中考英语语法知识总结(全)

初中英语语法
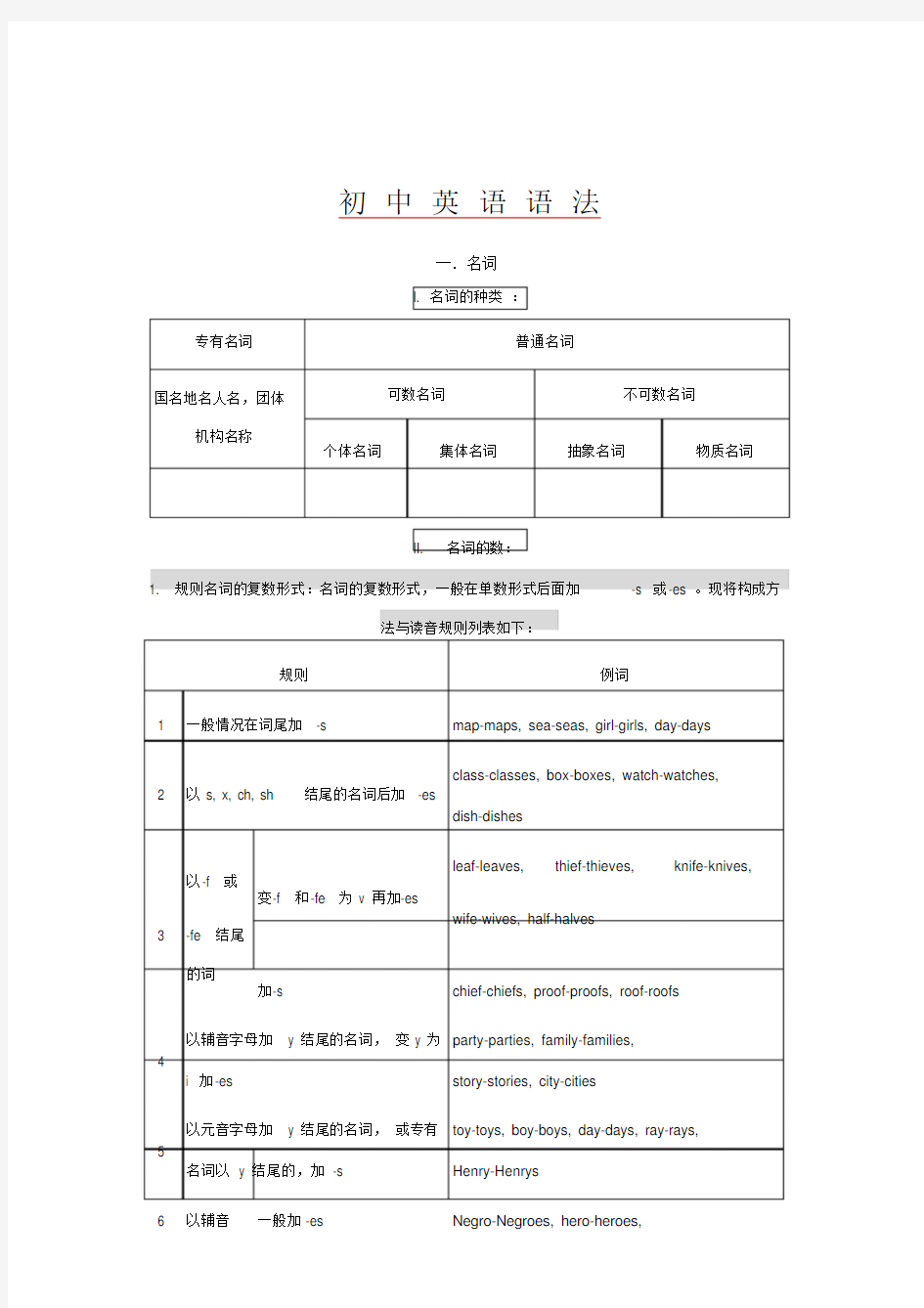
一.名词
I. 名词的种类:
专有名词普通名词
可数名词不可数名词
国名地名人名,团体
机构名称
个体名词集体名词抽象名词物质名词
II. 名词的数:
1. 规则名词的复数形式:名词的复数形式,一般在单数形式后面加-s 或-es 。现将构成方
法与读音规则列表如下:
规则例词
1 一般情况在词尾加-s map-maps, sea-seas, girl-girls, day-days
class-classes, box-boxes, watch-watches,
2 以s, x, ch, sh 结尾的名词后加-es
dish-dishes
leaf-leaves, thief-thieves, knife-knives, 以-f 或
变-f 和-fe 为v 再加-es
wife-wives, half-halves
3 -fe 结尾
的词
加-s chief-chiefs, proof-proofs, roof-roofs
以辅音字母加y 结尾的名词,变y 为party-parties, family-families,
4
i 加-es story-stories, city-cities
以元音字母加y 结尾的名词,或专有toy-toys, boy-boys, day-days, ray-rays,
5
名词以y 结尾的,加-s Henry-Henrys
6 以辅音一般加-es Negro-Negroes, hero-heroes,
字母加potato-potatoes, tomato-tomatoes
-o 结尾
piano-pianos, photo-photos, auto-autos,
不少外来词加-s
的名词
kilo-kilos, solo-solos
zero-zeros/zeroes, volcano-volcanoes/
两者皆可
volcanos
7 以元音字母加-o 结尾的名词加-s radio-radios, bamboo-bamboos, zoo-zoos
truth-truths, mouth-mouths, month-months, 8 以-th 结尾的名词加-s
path-paths,
2. 不规则名词复数:英语里有些名词的复数形式是不规则的,现归纳如下:
规则例词
man-men, woman-women, foot-feet,
1 改变名词中的元音字母或其他形式
goose-geese, mouse-mice
2 单复数相同sheep, deer, means, works, fish, yuan, jin,
3 只有复数形式trousers, clothes, thanks, goods, glasses,
4 一些集体名词总是用作复数people, police
class, family, crowd, couple, group, 部分集体名词既可以作单数(整体)
5 government, population, team, public,
也可以作复数(成员)
party
customs( 海关), times( 时代), spirits( 情
绪), drinks( 饮料), sands( 沙滩), papers( 文6 复数形式表示特别含义
件报纸), looks( 外表), brains( 头脑智力),
greens( 青菜)
7 表示加-s Americans, Australians, Germans, Greeks,
“某国Swedes, Europeans
人”
单复数同形Swiss, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese
以-man 或-woman结尾的改为
Englishmen, Frenchwomen
-men,-women
sons-in-law, lookers-on, passers-by,
将主体名词变为复数
story-tellers, boy friends
合成名
8
无主体名词时将最后一部分
词grown-ups, housewives, stopwatches
变为复数
将两部分变为复数women singers, men servants
III. 名词的所有格:
名词在句中表示所有关系的语法形式叫做名词所有格。所有格分两种:一是名词词尾加’s
构成,二是由介词of 加名词构成。前者多表示有生命的东西,后者多表示无生命的东西
1. ’s所有格的构成:
the boy ’s father, Jack ’s book, her
单数名词在末尾加’s
son-in- law’s photo,
一般在末尾加’the teachers ’room, the twins ’mother,
复数名词
不规则复数名词后
the chi ldren ’s toys, women ’s rights,
加’s
Dickens ’novels, Charles ’s job, the Smiths ’以s 结尾的人名所有格加’s或者’
house
表示各自的所有关系时, 各名词末Japan’s and America ’s problems, Jane ’s and
尾均须加’s Mary’s bikes
表示共有的所有关系时在最后一词Japan and America’s problems, Jane and Mary ’s 末加’s father
表示"某人家""店铺",所有格the doctor ’s, the barber ’s, the tailor ’s, my 后名词省略uncle ’s
2. ’s所有格的用法:
1表示时间today ’s newspaper, five weeks ’holiday
2 表示自然现象the earth ’s atmosphere, the tree ’s branches
表示国家城市等地方的the country ’s plan, the world ’s population, China’s 3
名词industry
the ship ’s crew, majority ’s view, the team ’s
4 表示工作群体
victory
5 表示度量衡及价值 a mile ’s journey, five dollars ’worth of apples
与人类活动有特殊关系
6 the life ’s time, the play ’s plot
的名词
a bird ’s eye view, a stone ’s throw, at one’s wit ’s
7 某些固定词组
end( 不知所措)
3. of 所有格的用法:
用于无生命的东西:the legs of the chair, the cover of the book
用于有生命的东西,尤其是有较长定语时:the classrooms of the first-year students
用于名词化的词:the struggle of the oppressed
二.冠词
冠词分为不定冠词(a, an ),定冠词(the ),和零冠词。
I. 不定冠词的用法:
1 指一类人或事,相当于 a kind of A plane is a machine that can fly.
2 第一次提及某人某物,非特指 A boy is waiting for you.
3 表示“每一”相当于every ,one We study eight hours a day.
4 表示“相同”相当于the same We are nearly of an age.
用于人名前,表示不认识此人或与 A Mr. Smith came t o visit you when you were out 5
某名人有类似性质的人或事That boy is rather a Lei Feng.
A couple of, a bit, once upon a time, in a
6 用于固定词组中
hurry, have a walk, many a time
用于quite, rather, many, half,
7 This room is rather a big one.
what, such 之后
用于so(as, too, how)+ 形容词之
8 She is as clever a girl as you can wish to meet.
后
II. 定冠词的用法:
1 表示某一类人或物The horse is a useful animal.
the universe, the moon, the Pacific
2 用于世上独一无二的事物名词前
Ocean
表示说话双方都了解的或上文提到过
3 Would you mind opening the door
的人或事
4 用于乐器前面play the violin, play the guitar
5 用于形容词和分词前表示一类人the reach, the living, the wounded
6 表示“一家人”或“夫妇”the Greens, the Wangs
用于序数词和形容词副词比较级最高
7 He is the taller of the two children.
级前
用于国家党派等以及江河湖海,山川群the United States, the Communist Party
8
岛的名词前of China, the French
9 用于表示发明物的单数名词前The compass was invented in China.
在逢十的复数数词之前,指世纪的某个
10 in the 1990 ’s
年代
11 用于表示单位的名词前I hired the car by the hour.
用于方位名词,身体部位名词,及表示
12 He patted me on the shoulder.
时间的词组前
III. 零冠词的用法:
专有名词,物质名词,抽象名词,人名Beijing University, Jack, China, love,
1
地名等名词前air
名词前有this, my, whose, some, no, I want this book, not that one. /
2
each, every 等限制Whose purse is this
季节,月份,星期,节假日,一日三餐
3 March, Sunday, National Day, spring
前
4 表示职位,身份,头衔的名词前Lincoln was made President of America.
5 学科,语言,球类,棋类名词前He likes playing football/chess.
6 与by 连用表示交通工具的名词前by train, by air, by land
husband and wife, knife and fork, day and 7 以and 连接的两个相对的名词并用时
night
8 表示泛指的复数名词前Horses are useful animals.
三.代词:
I. 代词可以分为以下七大类:
主格I, you, he, she, it, we, you, they
人称
1
代词
宾格me, you, him, her, it, us, you, them
2 物主形容词性my, your, his, her, its, our, their
代词名词性mine, yours, his, hers, its, ours, theirs
myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves,
3 反身代词
yourselves, themselves
4 指示代词this, that, these, those, such, some
5 疑问代词who, whom, whose, which, what, whoever, whichever, whatever
6 关系代词that, which, who, whom, whose, as
one/ some/ any, each/ every, none/ no, many/ much, few/ little/
a few/ a little,
7 不定代词
other/ another, all/ both, neither/ either
II. 不定代词用法注意点:
1. one, some 与any:
1) one 可以泛指任何人,也可特指,复数为ones。some多用于肯定句,any 多用于疑问句
和否定句。
One should learn to think of others.
Have you any bookmarks No, I don ’t have any bookmarks.
I have some questions to ask.
2) some 可用于疑问句中,表示盼望得到肯定的答复,或者表示建议,请求等。
Would you like some bananas ?
Could you give me some money ?
3) some 和any 修饰可数名词单数时,some表示某个,any 表示任何一个。
I have read this article in some magazine.
Please correct the mistakes, if any.
4) some 和数词连用表示“大约”,any 可与比较级连用表示程度。
There are some 3,000 students in this school.
Do you feel any better today ?
2. each 和every:
each 强调个别,代表的数可以是两个或两个以上,而every 强调整体,所指的数必须是三
个或三个以上。
Each student has a pocket dictionary. / Each (of us) has a dictionary. / We each
have a dictionary.
Every student has strong and weak points. / Every one of us has strong and weak points.
3. none 和no:
no 等于not any ,作定语。none 作主语或宾语,代替不可数名词,谓语用单数,代替可数
名词,谓语单复数皆可以。
There is no water in the bottle.
How much water is there in the bottle None.
None of the students are (is) afraid of difficulties.
4. other 和another:
1) other 泛指“另外的,别的”常与其他词连用
如:the other day, every other week, some other reason, no other way, the other
特指两者中的另外一个,复数为the others 。
如:He held a book in one hand and his notes in the other.
Two students in our class failed, but all the others passed the exam.
2) another 指“又一个,另一个”无所指,复数形式是others ,泛指“别的人或事”
如:I don ’t like this shirt, ple ase show me another (one).
The trousers are too long, please give me another pair / some others.
Some like football, while others like basketball.
5. all 和both, neither 和either
all 表示不可数名词时,其谓语动词用单数。both 和all 加否定词表示部分否定,全部否定
用neither 和none.
All of the books are not written in English. / Not all of the books are written in
English.
Both of us are not teachers. / Not both of us are teachers. / Either of us is a teacher.
四.形容词和副词
I. 形容词:
1) 形容词作定语通常前置,但在下列情况后置:
修饰some, any, every, no 和body, thing, one nobody absent, everything
1
等构成的复合不定代词时possible
以-able, -ible 结尾的形容词可置于有最高级或the best book available, the only 2
only 修饰的名词之后solution possible
3 alive, alike, awake, aware, asleep 等可以后置the only person awake
4 和空间、时间、单位连用时 a bridge 50 meters long
5 成对的形容词可以后置 a huge room simple and beautiful
6 形容词短语一般后置 a man difficult to get on with
2) 多个形容词修饰同一个名词的顺序:
代词数词性状形容词
冠词
冠词
指示代词大小
前的序数基数性质新旧国籍材料不定代词长短颜色
形容词词状态温度产地质地代词所有形状
词
格
名
词the
beautif
all a secon large
one ul new black Chinese silk
both this d short
four good cool yellow London stone such another next square
poor
your
3) 复合形容词的构成:
1 形容词+名词+ed kind-hearted 6 名词+形容词w orld-famous
2 形容词+形容词d ark-blue 7 名词+现在分词p eace-loving
3 形容词+现在分词o rdinary-looking 8 名词+过去分词s now-covered
4 副词+现在分词h ard-working 9 数词+名词+ed three-egged
5 副词+过去分词n ewly-built 10 数词+名词t wenty-year
II. 副词
时间副soon, now, early, finally, always, often, frequently,
1 5频度副词
词once, recently seldom, never
地点副here, nearby, outside,
2 6 疑问副词h ow, where, when, why
词upwards, above
方式副hard, well, fast, slowly, how, when, where, why,
3 7连接副词
词excitedly, really whether, however, meanwhile
程度副almost, nearly, very,
4 8 关系副词w hen, where, why
词fairly, quite, rather
III. 形容词和副词比较等级:
级和最高级
,比较
级和最高级
的构成一般是在形容
原级
。比较
形容词
和副词
的比较
等级
分为
词和副词后加-er 和-est ,多音节和一些双音节词前加more 和most。
1. 同级比较时常常用as?as?以及not so(as) ?as?
如:I am not so good a player as you are.
2. 可以修饰比较级的词有:
much, many, a lot, even, far, a bit, a little, still, yet, by far, any, a great deal 。
3. 表示一方随另一方变化时用“the more ?the more ?”句型。
如:The harder you work, the more progress you will make.
4. 用比较级来表达最高级的意思。
如:I have never spent a more worrying day.
5. 表示倍数的比较级有如下几种句型:
Our school is three times larger than yours./Our school is four times as large as
yours./Our school is four times the size of yours.
6. 表示“最高程度“的形容词没有最高级和比较级。
如:favourite, excellent, extreme, perfect 。
五.介词
I. 介词分类:
about, across, after, against, among, around, at, below,
1 简单介词
beyond, during, in, on
inside, into, onto, out of, outside, throughout, upon, within, 2 合成介词
without
according to, because of, instead of, up to, due to, owing to,
3 短语介词
thanks to
4 双重介词from among, from behind, from under, till after, in between
分词转化成的介
5 considering( 就而论), including
词
形容词转化成的
6 like, unlike, near, next, opposite
介词
II. 常用介词区别:
1 表示时间的in, on, at at 表示片刻的时间,in 表示一段的时间,on 总是与日子有关
since 指从过去到现在的一段时间,和完成时连用,from 指从2 表示时间的since, from
时间的某一点开始
in 指在一段时间之后,after 表示某一具体时间点之后或用在
3 表示时间的in, after
过去时的一段时间中
境范围
之
内,on 指与什么毗邻
,to 指在某环表示地理位置的in, on, in 表示在某范围
4
to
外
表示“在?上”的on,
5 on 只表示在某物的表面上,in 表示占去某物一部分
in
,与in 有关,across 表示在表面上通表示“穿过
”的through 表示从内部通过
6
through, across过,与on 有关
表示“关于”的about,
7 about 指涉及到,on 指专门论述
on
8 between 与among的区别b etween 表示在两者之间,among用于三者或三者以上的中间
besides 与except 的区besides 指“除了?还有再加上”,except 指“除了,减去什
9
别么”,不放在句首
with 表示具体的工具,in 表示材料,方式,方法,度量,单位,10 表示“用”的in, with
语言,声音
as 意为“作为,以?地位或身份”,like为“象?一样”,指
11 as 与like 的区别
情形相似
in 通常表示位置(静态),into 表示动向,不表示目的地或位
12 in 与into 区别
置
词
六.动
I.动词的时态:
1.动词的时态一共有16 种,以ask为例,将其各种时态的构成形式列表如下:
现在时过去将来时过去将来时
一般ask / asks asked shall/will ask should/would ask
am/is/are was/were shall/will be
进行should/would be asking asking asking asking
shall/will have should/would have
完成have/has asked had asked
asked asked
完成进have/has been shall/will have should/would have been
had been asking
行asking been asking asking
2. 现在完成时与一般过去时的区别:
1) 现在完成时表示过去发生的动作或存在的状况,但和现在有联系,强调的是对现在造成
的影响或结果,它不能同表示过去的时间状语连用,汉译英时可加“已经”等词。简言之,
利用过去,说明现在。
如:I have already read the novel written by the world-famous writer. ( 已经看过,
且了解这本书的内容)
2) 一般过去时只表示过去发生的动作或状态,和现在无关,它可和表示过去的时间状语连
用,汉译英时可加“过”,“了”等词。简言之,仅谈过去,不关现在。
如:I read the novel last month. ( 只说明上个月看了,不涉及现在是否记住)
I lived in Beijing for ten years. (只说明在北京住过十年,与现在无关)
3. 现在完成时与现在完成进行时的区别:
两者都可以表示“从过去开始一直持续到现在”,在含义上如着重表示动作的结果时,多用现在完成时,如着重表示动作一直在进行,即动作的延续性时,则多用现在完成进行时。一
般不能用于进行时的动词也不能用于现在完成进行时。
I have read that book. 我读过那本书了。
I have been reading that book all the morning. 我早上一直在读那本书。
4. 一般将来时的表达方式:
将来时用法例句
1 will/shall+ 动词表示将来发生的动作或存在的状态My sister will be ten next
原形year.
It ’s going to clear up.
be going to+ 动词
含有“打算,计划,即将”做某事,
2 We’re going to have a
原形或表示很有可能要发生某事
party tonight.
go, come, start, move, leave,
be + doing 进行时He is moving to the south.
3 arrive 等词可用进行时表示按计划
表示将来Are they leaving for Europe
即将发生的动作
I was about to leave when
be about to + 动the bell rang.
表示安排或计划中的马上就要发生的
4
词原形动作,后面一般不跟时间状语The meeting is about to
close.
We’re to meet at the
5 be to + 动词原形表示按计划进行或征求对方意见
school gate at noon.
The meeting starts at five 一般现在时表示将时刻表上或日程安排上早就定好的事o’clock.
6
来情,可用一般现在时表示将来The plane leaves at ten
this evening.
II. 动词的被动语态:
常用被动语常用被动语
构成构成态态
1 一般现在时am/is/are asked 6 过去进行时was/were being asked
2 一般过去时was/were asked 7 现在完成时have/has been asked
3 一般将来时shall/will be asked 8 过去完成时had been asked
4 过去将来时should/would be asked 9 将来完成时will/would have been
asked
动
含有情态
5现在进行时a m/is/are being asked 10 can/must/may be asked
词的
后加not ,短语
动词
的被动
态不可漏掉
动词
词或情态
被动
语态
的否定式是在第一个助动
构be
其中介副词
。固定结
going to, used to, have to, had better变为被动态时,只需将其后的动词变为被动
态。如:
Trees should not be planted in summer. / The boy was madefun of by his classmates.
Newspapers used to be sent here by the little girl.
汉语有一类句子不出现主语,在英语中一般可用被动结构表示。如:
It is believed that ?
It is generally considered that ?
注It is said that ?
意It is well known that ?
事It must be pointed out that ?
项It is supposed that ?
It is reported that ?
It must be admitted that ?
It is hoped that ?
意义
:如:
形式常表示被动
下面主动
The window wants/needs/requires repairing.
The book is worth reading twice.
The door won ’t shut. / The play won ’t act.
The clothes washes well. / The book sells well.
The dish tastes delicious. / Water feels very cold.
下面词
或短语
没有被动
态
:
leave, enter, reach, become, benefit, cost, equal, contain, last, lack, fit,
fail, have, appear, happen, occur, belong to, take place, break out, come about, agree with, keep up with, consist of, have on, lose heart 等等
七.情态
动
词
I. 情态动词基本用法:
情态
动词
用法否定式疑问
式与简
答
能力(体力,智力,技能)can not / cannot
can Can?do??
允许
或许
可(口语
中常用)/can ’t do
Yes,?can.
可能性(表猜测
,用于否定句
could couldn ’t do
或疑问
句中)
N o,?can’t.
May?do?Yes, ?may. may 可以(问句中表示请求)
may not do
No,?mustn’t/can ’t.
可能,或许
(表推测
)
祝愿(用于倒装句中)
might might not do M ight ?do?Yes,?might No,?might not.
Must?do?Yes, ?must.
必须
,应
该(表主观
要求)must not/mustn ’t
must No,?needn’t/don ’t 肯定,想必(肯定句中表推测
)do
have to.
Do?have to do ??
只好,不得不(客观
的必须
,
have to don’t have to do Yes,?do.
有时
态人称变
化)
No,?don’t.
Ought?to do ??
应当(表示义务责任,口语中ought not
ought to Yes,?ought.
多用should to/oughtn ’t to do
No,?oughtn’t.
将要,会
Shall ?do??
s hall not/shan ’t
方意见
用于一三人称征求对
shall Yes,?shall.
诺、命do
用于二三人称表示许
No,?shan’t.
等
令、警告、威胁
应当,应该(表义务责任)should
should Should?do?
备意味)not/shouldn ’t do
本该
(含有责
will 意愿,决心will not/won ’t do Will ?do??
请求,建议,用在问句中would Yes,?will.
would
would
委婉No,?won’t.
比较
not/wouldn ’t do
Dare?do??
句dare not/daren ’t
敢(常用于否定句和疑问
dare Yes,?dare.
中)do
No,?daren’t.
需要Need?do??
need not/needn ’t
need Yes,?must.
句
(常用于否定句和疑问
必须
do
中)No,?needn’t.
Used?to do ??
used Yes,?used.
not/usedn ’t/use n No,?use(d)n ’t. used to过去常常(现在已不再)
’t to do Did?use to do ??
didn ’t use to do Yes,?did.
No,?didn ’t.
II. 情态动词
must, may, might, could, can 表示推测:
现在存在的一般状态
进行;must + be doing 推测可能例。must + do(be) 是推测
以must为
过
的事情。
生
可能已经
正在进
行的事情;must +have done 是推测
发
1. must “肯定,一定”语气强,只用于肯定句中。
He must be a man from America. / He must be talking with his friend. / He must have
already arrived there.
2. may 和might “也许”,后者语气弱,更没有把握。可用于肯定句和否定句。
He may not be at home. / They might have finished their task.
3. can 和could “可能”,could 表示可疑的可能性,不及can’t语气强,用于肯定、否
句中。
定、疑问
The weather in that city could be cold now.
We could have walked there; it was so near. (推测某事本来可能发生,但实际上没有
发生)
Can he be in the office now No, he can ’t be there, for I saw him in the library
just now.(语气很强,常用于疑问句和否定句中)
III. 情态动词注意点:
1. can 和be able to:
于成功”,而can 无法表达此意。Be able
都可以表示能力。但be able to 可以表达“某事终
to 有更多的时态。另外,两者不能重叠使用。
2. used to 和would:
used to 表示过去常常做现在已经不再有的习惯,而would 只表示过去的习惯或喜好,不涉
在。
及现
3. need 和dare 作情态动词和实义动词的区别:
:needn’t/daren ’t do ;
时常用于否定句和疑问
句。其形式为
动词
两者作情态
Need/dare?do??
可用于肯定句,否定句和疑问
句。其形式为
:
词时
义动
做实
need(needs/needed)/dare(dares/dared) to do, don’t(doesn ’t/didn ’t) need/dare to
do
词
语动
八.非谓
I. 非谓语动词的分类、意义及构成:
构成
非谓语形
特征和作用式
时态和语态否定式复合结构
to do
具有名词,副词和形容词的作
to be done for sb.
to be doing
用
不定式to have been to do
to have
在句中做主、宾、定、表和状
done sth.
done
语
being done
现在分doing
在非谓
having been
词having done
语前加具有副词和形容词的作用
done
分词
not
在句中做定、表、宾补和状语过去
done
分词
being done
doing sb’s
具有名词的作用动名词having been
having done doing
在句中做主、宾、定和表语
done
II. 做宾语的非谓语动词比较:
情况常用动词
只接不定式做宾hope, want, offer, long, fail, expect, wish, ask, decide, pretend, 语的动词manage, agree, afford, determine, promise, happen
mind, miss, enjoy, imagine, practise, suggest, finish, escape,
excuse, appreciate, admit, prevent, keep, dislike, avoid, risk,
resist, consider
只接动名词做宾
语的动词或短语
can’t help, feel like, succeed in, be fond of, object to, get down
to, be engaged in, insist on, think of, be proud of, take pride in, set about, be afraid of, be tired of, look forward to, devote
中考英语语法点简要归纳
初中英语知识总结 一、出现以下词,用do填空: can , could, may, must, need, had better, why not, make, have to, let’s, see, hear, watch, notice, Will ( Would ) you please…? 二、出现以下词,用to do 填空: would like, want, begin, start, hope, decide, ask, wish, have something to do, tell, take time, it’s time, remember, forget, learn, teach, try, stop, plan, adj./疑问词后,take ,allow, encourage, warn, It’s +形容词+to do something, discuss, know, refuse, invite , get order, like, offer, lend, make up one’s mind to do, set one’s mind to do, enough, need 三、出现以下词,用doing 填空: finish, like, enjoy, mind, keep, be busy, there be, do some…, go doing, prevent, be worth, spend, practice, feel like, thank somebody for doing something ,stop, excuse somebody for doing something, can’t help, prefer…to…,look forward to…hate, mention, hav e fun doing,介词:at, in , on, of , from, for, about, with, without, ,make a contribution to, be used to, hear, see, watch, notice, listen, 四、基数词的特殊变化 one---first ; two---second; three---third; five---fifth; eight---eighth; nine---ninth; twelve---twelfth; twenty---twentieth; twenty-one---twenty-first 五、代词的变化: 主格―――宾格――所有格(adj.)――所有格(n.)―反身代词 I --------me--------my----------mine-------------myself you------you--------your-------yours------------yourself he-------him---------his-------his-------------himself she------her----------her-------hers-----------herself it-------it----------its--------its--------- itself we-------us---------our---------ours------------ourselves you------you--------your--------yours---------yourselves they-----them------their--------theirs---------themselves 六、表示天气的词 1. sun—sunny 2. cloud—cloudy 3. rain—rainy 4. wind—windy 5. fog—foggy 6. mist—misty 7. snow—snowy 8. shower—showery 七、表示方向的词 1. east—eastern—easterner(s) 2south—southern—southerner(s) 3.west—western—westerner(s) 4.north—northern—northerner(s) 八、国家---国家的(人) 1.China—Chinese 2.Japan—Japanese 3.Germany--German 4.Canada—Canadian 5.Sweden—Swedish 6. Australia--stralian
初中英语语法知识总结
英语作文常用谚语、俗语 1、A liar is not believed when he speaks the truth. 说谎者即使讲真话也没人相信。 2、A little knowledge is a dangerous thing. 一知半解,自欺欺人。 3、All rivers run into sea. 海纳百川。 4、All roads lead to Rome. 条条大路通罗马。 5、All work and no play makes Jack a dull boy. 只会用功不玩耍,聪明孩子也变傻。 6、A bad beginning makes a bad ending. 不善始者不善终。 7、Actions speak louder than words. 事实胜于雄辩。 8、A faithful friend is hard to find. 知音难觅。 9、A friend in need is a friend indeed. 患难见真情。 10、A friend is easier lost than found. 得朋友难,失朋友易。 11、A good beginning is half done. 良好的开端是成功的一半。 12、A good beginning makes a good ending. 善始者善终。 13、A good book is a good friend. 好书如挚友。 14、A good medicine tastes bitter. 良药苦口。 15、A mother's love never changes. 母爱永恒。
初中英语语法知识点总结
英语语法大全 初中英语语法学习提纲 一、词类、句子成分和构词法: 1、词类:英语词类分十种: 名词、形容词、代词、数词、冠词、动词、副词、介词、连词、感叹词。 1、名词(n.):表示人、事物、地点或抽象概念的名称。如:boy, morning, bag, ball, class, orange. 2、代词(pron.):主要用来代替名词。如:who, she, you, it . 3、形容词(adj..):表示人或事物的性质或特征。如:good, right, white, orange . 4、数词(num.):表示数目或事物的顺序。如:one, two, three, first, second, third, fourth. 5、动词(v.):表示动作或状态。如:am, is,are,have,see . 6、副词(adv.):修饰动词、形容词或其他副词,说明时间、地点、程度等如:now, very, here, often, quietly, slowly. 7、冠词(art..):用在名词前,帮助说明名词。如:a, an, the. 8、介词(prep.):表示它后面的名词或代词与其他句子成分的关系。如in, on, from, above, behind. 9、连词(conj.):用来连接词、短语或句子。如and, but, before .
10、感叹词(interj..)表示喜、怒、哀、乐等感情。如:oh, well, hi, hello. 2、句子成分:英语句子成分分为七种:主语、谓语、宾语、定语、状语、表语、宾语补足语。 1、主语是句子所要说的人或事物,回答是“谁”或者“什么”。通常用名词或代词担任。如:I’m Miss Green.(我是格林小姐) 2、谓语动词说明主语的动作或状态,回答“做(什么)”。主要由动词担任。如:Jack cleans the room every day. (杰克每天打扫房间) 3、表语在系动词之后,说明主语的身份或特征,回答是“什么”或者“怎么样”。通常由名词、代词或形容词担任。如:My name is Ping ping .(我的名字叫萍萍) 4、宾语表示及物动词的对象或结果,回答做的是“什么”。通常由名词或代词担任。 如:He can spell the word.(他能拼这个词) 有些及物动词带有两个宾语,一个指物,一个指人。指物的叫直接宾语,指人的叫间接宾语。间接宾语一般放在直接宾语的前面。如:He wrote me a letter . (他给我写了一封信) 有时可把介词to或for加在间接宾语前构成短语,放在直接宾语后面,来强调间接宾语。如:He wrote a letter to me . (他给我写了一封信) 5、定语修饰名词或代词,通常由形容词、代词、数词等担任。如: Shanghai is a big city .(上海是个大城市)
初中英语语法大全知识点总结
英语语法大全 初中英语语法 学习提纲 一、词类、句子成分和构词法: 1、词类:英语词类分十种: 名词、形容词、代词、数词、冠词、动词、副词、介词、连词、感叹词。 1、名词(n.):表示人、事物、地点或抽象概念的名称。如:boy, morning, bag, ball, class, orange. 2、代词(pron.):主要用来代替名词。如:who, she, you, it . 3、形容词(adj..):表示人或事物的性质或特征。如:good, right, white, orange . 4、数词(num.):表示数目或事物的顺序。如:one, two, three, first, second, third, fourth. 5、动词(v.):表示动作或状态。如:am, is,are,have,see . 6、副词(adv.):修饰动词、形容词或其他副词,说明时间、地点、程度等。如:now, very, here, often, quietly, slowly. 7、冠词(art..):用在名词前,帮助说明名词。如:a, an, the. 8、介词(prep.):表示它后面的名词或代词与其他句子成分的关系。如in, on, from, above, behind. 9、连词(conj.):用来连接词、短语或句子。如and, but, before . 10、感叹词(interj..)表示喜、怒、哀、乐等感情。如:oh, well, hi, hello. 2、句子成分:英语句子成分分为七种:主语、谓语、宾语、定语、状语、表语、宾语补足语。 1、主语是句子所要说的人或事物,回答是“谁”或者“什么”。通常用名词或代词担任。如:I’m Miss Green.(我是格林小姐) 2、谓语动词说明主语的动作或状态,回答“做(什么)”。主要由动词担任。如:Jack cleans the room every day. (杰克每天打扫房间) 3、表语在系动词之后,说明主语的身份或特征,回答是“什么”或者“怎么样”。通常由名词、代词 或形容词担任。如:My name is Ping ping .(我的名字叫萍萍) 4、宾语表示及物动词的对象或结果,回答做的是“什么”。通常由名词或代词担任。如:He can spell the word.(他能拼这个词) 有些及物动词带有两个宾语,一个指物,一个指人。指物的叫直接宾语,指人的叫间接宾语。间 接宾语一般放在直接宾语的前面。如:He wrote me a letter . (他给我写了一封信) 有时可把介词to或for加在间接宾语前构成短语,放在直接宾语后面,来强调间接宾语。如: He wrote a letter to me . (他给我写了一封信) 5、定语修饰名词或代词,通常由形容词、代词、数词等担任。如:
2014中考英语语法知识点总结:动词
2014中考英语语法知识点总结:动词 一定要记牢动词的现在分词,过去式,过去分词。比如:catch 的过去式和过去分词(caught,caught) 你可能就不知道吧?痛下决心,好好记一记吧。先讲系动词。 系动词:大概是最简单的动词了。你只需注意的是系动词除了be的形式之外,还有become,get,grow,turn,sound,look,smell,taste等,它们不能单独作谓语,必须和作表语的词语(如形容词, 名词等) 连用, 所以用的时候,可要小心为是呀!如:It smells delicious.(它闻起来味道很美)。delicious 是形容词,不是副词。 情态动词:首先要记住情态动词后必跟动词原形。 must的意思是"应当,必须",侧重于说话者的主观看法,没有时态变化,其否定式是mustn't,在"Must I(we) ...."的疑问句中,须注意的是其否定回答常用needn't。如:Must I go?(我一定要走吗?) No,you needn't.(不,不必。) need意为"需要"。既可作实义动词,又可作情态动词,因此在用法上需要注意。作实义动词时,need后跟名词,动名词,或不定式。如:I need to go. (我得走了。) 作情态动词时,后跟动词原形。如:You needn't come tomorrow if you are busy. (如果你忙,明天就不必来了。) 实意动词:我们跑(run),我们跳(jump),我们笑(laugh),这些都得用实意动词来表达。我们一起来看一看一些特殊的词吧。它们在接动名词和不定式时意义有所不同。 stop:这个词让好多同学大伤了一番脑筋,到底什么时候加to do,什么时候加 doing 呢?两者意义又有什么不同呢?OK, Come with me. 看下面两个句子。 When the teacher came in, they stopped to read. When the teacher came in, they stopped talking. 第一句的意思是"当老师进来时,他们停下来开始读书"。而第二句的意思是 "老师进来时,他们停止了说话"。所以stop to do sth表示"停止正在做的事情去干另一件事"。而stop doing表示"中断正在做的某事"。 forget,remember,regret 这三个词用法基本相同,只要记住+doing 表示"事情已经做过",+to do表示"事情还未做"就可以了。
初中英语语法大全汇总
初中英语语法大全汇总 (一) 一.词类( ) 名词英文名称(缩写为n.) 表示人或事物的名称例词等 冠词英文名称(缩写为.) 用在名词前帮助说明名词所指的人和或事物。例词a() 代词英文名称(缩写为) 用来代替名词、形容词或是数词例词 形容词英文名称(缩写为.) 用以修饰名词,表示人或事物的特征 例词. 数词英文名称(缩写为.) 表示数量或是顺序。例词 动词英文名称(缩写为v.) 表示动作或状态。例词() 副词英文名称(缩写为.) 修饰动词、形容词或其他副词。例词 介词英文单词(缩写为.) 表示名词、代词等和句中其他词的关系。例词. 连词英文单词(缩写为.) 用来连接词与词、短语与短语或句与句。例词. 感叹词英文单词(缩写为.) 表示说话时的喜悦、惊讶等情感。例词. 二.名词() 1.总的说来,名词分专有名词和普通名词两类。 专有名词: 表示具体的人,事物,地点或机构的专有名称。 中国亚洲北京。 专有名词的第一个字母要大写。 普通名词: 表示某些人,某类事物,某种物质或抽象概念的名称。例如: 老师茶改革 普通名词又可进一步分为四类 1) 个体名称: 表示单个的人和事物。 马汽车房间苹果风扇照片 2) 集体名称: 表示一群人或一些事物的名称。 人们家庭军队政府集团 3) 物质名词:表示物质或不具备确定形状和大小的个体的物质。 火钢空气水牛奶 4)抽象名词:表示动作,状态,品质或其他抽象概念。 劳动健康生活友情耐力 2.名词按其所表现的事物的性质分为可数名词和不可数名词。 可数名词( )有复数形式,如: a 不可数名词( )一般没有复数形式. 抽象名词, 物质名词和专有名词一般是不可数名词。 沙糖 有少数名词即可作可数名词,也可作不可数名词,但含义不同。 玻璃玻璃杯纸报纸,文件 名词的功能 名词在句中作主语, 宾语,介词宾语,宾语补助语,表语以及名词短语作状语。
中考英语语法笔记整理大全
中考英语语法笔记整理大全 2015.8 名词 表示人、事物、地方、现象或抽象概念等的名称的词。 知识梳理:提纲挈领,抓住重点和难点! 、名词的分类 注:1. 加冠词。 2、有普通名词构成的专有名词前要用定冠词“ the”但它不大写。 3、有些不可数名词有时表示为具体的东西时,则变为可数名词,而且以四上也有了变化。eg. beer ----a beer 一杯啤酒,work--- a work 工厂,著作,glass---a glass 一个玻璃杯,room 空间---a room 一个房间 、名词的数:表示可以计算数目的人或物称为可数名词。 1、可数名词有单、复数两种形式:可数名词的单数形式要在名词前加“a或an”;复数形式是在名词 后加-s或-es
2. ①改变单数名词中的元音字母 eg. man--men, woma n—wome n, tooth —teeth, foot—feet, goose—geese, mouse--mice ②单复数同形eg. Chinese-Chinese, deer-deer, fish-fish, sheep-sheep,… ③由man和woman构成的合成词,每个名词都要变复数 eg. a man doctor—men doctors, a woma n teacher--wome n teachers 注意:有些名词表示一种物体具有不可分割的相同的两部分,在使用时只有复数形式 eg. trousers, clothes, glasses, shorts,scissors, etc有些名词从形式上看是复数, 实际上是单数(其后的谓语动词要用单数).eg. maths, phyiscs, politics, news 3. 不可数名词:表示不能计算数目的人或物,称为不可数名词。他们前面不能用a/an,没有复数形式。物质名词和抽象名词都属于不可数名词。不可数名词一般只有单数形式,但有其特殊用法: ⑴同一个词,变成复数形式,意义不同。eg. food食物---foods各种食物, time 时间---times 时代,green 绿色---greens 青菜 (2) 有些不可数名词用复数代指具体的事物 eg. hope ---hopes 希望hardship --- hardships 艰苦 (3) 物质名词在表示数量时,常用某个量词+of来表示 eg. a cup of tea, seve n pieces of bread, severalbags of rice, … 三、名词的所有格 名词的所有格是表示名词之间的所有关系,有两种表示形 式,一种是在名词后+';另一种疋用of,表示 …勺”。 1. (1) 一般词的所有格,直接在词尾+'。eg. Mr. Mott 's robot, children 's clothes (2)以s结尾的名词所有格只在词尾+ ' eg. teachers 'books (3)两人共有的物体,则在第二个名词后
(完整版)人教版初中英语语法和知识点总结以及练习题
初一至初三全程英语知识点总结及练习 初一年级(上) 【知识梳理】 I. 重点短语 1. Sit down 2. on duty 3. in English 4. have a seat 5. at home 6. look like 7. look at 8. have a look 9. come on 10. at work 11. at school 12. put on 13. look after 14. get up 15. go shopping II. 重要句型 1. help sb. do sth. 2. What about ?? 3. Let's do sth. 4. It's time to do sth. 5. It's time for ? 6. What's ?? It is ?/ It's ? 7. Where is ?? It's ?. 8. How old are you? I'm ?. 9. What class are you in? I'm in ?. 10. Welcome to ?. 【名师讲解】 1.in/on 在表示空间位置时, in 表示在某个空间 的范围以内, 例如: There is a bird in the tree. 树上有只鸟。 2. this/that/these/those (1) this 常常用来指在时间、地点上更接近讲话 人的人和事, 时间、地点上离讲话人更远一点的 人和事, look in that one over there. 11. What's ?plus ?? It's ?. 12. I think ? 13. Who's this? This is ?. 14. What can you see ? I can see ?. 15. There is (are) ?. 16. What color is it (are they)? It's (They're) ? 17. Whose ?is this? It's ?. 18. What time is it? It's ?. III. 交际用语 1. Good morning, Miss/Mr ?. 2. Hello! Hi! 3. Nice to meet you. Nice to meet you, too. 4. How are you? I'm fine, thank you/thanks. And you? 5. See you. See you later. 6. Thank you! You're welcome. 7. Goodbye! Bye! 8. What's your name? My name is ?. 9. Here you are. This way, please. 10. Who's on duty today? 11. Let's do. 12. Let me see. IV. 重要语法 those 时 that 的复数形式。 你看看这个盒子,我去看那边的那个盒 子。 on 表示在某一个物体的表面之上。 There is a picture on the wall. 墙上有张图。 these 是 this 的复数形式。 that 常常用来指在 例如: You look in this box and I'll
初三英语语法知识点归纳
初中英语语法速记口诀大全 很多同学认为语法枯燥难学,其实只要用心并采用适当的学习方法,我们就可以愉快地学会英语,掌握语法规则。笔者根据有关书目和多年教学经验,搜集、组编了以下语法口诀,希望对即将参加中考的同学们有所帮助。 一、冠词基本用法 【速记口诀】 名词是秃子,常要戴帽子, 可数名词单,须用a或an, 辅音前用a,an在元音前, 若为特指时,则须用定冠, 复数不可数,泛指the不见, 碰到代词时,冠词均不现。 【妙语诠释】冠词是中考必考的语法知识之一,也是中考考查的主要对象。以上口诀包括的意思有:①名词在一般情况下不单用,常常要和冠词连用;②表示不确指的可数名词单数前要用不定冠词a或an,确指时要用定冠词the;③如复数名词表示泛指,名词前有this,these,my,some等时就不用冠词。 二、名词单数变复数规则 【速记口诀】 单数变复数,规则要记住, 一般加s,特殊有几处: 末尾字母o,大多加s, 两人有两菜,es不离口, 词尾f、fe,s前有v和e; 没有规则词,必须单独记。 【妙语诠释】①大部分单数可数名词变为复数要加s,但如果单词以/t?蘩/、/?蘩/、/s/发音结尾(也就是单词如果以ch,sh,s,x等结尾),则一般加es;②以o结尾的单词除了两人(negro,hero)两菜(tomato,potato) 加es外,其余一般加s;③以f或fe结尾的单词一般是把f,fe变为ve再加s;④英语中还有些单词没有规则,需要特殊记忆,如child—children,mouse—mice,deer—deer,sheep—sheep,Chinese—Chinese,ox—oxen,man—men,woman—women,foot—feet,tooth —teeth。 三、名词所有格用法 【速记口诀】 名词所有格,表物是“谁的”, 若为生命词,加“’s”即可行, 词尾有s,仅把逗号择; 并列名词后,各自和共有, 前者分别加,后者最后加; 若为无生命词,of所有格, 前后须倒置,此是硬规则。 【妙语诠释】①有生命的名词所有格一般加s,但如果名词以s结尾,则只加“’”;②并列名词所有格表示各自所有时,分别加“’s”,如果是共有,则只在最后名词加“’s”;③
初中生中考必须掌握的英语语法大汇总
语法知识是在掌握一定量的单词和短语的基础上才能获得的。因此,单词的形态变化是语法学习的基础之基础。而九种基本时态和含有不复杂的状语从句及宾语从句的复合句是初中生学习的重点也是语法学习的难点。 总之,语法部分是英语学习的重点和难点。语法知识掌握得好,将大大加快英语学习的进程。本文帮大家归纳了词法、九种基本时态以及初中生需要掌握五种基本从句,希望对广大中学生有所帮助。 1词法 ▊ 1.名词 1.1 名词的可数与不可数 可数名词指表示的人或事物可以用数来计量,它有单数与复数两种形式。不可数名词指所表示的事物不能用数来计量。物质名词与抽象名词一般无法用数目,来统计,都成为不可数名词。 不可数名词前一般不能用冠词a、an来表示数量,没有复数形式。要表示“一个……”这一概念,就须加a piece of这一类短语。要注意许多名词在汉语里看来是可数名词,在英语里却不可数。如:chalk,paper,bread,rice,grass,news等。 1.2 名词复数的规则变化 A.一般情况下加-s。 B.以s, x, ch, sh, 结尾的加-es C.以辅音字母加y结尾的改y为i再加-es D.以f,fe结尾的,去掉f或fe,变成v再加-es 1.3 名词的所有格 A.单数名词词尾加’s,复数名词词尾若没有s,也要加’s。 如:the worker's bike,the Children’ s ball
B.表示几个人共有一样东西,只需在最后一个人的名字后加’ s若表示各自所有,则需在各个名字后’ s。 如:This is Lucy and Licy’ s room. These are Kate's and jack’ s rooms. C. 如果是通过在词尾加—s构成的复数形式的名词,只加’。 如:the students’ books,the girls’ blouses (另外:名词+of+名词名词是有生命的,我们就用’s结构来表示所有关系。如果名词所表示的事物是无生命的,我们就要用名词+of+名词的结构来表示所有关系。) ▊ 2.代词 人称代词,物主代词,反身代词,指示代词,不定代词 2.1 人称代词 第一人称单数 I me my mine myself 复数we us our ours ourselves 第二人称 单数you you your yours yourself 复数you you your yours yourselves 第三人称 单数he him his his himself
小学英语语法总复习知识点归纳
小学英语语法汇总 一、时态 1.一般现在时 (1)表示经常发生的动作或事情,通常用“usually通常, often常常, every…每…, sometimes有时,always总是,”等词。 (2)基本结构: I / You / We / They He / She / It 肯定句动词原形动词第三人称单数形式 否定句don’t + 动原doesn’t + 动原 一般疑问句(Yes/No) Do… ? Yes, I do.Does…(动词原形)…?No,she doesn’t. 特殊疑问句What do …?How does she…(动词原形)…? (3) 动词第三人称单数形式(同名词单数变成复数方法相同) 1 一般情况+s 如:walk-walks 2. 辅音字母+y结尾去y +ies fly-flies 3. 结尾是s, x,sh, ch +es watch-watches 4. 特殊的do-does ,have-has, go-goes 2.现在进行时, (1)表示正在发生的动作,通常用“now现在, look看,linsen听”. (2)基本形式:be + 动词ing eg: I am(not) doing my homework. You/We/They are(not) reading. He/She/It is(not) eating. What are you doing? Is he reading? (3)动词的现在分词形式(动词+ing) 一般情况+ing walk—walking 结尾是不发音的e -e + ing come—coming 重读闭音节双写最后一 个字母+ing run-running swim-swimming 3. 一般过去时 (1)表示过去已经发生的事情,通常用“last …上一个…, just now刚才, a moment ago刚才,yesterday昨天”等词。(2)be 动词的过去式: am/is—was are—were (3)过去式基本结构 肯定句(Positive)动词过去式I went shopping last night. 否定句(Negative) Didn’t + 动词原形I didn’t go shopping last night. 一般疑问句(Yes/No) Did …+ 动词原形…?Did you go shopping last night? 特殊疑问句(wh-) What did…+ 动词原形…?What did you do last night? (4)词过去式的变化: 规则动词的变化: 一般动词+ed planted,watered,climbed 以不发音的e结尾+d liked 辅音字母加y结尾-y+ ied study—studied, cry- cried 重读闭音节单词,末尾只有一个辅音字母双写最后一个 字母+ed stop –stopped plan - planned
2020最新中考英语语法知识点归纳
马上就要中考了,祝大家中考都考上一个理想的高中!欢迎同学们下载,希望能帮助到你们! 2020最新中考英语语法知识点归纳 一、词类、句子成分和构词法: 1、词类:英语词类分十种: 名词、形容词、代词、数词、冠词、动词、副词、介词、连词、感叹词。 1、名词(n.):表示人、事物、地点或抽象概念的名称。如:boy, morning, bag, ball, class, orange. 2、代词(pron.):主要用来代替名词。如:who, she, you, it . 3、形容词(adj..):表示人或事物的性质或特征。如:good, right, white, orange . 4、数词(num.):表示数目或事物的顺序。如:one, two, three, first, second, third, fourth. 5、动词(v.):表示动作或状态。如:am, is,are,have,see . 6、副词(adv.):修饰动词、形容词或其他副词,说明时间、地点、 程度等。如:now, very, here, often, quietly, slowly.
7、冠词(art..):用在名词前,帮助说明名词。如:a, an, the. 8、介词(prep.):表示它后面的名词或代词与其他句子成分的关系。如in, on, from, above, behind. 9、连词(conj.):用来连接词、短语或句子。如and, but, before . 10、感叹词(interj..)表示喜、怒、哀、乐等感情。如:oh, well, hi, hello. 2、句子成分:英语句子成分分为七种:主语、谓语、宾语、定语、 状语、表语、宾语补足语。 1、主语是句子所要说的人或事物,回答是“谁”或者“什么”。通 常用名词或代词担任。如:I’m Miss Green.(我是格林小 姐) 2、谓语动词说明主语的动作或状态,回答“做(什么)”。主要由动词 担任。如:Jack cleans the room every day. (杰克每天打 扫房间) 3、表语在系动词之后,说明主语的身份或特征,回答是“什么”或者 “怎么样”。通常由名词、代词或形容词担任。如:My name is Ping ping .(我的名字叫萍萍) 4、宾语表示及物动词的对象或结果,回答做的是“什么”。通常由 名词或代词担任。如:He can spell the word.(他能拼这个 词) 有些及物动词带有两个宾语,一个指物,一个指人。指物的叫直接
中考英语语法知识总结(全)
.代词: I. 代词可以分为以下七大类: II. 1. one, some与any: 1) one可以泛指任何人,也可特指,复数为ones。some多用于肯定句,any多用于疑问句和否定句。 One should learn to think of others. Have you any bookmarks? No, I don’t have any bookmarks. I have some questions to ask. 2) some可用于疑问句中,表示盼望得到肯定的答复,或者表示建议,请求等。 Would you like some bananas? Could you give me some money? 3) some 和any修饰可数名词单数时,some表示某个,any表示任何一个。 I have read this article in some magazine. Please correct the mistakes, if any. 4) some和数词连用表示“大约”,any可与比较级连用表示程度。 There are some 3,000 students in this school. Do you feel any better today? 2. each和every: each强调个别,代表的数可以是两个或两个以上,而every强调整体,所指的数必须是三个或三个以上。 Each student has a pocket dictionary. / Each (of us) has a dictionary. / We each have a dictionary. Every student has strong and weak points. / Every one of us has strong and weak points. 3. none和no: no等于not any,作定语。none作主语或宾语,代替不可数名词,谓语用单数,代替可数名词,谓语单复数皆可以。 There is no water in the bottle. How much water is there in the bottle? None. None of the students are (is) afraid of difficulties. 4. other和another:
初中英语语法大全精华版
初中英语语法大全 语法网络图 一.名词 I. 名词的种类: II. 1. 规则名词的复数形式:名词的复数形式,一般在单数形式后面加-s或-es。现将构成方法与读音规则列表如下: leaf-leaves, thief-thieves, knife-knives, 2.
III. 名词的所有格: 名词在句中表示所有关系的语法形式叫做名词所有格。所有格分两种:一是名词词尾加’s构成,二是由介词of 加名词构成。前者多表示有生命的东西,后者多表示无生命的东西。 1. ’s 2. ’s
3. of所有格的用法: 用于无生命的东西:the legs of the chair, the cover of the book 用于有生命的东西,尤其是有较长定语时:the classrooms of the first-year students 用于名词化的词:the struggle of the oppressed 二.冠词 冠词分为不定冠词(a, an),定冠词(the),和零冠词。 I. That boy is rather a Lei Feng. II.
III. 三.代词: I. 代词可以分为以下七大类: II. 不定代词用法注意点: 1. one, some与any: 1) one可以泛指任何人,也可特指,复数为ones。some多用于肯定句,any多用于疑问句和否定句。One should learn to think of others. Have you any bookmarks? No, I don’t have any bookmarks. I have some questions to ask.
中考英语语法点整理
中考英语语法讲解资料及练习目录 第1讲:名词...................................................................................................1-3 第2讲:代词....................................................................................................3-5 第3讲:形容词.................................................................................................5-7 第4讲:副词....................................................................................................7-10 第5讲:动词..................................................................................................10-12 第6讲:不定式..............................................................................................12-13 第7讲介词....................................................................................................13-17 第8讲:连词..................................................................................................17-21 第9讲:时态(一) (22) 第10讲:时态(二).......................................................................................22-28 第11讲:被动语态........................................................................................28-30 第12讲:句子种类(一) (30) 第13讲:句子种类(二)............................................................................30-32 第14讲:宾语从句........................................................................................32-33 第15讲:状语从句........................................................................................33-35 第16讲:就近原则........................................................................................35-36
初中英语语法基础知识汇总
初中英语语法基础知识汇总(1) 英语语法基础知识词类-名词Noun 名词(Noun.-n.) 第一部分:名词基础知识 定义:人、地、物、事或观念等名称叫做名词。 人:Edison(爱迪生),Helen(海伦),Mr.Wang(王先生) 地:Asia(亚洲),China(中国),New York(纽约) 物:book(书),dog(狗),tree(树),water(水) 事或观念:work(工作),music(音乐),truth(真理) 注: 1.如人名、地名、国名等属于该名称持有者专用的名称,其第一字母必须大写,如E dison,New York,China。 2.名词亦有可数和不可数之分,如果是可数的就有单数和复数的区别。所谓复数就是多于一个的意思,通常是在单数名词的词尾加“-s,es,ies,…”以示其为复数。例如: a book(一本书)two books(两本书) one boy(一个男孩)some boys(一些男孩) one girl(一个女孩)many girls(许多女孩) 名词在句子中的主要功能如下: (1)作句子的主语,例: Miss Lin is our English teacher. (林小姐是我们的英语老师。) (2)作句子的主语补语或宾语补语,例: John and Tom are good friends. (约翰和汤姆是好朋友。—主语补语) I call my puppy “Luck”. (我叫我的小狗“来福”。—宾语补语)
(3)作及物动词的直接宾语,例: Can you ride a bicycle?(你会骑自行车吗?) (4)作介词的宾语,例: You can go by taxi.(你可以乘出租车去。) 第二部分:名词单复数-单数变复数 一、绝大多数的可数名词的复数形式,是在该词末尾加上后辍-s。 读音变化:结尾是清辅音读[s],结尾是浊辅音或元音读[z]。 例:friend→friends; cat→cats; style→styles; sport→sports; piece→pieces 二、凡是以s、z、x、ch、sh结尾的词,在该词末尾加上后辍-es构成复数。 读音变化:统一加读[iz]。 例:bus→buses; quiz→quizzes; fox→foxes; match→matches; flash→flashes 三、以辅音字母+y结尾的名词,将y改变为i,再加-es。 读音变化:加读[z]。 例:candy→candies; daisy→daisies; fairy→fairies; lady→ladies; story→stories 四、以-o结尾的名词,如果不是外来词或缩写,就加-es,否则加-s构成复数。 读音变化:加读[z]。 例:tomato→tomatoes; potato→potatoes; torpedo→torpedoes; bingo→bingoes 反例:silo→silos; piano→pianos(外来词); photo→photos; macro→macros(缩写词)五、以-f或-fe结尾的名词,多为将-f或-fe改变为-ves,但有例外。 读音变化:尾音[f]改读[vz]。 例:knife→knives; life→lives; leaf→leaves; staff→staves; scarf→scarves 反例:roof→roofs 还有一些不规则变化,请参照中学英语频道相关文章。 第三部分:名词所有格 A. 's用在单数名词以及不以s结尾的复数名词之后: a man's jo b 男人的活儿
