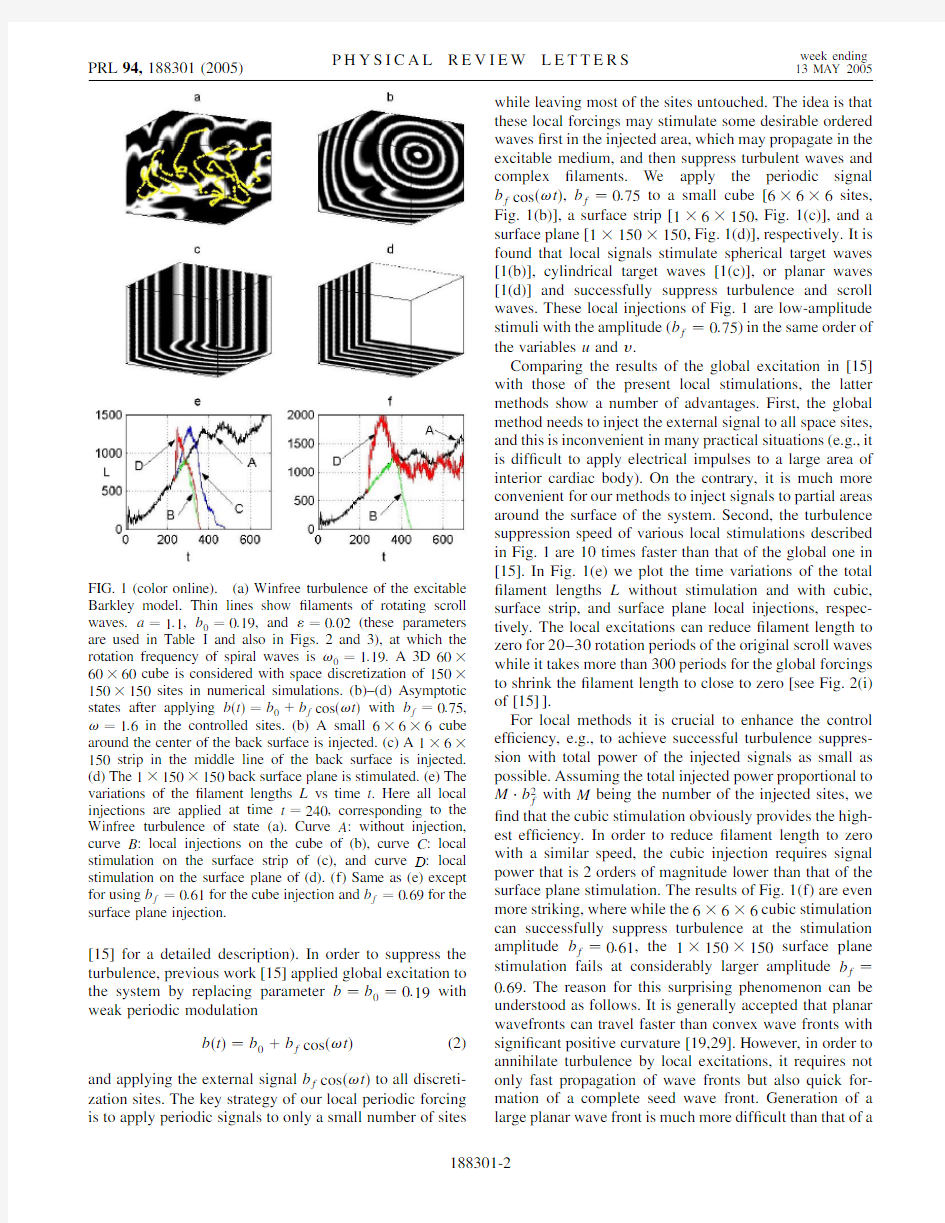
where"is the ratio of the time scale of the activator u(the voltages of cardiac cell membrane)over that of the inhibi-tor v(the transmembrane currents).Spiral waves of the2D Barkley model cannot break up to turbulence.On the other hand,in3D space this model can support scroll waves which can develop to Winfree turbulence with certain parameter combination due to negative-tension instability of vortex?laments[15,28].Figure1demonstrates our attempts in suppressing such turbulence through various local stimulations.An example of Winfree turbulence of the Barkley model is shown in Fig.1(a),where turbulence formation through the mechanism of?lament expansion and stretching is clearly shown(please refer to Fig.2of
[15]for a detailed description).In order to suppress the turbulence,previous work [15]applied global excitation to the system by replacing parameter b b 0 0:19with weak periodic modulation
b t b 0 b f cos !t
(2)
and applying the external signal b f cos !t to all discreti-zation sites.The key strategy of our local periodic forcing is to apply periodic signals to only a small number of sites
while leaving most of the sites untouched.The idea is that these local forcings may stimulate some desirable ordered waves ?rst in the injected area,which may propagate in the excitable medium,and then suppress turbulent waves and complex ?laments.We apply the periodic signal b f cos !t ,b f 0:75to a small cube [6 6 6sites,Fig.1(b)],a surface strip [1 6 150,Fig.1(c)],and a surface plane [1 150 150,Fig.1(d)],respectively.It is found that local signals stimulate spherical target waves [1(b)],cylindrical target waves [1(c)],or planar waves [1(d)]and successfully suppress turbulence and scroll waves.These local injections of Fig.1are low-amplitude stimuli with the amplitude (b f 0:75)in the same order of the variables u and v .
Comparing the results of the global excitation in [15]with those of the present local stimulations,the latter methods show a number of advantages.First,the global method needs to inject the external signal to all space sites,and this is inconvenient in many practical situations (e.g.,it is dif?cult to apply electrical impulses to a large area of interior cardiac body).On the contrary,it is much more convenient for our methods to inject signals to partial areas around the surface of the system.Second,the turbulence suppression speed of various local stimulations described in Fig.1are 10times faster than that of the global one in [15].In Fig.1(e)we plot the time variations of the total ?lament lengths L without stimulation and with cubic,surface strip,and surface plane local injections,respec-tively.The local excitations can reduce ?lament length to zero for 20–30rotation periods of the original scroll waves while it takes more than 300periods for the global forcings to shrink the ?lament length to close to zero [see Fig.2(i)of [15]].
For local methods it is crucial to enhance the control ef?ciency,e.g.,to achieve successful turbulence suppres-sion with total power of the injected signals as small as possible.Assuming the total injected power proportional to M b 2f with M being the number of the injected sites,we ?nd that the cubic stimulation obviously provides the high-est ef?ciency.In order to reduce ?lament length to zero with a similar speed,the cubic injection requires signal power that is 2orders of magnitude lower than that of the surface plane stimulation.The results of Fig.1(f)are even more striking,where while the 6 6 6cubic stimulation can successfully suppress turbulence at the stimulation amplitude b f 0:61,the 1 150 150surface plane stimulation fails at considerably larger amplitude b f 0:69.The reason for this surprising phenomenon can be understood as follows.It is generally accepted that planar wavefronts can travel faster than convex wave fronts with signi?cant positive curvature [19,29].However,in order to annihilate turbulence by local excitations,it requires not only fast propagation of wave fronts but also quick for-mation of a complete seed wave front.Generation of a large planar wave front is much more dif?cult than that of
a
FIG.1(color online).(a)Winfree turbulence of the excitable Barkley model.Thin lines show ?laments of rotating scroll waves.a 1:1,b 0 0:19,and " 0:02(these parameters are used in Table I and also in Figs.2and 3),at which the rotation frequency of spiral waves is !0 1:19.A 3D 60 60 60cube is considered with space discretization of 150 150 150sites in numerical simulations.(b)–(d)Asymptotic states after applying b t b 0 b f cos !t with b f 0:75,! 1:6in the controlled sites.(b)A small 6 6 6cube around the center of the back surface is injected.(c)A 1 6 150strip in the middle line of the back surface is injected.(d)The 1 150 150back surface plane is stimulated.(e)The variations of the ?lament lengths L vs time t .Here all local injections are applied at time t 240,corresponding to the Winfree turbulence of state (a).Curve A :without injection,curve B :local injections on the cube of (b),curve C :local stimulation on the surface strip of (c),and curve D :local stimulation on the surface plane of (d).(f)Same as (e)except for using b f 0:61for the cube injection and b f 0:69for the surface plane injection.
small spherical wave front.In our case the latter factor turns to be crucial and this leads to the possibility that the overall ef?ciency of the surface plane stimulation can be considerably lower than that of the cubic stimulation as we see in Figs.1(e)and1(f).In order to quantitatively com-pare the ef?ciencies of different schemes of turbulence suppression we present Table I which clearly shows that the local pacing on a cube has obviously the best overall properties with both lower power of injected signals and fast suppression of Winfree turbulence.We therefore focus our further effort on the detailed characterization of the cubic stimulation method.
As shown in Fig.2,we?nd that with the same Barkley model the results of the cubic stimulation depend on forc-ing parameters including forcing frequency,forcing ampli-tude,and injection area.Figure2shows the parameter range where local forcing can successfully suppress the existing turbulent scroll waves.There are several charac-teristic boundaries to this range.First,this range is re-stricted within a frequency zone[Fig.2(a)],and frequencies above or below do not provide successful turbulence suppression.The forcing frequency needs to be higher than a threshold!0(!0 1:19is the rotation frequency in2D system).This is because target waves generated by the local excitation can suppress existing scroll waves only if its frequency is higher than that of the latter[30].On the other hand,there is an upper bound to the effective forcing frequency.The target waves are generated by the periodic signals in the presence of turbu-lence and scroll waves.In order to effectively stimulate target waves,the forcing frequency should not be too far from!0for achieving a1:1resonant excitation from the existing scroll wave background.This gives rise to the upper bound of the zone of Fig.2(a).Second,the injection area and the forcing amplitude need to be suf?ciently large. Our cubic stimulation fails for n 4(n n n sites are injected)and b f 0:53[Figs.2(b)–2(d)].The reasons for these conditions are clear.In order to suppress turbulence with local forcing,the forcing amplitude needs to be larger than a threshold to stimulate spherical target wave fronts. In addition,the injection area needs to be larger than a threshold so that the wave fronts generated have a curva-ture smaller than a critical value to allow target wave propagation[31].Nevertheless,when n and b f are above the thresholds the speed of turbulence annihilation is no longer sensitive to n and b f.In other words,a further increase of n and b f does not effectively reduce the sup-pression time.The thresholdlike behaviors of the local cubic stimulation shown in Figs.2(b)–2(d)suggest some optimal parameter combination to achieve high control ef?ciency(e.g.,n 6,b f 0:7).This optimization al-lows fast turbulence suppression with low signal power, meaning fast curing with low electrical power application and low cardiac tissue disturbance during de?brillation. Figure3demonstrates the mechanism of suppression of Winfree turbulence by local cubic stimulation.The local excitation on a small cube stimulates spherical target wave fronts,which invade the turbulent surrounding and sup-press turbulence by pushing the?laments of the scroll waves out of the excitable medium during their propaga-tion[Figs.3(a)–3(d).In Figs.3(e)and3(f)we show how the ordered waves wipe out the remaining?laments and drive the system to the desirable rest state,after lifting the periodic forcing at the turbulent state of Fig.3(c).
In conclusion,we have developed an effective local periodic forcing method for eliminating Winfree turbu-lence in3D excitable media and revealed its desirable advantages of ef?ciency,convenience,and
rapidity. FIG.2.Turbulence suppression speed R 1=T of the cubic (n n n)injection plotted for different signal parameters where T is the time needed for turbulence suppression.
(a)n 6,b f 0:75.R plotted vs!.(b)b f 0:75,! 1:6. R vs n.(c)! 1:6,n 6,R vs b f.(d)The boundary of the controllable region in b f;n plane for! 1:6.Controllability is de?ned such that the?lament length shrinks to zero at t 500 for the given parameters.
TABLE https://www.360docs.net/doc/1214924257.html,parison of various excitation methods.The results denoted by ’s are cited from[15].
Global(150 150 150)Cube area around surface(6 6 6)Strip surface(1 6 150)Plane surface(1 150 150) The optimal frequency 1.2* 1.6 1.63 1.61
Excitation amplitude b f0.03*0.750.750.75
Number of sites injected M4:096 10621680025600
Total signal power Mb2
f 379012245014400
Time for turbulence suppression 1500*120196120
Finally,we emphasize that the model used in this Letter is too simple for simulating actual cardiac systems.In order to give some useful instruction for practical cardiac de?b-rillation,further investigation taking into account more realistic cardiac activities is needed.On the other hand,since the simpli?ed model catches the general feature of excitable media,our local excitation method is expected to be applicable for suppressing turbulence of excitable sys-tems in wide ?elds,e.g.,chemical reaction systems and neural network systems besides the cardiological ones.For instance,we have checked that our local excitation method works in other excitable and oscillatory models,such as the Ba
¨r equation and the Ginzburg-Landau equation.This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Nonlinear Science Project of China.
*Corresponding author.
Electronic address:ganghu@https://www.360docs.net/doc/1214924257.html,
Present address:Beijing-Hong Kong-Singapore Joint Center of Nonlinear and Complex Systems,Beijing Normal University Branch,Beijing.
[1] A.T.Winfree,When Time Breaks Down (Princeton
University Press,Princeton,NJ,1987).
[2]For reviews,see Chaos 8,No.1(1998)and 12,No.3
(2002).
[3] A.T.Winfree,Science 266,1003(1994).[4]R.A.Gray et al.,Science 270,1222(1995).
[5] A.V .Pan?lov and P.Hogeweg,Science 270,1223(1995);
Phys.Rev.E 53,1740(1996).
[6]L.Glass,Phys.Today 49,No.8,40(1996).
[7]R.A.Gray,A.M.Pertsov,and J.Jalife,Nature (London)
392,75(1998).
[8] F.X.Witkowski et al.,Nature (London)392,78(1998).[9]M.S.Eisenberg et al.,Sci.Am.254,No.5,25(1986).[10]L.W.Piller,Electronic Instrumentation Theory of Cardiac
Technology (Staples Press,London,1970).[11]L.Tung,Proc.IEEE 84,366(1996).
[12]V .N.Biktashev and A.V .Holden,J.Theor.Biol.169,101
(1994).
[13] A.V .Pan?lov et al.,Phys.Rev.E 61,4644(2000).
[14]S.Sinha,A.Pande,and R.Pandit,Phys.Rev.Lett.86,
3678(2001).
[15]S.Alnonso,F.Sagues,and A.S.Mikhailov,Science 299,
1722(2003).
[16]M.Vinson et al.,Nature (London)386,477(1997).
[17]Y .Braiman and I.Goldhirsch,Phys.Rev.Lett.66,2545
(1991).
[18]For example,E.G.Daoud et al.,Circulation 94,1036
(1996);J.M.Kalman et al.,J.Cardiovasc.Electrophysiol.7,867(1996).
[19] A.T.Stamp,G.V .Osipov,and J.J.Collins,Chaos 12,931
(2002).
[20]Hu Gang and Qu Zhilin,Phys.Rev.Lett.72,68(1994).[21]I.Aranson,H.Levine,and L.Tsimring,Phys.Rev.Lett.
72,2561(1994).
[22]V .S.Zykov et al.,Phys.Rev.Lett.92,018304(2004).[23]G.M.Hall and D.J.Gauthier,Phys.Rev.Lett.88,198102
(2002).
[24]I.Wygnanski,AIAA Report No.97-2117.
[25]G.Baier,S.Sahle,and J.Chen,J.Chem.Phys.110,3251
(1999).
[26]H.Zhang,B.Hu,and G.Hu,Phys.Rev.E 68,026134
(2003);H.Zhang et al.,Phys.Rev.E 66,046303(2002).
[27] D.Barkley,M.Kness,and L.S.Tuckerman,Phys.Rev.A
42,2489(1990).
[28]V .N.Biktashev,A.V .Holden,and H.Zhang,Phil.Trans.
R.Soc.A 347,611(1994);F.H.Fenton et al.,Chaos 12,852(2002).
[29]J.J.Tyson and J.P.Keener,Physica (Amsterdam)32D ,
327(1988).
[30]K.J.Lee,Phys.Rev.Lett.79,2907(1997);F.Xie,Z.Qu,
J.N.Weiss,and A.Gar?nkel,Phys.Rev.E 59,2203(1999).
[31]V .S.Zykov,Simulation of Wave Processes in Excitable
Media (Manchester University Press,New York,1987),p.
117.
FIG.3(color online).(a)–(d)Demonstration of the mecha-nism of the local cubic injection of Fig.1(b).Local periodic forcings generate spherical target waves near the injected area,which then propagate in the space and push turbulence and all scroll wave ?laments out of the excitable medium.(e),(f)The evolution of the medium after the injection signals are lifted at t 331[i.e.,from state (c)].The system approaches the desir-able rest state without the external forcing,and complete black (indicating the desirable rest state)is observed after t 360.
人教版九年级全册英语重点语法知识点复习提纲
人教版九年级全册英语重点语法知识点复习提纲 一. 介词by的用法(Unit-1重点语法) 1. 意为“在……旁”,“靠近”。 Some are singing and dancing under a big tree. Some are drawing by the lake. 有的在大树下唱歌跳舞。有的在湖边画画儿。 2. 意为“不迟于”,“到……时为止”。 Your son will be all right by supper time. 你的儿子在晚饭前会好的。 How many English songs had you learned by the end of last term? 到上个学期末你们已经学了多少首英语歌曲? 3. 表示方法、手段,可译作“靠”、“用”、“凭借”、“通过”、“乘坐”等。 The monkey was hanging from the tree by his tail and laughing. 猴子用尾巴吊在树上哈哈大笑。 The boy’s father was so thankful that he taught Edison how to send messages by railway telegraph. 孩子的父亲是那么的感激,于是他教爱迪生怎样通过铁路电报来传达信息。 4. 表示“逐个”,“逐批”的意思。 One by one they went past the table in the dark. 他们一个一个得在黑暗中经过这张桌子。 5. 表示“根据”,“按照”的意思。 What time is it by your watch? 你的表几点了? 6. 和take , hold等动词连用,说明接触身体的某一部分。 I took him by the hand. 我拉住了他的手。
材料收集系统
计算机工程学院 CBT模块 实习报告 选题名称:高校材料收集系统 专业:计算机科学与技术 班级: 姓名: xxx 学号: 指导教师: 2014 年 06 月 14 日
C B T模块实习任务书 指导教师(签章): 年月日
摘要: 我国高校对材料的收集本来就存在很多问题,其中一个比较突出的问题就是手工操作程度比较高,在高等学校扩招之前,这个问题并不是很突出,但是随着高校的扩招,高校需要处理的材料比过去增加了一倍以上,如何高效的收集这些材料成为一个急需解决的问题。随着科学技术的不断提高,计算机科学日渐成熟,其强大的功能人们已经深刻意识到,它已进入人类社会的各个领域并发挥着越来越重要的作用,同时与我们的生活和工作也息息相关。作为计算机应用的一部分,使用计算机对高校材料进行收集,具有手工收集所无法比拟的优点。例如:收集迅速、查找方便、可靠性高、存储量大、保密性好、成本低等。这些优点能够极大地提高高校材料收集的效率。在以人为本的设计理念下,本系统非常容易被接受,它具有简单实用、便于管理等特点。 关键词:材料收集;以人为本;简单实用
目录 1 课题综述 (3) 1.1 开发背景 (3) 1.2 开发意义 (3) 1.3 实现目标 (3) 2 系统分析 (3) 2.1 应用程序设计图 (3) 2.1.1 管理员登陆 (4) 2.1.2教师登录 (4) 2.1.3管理员管理模块 (5) 3 数据库设计 (6) 3.1 数据库概念设计 (6) 3.2 数据库逻辑设计 (7) 3.3 数据库物理设计 (7) 4 运行与代码 (8) 4. 1 管理员登录 (8) 4. 2 教师登录 (9) 4. 3 关键代码 (10) 总结 (12) 致谢 (13) 参考文献 (14)
人教版初中英语中考英语语法总结
中考英语语法总结 一、祈使句结构 1 祈使句结构 祈使句用以表达命令,要求,请求,劝告等。 1)祈使句有两种类型,一种是以动词原形开头,在动词原形之前加do (但只限于省略第二人称主语的句子)。 Take this seat. Do be careful. 否定结构: Don't move. Don't be late. 2)第二种祈使句以let开头。 Let 的反意疑问句 a. Let's 包括说话者 Let's have another try,shall we / shan't we = Shall we have another try b. Let us 不包括说话者 Let us have another try,will you / won't you = Will you please let us have another try
否定结构: Let's not talk of that matter. Let us not talk of that matter. 二、感叹句结构 感叹句结构 感叹句通常有what, how引导,表示赞美、惊叹、喜悦、等感情。 what修饰名词,how 修饰形容词,副词或动词,感叹句结构主要有以下几种: 掌握它的搭配,即掌握了感叹句的重点。 How +形容词+ a +名词+ 陈述语序 How+形容词或副词+ 陈述语序 What +名词+ 陈述语序 What+a+形容词+名词+ 陈述语序 What+ 形容词+复数名词+ 陈述语序 What+ 形容词+不可数名词+ 陈述语序 How clever a boy he is! How lovely the baby is! What noise they are making! What a clever boy he is!
企业内部管理系统
企业内部管理系统 Modified by JEEP on December 26th, 2020.
摘要 随着社会的发展,信息化成为时代的主题,企事业内部文档管理系统是企业管理中一个较重要的环节,是从业人员日常工作和个人信息的一项基本资料的保留,也是信息保密及防止资料外泄的重要手段,实现文档管理的电子化是现在的发展要求。企业内部文档管理系统有效的解决了纸质手工处理时效率低下和文件易丢失的问题,使得资料保留更完整查询更方便快捷。由此本课题进行企事业内部文档管理系统的研究是具有深刻意义的。 经过详细的需求分析和系统设计之后,系统选择以动态网页技术、SQL server 2000数据库开发工具等为开发工具,在此基础上基于B/S(浏览器/服务器)系统模式,实现数据库的连接并完成企事业内部文档管理系统的功能,以更好地满足各单位的需求。 经过详细设计后将系统主要分为以下的功能模块:目录管理模块、用户登录模块、文件管理模块、文件检索模块、系统管理模块,完成了用户信息管理及查询等方面的基本功能,更有效的提高系统处理的效率以适应人员的工作需求。 本文简单的介绍了系统的需求分析、总体设计,对数据库设计、详细设计以及系统实现的技术和方法进行了详细的说明。 社会在发展。一切都应该进步否则都将会逐步被淘汰,只有不断完善不断进取才可以更好适应于社会,生存与社会,发展于社会,才可以更好的服务于社会。 关键字:信息化、文档管理系统、、B/S系统模式 目录 8 8 9 9 2 5 5 5 6 7 8
第1章引言 1.1概述 社会的发展是多元的,由此在丰富了我们生活的同时也使得管理更繁冗,更沉重。应运而生的企事业内部文档管理系统,是利用计算机对公司内部人员和文档资料进行的信息管理,它可以对企业中的工作人员进行管理和查询,也可以对文档进行合理的处理如添加、删除、附加等等。文档管理信息化避免了以往手工录入的种种弊端,提高了信息管理的效率,节省了工作的时间和管理人员的劳力。而且它通过数据库的统一管理减少了数据处理的诸多错误,保证了系统管理的统一性,也增加了保密性。另外,文档信息是公司进行其它管理的前提,所以说内部文档管理系统是企业管理中一项重要的组成部分。采用文档管理的信息化不仅可以很好的避免以往的信息处理的弊端,还可以拓宽出更多的功能应用,比如说文件的权限设置,在系统中可以对重要的文件进行安全设置保证它的访问权限,增强文件的安全性。企业信息管理信息化在现在的发展中具有不可忽视的优势,也是未来企业管理不可缺少的,也是社会发展进步所必需,是进行一切行为的根本。 1.2课题背景 文档管理是企业日常管理的一部分,对于工作的日常运行来说是很重要的。然而现在许多机关、企事业单位的文档管理仍停留在基于纸介质的手工处理阶段,手工处理文档有许多缺点,比如说文档堆积多、重复劳动的工作多、分类管理困难、查询困难、利用率低、纸张浪费严重等问题,同时,另一个较严重的问题就是纸介质的文档,保存的时候容易受环境因素的影响,保存期限很受限制,而且纸质文档对森林的破坏也是较严重的。在企事业单位信息化建设中,文档管理的电子化是一项比较基本和典型的要求。企事业文档管理的电子化,有助于文档的长期保存、方便使用者的查询、也节省纸张开支。此外,电子文档的集中管理可以保证数据的统一性,也可对数据库的管理进行权限的设置,这就有助于保障文档的安全性和保密性。 针对这个方面国外发展相对较迅速,国外很多国家地方已配备了十分先进的管理信息系统,而且由许多国外开发的带有图形化界面的文档管理信息系统,以其高质量和高安全性一直享有相当好的口碑,但是这一类软件结构复杂,由于语言的障碍等诸多原因,不便于我们某些企业的迅速掌握,其次我们也可能很难接受相对高昂的价格,所以我们应该开发出拥有自主知识产权的高水平软件产品,为管理做好强大的支撑平台。现在,建立在计算机网络基础之上的企事业内部文档管理系统的应用和概念正逐渐的进入人们的生活,向文档管理信息化管理更进了一步。 在当前信息产业的强烈影响下企业的发展都在发生着变化,主要一个方面就发生在管理信息系统上。企业内部管理等多方面的需要,使现在的企业不得不建设管理信息系统,虽说现在已经有很多成型的税务MIS系统,但是多数是基于C/S结构开发的。针对
初三英语语法知识点
1) leave的用法 1.“leave+地点”表示“离开某地”。例如: When did you leave Shanghai? 你什么时候离开上海的? 2.“leave for+地点”表示“动身去某地”。例如: Next Friday, Alice is leaving for London. 下周五,爱丽斯要去伦敦了。 3.“leave+地点+for+地点”表示“离开某地去某地”。例如:Why are you leaving Shanghai for Beijing? 你为什么要离开上海去北京? 2) 情态动词should“应该”学会使用
should作为情态动词用,常常表示意外、惊奇、不能理解等,有“竟会”的意思,例如: How should I know? 我怎么知道? Why should you be so late today? 你今天为什么来得这么晚? should有时表示应当做或发生的事,例如: We should help each other.我们应当互相帮助。 我们在使用时要注意以下几点: 1. 用于表示“应该”或“不应该”的概念。此时常指长辈教导或责备晚辈。例如: You should be here with clean hands. 你应该把手洗干净了再来。 2. 用于提出意见劝导别人。例如: You should go to the doctor if you feel ill. 如果你感觉不舒服,你最好去看医生。
3. 用于表示可能性。should的这一用法是考试中常常出现的考点之一。例如: We should arrive by supper time. 我们在晚饭前就能到了。 She should be here any moment. 她随时都可能来。 3) What...? 与Which...? 1. what 与which 都是疑问代词,都可以指人或事物,但是what仅用来询问职业。如: What is your father? 你父亲是干什么的? 该句相当于: What does your father do? What is your father's job? Which 指代的是特定范围内的某一个人。如:
集体智慧收集系统及其方法与制作流程
本技术涉及集体智慧收集系统。本技术提供集体智慧收集系统及用此的集体智慧收集方法,包括:专家意见管理部,其接收和存储关于提出的事项由至少一个专家参与并传输的赞成或反对意见、有关该意见的至少一个依据以及说明等专家意见数据;背景知识管理部,其将所述专家意见管理部接收的至少一个专家意见数据提供给多个参与者,将多个专家意见数据加工后将此保存为有关所述事项的背景知识数据;参与数据管理部,其将保存在背景知识管理部的背景知识数据提供给参与者,接收所述参与者输入的参与者意见数据后处理为集体智慧收集数据;专家意见顺序管理部,其基于保存在所述参与数据管理部的所述集体智慧数据决定顺序,基于所述顺序更新必读意见数据和选读意见数据,提供给所述背景知识管理部。 技术要求 1.一种集体智慧接收系统,其特征在于,包括: 专家意见管理手段,其接收和存储关于提出的事项由至少一个专家参与并传输的赞成或 反对意见、有关该意见的至少一个依据以及说明等专家意见数据; 背景知识管理手段,其将所述专家意见管理部接收的至少一个专家意见数据提供给多个 参与者,基于对多个专家意见数据的同意和不同意数据、赋予分数数据分成至少一个必 读意见数据和至少一个选读意见数据,将此保存为有关所述事项的背景知识数据;
参与数据管理手段,其将保存在所述背景知识管理手段的背景知识数据提供给参与者,并接收所述参与者阅读所述背景知识数据后输入的对所述必读意见数据和选读意见数据的同意或不同意数据,以及包括赋予分数数据的参与者意见数据后处理成集体智慧收集数据; 专家意见顺序管理手段,其基于保存所述参与数据管理手段的所述参与者意见数据决定顺序,基于所述顺序更新必读意见数据和选读意见数据后提供给所述背景知识管理部。 2.根据权利要求1所述的集体智慧收集系统,其特征在于, 还包括:通过所述参加者或参与者收到少数的同意但对于赋分高的意见赋予顺序上升地位的少数意见管理手段。 3.根据权利要求2所述的集体智慧收集系统,其特征在于, 所述少数意见管理手段管理的意见是至少一个所述选读意见数据。 4.根据权利要求1所述的集体智慧收集系统,其特征在于, 还包括:所述参与者阅读所述必读意见数据和选读意见数据的过程中提供该意见数据的出处及反对或补充意见等信息数据的意见历史记录管理手段。 5.根据权利要求1所述的集体智慧收集系统,其特征在于, 还包括:基于保存在所述参与数据管理手段的集体智慧收集数据生成设定形态的报告书提供给所述事项的提供者,为了使所述事项的提供者验证,提供作为所述报告书基础的集体智慧数据的结果验证管理手段。 6.根据权利要求1所述的集体智慧收集系统,其特征在于, 根据所述专家意见顺序管理手段的所述必读意见数据和选读意见数据被实时更新。 7.根据权利要求1所述的集体智慧收集系统,其特征在于,
(完整版)人教版初中英语语法完整总结
1 . (see 、hear 、notice 、find 、feel 、listen 从句感觉/对什么有信心,自信 to 、look at ( 感官动词)+(sb. )+do sth. eg : I am/ feel confident of myspoken English. eg:I like watching monkeys jump. I feel that I can pass the test . 2 . (比较级and 比较级)表示越来越怎么样18. be + doing 表:1现在进行时2将来时 eg:the more the more 越来越多19 . be able to (+ v 原) = can (+ v 原)能够?? 3. a piece of cake =easy 小菜一碟(容易)eg : She is able to sing .= She can sing. 4 . agree with sb赞成某人20. be able to do sth. 能够干什么 5 . all kinds of 各种各样a kind of 一样e g :she is able to sing . 6 . all over the world = the whole world 整个21. be afraid to do (of sth 恐惧,害怕??世界eg : I'm afraed to go out at night . 7. along with 同??一道,伴随??I'm afraid of dog. eg : I will go along with you. 我将和你一起去22. be allowed to do 被允许做什么 The students planted trees along with their eg: I'm allowed to watch TV. 我被允许看电视teachers. 学生同老师们一起种树I should be allowed to watch TV. 我应该被允 8. as soon as 一怎么样就怎么样 许看电视 9 . as you can see 你是知道的(正如你所见)23. be angry with sb 生某人的气 10 . ask for ??求助向?要?(直接接想要的东e g : Don't be angry with me. 西)24. be angry with(at) sb for doing sth 12. ask sb to do sth询问某人某事 为什么而生某人的气 ask sb not to do 叫某人不要做某事25. be as ?原级?as 和什么一样 13 . at the age of 在??岁时eg : She is as tall as me. 她和我一样高 eg :I amsixteen. = I am at the age of sixteen . 26. be ashamed to 14. at the beginning of ????的起初;??27. be away from远离 的开始28. be away from 从??离开 15. at the end of + 地点/+时间最后;尽头;末29. be bad for对什么有害 尾eg : Reading books in the sun is bad for your eg : At the end of the day eyes. 在太阳下看书对你的眼睛不好 16. at this time of year 在每年的这个时候30. be born 出生于 17. be /feel confident of sth /that clause + 31. be busy doing sth 忙于做什么事
公司内部管理系统.
内部管理系统(人事管理系统+客户关系管理系统) 需 求 分 析 说 明 书 2015.10.9 一、人事管理系统部分 1、系统人员类型
公司的人员类型有以下几种:普通员工、部门经理、总经理、人事部经理和人事助 2、系统基本功能图解 2.1 基本机构图 2.2用例图解
3、功能详情 3.3.1 登录页面 需要登录的人员,对于不同的身份,他们的权限是不一样的。当用户输入ID和密码时,查询数据库,如用户名和密码正确,则进入相应的员工信息页面,若不正确,则提示用户用户名或密码错误,仍显示当前页面 3.3.2 查询员工资料 该模块主要查看自己/同事的资料,以更好促进公司员工之间的相互了解。同时也可以修改自己的部分信息。 主要功能包括:
●查询自己的详细信息:员工ID、员工姓名、电子邮件、所在部门名称(不是部门ID)、经理、 分机和自我介绍等 ●修改自己的自我介绍 ●修改自己的登录密码 ●查询、搜索其他同事的相关信息 3.3.3 员工资料管理 人事部门负责维护员工的基本资料。当员工第一天来公司报道时,人事部门将员工的基本资料(姓名、性别、出生日期、电子邮件及所属部门等)录入到数据中,并打印一份报道单给员工,上门列出了该员工的登录ID、公司邮件的地址、该员工的部门名称以及该员工的同部门同事列表。 主要功能包括: ●添加/修改/删除员工 ●按任意条件搜索员工(支持模糊查询) ●打印员工报道单 上传/修改员工的照片。 3.3.4请假模块 请假申请: 员工根据工龄享受年假。如果员工是本年度才加入公司的,则需根据报到日期按公司规章制度计算假期期数。员工请假不可以超过规定的请假小时数。员工可以通过本模块提交/查看/取消申请。 主要功能包括: ●显示员工本人年假总小时数、已使用小时数、当前可用小时数 ●用日历的方式显示可请假的日期,并突出显示国定节假日 查看员工本人某段时期内的请假记录、申请、批准状态等。 请假审核: 该模块只允许经理访问。经理可以查看下属的请假记录,批准/否决其中申请。
九年级英语全册所有必考语法点都在这里了,初三都在看!
一. 介词by的用法 1. 意为“在……旁”,“靠近”。 Some are singing and dancing under a big tree. Some are drawing by the lake. 有的在大树下唱歌跳舞。有的在湖边画画儿。 2. 意为“不迟于”,“到……时为止”。 Your son will be all right by supper time. 你的儿子在晚饭前会好的。 How many English songs had you learned by the end of last term? 到上个学期末你们已经学了多少首英语歌曲? 3. 表示方法、手段,可译作“靠”、“用”、“凭借”、“通过”、“乘坐”等。 The monkey was hanging from the tree by his tail and laughing. 猴子用尾巴吊在树上哈哈大笑。 The boy’s father was so thankful that he taught Edison how to send messages by railway telegraph. 孩子的父亲是那么的感激,于是他教爱迪生怎样通过铁路电报来传达信息。 4. 表示“逐个”,“逐批”的意思。 One by>他们一个一个得在黑暗中经过这张桌子。 5. 表示“根据”,“按照”的意思。 What time is it by your watch? 你的表几点了? 6. 和take , hold等动词连用,说明接触身体的某一部分。 I took him by the hand. 我拉住了他的手。 7. 用于被动句中,表示行为主体,常译作“被”、“由”等。
问题收集系统数据库
—现场采集EQMS电子化问题解决系统用户手操作册
目录 第一章功能介绍 (3) 第二章软件登陆 (4) 2.1 软件登陆 (4) 2.2 密码修改 (4) 2.3 退出系统 (6) 第三章操作步骤 (7) 3.1 生产工序问题采集 (7) 3.2 客户退回问题采集 (13) 3.3 仓库翻板问题采集 (18) 3.4 线上采集返修明细 (23) 3.5 线上采集综合查询 (24) 3.6 线上采集分析报表 (25) 3.7 线上采集TOP10排名 (29) 第四章常见问题(FAQ) (34)
第一章功能介绍 现场采集主要实现如下功能 ●质量数据的采集录入和查询 ●多维度数据汇总和报表统计 ●TOP问题分析决策及问题上升
第二章软件登陆 2.1 软件登陆 ●点击用户名:输入管理员分配给你的用户名 ●例如:周琴的用户名是”zhouqin” ●点击密码:输入管理员分配给你的密码,初始密码为1234 ●点击登陆按钮,登陆系统 2.2 密码修改
●登陆进入系统后,方能修改用户密码 ●查看欢迎您确认登陆系统的是你本人 ●点击修改密码按钮 ●弹出小窗口 ●输入旧密码:输入你原来的密码,如果忘记原密码请联系管理员 ●输入新密码:输入你想要设置的新密码 ●校验密码:再次输入你想要设置的新密码 ●点击确认按钮:确认你修改的信息 ●出现右图错误表示你输入的旧密码有误 ●出现下图错误表示你输入的两次密码数据不匹配,请核实你的输入密码信息,或重新录入
2.3 退出系统 ●正常的退出系统有助于信息数据的不丢失,不被篡改 ●尤其是多人使用同一台机器的时候,希望使用完系统的用户能安全退出 ●点击退出按钮安全退出
人教版英语九年级语法知识点
1. by + doing 通过……方式如:by studying with a group by 还可以表示:"在…旁","靠近","在…期间"、"用,""经过","乘车"等如:I live by the river. I have to go back by ten o'clock. The thief entered the room by the window. The student went to park by bus. 2. talk about 谈论,议论,讨论 如:The students often talk about movie after class. 学生们常常在课后讨论电影。talk to sb. === talk with sb. 与某人说话 3. 提建议的句子: ①What/ how about +doing sth.? 如:What/ How about going shopping? ②Why don't you + do sth.? 如:Why don't you go shopping? ③Why not + do sth. ? 如:Why not go shopping? ④Let's + do sth. 如:Let's go shopping ⑤Shall we/ I + do sth.? 如:Shall we/ I go shopping? 4. a lot 许多常用于句末如:I eat a lot. 我吃了许多。 5. too…to 太…而不能常用的句型too+adj./adv. + to do sth. 如:I'm too tired to say anything. 我太累了,什么都不想说。 6. aloud, loud与loudly的用法三个词都与"大声"或"响亮"有关。 ①aloud是副词,重点在出声能让人听见,但声音不一定很大, 常用在读书或说话上。通常放在动词之后。aloud没有比较级 形式。如: He read the story aloud to his son.他朗读那篇故事给他儿子听。 ②loud可作形容词或副词。用作副词时,常与speak, talk, laugh等动词连用,多用于比较级,须放在动词之后。如: She told us to speak a little louder. 她让我们说大声一点。 ③loudly是副词,与loud同义,有时两者可替换使用,但往往 含有令人讨厌或打扰别人的意思,可位于动词之前或之后。 如: He does not talk loudly or laugh loudly in public. 他不当众大声谈笑。 7. not …at all 一点也不根本不如: I like milk very much. I don't like coffee at all. 我非常喜欢牛奶。我一点也不喜欢咖啡。 not经常可以和助动词结合在一起,at all 则放在句尾 8. be / get excited about sth.=== be / get excited about doing sth. === be excited to do sth. 对…感兴奋如: I am / get excited about going to Beijing.=== I am excited to go to Beijing. 我对去北京感到兴奋。 9. ①end up doing sth 终止做某事,结束做某事如: The party ended up singing. 晚会以唱歌而结束。 ②end up with sth. 以…结束如: The party ended up with her singing. 晚会以她的歌唱而告终。 10. first of all 首先. to begin with 一开始later on 后来、随 11. also 也、而且(用于肯定句)常在句子的中间 either 也(用于否定句)常在句末 too 也(用于肯定句) 常在句末 12. make mistakes 犯错如:I often make mistakes. 我经常犯错。
内部管理系统详细设计方案完整版
内部管理系统详细设计 方案 集团标准化办公室:[VV986T-J682P28-JP266L8-68PNN]
内部管理系统详细设计方案【最新资料,WORD文档,可编辑】
设计方案简介 本设计方案是为内部管理程序开发而编写的,它包括了系统可行性研究,系统模块设计,模块的具体流程设计,一些需要进一步讨论或者研究的问题,需要的资料与硬件,数据表的定义等。但它没有包含关于编码的更多主题。例如编码的约定,注解的格式等。尽管这些问题对于实现这个系统都是非常重要的,但因为是设计方案它没有被包括在其中。 整个设计方案的大致目录如下: 一.内部管理系统项目方案(第2页-第20页) 1.项目开发背景(第2页) 2.项目可行性研究(第2页-第6页) 3.系统的大致模块划分(第6页-第18页) 3.1 市场部(第6页-第17页) 3.1.1 系统登陆模块(第8页) 3.1.2 系统设置模块(第8页) 3.1.3 事件添加模块(第8页-第9页) 3.1.4 事件查找编辑(第9页-第11页) 3.1.5 事件参数设置(第11页) 3.1.6 事件跟踪模块(第11页-第13页) 3.1.7 人事基本管理(第13页) 3.1.8 部门参数设置(第14页) 3.1.9 资料票据管理(第14页-第15页) 3.1.10 业务收入统计(第15页) 3.1.11 工资参数设置(第15页) 3.1.12 员工工资管理(第15页-第16页) 3.1.13 数据加密备份模块(第16页) 3.1.14 数据库管理模块(第16页-第17页) 3.2 网管部(第17页) 3.3 制作部(第17页-第18页) 4.数据流图(第19页-第20页) 4.1 市场部业务数据流图(第19页) 4.2 市场部工资数据流图(第20页) 二.内部管理系统所需资料(第21页) 三.内部管理系统所需硬件(第22页) 四.数据库设计(第23页-第25页) 1.上层数据库设计(第23页) 2.市场部数据库设计(第24页-第25页) 五.项目工作量估算(第26页) 内部管理系统项目方案
初三英语语法知识点归纳
初中英语语法速记口诀大全 很多同学认为语法枯燥难学,其实只要用心并采用适当的学习方法,我们就可以愉快地学会英语,掌握语法规则。笔者根据有关书目和多年教学经验,搜集、组编了以下语法口诀,希望对即将参加中考的同学们有所帮助。 一、冠词基本用法 【速记口诀】 名词是秃子,常要戴帽子, 可数名词单,须用a或an, 辅音前用a,an在元音前, 若为特指时,则须用定冠, 复数不可数,泛指the不见, 碰到代词时,冠词均不现。 【妙语诠释】冠词是中考必考的语法知识之一,也是中考考查的主要对象。以上口诀包括的意思有:①名词在一般情况下不单用,常常要和冠词连用;②表示不确指的可数名词单数前要用不定冠词a或an,确指时要用定冠词the;③如复数名词表示泛指,名词前有this,these,my,some等时就不用冠词。 二、名词单数变复数规则 【速记口诀】 单数变复数,规则要记住, 一般加s,特殊有几处: 末尾字母o,大多加s, 两人有两菜,es不离口, 词尾f、fe,s前有v和e; 没有规则词,必须单独记。 【妙语诠释】①大部分单数可数名词变为复数要加s,但如果单词以/t蘩/、/蘩/、/s/发音结尾(也就是单词如果以ch,sh,s,x等结尾),则一般加es;②以o结尾的单词除了两
人(negro,hero)两菜(tomato,potato) 加es外,其余一般加s;③以f或fe结尾的单词一般是把f,fe变为ve再加s;④英语中还有些单词没有规则,需要特殊记忆,如child—children,mouse—mice,deer—deer,sheep—sheep,Chinese—Chinese,ox—oxen,man—men,woman—women,foot—feet,tooth —teeth。 三、名词所有格用法 【速记口诀】 名词所有格,表物是“谁的”, 若为生命词,加“’s”即可行, 词尾有s,仅把逗号择; 并列名词后,各自和共有, 前者分别加,后者最后加; 若为无生命词,of所有格, 前后须倒置,此是硬规则。 【妙语诠释】①有生命的名词所有格一般加s,但如果名词以s结尾,则只加“’”;②并列名词所有格表示各自所有时,分别加“’s”,如果是共有,则只在最后名词加“’s”;③如果是无生命的名词则用of表示所有格,这里需要注意它们的顺序与汉语不同,A of B要翻译为B的A。 四、接不定式作宾语的动词 【速记口诀】 三个希望两答应,两个要求莫拒绝; 设法学会做决定,不要假装在选择。 【妙语诠释】三个希望两答应:hope,wish,want,agree,promise 两个要求莫拒绝:demand,ask,refuse 设法学会做决定:manage,learn,decide 不要假装在选择:petend,choose 五、接动名词作宾语的动词
雨水收集系统操作
系统操作说明及维护事项 一、系统工作概述 当降雨开始时,雨水经过安全分流井、电动弃流及过滤装置预处理之后流入雨水蓄水池,当雨水蓄水池的液位达到高水位时,雨水不再进入雨水蓄水池,从前段安全分流井排放掉。 雨水经过预处理后存储于地下蓄水池内,后面设置一体净化消毒器,通过增压泵提升并经一体化器将处理好的净化雨水送至清水箱,最后送至各用水点。 具体完成的功能如下: (1)、雨水在进入蓄水池之前,设置了安全分流井,当蓄水池高位时,多余的雨水可以在室外从安全井溢流掉,无需在地下室设置排污井; (2)、雨水弃流井配备我公司电动弃流装置和过滤装置,可以拦截前期的污染物,同时抛弃掉污染严重的前期雨水,使进入水池的雨水干净; (3)、系统控制采用雨水变频系统控制器进行控制,控制器采用芯片程序控制,配有显示屏,可以做到对各蓄水液位的监控,水泵的工作,净 化设备的控制,同时监控供水、排水、补水等情况; (4)、当蓄水池1使用至中水位时,蓄水池2自动向蓄水池1补水,当蓄水池2没水时,自来水补水会自动向蓄水池 1补水,以达到净化系统 能够持续的向清水池; (5)、当蓄水池使用至低水位时,雨水提升泵会停泵,自动保护; (6)、系统可以手自动供水并在缺水时进行自来水补水。 二、系统控制操作说明
在控制箱中分别都有手自动控制部分,都可以实现手动控制,自动控制两种模式,同时具备变频控制,下面分别介绍: 雨水系统控制箱: 该系统的控制箱是集成控制,对整个系统进行控制,面板介绍(如图是多功能控制箱): (1)、“手自动切换”是用于控制中的手动状态和自动状态以及停止状态的切换。 当自动状态时,净化设备会随用水需求自动启动进行净化处理,完成供水,当缺水时也会自动停泵,进行市政自来水补水。
企业内部通讯系统
开发背景和系统分析 视频001 前言 例001 企业内部通信系统 1.1 开发背景 ×××有限公司是一个中型的私营企业,企业内部的员工经常需要沟通和交流工作中的常见问题,频繁地使用电话会影响其他工作人员;另外,在实验室、档案室等需要安静气氛的环境中,使用电话沟通更不方便。为了便于职工之间的交流,或是工作信息的传递,企业内部通信系统的开发就显得十分迫切而重要。于是,该公司决定根据企业的内部结构,开发一个符合本企业工作流程的通信系统。它可以帮助企业快速搭建内部即时通信结构,大幅度提高企业的工作效率,使上级与下级之间的交流更方便。 1.2 需求分析 通过与×××有限公司的沟通和需求分析,要求企业内部通信系统具有以下功能。 ??系统操作简单,界面友好。 ??规范、完善的基础信息设置。 ??支持网络通信。 ??支持系统托盘和程序最小化功能,避免影响其他工作。 ??使用独立的本地数据库。 ??自动搜索和手动添加网络内的通信用户。 1.3 可行性分析 根据《GB8567-88计算机软件产品开发文件编制指南》中可行性分析的要求,制定可行性研究报告如下。 1.引言 ??编写目的 以文件的形式给企业的决策层提供项目实施的参考依据,其中包括项目存在的风险、项目需要的投资和能够收获的最大效益。 ??背景 ×××有限公司是一家中型的私有企业,为了提高企业的工作效率、实现信息化管理,公司决定开发企业内部通信系统。 2.可行性研究的前提 ??要求
企业内部通信系统必须提供网络通信功能,在通信过程中禁止使用聊天表情、文件传送等功能,避免资料外泄,或因发送错误而导致上级资料的丢失以及其他损失。最重要的是必须适应任何操作系统,也就是实现跨平台技术,因为企业内部的工作需要,工作环境中使用了多个操作系统来完成不同的工作。另外,系统不需要使用服务器中转和记录通信内容,可以独立完成通信任务,排除职工对领导监视工作进度等逆反心理。 ??目标 企业内部通信系统的目标是实现企业的信息化通信,提高企业通信能力,提高任务理解和执行能力,减少没有必要的人员流动和资金损耗,以最快的速度提升企业的市场竞争力。 ??条件、假定和限制 为实现企业的信息化通信,必须对操作人员进行培训,需要花费部分时间和精力来完成。为不影响企业的正常运行,企业内部通信系统必须在两个月的时间内交付用户使用。 系统分析人员需要2天内到位,用户需要3天时间确认需求分析文档。去除其中可能出现的问题,例如用户可能临时有事,占用4天时间确认需求分析。那么程序开发人员需要在1个月零19天的时间内进行系统设计、程序编码、系统测试、程序调试和网站部署工作。其间,还包括了员工每周的休息时间。 ??评价尺度 根据用户的要求,项目主要以企业通信功能为主,对于通信信息仅提供本次系统启动后的通信内容。由于职工人数过多,而公司在楼内公告板上的公告信息,难以及时通知每位职工,系统中公告功能要及时地通知所有员工最新的公告内容。 3.投资及效益分析 ??支出 根据系统的规模及项目的开发周期(两个月),公司决定投入4个人。为此,公司将直接支付3万元的工资及各种福利待遇。在项目安装及调试阶段,用户培训、员工出差等费用支出需要1万元。在项目维护阶段预计需要投入2万元的资金。累计项目投入需要6万元资金。 ??收益 用户提供项目资金12万元。对于项目运行后进行的改动,采取协商的原则根据改动规模额外提供资金。因此从投资与收益的效益比上,公司可以获得6万元的利润。 项目完成后,会给公司提供资源储备,包括技术、经验的积累,其后再开发类似的项目时,可以极大地缩短项目开发周期。 4.结论 根据上面的分析,在技术上不会存在问题,因此项目延期的可能性很小。在效益上公司投入4个人、2个月的时间获利6万元,效益比较可观。在公司今后发展上可以储备网站开发的经验和资源。因此认为该项目可以开发。 1.4 编写项目计划书 根据《GB8567-88计算机软件产品开发文件编制指南》中的项目开发计划要求,结合单位实际情况,设计项目计划书如下。
人教版九年级英语各单元知识点总结
九年级英语全册各单元知识点总结 Unit 1 How can we become good learners? 一、短语: 1.have conversation with sb. 同某人谈话 2.connect …with… 把…和…连接/联系起来 3.the secret to… ……的秘诀 4.be afraid of doing sth./to do sth. 害怕做某事 5.look up 查阅 6.repeat out loud 大声跟读 7.make mistakes in 在……方面犯错误8.get bored 感到厌烦 9.be stressed out 焦虑不安的10.pay attention to 注意;关注 11.depend on 取决于;依靠12.the ability to do sth. 做某事的能力 二、知识点: 1. by + doing:通过……方式(by是介词,后面要跟动名词,也就是动词的ing形式); 2. a lot:许多,常用于句末; 3. aloud, loud与loudly的用法,三个词都与“大声”或“响亮”有关。 ①aloud是副词,通常放在动词之后。 ①loud可作形容词或副词。用作副词时,常与speak, talk, laugh等动词连用,多用于比较级, 须放在动词之后。 ①loudly是副词,与loud同义,有时两者可替换使用,可位于动词之前或之后。 4. not …at all:一点也不,根本不,not经常可以和助动词结合在一起,at all 则放在句尾; 5. be / get excited about sth.:对…感到兴奋; 6. end up doing sth:终止/结束做某事;end up with sth.:以…结束; 7. first of all:首先(这个短语可用在作文中,使得文章有层次); 8. make mistakes:犯错make a mistake 犯一个错误; 9. laugh at sb.:笑话;取笑(某人)(常见短语) 10. take notes:做笔记/记录; 11. native speaker 说本国语的人; 12. make up:组成、构成; 13. deal with:处理、应付; 14. perhaps = maybe:也许; 15. go by:(时间)过去; 16.each other:彼此; 17.regard… as … :把…看作为…; 18.change… into…:将…变为…; 19. with the help of sb. = with one's help 在某人的帮助下(注意介词of和with,容易出题) 20. compare … to …:把…比作… compare with 拿…和…作比较; 21. instead:代替,用在句末,副词; instead of sth / doing sth:代替,而不是(这个地方考的较多的就是instead of doing sth,也就是说如果of后面跟动词时,要用动名词形式,也就是动词的ing形式) 22.Shall we/ I + do sth.? 我们/我…好吗? 23. too…to:太…而不能,常用的句型是too+形容词/副词+ to do sth.
人教版初中英语语法完整总结(最新最全)
1 .(see 、hear 、notice 、find 、feel 、listen to 、 look at (感官动词)+(sb.)+do sth. eg:I like watching monkeys jump. 2 .(比较级 and 比较级)表示越来越怎么样eg:the more the more 越来越多 3. a piece of cake =easy 小菜一碟(容易) 4 .agree with sb 赞成某人 5 .all kinds of 各种各样 a kind of 一样 6 .all over the world = the whole world 整个世界 7. along with同……一道,伴随…… eg : I will go along with you.我将和你一起去The students planted trees along with their teachers. 学生同老师们一起种树 8. as soon as 一怎么样就怎么样 9 .as you can see 你是知道的(正如你所见) 10 .ask for ……求助向…要…(直接接想要的东西) 12. ask sb to do sth 询问某人某事 ask sb not to do 叫某人不要做某事 13 .at the age of 在……岁时 eg:I am sixteen. = I am at the age of sixteen . 14.at the beginning of …… ……的起初;……的开始 15. at the end of +地点/+时间最后;尽头;末尾 eg : At the end of the day 16.at this time of year 在每年的这个时候 17. be /feel confident of sth /that clause +从句感觉/对什么有信心,自信 eg : I am / feel confident of my spoken English. I feel that I can pass the test . 18. be + doing 表:1 现在进行时 2 将来时 19 .be able to (+ v 原) = can (+ v 原)能够…… eg : She is able to sing .= She can sing. 20. be able to do sth. 能够干什么 eg :she is able to sing . 21. be afraid to do (of sth 恐惧,害怕…… eg : I'm afraed to go out at night . I'm afraid of dog. 22. be allowed to do 被允许做什么 eg: I'm allowed to watch TV. 我被允许看电视 I should be allowed to watch TV. 我应该被允许看电视 23. be angry with sb 生某人的气 eg : Don't be angry with me. 24. be angry with(at) sb for doing sth 为什么而生某人的气 25.be as…原级…as 和什么一样 eg : She is as tall as me. 她和我一样高 26.be ashamed to 27.be away from 远离 28. be away from 从……离开 29. be bad for 对什么有害 eg : Reading books in the sun is bad for your eyes. 在太阳下看书对你的眼睛不好 30. be born 出生于 31.be busy doing sth 忙于做什么事
